Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Genres of Texts
Hochgeladen von
Bunda Emi AchmadOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Genres of Texts
Hochgeladen von
Bunda Emi AchmadCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Genres of Texts
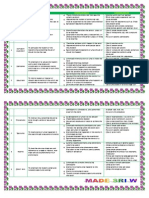
No. Type of Genres Social Function Text Structure Linguistic Features
A. Story Genres
To amuse, entertain and to deal with actual of various experience in different ways. Orientation, Evaluation, Complication, Rsolution, Rorientation Focus on spcifique participants Use of past tense Use of temporal conjunctions and temporal circumstances Use of material (or action) processes Use of relational and mental processes Short, telegraphic information about story summarized in one-sentence headline Use of material or action processes to re-tell story Use of projecting verbal processes in source stage Focus on circumstantial meanings Often dramatic use of participant structure Use of exclammative rhetorical question and intensifiers to point or the significance of events Use of temporal and continuative conjunctions Use of material or action processes (in present or past tense) Use of relation and mental processes to evaluate events
1.
Narrative
Factual text which inform readers events of the day News wrohty which are considered newsworthy or important vent(s), Background vent(s), Sources. 2. News Item
3.
Anecdote
To share with others an account of an unusual or amusing incident.
Abstract Orientation Crisis Reaction Coda
4.
Recount
To retell events for the purpose of informing or Orientation entertaining Events Reorientation To retell an event with a humorous twist. Orientation Events Twist
5.
Spoof
Focus on individual participants Use of past tense Focus on a temporal sequence of events Use of material (or action) clauses Focus on individual participants Use of past tense Use of material (or action) processes Circumstance of time and place
B. Factual Genres
To describe how something is accomplished through Goal a sequence of action or steps. Materials Step 1 - n To explain the processes involved in the formation A general statement or workings of natural or socio-cultural phenomena. to position the reader A sequenced explanation of way or how something occurs To describe the things are, with reference to arrange General classification, or natural, manmade and social phenomena in our Description (parts, environment qualities, habits or behavior (if living); uses (if non living) To persuade the reader or listener that something is Thesis the case. Arguments Reiterations / summing up Focus on generalized human agents Use of simple present tense Use of mainly temporal conjunctive relations Use of mainly material (action) clauses Focus on generic, non human participants Use simple present tense Use of temporal and causal conjunctive relations Use of mainly material or action clauses; some passive to theme right Focus on generic participants Use simple present tense Use of being and having clauses
6.
Procedure
7.
Explanation
8.
Report
9.
Analytical Exposition
Focus on generic human or non human participants More use of modality and modulation Few temporal conjunctive relation Reasoning expressed as verb and nouns Use material, relation and mental process
10.
Hortatory Exposition
To persuade the reader or listener that something Thesis should or should not be the case. Arguments Recommendation
11.
Discussion
12.
Description
13.
Review
To present (at least) two points of view about an Issue issue Arguments for and against or statements of differing points of view Conclusion or recommendations To describe a particular person, place or thing Identification Focus on specific participants Description Use of attributive and identifying process Frequent use of epithets and classifier in nominal groups Use of simple present tense To critique an art work or event for a public Orientation Focus on particular participants audience Interpretative recount Direct expression of opinion through use of attitudinal lexis Evaluation Use of elaborating and extending clause and Evaluation group complexes to package the summation information Use of metaphorical language
Focus on generic human or non human participants Use material, relation and mental process Use simple present tense Focus on generic human or non human participants More use of modality and modulation Use of logical conjunctive relation Reasoning expressed as verb and nouns Use material, relation and mental process
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Instructional Genre (School Genres) : Dr. Rudi Hartono, S.S., M.PDDokument50 SeitenInstructional Genre (School Genres) : Dr. Rudi Hartono, S.S., M.PDRizky RamaDhan PerDanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analytical Exposition TextDokument5 SeitenAnalytical Exposition TextYanti NtiNoch keine Bewertungen
- No Purpose Generic Structure Language FeaturesDokument3 SeitenNo Purpose Generic Structure Language FeaturesMahfud Al-FathirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Macam-Macam Text Genre & ContohnyaDokument9 SeitenMacam-Macam Text Genre & ContohnyaFadhlanminnaallah Wani'mah WamaghfiratawarahmahNoch keine Bewertungen
- English Text Types - Genre of The Text: Name:Enti Susanti Npm:A1B015090 1.narrative TextDokument10 SeitenEnglish Text Types - Genre of The Text: Name:Enti Susanti Npm:A1B015090 1.narrative TextEko SuwignyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Discussion TextDokument6 SeitenDiscussion Textabdi_pramana999Noch keine Bewertungen
- Text Type/macam Teks Bahasa InggrisDokument5 SeitenText Type/macam Teks Bahasa InggrisLoneliness CurlyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jenis-Jenis English TextDokument5 SeitenJenis-Jenis English TextReny YudiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jenis Jenis TeksDokument4 SeitenJenis Jenis TekslarasdwinugrahaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Macam Macam Text and Social FunctionsDokument5 SeitenMacam Macam Text and Social FunctionsRick DoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Generic Structure of English TextsDokument3 SeitenGeneric Structure of English TextsZarnuzi Alwi Al AwwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jenis-Jenis Text Dalam Bahasa InggrisDokument9 SeitenJenis-Jenis Text Dalam Bahasa InggrisZaen Yuki-TechNoch keine Bewertungen
- Based On Generic Structure and Language Feature Dominantly UsedDokument5 SeitenBased On Generic Structure and Language Feature Dominantly UsedVella AnggrainiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Text Types For SmaDokument7 SeitenText Types For Smastevent wondalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bahasa Inggris EcaDokument4 SeitenBahasa Inggris EcaRIO ANGGORO PUTRANoch keine Bewertungen
- Narrative TextDokument5 SeitenNarrative TextDewa Ayu VeronicaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jenis-Jenis Teks (Genre) Dalam Bahasa Inggris: ProcedureDokument7 SeitenJenis-Jenis Teks (Genre) Dalam Bahasa Inggris: ProcedurereztrianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Peta Materi Bahasa InggrisDokument51 SeitenPeta Materi Bahasa Inggrislio100% (1)
- 1st Quarter ENGLISH ReviewerDokument4 Seiten1st Quarter ENGLISH ReviewerKier Clarence TaguiamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Genre of The TextDokument9 SeitenGenre of The TextJack SudartoNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Write A StudyDokument5 SeitenHow To Write A StudySomya TewariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Compare Narrative and Recount Text StructuresDokument3 SeitenCompare Narrative and Recount Text StructuresKresna Thufail ANoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4 - Research DesignDokument74 SeitenChapter 4 - Research DesignRoan Suanque MartirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Narrative ResearchDokument9 SeitenNarrative ResearchFil LuayonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Text Genre and SyllabusDokument11 SeitenTypes of Text Genre and SyllabusNaydiNoch keine Bewertungen
- RG Gr5 VerticalStdsMapsDokument12 SeitenRG Gr5 VerticalStdsMapspeanut2627Noch keine Bewertungen
- Narrative Research DesignDokument2 SeitenNarrative Research DesignSheilaMacatangayNoch keine Bewertungen
- ..To Understand The Qualitative Approaches Through ExamplesDokument19 Seiten..To Understand The Qualitative Approaches Through ExamplesBea FernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Qualitative MethodsDokument52 Seiten1 Qualitative MethodspaewoonNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12 Jenis TextDokument5 Seiten12 Jenis TextAstrinaLNoch keine Bewertungen
- Text TypesDokument36 SeitenText TypesMeddy AllotsakateluNoch keine Bewertungen
- Qualitative Research MethodsDokument6 SeitenQualitative Research Methodssajidobry_847601844Noch keine Bewertungen
- Genre-Based Writing DR PDFDokument9 SeitenGenre-Based Writing DR PDFMala FakaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Text Types SummaryDokument10 SeitenText Types SummaryAmir ArragilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentasi PLPGDokument17 SeitenPresentasi PLPGanon_742581406Noch keine Bewertungen
- TARGETS (Budget of Work)Dokument4 SeitenTARGETS (Budget of Work)Ma. Victoria RamosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multicultural Teaching MethodsDokument2 SeitenMulticultural Teaching Methodslakshita2811Noch keine Bewertungen
- 12 Kinds of TextsDokument10 Seiten12 Kinds of Textskristoatscribd100% (10)
- Wenzel Udl Science Lesson Plan Section 1 The PlanDokument4 SeitenWenzel Udl Science Lesson Plan Section 1 The Planapi-273149494Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tabel EnglishDokument4 SeitenTabel EnglishAnangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kinds of The TextsDokument11 SeitenKinds of The TextsIrma SasmitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study Writing ToolsDokument11 SeitenCase Study Writing ToolsNajneen Jahan NehaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Narrative, Recount, SpoofDokument3 SeitenNarrative, Recount, SpoofChandra SaputraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12.1 My Journey So FarDokument5 Seiten12.1 My Journey So FarMarilu Velazquez MartinezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analyzing Historical Recount Texts Using PBLDokument17 SeitenAnalyzing Historical Recount Texts Using PBLSari RamadhaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reporting Verbs in ResearchDokument6 SeitenReporting Verbs in Researchedsonmamaradlo23Noch keine Bewertungen
- Materi Qualitative Descriptive ResearchDokument2 SeitenMateri Qualitative Descriptive ResearchJuniatin BimaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Qualitative Research - Anki CorrectedDokument7 SeitenQualitative Research - Anki CorrectedThirumanjari KarthikeyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6Q Interpretative Phenomenological AnalysisDokument21 Seiten6Q Interpretative Phenomenological AnalysisJessa Mae S. DARULLONoch keine Bewertungen
- Edla Assignment 3Dokument25 SeitenEdla Assignment 3api-318423851Noch keine Bewertungen
- Group 5 Bahasa Inggris Tingkat Lanjut DoneDokument9 SeitenGroup 5 Bahasa Inggris Tingkat Lanjut Donerachmaplg19Noch keine Bewertungen
- Qualitative Research: Material From Groat and Wang (2013) Prepared by Neil Menjares, MSDokument33 SeitenQualitative Research: Material From Groat and Wang (2013) Prepared by Neil Menjares, MSaldreinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Descriptive PhenomenologyDokument6 SeitenDescriptive PhenomenologyRussel Martinez PaganaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Task1. Rhetorical Analysis of The Text (Scheme)Dokument7 SeitenTask1. Rhetorical Analysis of The Text (Scheme)Roman LytvynNoch keine Bewertungen
- Running Out Of Time: Introducing Behaviorology To Help Solve Global ProblemsVon EverandRunning Out Of Time: Introducing Behaviorology To Help Solve Global ProblemsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common Core Snapshot: Administrator's Guide to the Common CoreVon EverandCommon Core Snapshot: Administrator's Guide to the Common CoreNoch keine Bewertungen
- How to Research Qualitatively: Tips for Scientific WorkingVon EverandHow to Research Qualitatively: Tips for Scientific WorkingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Genres of TextsDokument3 SeitenGenres of TextsBunda Emi AchmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- To Whom It May Concern Nawal IsmailDokument2 SeitenTo Whom It May Concern Nawal IsmailBunda Emi AchmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soal Big U Akh SM I Kls Ix 2011Dokument8 SeitenSoal Big U Akh SM I Kls Ix 2011Bunda Emi AchmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- To Whom It May Concern Nawal IsmailDokument2 SeitenTo Whom It May Concern Nawal IsmailBunda Emi AchmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- To Whom It May Concern Nawal IsmailDokument2 SeitenTo Whom It May Concern Nawal IsmailBunda Emi AchmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nuptkenc Nuptkenc2: Daftar PTKDokument12 SeitenNuptkenc Nuptkenc2: Daftar PTKBunda Emi AchmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- CorelDRAW Graphics Suite X6Dokument1 SeiteCorelDRAW Graphics Suite X6Bunda Emi AchmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bianglala Basmah Blog Font StylesDokument58 SeitenBianglala Basmah Blog Font StylesBunda Emi AchmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tiket PesawatDokument1 SeiteTiket PesawatBunda Emi AchmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Windows 8 Pro VL x64 en-US Pre-Activated Aug2013Dokument2 SeitenWindows 8 Pro VL x64 en-US Pre-Activated Aug2013Bunda Emi AchmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wep Key STCDokument1 SeiteWep Key STCBunda Emi AchmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Listening Cd1Dokument7 SeitenListening Cd1Iulian Teodor0% (1)
- The Reception Office: Monday September 28, 2020Dokument2 SeitenThe Reception Office: Monday September 28, 2020Chikanma OkoisorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Etienne Gilson - The Christian Philosophy of St. Augustine PDFDokument418 SeitenEtienne Gilson - The Christian Philosophy of St. Augustine PDFMihai Sarbu95% (21)
- Binary Classification MetricsDokument6 SeitenBinary Classification MetricssharathdhamodaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Process States and Memory Management LabDokument8 SeitenProcess States and Memory Management LabJámesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Recruitment Needs Are of Three Types: PlannedDokument7 SeitenRecruitment Needs Are of Three Types: PlannedShraddha MomayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- grr5504 1e Emeraldcity Playersguidev11Dokument94 Seitengrr5504 1e Emeraldcity Playersguidev11Kánya Zoltán100% (1)
- Open Area Test SitesDokument15 SeitenOpen Area Test SitesSravani KorapakaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Employee Wellbeing ProgramDokument5 SeitenEmployee Wellbeing ProgramManish SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MaterialDokument2 SeitenMaterialPhạm TuyểnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Apsa StyleDokument4 SeitenApsa StyleLincoln DerNoch keine Bewertungen
- 04 - 2018-A2LA Presentation - P2 - Changes in 17025-2017 - Rob KnakeDokument33 Seiten04 - 2018-A2LA Presentation - P2 - Changes in 17025-2017 - Rob KnakekrishnakumariNoch keine Bewertungen
- SOFTWARE ARCHITECTURE DOCUMENT-OnlineCateringService Sample ExampleDokument10 SeitenSOFTWARE ARCHITECTURE DOCUMENT-OnlineCateringService Sample ExampleMehwish HussainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study PlanDokument1 SeiteStudy PlanMTINoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 Loaders and Linkers: - Machine-Independent Loader FeatureDokument7 SeitenChapter 3 Loaders and Linkers: - Machine-Independent Loader FeatureNimisha JithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Identifying VariablesDokument25 SeitenIdentifying Variablesapi-236248022Noch keine Bewertungen
- Flex Module (IFLEX MFLEX UFLEX) Level 1Dokument79 SeitenFlex Module (IFLEX MFLEX UFLEX) Level 1John Mark EspalmadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2004 - Rosser - Faculty Members Intentions To Leave PDFDokument26 Seiten2004 - Rosser - Faculty Members Intentions To Leave PDFCarlos Arturo HoyosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arithmetic SequencesDokument3 SeitenArithmetic SequencestuvvacNoch keine Bewertungen
- SAP Sample Questions ReviewDokument18 SeitenSAP Sample Questions ReviewYasir Yamin SadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Essay One Othering and Rhetorical AnalysisDokument7 SeitenEssay One Othering and Rhetorical Analysisapi-324018733Noch keine Bewertungen
- Soft Uni SolutionsDokument8 SeitenSoft Uni Solutionsnrobastos1451Noch keine Bewertungen
- Design Rule Check: By:-Chandan ROLL NO. 15/914 B.SC (Hons.) ELECTRONICS ScienceDokument9 SeitenDesign Rule Check: By:-Chandan ROLL NO. 15/914 B.SC (Hons.) ELECTRONICS ScienceChandan KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- UT71 Computer Interface SoftwareDokument3 SeitenUT71 Computer Interface SoftwareOrlando FernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Beer Lambert LawDokument2 SeitenBeer Lambert LawMuhammad ZubairNoch keine Bewertungen
- Environtment Factor - Light Rev Asr 130918Dokument60 SeitenEnvirontment Factor - Light Rev Asr 130918Irvan MahmudiNoch keine Bewertungen
- C T Butler and Amy Rothstein On Conflict and Consensus A Handbook On Formal Consensus DecisionmDokument53 SeitenC T Butler and Amy Rothstein On Conflict and Consensus A Handbook On Formal Consensus DecisionmdefoedefoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- CRL 1790Dokument3 SeitenCRL 1790nandhus2227Noch keine Bewertungen
- Excel Spreadsheet SoftwareDokument22 SeitenExcel Spreadsheet SoftwareJared Cuento TransfiguracionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Virtual Image.: 1 (A) Fig. 8.1 Is A Ray Diagram of A Convex Lens Being Used As A Magnifying Glass To Produce ADokument11 SeitenVirtual Image.: 1 (A) Fig. 8.1 Is A Ray Diagram of A Convex Lens Being Used As A Magnifying Glass To Produce AahmedNoch keine Bewertungen