Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
CONSTI NOTES - October 3, 2011 Q: Q: A: Q: A: Q: A: Q: A
Hochgeladen von
Kim BalauagOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
CONSTI NOTES - October 3, 2011 Q: Q: A: Q: A: Q: A: Q: A
Hochgeladen von
Kim BalauagCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
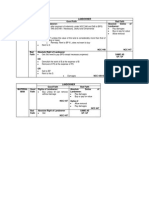
CONSTI NOTES | October 3, 2011 Q: Can a vice-president be appointed as Ombudsman? Q: Can a President be sued? A: No, he has immunity Q: Absolutely?
A: No, only applies when he is currently sitting as President Q: Does the immunity extend to the Vice-President? Procedure in Answering Questions 1. Look at the text and see if there is a provision that directly answers the question 2. If there is a provision, look at jurisprudence and see how the provision is interpreted 3. If there is no provision, look at jurisprudence 4. If there is no provision and jurisprudence, look at the legislative history of a text that is related to the question The role of the legislature is to provide policies for acts of the future Legislature looks forward, executive looks at the present, and the judiciary examines the past If there is a hiatus but there is a need to act, the President needs to act = Reason for the concept of residual powers Marcos v. Manglapus SC: The President has the powers to fill in interstices. SC: There is freedom to travel outside the country but such freedom is not guaranteed in going back to the country If you make a law that protects the evil ones then you are actually giving more protection to the good ones Residual powers are limited to the text of the Constitution There is nothing in the Constitution that states that the President should take his oath exactly at 12 noon of June 30 Q: What happens if the President is delayed in taking his oath? Only the law can move the election Q: What is a SONA? A: A SONA is a report of the President done on the th opening of the regular session of the Congress on the 4 Monday of July Q: What happens if the President does not make a report? A: He is still the President but the House of Representatives can initiate an impeachment complaint against him under Article XI Section 2 for culpable violation of the Constitution. Q: Who determines first the definition of the word culpable A: The House of Representatives Q: Can the SC review this definition? A: Yes, it is not a political question if there is a showing that there is abuse of discretion Q: What is grave abuse? A: Arbitrary or whimsical decisions
Q: Can the decisions of the SC be reviewed? A: No, but the members of the SC can be impeached Q: What happens if the President is abroad? Does the VP become President? A: No, there is no such thing as temporary absence of the President. He is still President Q: Can the President delegate his power? A: Yes, under the doctrine of qualified alter ego which states that the President can delegate somebody to do executive acts as if he himself is the one doing it. But the President remains as the only executive Stages of Appointment 1. Appointment 2. Acceptance The Commission on Appointments is composed of legislators presided by the Senate President. Members of the Commission can veto the appointments of: 1. Members of ConCon 2. Members of Constitutional offices/body 3. Generals Appointments not decided upon before the closing of the regular session of the Congress is deemed invalid Ambassadors are representative of the Head-of-State and as such the President can choose them at will The list of appointment that needs confirmation by the Commission on Appointments is exclusive The Commission on Appointment is a separate constitutional body
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Delhi Public School: Chapter-Working of InstitutionsDokument6 SeitenDelhi Public School: Chapter-Working of InstitutionsKrishna ANoch keine Bewertungen
- Impeachment in The PhilippinesDokument3 SeitenImpeachment in The Philippineseunisflamme100% (1)
- Constitutional Law 1Dokument6 SeitenConstitutional Law 1Skull RIDER 69Noch keine Bewertungen
- Doctrine of Qualified Political Agency. Under This Doctrine, The President Exercises ExecutiveDokument9 SeitenDoctrine of Qualified Political Agency. Under This Doctrine, The President Exercises ExecutiveTAU MU OFFICIALNoch keine Bewertungen
- November 16 Consti Law NotesDokument6 SeitenNovember 16 Consti Law NotesJohn Mark Damian IINoch keine Bewertungen
- The United States ExecutiveDokument4 SeitenThe United States ExecutiveNisha ChhetryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philippine Constitution exercises on suffrage, accountability, social justice and moreDokument2 SeitenPhilippine Constitution exercises on suffrage, accountability, social justice and moreKESHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hist8 - Union ExecutiveDokument4 SeitenHist8 - Union ExecutiveBFF ForeverNoch keine Bewertungen
- UCSPDokument3 SeitenUCSPFernandez, Nadine Kate T.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Power of US PresidentDokument3 SeitenPower of US PresidentManjira KarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Branches ReadingsDokument3 SeitenBranches Readingsapi-328061525Noch keine Bewertungen
- Warrior Notes Constitutional LawDokument140 SeitenWarrior Notes Constitutional LawLeaneSacaresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Const. Law (Transcribed)Dokument7 SeitenConst. Law (Transcribed)James DecolongonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Commander-in-Chief Powers and Martial Law SafeguardsDokument21 SeitenCommander-in-Chief Powers and Martial Law SafeguardsEli John NovelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Judiciary 1Dokument5 SeitenJudiciary 1KriegerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Executive Presidency in Sri LankaDokument6 SeitenExecutive Presidency in Sri LankaShifan TariqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Document (17)Dokument5 SeitenDocument (17)AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- US Executive Power: President & Cabinet RolesDokument16 SeitenUS Executive Power: President & Cabinet RolesSejal Sharma 20SA1103Noch keine Bewertungen
- EXECUTIVE Ques and Ans CLASS 11 Political ScienceDokument5 SeitenEXECUTIVE Ques and Ans CLASS 11 Political Sciencesainimegha0801Noch keine Bewertungen
- Types and Features of Bangladesh ConstitutionDokument5 SeitenTypes and Features of Bangladesh Constitutionzeorna StoreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Working of Institution Class 9 NotesDokument5 SeitenWorking of Institution Class 9 NotesMridula ThakurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Executive 16594416679791656505812630Dokument28 SeitenExecutive 16594416679791656505812630Ajeet Singh ChoudharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Are The Branches of GovernmentDokument3 SeitenWhat Are The Branches of GovernmentGrant NaillingNoch keine Bewertungen
- COI Unit II PPTDokument54 SeitenCOI Unit II PPTashukush2009Noch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment (Question System of Government )Dokument5 SeitenAssignment (Question System of Government )nangkhinlawonthitsarNoch keine Bewertungen
- REALES, Jethro QUIZ 3Dokument1 SeiteREALES, Jethro QUIZ 3Jethroret RealesNoch keine Bewertungen
- UPSC Civil Services Examination: Governor Powers, Tenure, AppointmentDokument5 SeitenUPSC Civil Services Examination: Governor Powers, Tenure, Appointmentsanjayrakshita100% (1)
- Presidential Powers & Cabinet FunctionsDokument8 SeitenPresidential Powers & Cabinet FunctionsPaula Bianca Cedillo CorsigaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Essential Features of the US ConstitutionDokument6 SeitenEssential Features of the US ConstitutionRAGIB SHAHRIAR RAFINoch keine Bewertungen
- Judicial, Ergo, It Must Be Executive."Dokument4 SeitenJudicial, Ergo, It Must Be Executive."Andrea TancincoNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Seven Pillars of Democracy: A US Constitution JourneyVon EverandThe Seven Pillars of Democracy: A US Constitution JourneyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presidential and Parliamentary Form of Government: PresidentDokument8 SeitenPresidential and Parliamentary Form of Government: PresidentsvNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comparing Presidential & Parliamentary Systems of GovernmentDokument13 SeitenComparing Presidential & Parliamentary Systems of GovernmentVarsha Daveson100% (1)
- Poli FinalDokument197 SeitenPoli Finalnikkibeverly73Noch keine Bewertungen
- MIDTERM EXAM Consti 1 Sy 09-10 Sem1Dokument5 SeitenMIDTERM EXAM Consti 1 Sy 09-10 Sem1leiben17393875% (8)
- Causes of Removal of The PresidentDokument13 SeitenCauses of Removal of The PresidentKj AdevienteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Government Forms and Functions ExplainedDokument29 SeitenGovernment Forms and Functions ExplainedAlina ZahidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Constitutions: Legal RulesDokument6 SeitenConstitutions: Legal RulesMd.Shadik UllahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answer:: Insights Mission 2018 Static Test 9 SynopsisDokument6 SeitenAnswer:: Insights Mission 2018 Static Test 9 SynopsisPulkit MisraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Consitution Test Study GuideDokument5 SeitenConsitution Test Study GuideerinsimoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Role of President in IndiaDokument10 SeitenRole of President in IndiaMansi LangyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Distilled Con-Law OutlineDokument14 SeitenDistilled Con-Law OutlineAnonymous 4WLSqyNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Glimpse of the Philippine Legislative ProcessDokument3 SeitenA Glimpse of the Philippine Legislative ProcessJoyce Ann CastilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Breakout SessionDokument9 SeitenBreakout SessionmyraujaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Separation of PowersDokument8 SeitenSeparation of PowersM Vijay AbrajeedhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wa0038.Dokument9 SeitenWa0038.Talha RahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Approach-Not Concerned About Labels, But WasDokument3 SeitenApproach-Not Concerned About Labels, But Wasjhuang015Noch keine Bewertungen
- Final Draft Art 6Dokument42 SeitenFinal Draft Art 6Karisse ViajeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0-SLIC Tutorial 2Dokument3 Seiten0-SLIC Tutorial 2WY HeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz Answers: Multiple ChoiceDokument1 SeiteQuiz Answers: Multiple Choiceapi-278203882Noch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Branches ofDokument11 Seiten3 Branches ofGloria SunshineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indian PresidentDokument6 SeitenIndian PresidentZafar IqbalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9 DPDokument6 Seiten9 DPsaksham18bNoch keine Bewertungen
- 501 III Separation of PowersDokument2 Seiten501 III Separation of PowersajemlipokmenlaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2ND Semester NotesDokument27 Seiten2ND Semester NotesAryan PanwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Civics ch-2Dokument11 SeitenCivics ch-2Sadik farhat MollaNoch keine Bewertungen
- President: Election of The PresidentDokument8 SeitenPresident: Election of The PresidentDhruva Chandra PandeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- unit 5Dokument6 Seitenunit 5KanishkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Political Law PrinciplesDokument21 SeitenPolitical Law PrinciplesRae CerdeñoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Republic v. T.A.N. Properties Land Certification CaseDokument1 SeiteRepublic v. T.A.N. Properties Land Certification CaseKim BalauagNoch keine Bewertungen
- Property ReviewerDokument7 SeitenProperty ReviewerKim BalauagNoch keine Bewertungen
- CONSTI NOTES - October 3, 2011 Q: Q: A: Q: A: Q: A: Q: ADokument1 SeiteCONSTI NOTES - October 3, 2011 Q: Q: A: Q: A: Q: A: Q: AKim BalauagNoch keine Bewertungen
- PIL LectureDokument2 SeitenPIL LectureKim BalauagNoch keine Bewertungen
- Property Digest (Part IV)Dokument2 SeitenProperty Digest (Part IV)Kim BalauagNoch keine Bewertungen
- LocGov Digest (11.12.13)Dokument10 SeitenLocGov Digest (11.12.13)Kim BalauagNoch keine Bewertungen
- NEEICO vs. NLRCDokument1 SeiteNEEICO vs. NLRCKim BalauagNoch keine Bewertungen
- PropertyDokument1 SeitePropertyKim BalauagNoch keine Bewertungen
- RA 9048 and RA 9255Dokument2 SeitenRA 9048 and RA 9255Kim BalauagNoch keine Bewertungen
- CONSTI NOTES - October 3, 2011 Q: Q: A: Q: A: Q: A: Q: ADokument1 SeiteCONSTI NOTES - October 3, 2011 Q: Q: A: Q: A: Q: A: Q: AKim BalauagNoch keine Bewertungen
- Criminal Law 1 - October 5, 2011Dokument2 SeitenCriminal Law 1 - October 5, 2011Kim BalauagNoch keine Bewertungen
- RA 9851 Analysis of Constitutionality, Sources of Law, TreatiesDokument2 SeitenRA 9851 Analysis of Constitutionality, Sources of Law, TreatiesKim BalauagNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revenue Regulation No. 16-2005Dokument0 SeitenRevenue Regulation No. 16-2005Kaye MendozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rule 117 CompilationDokument15 SeitenRule 117 CompilationKim BalauagNoch keine Bewertungen
- Succession Digest Compilation (07.22.13)Dokument10 SeitenSuccession Digest Compilation (07.22.13)Kim BalauagNoch keine Bewertungen
- De Leon v. EsguerraDokument1 SeiteDe Leon v. EsguerraKim BalauagNoch keine Bewertungen
- 05 - Liability of Parties (Pp. 726-772)Dokument6 Seiten05 - Liability of Parties (Pp. 726-772)Kim BalauagNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pril Notes 1Dokument2 SeitenPril Notes 1Kim BalauagNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sime Darby v. CTADokument6 SeitenSime Darby v. CTAKristine De LeonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Republic Act No. 53: Revelation of Secrets by An OfficerDokument1 SeiteRepublic Act No. 53: Revelation of Secrets by An OfficerKim BalauagNoch keine Bewertungen
- Int'l Catholic Migration vs. CallejaDokument1 SeiteInt'l Catholic Migration vs. CallejaKim BalauagNoch keine Bewertungen
- Corfu Channel Case PDFDokument73 SeitenCorfu Channel Case PDFKim Balauag100% (1)
- 56 HVLR 72 Seavey Principles of TortsDokument15 Seiten56 HVLR 72 Seavey Principles of TortsKim BalauagNoch keine Bewertungen
- Savings Bank Forgery CaseDokument2 SeitenSavings Bank Forgery CaseKim Balauag100% (1)
- Assoc. of Baptists vs. FieldmanDokument1 SeiteAssoc. of Baptists vs. FieldmanKim BalauagNoch keine Bewertungen
- Santos Ventura Hocorma Foundation Inc Vs SantosDokument2 SeitenSantos Ventura Hocorma Foundation Inc Vs SantosKim BalauagNoch keine Bewertungen
- NEEICO vs. NLRCDokument1 SeiteNEEICO vs. NLRCKim BalauagNoch keine Bewertungen
- Santos Ventura Hocorma Foundation Inc Vs SantosDokument2 SeitenSantos Ventura Hocorma Foundation Inc Vs SantosKim BalauagNoch keine Bewertungen
- US Vs Ah ChongDokument1 SeiteUS Vs Ah ChongKim Balauag100% (1)
- People Vs Coral, 230 SCRA 499 and Other Labor CasesDokument3 SeitenPeople Vs Coral, 230 SCRA 499 and Other Labor CasesVenus Jane FinuliarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brief Aim of UNCSWDokument3 SeitenBrief Aim of UNCSWhweta173Noch keine Bewertungen
- PCVL Nle B1 PDFDokument33 SeitenPCVL Nle B1 PDFWEINDLY AYONoch keine Bewertungen
- Zudio Case StudyDokument2 SeitenZudio Case StudySachin MaruNoch keine Bewertungen
- DAILY NATION Monday July 27, 2020 PDFDokument20 SeitenDAILY NATION Monday July 27, 2020 PDFDixie CheeloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complicity HandoutDokument5 SeitenComplicity HandoutAnonymous yr4a85Noch keine Bewertungen
- E-Marketing 5/E: Chapter 8: Segmentation and Targeting StrategiesDokument25 SeitenE-Marketing 5/E: Chapter 8: Segmentation and Targeting Strategiesemmy emmyNoch keine Bewertungen
- First Division: Ynares-Santiago, J.Dokument62 SeitenFirst Division: Ynares-Santiago, J.Rose De JesusNoch keine Bewertungen
- After Watching The Video Answer The Following Questions. LinkDokument9 SeitenAfter Watching The Video Answer The Following Questions. LinkVivian Veronica Samaniego ParanzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cabral v. PunoDokument3 SeitenCabral v. PunoJoni Puray100% (1)
- Warrant Trial CRPCDokument17 SeitenWarrant Trial CRPCvinay sharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prosecution PillarDokument35 SeitenProsecution PillarChrìs Nìem100% (1)
- Claim No Easy Victories: A HIstory and Analysis of Anti-Racist ActionDokument7 SeitenClaim No Easy Victories: A HIstory and Analysis of Anti-Racist ActionMakhnov1919Noch keine Bewertungen
- Policy MemoDokument5 SeitenPolicy Memoapi-301581633Noch keine Bewertungen
- Resiyana Nurmalia P - Bahasa Inggris HukumDokument3 SeitenResiyana Nurmalia P - Bahasa Inggris HukumResya NurmaliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Full Document: Proposed-Draft Constitution Consultative-CommitteeDokument114 SeitenFull Document: Proposed-Draft Constitution Consultative-CommitteeEnpold BangsamoroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nivea Case StudyDokument2 SeitenNivea Case StudyHumaira SalmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- People vs. GuillermoDokument2 SeitenPeople vs. GuillermoRaymundNoch keine Bewertungen
- TENCHAVES V ESCANO Gr. No. L-19671Dokument4 SeitenTENCHAVES V ESCANO Gr. No. L-19671Nichole LusticaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dismissed Without Prejudice - CertiorariDokument9 SeitenDismissed Without Prejudice - CertiorariDonna Flores-TrinidadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philippine Government Structure Short QuizDokument6 SeitenPhilippine Government Structure Short QuizAaron PaulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Significance and determinants of foreign policyDokument3 SeitenSignificance and determinants of foreign policyAsad ChishtiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11 Chapter 3Dokument45 Seiten11 Chapter 3yaso01Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fire Prevention and Response Plan for Greenergie PlantDokument8 SeitenFire Prevention and Response Plan for Greenergie PlantMelba MangabatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Labor Relations Law EssentialsDokument25 SeitenLabor Relations Law EssentialsKarl Estacion IV100% (1)
- Office of The Solicitor General For Plaintiff-Appellant. Pedro Samson C. Animas For Defendant-AppelleeDokument4 SeitenOffice of The Solicitor General For Plaintiff-Appellant. Pedro Samson C. Animas For Defendant-AppelleeFrederick EboñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nation Building and Contestet IdentitiesDokument384 SeitenNation Building and Contestet IdentitiesLaura ȘtefănuțNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reconstruction easements as a restriction on the right to buildDokument25 SeitenReconstruction easements as a restriction on the right to buildHab BaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mandati ParlamentarDokument162 SeitenMandati Parlamentar'Nadi Pilavi'Noch keine Bewertungen
- FIPP World Magazine Trends - Special Report - Magazine MediaDokument30 SeitenFIPP World Magazine Trends - Special Report - Magazine MediaPedro AguiarNoch keine Bewertungen