Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Lesson 2 Vector Spaces
Hochgeladen von
Gauthier ToudjeuCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Lesson 2 Vector Spaces
Hochgeladen von
Gauthier ToudjeuCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Lesson2
Matrices: Vector spaces and linear
independence
PP 9 - 14
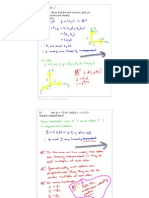
Vector spaces
In Physics: north
In basic maths:
a vector in 2D
a vector in 3D
In general: is a
vector in n-space with every a real
number
CopyRight: TUT - EL Voges 2
v 60km/h =
a 3; 2 =< >
b 2; 1;5 =< >
1 2 n
x a ,a ,...,a =< >
a
i
Notation
: the set of all vectors in n - space
: the set of all vectors in the form
NB! Vector can refer to almost
anything a set of real numbers,
a set of complex numbers,
a set of matrices ect.
3 CopyRight: TUT - EL Voges
R
n
2
R
, a b < >
What is a vector space?
If V is a set of elements on which two
operations called vector addition and
vector multiplication are defined then V is
a vector space if the eight axioms on
page 10 are satisfied.
A vector space is a set of elements
CopyRight: TUT - EL Voges 4
Example 1
Examples of vector spaces
The set of real numbers, R
The set of ordered pairs, R
The set of triples, R
The set of complex numbers,
The set of all m n matrices
The set of all polynomials of degree n
CopyRight: TUT - EL Voges 5
n
C
s
Linear dependence
Linear combination - scalar
multiplication and vector addition.
The set of vectors is linearly
dependent.
CopyRight: TUT - EL Voges 6
1 2
c k a k b = +
{ }
, , a b c
Linear independence
Consider the set of vectors
The set is linearly independent if and
only if
CopyRight: TUT - EL Voges 7
{ }
1 2
; ;...
n
x x x
1 2 1 2
... 0
n n
k x k x k x + + =
1 2
... 0
n
k k k = = = =
Example 2a
Show that the unit vectors and in
two dimensions is linearly independent.
Note: Geometrically and are
perpendicular and thus not multiples of
one another
CopyRight: TUT - EL Voges 8
i
j
i
j
Example 2
b) Are and
linearly independent?
c) Show that ,
and are linearly
dependent.
9 CopyRight: TUT - EL Voges
a 2; 6 =< >
b 1; 3 =< >
a 1;1;1 =< >
2; 1; 4 b =< >
5; 2; 7 c =< >
Example 2d
Test the following set for linear
independence
10 CopyRight: TUT - EL Voges
1 1 1
0 , 2 , 2
0 0 3
( ( (
( ( (
`
( ( (
( ( (
)
Basis and dimension
Basis: consider the set
of vectors, denoted by
in a vector space V. If this set is linearly
independent in V such that
Then B is called a basis for V.
CopyRight: TUT - EL Voges 11
{ }
1 2
B ; ;...;
n
x x x =
( )
1 2
S ; ;...;
n
x x x
( )
1 2
S ; ;...; V
n
x x x =
Basis and dimension
Every vector in V can be written as a
unique linear combination
Any other basis of V must also contain
n linearly independent vectors
The vector space has dimension n
(the number of vectors in a basis)
CopyRight: TUT - EL Voges 12
y
1 2 1 2
y ...
n n
k x k x k x = + +
Example 3a
Is the following set a basis for a three
dimensional Euclidean space? Motivate.
13 CopyRight: TUT - EL Voges
1 1 3
0 , 2 , 2
1 3 5
( ( (
( ( (
`
( ( (
( ( (
)
Example 3b
Is the following set a basis for a three
dimensional Euclidean space? Motivate.
14 CopyRight: TUT - EL Voges
1 1 1
0 , 2 , 2
0 0 3
( ( (
( ( (
`
( ( (
( ( (
)
Next Week
Revise eigenvalues and eigenvectors
(Maths III)
Note available on myTUTor
Class test 1a
CopyRight: TUT - EL Voges 15
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (894)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- 2010 HD Part Cat. LBBDokument466 Seiten2010 HD Part Cat. LBBBuddy ButlerNoch keine Bewertungen
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- Factors of Active Citizenship EducationDokument2 SeitenFactors of Active Citizenship EducationmauïNoch keine Bewertungen
- PC Troubleshooting: Mr. Joseph B. Ramirez JRDokument112 SeitenPC Troubleshooting: Mr. Joseph B. Ramirez JRGauthier ToudjeuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eigen Problems: RevisionDokument20 SeitenEigen Problems: RevisionGauthier ToudjeuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Legends and Lairs - Elemental Lore PDFDokument66 SeitenLegends and Lairs - Elemental Lore PDFAlexis LoboNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management For EngineersDokument561 SeitenManagement For Engineersraja_haseeb806686% (14)
- Ansible Playbook for BeginnersDokument101 SeitenAnsible Playbook for BeginnersFelix Andres Baquero Cubillos100% (1)
- Signals in MatLab PDFDokument18 SeitenSignals in MatLab PDFPratik SarkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lewis Corporation Case 6-2 - Group 5Dokument8 SeitenLewis Corporation Case 6-2 - Group 5Om Prakash100% (1)
- ZTE LTE Random AccessDokument65 SeitenZTE LTE Random AccessGauthier Toudjeu100% (2)
- WCDMA Air Interface ConceptsDokument27 SeitenWCDMA Air Interface ConceptsGauthier ToudjeuNoch keine Bewertungen
- GSM RN Optimization ISSUE1.4Dokument25 SeitenGSM RN Optimization ISSUE1.4Gauthier ToudjeuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2 ProblemsDokument7 SeitenUnit 2 ProblemsPeersahbNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1i StateSpaceModelOverview PDFDokument18 Seiten1i StateSpaceModelOverview PDFGauthier ToudjeuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Matrices Worksheet 2 Eigen ProblemsDokument6 SeitenMatrices Worksheet 2 Eigen ProblemsGauthier ToudjeuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 2 S1 2014Dokument3 SeitenAssignment 2 S1 2014Gauthier ToudjeuNoch keine Bewertungen
- WR1 EMT451T 2012B Memo A1Dokument5 SeitenWR1 EMT451T 2012B Memo A1Gauthier ToudjeuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Management Business Plan and Technology Strategy for Huawei TechnologiesDokument17 SeitenEngineering Management Business Plan and Technology Strategy for Huawei TechnologiesGauthier Toudjeu100% (1)
- Example 2: A) Show That The Unit Vectors I and J in Two Dimensions Are Linearly IndependentDokument4 SeitenExample 2: A) Show That The Unit Vectors I and J in Two Dimensions Are Linearly IndependentGauthier ToudjeuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arc and Sunn 2013Dokument36 SeitenArc and Sunn 2013Gauthier ToudjeuNoch keine Bewertungen
- REVISION: Eigen Problems: 1. Definitions and TheoremsDokument13 SeitenREVISION: Eigen Problems: 1. Definitions and TheoremsGauthier ToudjeuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Mathematics Iv (Emt451T/Mma401T) Class Test I Time: 45 Minutes Total Marks: 30Dokument1 SeiteEngineering Mathematics Iv (Emt451T/Mma401T) Class Test I Time: 45 Minutes Total Marks: 30Gauthier ToudjeuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complex Functions C - IntegrationDokument10 SeitenComplex Functions C - IntegrationGauthier ToudjeuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Z TransformsDokument35 SeitenZ TransformsGauthier ToudjeuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complex Functions A - DifferentiationDokument3 SeitenComplex Functions A - DifferentiationGauthier ToudjeuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Better Living with SQL: Master Database Queries in 40 CharactersDokument7 SeitenBetter Living with SQL: Master Database Queries in 40 CharactersTalha YasinNoch keine Bewertungen
- FACET Proposal Guidelines for New ExperimentsDokument3 SeitenFACET Proposal Guidelines for New ExperimentsGauthier ToudjeuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bloodshed Dev-C++ Is Distributed Under The GNU General Public License.Dokument7 SeitenBloodshed Dev-C++ Is Distributed Under The GNU General Public License.onaibaf13Noch keine Bewertungen
- Business PlanDokument12 SeitenBusiness PlanGauthier ToudjeuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Matlab BasicDokument23 SeitenMatlab BasicGauthier ToudjeuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Better Living with SQL: Master Database Queries in 40 CharactersDokument7 SeitenBetter Living with SQL: Master Database Queries in 40 CharactersTalha YasinNoch keine Bewertungen
- La Place TransformDokument35 SeitenLa Place TransformAhmed Sakr (أحمد صقر)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Dev CPP NewsDokument5 SeitenDev CPP NewsAndrew HubbardNoch keine Bewertungen
- Excel Create Run MacroDokument5 SeitenExcel Create Run MacroRamadhani MuhakamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mosfet 101Dokument15 SeitenMosfet 101Victor TolentinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ball Valves Pentair Valves and ControlsDokument16 SeitenBall Valves Pentair Valves and ControlsABDUL KADHARNoch keine Bewertungen
- TJUSAMO 2013-2014 Modular ArithmeticDokument4 SeitenTJUSAMO 2013-2014 Modular ArithmeticChanthana ChongchareonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Propoxur PMRADokument2 SeitenPropoxur PMRAuncleadolphNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oxygen Cost and Energy Expenditure of RunningDokument7 SeitenOxygen Cost and Energy Expenditure of Runningnb22714Noch keine Bewertungen
- ERIKS Dynamic SealsDokument28 SeitenERIKS Dynamic Sealsdd82ddNoch keine Bewertungen
- LEARNING ACTIVITY Sheet Math 7 q3 M 1Dokument4 SeitenLEARNING ACTIVITY Sheet Math 7 q3 M 1Mariel PastoleroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Precision Machine Components: NSK Linear Guides Ball Screws MonocarriersDokument564 SeitenPrecision Machine Components: NSK Linear Guides Ball Screws MonocarriersDorian Cristian VatavuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hi-Line Sportsmen Banquet Is February 23rd: A Chip Off The Ol' Puck!Dokument8 SeitenHi-Line Sportsmen Banquet Is February 23rd: A Chip Off The Ol' Puck!BS Central, Inc. "The Buzz"Noch keine Bewertungen
- Evaluative Research DesignDokument17 SeitenEvaluative Research DesignMary Grace BroquezaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crystallizers: Chapter 16 Cost Accounting and Capital Cost EstimationDokument1 SeiteCrystallizers: Chapter 16 Cost Accounting and Capital Cost EstimationDeiver Enrique SampayoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Build A Program Remote Control IR Transmitter Using HT6221Dokument2 SeitenBuild A Program Remote Control IR Transmitter Using HT6221rudraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem Set SolutionsDokument16 SeitenProblem Set SolutionsKunal SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SDS OU1060 IPeptideDokument6 SeitenSDS OU1060 IPeptideSaowalak PhonseeNoch keine Bewertungen
- STS Prelim ExamDokument2 SeitenSTS Prelim ExamMychie Lynne MayugaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Features of The Microcredit Regulatory Authority Act, 2006Dokument10 SeitenBasic Features of The Microcredit Regulatory Authority Act, 2006Asif Hasan DhimanNoch keine Bewertungen
- !!!Логос - конференц10.12.21 копіяDokument141 Seiten!!!Логос - конференц10.12.21 копіяНаталія БондарNoch keine Bewertungen
- SEC QPP Coop TrainingDokument62 SeitenSEC QPP Coop TrainingAbdalelah BagajateNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brochure en 2014 Web Canyon Bikes How ToDokument36 SeitenBrochure en 2014 Web Canyon Bikes How ToRadivizija PortalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bala Graha AfflictionDokument2 SeitenBala Graha AfflictionNeeraj VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prlude No BWV in C MinorDokument3 SeitenPrlude No BWV in C MinorFrédéric LemaireNoch keine Bewertungen
- Checklist of Requirements For OIC-EW Licensure ExamDokument2 SeitenChecklist of Requirements For OIC-EW Licensure Examjonesalvarezcastro60% (5)
- Peran Dan Tugas Receptionist Pada Pt. Serim Indonesia: Disadur Oleh: Dra. Nani Nuraini Sarah MsiDokument19 SeitenPeran Dan Tugas Receptionist Pada Pt. Serim Indonesia: Disadur Oleh: Dra. Nani Nuraini Sarah MsiCynthia HtbNoch keine Bewertungen
- SOP-for RecallDokument3 SeitenSOP-for RecallNilove PervezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Role of PAODokument29 SeitenRole of PAOAjay DhokeNoch keine Bewertungen