Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Endocrine System - de Jesus MD
Hochgeladen von
KerenTabuenaOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Endocrine System - de Jesus MD
Hochgeladen von
KerenTabuenaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Endocrine system Flordeliza M.
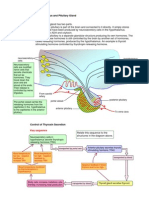
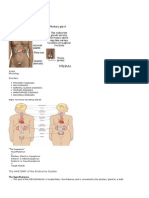
De Jesus, MD Pituitary gland/hypophysis cerebri Small oval structure attached to the undersurface of the brain by the infubdibulum Located in the sella turcica of the sphenoid bone Its hormone secretion influences the activities of many other endocrine glands, hence referred to as the master endocrine gland Vital to life Divided into 2 lobes anterior (adenohypophysis) and posterior (neurohypophysis) Hypothalamic connections Hypothalamo-hypophysial portal system blood vessels connecting the anterior lobe to the hypothalamus. This transmits the releasing factors to the anterior lobe Hypothalamo-hypophysial nerve tract connection of the posterior lobe of pituitary to the supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei of the hypothalamus. Hormones vassopressin and oxytocin are released at the axon terminals in the posterior lobe of pituitary Blood supply and venous drainage of the pituitary gland Superior and inferior hypophyseal arteries from the internal carotid artery Veins drain into the intercavernous sinus Pineal gland Small gland shape like a pine cone (hence its name) Located in the midline attached to the posterior end of the roof of 3rd ventricle, over hanging the midbrain Roughly 1 cm in length Function of pineal gland Secretes melatonin, serum concentration of which is low during daylight, increase to a peak during the dark Melatonin is not a major regulator of sleep pattern, but undoubtedly has some effects Decrease serum level among elderly insomniacs Has anti-gonadotropic effects Thyroid gland Encapsulated bilobed gland Enclosed by the pretracheal fascia outside the capsule An isthmus connects the 2 lobes across the midline, in front of 2nd -4th tracheal rings Weighs about 25 gms Blood supply of thyroid gland The blood supply of thyroid gland comes from: External carotid superior thyroid Thyrocervical artery inferior thyroid Arch of aorta/left common carotid/or brachiocephalic thyroidea ima
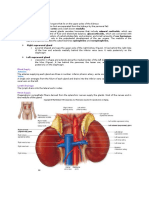
Function of thyroid gland Secretion of thyroxin and triidothyronine, which increase metabolic activity of most cells in the body, increase oxygen consumption and heat production Also produces the hormone thyrocalcitonin, that lowers the blood calcium level Not under the control of the pituitary but stimulated by hypercalcemia and suppressed by hypocalcemia Parathyroid gland Weighs about 25 mg Located on the posterior surface of the thyroid gland Usually 2 pairs, upper pair being more constant in position at the middle part of posterior surface of thyroid gland Blood supply comes from superior and inferior thyroid arteries Function of parathyroid glands Secrete parathormone Osteoclastic hormone, mobilize calcium from bones, increase absorption of calcium from intestine, increase reabsorption of calcium in proximal convoluted tubules Thymus gland A bilobed organ located in the superior mediastinum directly behind the manubrium. It is the primary or central lymphoid organ Its function is production of T (thymic) lymphocytes that are seeded to the rest of the lymphatic system. Thymic hormone Thymosin - influences the maturation and function of lymphocytes within the thymus and elsewhere in the body Blood supply of thymus gland Inferior thyroid artery Internal thoracic artery Suprarenal glands Paired glands Yellowish retroperitoneal organs that lie on the upper pole of the kidneys Surrounded by renal ( Gerotas) fascia but separated from the kidney by perirenal fats Right suprarenal gland Pyramidal, caps the upper pole of the right kidney Relations Anterior right lobe of the liver Medially partly overlapped by inferior vena cava Posteriorly rests on the diaphragm
Left suprarenal gland Cresentic or semilunar, extends along the medial border of the left kidney from upper pole to the hilus. Relations Anterior pancreas, lesser sac, and stomach Posterior rest on the diaphragm Blood supply and venous drainage Blood supply Superior suprarenal from inferior phrenic artery Middle suprarenal from abdominal aorta Inferior suprarenal from renal artery Venous drainage Right suprarenal vien, drains directly in the inferior vena cava - Left suprarenal vein, drains into the left renal vein Parts of suprarenal glands Suprarenal cortex, function controlled by anterior lobe of pituitary through a hormone adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) Hormones secreted by the cortex Mineral corticoids, control fluid and electrolyte balace Glucocorticoids, control metabolism of carbohydrates, fats and proteins Small amount of sex hormone, probably paly a role in the prepubertal development of sex organs Suprarenal medulla Secretes athecholamines, epinephrine and norepinephrine Pancreas Endocrine function of pancreas Endocrine part of pancreas islets of Langerhans, numerous in the tail Four cells in the islets Alpha - secretes glucagon in response to increas blood glucose Beta - secretes insulin Delta secretes somatostatin Insulin Insulin promotes rapid absorption, storage and utilization of glucose and with important effects in fats and protein metabolism
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Anatomi Endokrin Mei 2019Dokument64 SeitenAnatomi Endokrin Mei 2019insiya insiyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy Endocrine System PPT 2023Dokument70 SeitenAnatomy Endocrine System PPT 2023bereket bekeleNoch keine Bewertungen
- PancreasDokument35 SeitenPancreasPaskalisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture Endokrin 2014Dokument22 SeitenLecture Endokrin 2014via73Noch keine Bewertungen
- Primary Endocrine Organs Hypothalamus & Pituitary Gland: Regulate Many Body SystemsDokument5 SeitenPrimary Endocrine Organs Hypothalamus & Pituitary Gland: Regulate Many Body SystemsGizem OsmanogluNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine System 1Dokument1 SeiteEndocrine System 1grace_wong6051Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pankreas & LienDokument38 SeitenPankreas & LienopimadridistaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Key Features: The Hypothalamus and Pituitary GlandDokument2 SeitenKey Features: The Hypothalamus and Pituitary GlandeibsourceNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 - Adrenal Glands (386-389, 184-187, 215-217)Dokument18 Seiten3 - Adrenal Glands (386-389, 184-187, 215-217)Osama adel Mohamed SmadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hormon Hipotalamus HipofisisDokument20 SeitenHormon Hipotalamus HipofisisSyam UnhasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine Histology NotesDokument5 SeitenEndocrine Histology NotesJulie TranNoch keine Bewertungen
- DR Zainuri Kuliahanatomi EndocrineDokument57 SeitenDR Zainuri Kuliahanatomi EndocrinetomyhardiantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine Gland....Dokument62 SeitenEndocrine Gland....Sabita TripathiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9 The Endocrine SystemDokument10 Seiten9 The Endocrine SystemSenthereng MoaisiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine System .Dokument19 SeitenEndocrine System .NOOB GAM1NGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endo All MergeDokument586 SeitenEndo All MergeShivani DurgeNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Endocrine System NotesDokument6 SeitenThe Endocrine System NotesRohit AnthuliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- HistoEndocrineSystem by DR - NaDokument64 SeitenHistoEndocrineSystem by DR - NaAymen MouradNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hyperthyroidism Case ProperDokument19 SeitenHyperthyroidism Case ProperHedy Mae BautistaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Surgical Anatomy of Pancreas: DR GaneshDokument42 SeitenSurgical Anatomy of Pancreas: DR GaneshGanesh MarutinathNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine System 2023-2024Dokument16 SeitenEndocrine System 2023-2024michaelsoncole410Noch keine Bewertungen
- PBL Endocrine Week 1 Jason Leonard Wijaya 01071180063Dokument8 SeitenPBL Endocrine Week 1 Jason Leonard Wijaya 01071180063Jason LeonardNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thyroid and Parathyroid GlandsDokument5 SeitenThyroid and Parathyroid GlandsChristopher PhilipsNoch keine Bewertungen
- BS ParatiroidDokument21 SeitenBS ParatiroidNo StradamusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Suprarenal Glands ClintDokument1 SeiteSuprarenal Glands ClintBianca WatanabeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and PhysioDokument4 SeitenAnatomy and PhysioRhiza PagdangananNoch keine Bewertungen
- AP100 Final Exam Study GuideDokument27 SeitenAP100 Final Exam Study Guidebhilligoss35100% (1)
- Final Review Renal SystemDokument30 SeitenFinal Review Renal SystemCarolyne CharvozNoch keine Bewertungen
- It Means Shield It Is Most Vascular GlandDokument9 SeitenIt Means Shield It Is Most Vascular GlandDr santoshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine SystemDokument36 SeitenEndocrine SystemMohamadMahdiKesserwan100% (4)
- EndocrineDokument70 SeitenEndocrinehamidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 13 Endocrine System NotesDokument12 SeitenChapter 13 Endocrine System NotesJane XuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7.2 Suprarenal Glands f2f-s1b2-23Dokument17 Seiten7.2 Suprarenal Glands f2f-s1b2-23shlokNoch keine Bewertungen
- ENDOCRINOLOGYDokument63 SeitenENDOCRINOLOGYYuni IndrianiNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Adrenal Gland: Anatomy, Embryology & PhysiologyDokument29 SeitenThe Adrenal Gland: Anatomy, Embryology & PhysiologyrajarshikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Overview of The Structures of The Endocrine SystemDokument45 SeitenOverview of The Structures of The Endocrine SystemVijay MgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy of PancreasDokument6 SeitenAnatomy of PancreasNariska CooperNoch keine Bewertungen
- ANA Trans - Endo ReproDokument14 SeitenANA Trans - Endo ReproSan LapuhapuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adrenal Gland-1Dokument2 SeitenAdrenal Gland-1Nnanyelugo AdaobiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adrenal GlandDokument15 SeitenAdrenal GlandSivanandan Ramar100% (1)
- HypothalamusDokument5 SeitenHypothalamusBoneGrissleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine SystemDokument25 SeitenEndocrine Systemangel_maui100% (13)
- Anatomy NotesDokument32 SeitenAnatomy NotesRufaidy IbrahimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pit GlandDokument17 SeitenPit GlandAaa JjjjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypothlamic-Pituitary Physiology: Mona Abou Chebl MD. METABOLISM-2017 Lectures 1-2 March 20 2018Dokument197 SeitenHypothlamic-Pituitary Physiology: Mona Abou Chebl MD. METABOLISM-2017 Lectures 1-2 March 20 2018rachid09Noch keine Bewertungen
- Definitions - Topic 14 CAIE Biology A-LevelDokument6 SeitenDefinitions - Topic 14 CAIE Biology A-LevelExcelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine System IntroductionDokument8 SeitenEndocrine System IntroductionAlchemi Mij PoolscanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ANATOMY Endocrine TranscribedDokument9 SeitenANATOMY Endocrine TranscribedYanyan PanesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine SystemDokument10 SeitenEndocrine SystemPeej Reyes100% (1)
- Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDokument9 SeitenChemical Coordination and IntegrationAjay JamwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pituitary GlandDokument5 SeitenPituitary Glandearly birdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine System ReviewDokument16 SeitenEndocrine System Reviewarjohnson83Noch keine Bewertungen
- Physio SeminarDokument21 SeitenPhysio SeminarNandini BhargavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and Physiology Cardiovascular System The HeartDokument6 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology Cardiovascular System The Heartmark OrpillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine GlandsDokument13 SeitenEndocrine GlandsJoan GalarceNoch keine Bewertungen
- L14Dokument2 SeitenL14MilenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thalamus and HypothalamusDokument19 SeitenThalamus and Hypothalamusapi-266034924Noch keine Bewertungen
- PancreasDokument2 SeitenPancreasSam TagardaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypothlamic-Pituitary Physiology: Mona Abou Chebl MD. METABOLISM-2018 Lectures 1-2 March 14 2018Dokument213 SeitenHypothlamic-Pituitary Physiology: Mona Abou Chebl MD. METABOLISM-2018 Lectures 1-2 March 14 2018rachid09Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lipids LecDokument7 SeitenLipids LecKerenTabuenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbohydrates LabDokument11 SeitenCarbohydrates LabKerenTabuenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CarbohydratesDokument3 SeitenCarbohydratesKerenTabuenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SCLDokument39 SeitenSCLKerenTabuenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 (1) - Man As The Acting PersonDokument41 Seiten5 (1) - Man As The Acting PersonJeprel Del PradoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Structure FunctionDokument35 SeitenCell Structure FunctionKerenTabuenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conscience Subjtv NormDokument13 SeitenConscience Subjtv NormRiza Mae MerryNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Objective Norm of MoralityDokument20 SeitenThe Objective Norm of MoralityAlecza Mae SavellaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SA - Lecture 7 - Rural & Urban CommunitiesDokument21 SeitenSA - Lecture 7 - Rural & Urban CommunitiesKerenTabuenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Newtons Laws of MotionDokument33 SeitenNewtons Laws of Motionapi-237070241Noch keine Bewertungen
- VariationDokument14 SeitenVariationYongguk BangNoch keine Bewertungen
- HUMAN IMMUNE SYSTEM - Notes RepairedDokument19 SeitenHUMAN IMMUNE SYSTEM - Notes RepairedLoren EscotoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Connecting The Immune System, Systemic Chronic Inflammation and The Gut Microbiome - The Role of Sex.Dokument23 SeitenConnecting The Immune System, Systemic Chronic Inflammation and The Gut Microbiome - The Role of Sex.MariaAndreaLaraSalasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module # 3 Physiological Changes in Aging Affecting Various SystemsDokument30 SeitenModule # 3 Physiological Changes in Aging Affecting Various SystemsJann ericka JaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thyroid Eye Disease Diagnosis and TreatmentDokument486 SeitenThyroid Eye Disease Diagnosis and TreatmentUnsmil UnguNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Nunology of The Pineal Gland by DR - NEB HERUDokument107 SeitenThe Nunology of The Pineal Gland by DR - NEB HERUNeb Heru95% (41)
- Embryology and Anatomy of The Thymus Gland: Carla PalumboDokument2 SeitenEmbryology and Anatomy of The Thymus Gland: Carla PalumbokatyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine ClarkDokument834 SeitenEndocrine ClarkKhaled AbdelgalelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Consumer Behaviour Asia Pacific 1st Edition Hoyer Test BankDokument26 SeitenConsumer Behaviour Asia Pacific 1st Edition Hoyer Test BankMatthewMossfnak100% (55)
- Unit 1-Lecture 3 Intro To Immuno-Acquired ImmunityDokument65 SeitenUnit 1-Lecture 3 Intro To Immuno-Acquired ImmunityBecky GoodwinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Immunology Uworld Notes (Step 1)Dokument12 SeitenImmunology Uworld Notes (Step 1)Burkitt's LymphomaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diagnosis Unknown EbookDokument252 SeitenDiagnosis Unknown Ebookapi-3738852Noch keine Bewertungen
- LECTURE 1 Endocrine Diseases Lecture 1 January 10-020Dokument68 SeitenLECTURE 1 Endocrine Diseases Lecture 1 January 10-020aleen qawareetNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ebook PDF Diagnostic Histopathology of Tumors 2 Volume Set 5th Edition PDFDokument40 SeitenEbook PDF Diagnostic Histopathology of Tumors 2 Volume Set 5th Edition PDFjoe.andes67297% (36)
- 01 E The Honeymoon Phase Do BetaCells Transiently ReviveDokument40 Seiten01 E The Honeymoon Phase Do BetaCells Transiently ReviveTamara Zelenovic VasiljevicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Patho FEU PGI BCA Exit Exam May 2020Dokument34 SeitenPatho FEU PGI BCA Exit Exam May 2020Sheryl Layne LaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paediatric Chest X-RayDokument10 SeitenPaediatric Chest X-Raypheeplukz100% (1)
- Parasites and Cancer and JCNDokument7 SeitenParasites and Cancer and JCNapi-3708784100% (1)
- Immunology Arranged (MedicalBooksVN - Com)Dokument25 SeitenImmunology Arranged (MedicalBooksVN - Com)于千晏Noch keine Bewertungen
- T CellDokument19 SeitenT CellSachin AnandNoch keine Bewertungen
- Immuno Sero Lec Prelim TransDokument15 SeitenImmuno Sero Lec Prelim TransLoren EscotoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lymphatic System HistologyDokument88 SeitenLymphatic System Histologybellabelbon100% (1)
- Advances in Immunology: T Hla SDokument8 SeitenAdvances in Immunology: T Hla Sodiseu81Noch keine Bewertungen
- Histology of Thymus by Dr. RoomiDokument21 SeitenHistology of Thymus by Dr. RoomiMudassar Roomi100% (3)
- Allergy and Immunology Adelman - Manual of Diagnosis and Therapy 4th EdDokument516 SeitenAllergy and Immunology Adelman - Manual of Diagnosis and Therapy 4th Edhunesh1981Noch keine Bewertungen
- Outlines in PathologyDokument200 SeitenOutlines in PathologyLisztomaniaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Végleges - Absztraktok - 04 - 2 9Dokument55 SeitenVégleges - Absztraktok - 04 - 2 9Bálint L'Obasso TóthNoch keine Bewertungen
- Relatorio TreportDokument3 SeitenRelatorio TreportFabio ApolinarioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intrathyroidal Lymphoepithelial (Branchial) Cyst: Diagnostic and Management Challenge of A Rare EntityDokument5 SeitenIntrathyroidal Lymphoepithelial (Branchial) Cyst: Diagnostic and Management Challenge of A Rare EntityMeliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Immunology NotesDokument37 SeitenImmunology NotesSanthosh Kalash100% (1)
- Nucleus Nuclear Chromatin Cytoplasm:: The Lymphoid SystemDokument9 SeitenNucleus Nuclear Chromatin Cytoplasm:: The Lymphoid SystemHiraya ManawariNoch keine Bewertungen