Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Definition of Changing Price
Hochgeladen von
Fia RahmaOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Definition of Changing Price
Hochgeladen von
Fia RahmaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
DEFINITION OF CHANGING PRICE General price usually arise when all price of service and Products are changes
in Economic. Generally, the increasing in price called inflation, meanwhile decreasing in price called deflation. What causes inflation? several evidence show that inflation causes by high growth of Economic, the highest of cost of general elected , and expand of international inflation. In other side, special changing price arise when price of some Products, service change through up and down of supply and demand. As consumer, we realize that inflation effected to our standard material of life. We quickly feel the impact when oil or Big Mac up. Disturbance of social and politic which of affected by hiperinflation is extraordinary. There are several phrase of inflation accounting; atribute : chareteristic from one post which Measures by accounting decision. Equity income : increase current cost non-moneter asset. hiperinflasi : the high inflation level , ex. when general level price in Economic increase more than 25% every year. inflasi : the increase general price in all of produt and service in Economic. Moneter asset : claim to several fix currency in future, ex. cash and receivables. Moneter income : Increase of general purchasing power arise when moneter liability retained during inflation period. Moneter liabilities : requirement to pay some fix currency in future. nonmoneter asset : asset which is not fix claim to cash. nonmoneter liabilities : payable which not required to pay some cash in future. Why are Financial Statement During Periods of Changing Prices? Potentially Misleading
During periods of inflation, revenues are based on the general purchasing power of the certain period. Expenses, such as depreciation and amortization, may be based on currency of higher general purchasing power because their related assets were typically acquired in the past when GPLs were lower. Deducting expenses based on historical purchasing power from revenues that expressed in currency of certain purchasing power yields a nonsensical index of performance. Overstatement in reporter income may lead to ; 1. comparable higher taxes 2. higher dividen from stockholders 3. higher wages from employee 4. Policy which deny from goverment host
In inflation period, revenue usually show in currency which have purcahsing power less than expenditures. Thats why , it will useful if we recognize effect inflation in explisit, because of reasons : 1. Effect of changing price depend on parsial to transaction and Company condition. 2. handling problem affected by changing price depend on deeper understanding to that problem 3. manager statement about problem which affected by changing price more beliveable if Company publish financial information about that problem Types of Adjustments for Changing Prices combination of statistic is to Measures general or special changing price usually not going together. to calculate changes influance level general price to financial report called by historical cost-constant purchasing power model and accounting for special changing price called by current cost model. General Price Level Adjustments To measure income such that it represents an amount that could be describe from the business while preserving the general purchasing power of the firms original investment. Amount currency adjusted by level changing price called by fix currency-historical cost. amount currency not adjusted called nominal. price index General level changing price Measures by general price level (GPL), where: p commodity price and q amount of consumtion. For example if there is a family with 4 people spend $ 20.000 to buy some product & service in end periode year-1 ( based year = beginning year -2 ) and $ 22.000 to buy same product one year later. So, price index for ends year -2 is $ 22.000/20.000 or 1,100. This number mean that level of inflation 10% in second year ( year 2). In same way, if 2 years later ( end of year 3 ) that family spend $ 23.500 for same product , so the general price index $ 23.500/20.000 or 1,175, or 17,5% since based year. Price index for based year is $20.000/20.000 or 1,000 Utilizing Price Index Number of price index use in transalation of Money which pay in past periode to purchasing power equivalent in ending periode (fix purchasing-historical cost). the formula that used is: GPLC/GPLtd x Jumlah nominaltd=PPEc where: GPL c = general price index = current year
td PPE
= transaction date = purchasing power equivalent
For example, assume we spend $ 500 in ending year, and $ 700 one year later. We will try to calculate how much expenditure in purchasing power equivalent in Third year, use number of price index , from past example so we can calculate ; Third year (3) Ending Year-1 Year-2 Amount of expenditure $ 500 $ 700 Adjusted factor 1,175/1000 1,175 / 1000 Equivalent purchasing power $ 587,50 $ 747,43
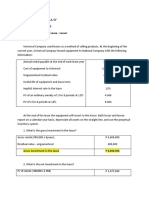
From that calculation, we know that if we want to buy a products with price $ 500 in year -1, we need $ 587,50 for the same Products in year -3. And in year 2 when we pay $ 700, so we need $ 747,43 for end year -3. If all transaction do as same as certain periode , so price level adjusted in short way can use. When we want to show revenue as purchasing power equivalent in ends periode, we can use this formula GPLc/GPLavg x Total revenue = PPEc General Level Price Adjusted Object In traditional, profit ( net wealth after tax ) is part of wealth ( net asset ) which can put by Company in certain periode accounting, without reduce wealth under their level. With assumption Theres no investment by owner in that periode. For example , we assume that Company in Argentina begin their calendar year with cash ARS100.000, which convertion become inventor ( ex. 10.000 unit of CD ( compact Disc) , with 10 peso for 1 unit ). This Company sell all inventories in one year with increasing price 50%. Assumption theres no inflation, so profit bussines ARS 50.000, the different between beggining and ending net asset ($150.000-100.000). So, the Company have same amount as in beginning investment. Now, if inflation level 21%, with average general price level 1,10 in one year ( 1,21 in ends year ), so companys profit will adjusted and calculation by that infaltion; Nominal of Peso Revenue Expanditures Operational profit Moneter Loss ARS 150.000 (100.000) ARS 50.000 = Adjustment factor 1,21/1,10 1,21/1,00 Current Peso ARS165.000 (121.000) ARS 44.000 (15.000)
Net Profit
ARS 50.000
ARS 29.000
In that calculation , there are moneter loss, where is it from? In inflation periode, companys wealth which not realtion with operasional activity has change. This change comes from moneter asset or liabilities claim to pay some money in future. Moneter asset include cash, receivables, generally reduce the purchasing power in inflation periode. Moneter liabilities include almost payable, which in generally have an increasing purchasing power in inflation periode. IAS29 decision by International Accounting Standard Counsil, adjust with this changing price for accounting. This show below of net income report from VESTEL, which adjust with inflation.
IAS 29 - Financial reporting in Hiperinflation Economics (IAS29) require the financial report show in currency of hiperinflation Economic in order to disclosure the measuring unit for ends date of balance. And the adjustment numbers in past periode explain in same unit. In one condition IAS 29 must be applicated is three years cumulative inflation level which close or more than 100%. For example in VESTEL cumulative three yearss inflation level per 31 december 2005 is 36% :70 % based on grocery price index in Turki by Statistic Departement of Turki. Both index has converted as shown ; Year Index Convertion Factor 2005 8.785,7 1.000,0 2004 8.403,8 1.045,0 2003 7.382,1 1.190,0
Restatement in balance account and net income use general index price and relevant convertion factors not means that Company can realize or complete the same value of asset and liabilities as shown in balance sheet. This is not mean that Company can pay back or complete the equity value of stockholders. Current Cost Adjusted Current cost model different with conventional accounting in two aspect. First, valuation asset at current cost than historical cost. because in base asset same with current discount from futere cash flow. second, income defined as net asset after tax Company, that is total Resources which is distributable of Company in periode (not include tax considarable)while maintain production capacity or physic capital. one way to mantain capital is adjust beginning net asset Company, (i.e. current billing price, list price from supplier, and others) to reflect changing current cost equivalent from asset in period. For example ; current cost model , transaction of companys partner can illustrated with accounting equalization ; ( in thousand) Asset = Liability + Owners equity No 1 2 3 4 5 Cash 100.000 (100.000) 150.000 Inventory 100.000 40.000 (140.000) Equity 100.000 150.000 ( revenue ) 40.000 reval OE (140.000) expense
First line , show influence of beginning Investment Company ARS 100.000. Second line show cash exchange with inventory. Third line show sold of inventory for get cash, which increase owners equity in same amount. To describe certain expense to sales, company increase the support value of inventory 40%, as shown in fourth line. Guarantee for inventory 40% is increasing for revaluation account owners equity ARS40.000. Company explain that to defend their operasional capacity, the increasing of assets expense which consume to get revenue in certain year must be attend. Company also pressure that disclosure of current cost also see special changing price which give influence for Company. Current Cost Adjusted With General Price Level This topic related to explain changing price can merger chareteristik of general price level model dan current cost. This Measures, call as current cost adjusted with general prices, using general price index or special. Another purpose of Current cost, is to report net assets company in current cost, and to report total income which withdrawn net wealth after tax. One charateristic from current cost model which adjusted with level price is disclosure changing current cost from nonmoneter assets company after deduction inflation. The purpose to showing part of changing nonmoneter asset more or less from changing of general purchasing power. For example ; we assume that current cost from Machines equipment in beginning year is $1.000, in ending year the changing cost become $1.250. General price level in the same year increase from 100 to 110. Its mean that we will need $110 in end year to get what we can buy with $100 in beggining year. And the different changing price of There are two disclosure rather include in stockholderss equity mean as : The increasing of non moneter asset causes general inflation is total amount / balance from Company in order to face that general inflation. The second component, example the increasing current cost more than general inflation, in some opinion means that it is unrealized equity income fron nonmoneter asset.
This shown below Financial reporting from Grupo Modello which cost current adjusted with level price ;
2. Accounting Policy - Representation standard : Consolidation financial reporting Grupo Modello include inflation to financial information. - Comparability : the numbers which show in consolidation financial reporting with notes explain consistently in peso purchasing power 31 december 2005 with applicate factors from National Consumer Price Index (NCPI). - Cureent asset : This account recognize in book value , and restatement during apply inflation factor from NCPI to net value change based on appraisal. - Inventory : this account revaluated by using changing method . without more than unrealized net value. - Depreciaton : this account calaculate based on restatement value of current asset, based on profitability period Economic life from appraisal and technic di vision of Grupo Modello.
- Restatement stackholders equity : component of stockholderss equity restatement by using factor from NCPI, and show in consolidation financial reporting as restatement value. - Cumulative profit or Loss from parents nonmoneter asset : this account is cumulative changing value of nonmoneter asset which causes another general inflation.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- E-Government Services and User Acceptance: The Unified Models' PerspectiveDokument14 SeitenE-Government Services and User Acceptance: The Unified Models' PerspectiveFia RahmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tugas Hal 279Dokument5 SeitenTugas Hal 279Fia RahmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jurnal IlmiahDokument21 SeitenJurnal IlmiahFia RahmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ecom Adoption in MalaysiaDokument6 SeitenEcom Adoption in MalaysiasdaqtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ecom Adoption in MalaysiaDokument6 SeitenEcom Adoption in MalaysiasdaqtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ecom Adoption in MalaysiaDokument6 SeitenEcom Adoption in MalaysiasdaqtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Beams10e Ch01 Business CombinationsDokument40 SeitenBeams10e Ch01 Business CombinationsArifta Nur RahmatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Saldaga LyricsDokument1 SeiteSaldaga LyricsFia RahmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- When Your Cold Words Reach My HeartDokument1 SeiteWhen Your Cold Words Reach My HeartFia RahmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Reporting and Changing PricesDokument6 SeitenFinancial Reporting and Changing PricesFia RahmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Reporting and Changing PricesDokument6 SeitenFinancial Reporting and Changing PricesFia RahmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- CFA RC Team-Eternals UFE Mongolia-1Dokument21 SeitenCFA RC Team-Eternals UFE Mongolia-1oyunnominNoch keine Bewertungen
- Logistics Service Enterprise Application FormDokument9 SeitenLogistics Service Enterprise Application FormGabriel EmersonNoch keine Bewertungen
- K ElectricDokument9 SeitenK ElectricAyesha Bareen.Noch keine Bewertungen
- 360 Degree Deal in Music Recording ContractsDokument8 Seiten360 Degree Deal in Music Recording ContractsPriyansh Singh RajputNoch keine Bewertungen
- Corporate Finance 2 SyllabusDokument11 SeitenCorporate Finance 2 SyllabusMai NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Box Truck Business PlanDokument28 SeitenBox Truck Business PlanDee DawaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question 1Dokument5 SeitenQuestion 1Yono SéNoch keine Bewertungen
- Roku Inc (ROKU US) - AdjustedDokument9 SeitenRoku Inc (ROKU US) - Adjustedjustinbui85Noch keine Bewertungen
- Report INDDokument13 SeitenReport INDKacangHitamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assets Liabilities & EquityDokument3 SeitenAssets Liabilities & EquityJasmine ActaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Palantir Q1 2023 Business UpdateDokument29 SeitenPalantir Q1 2023 Business UpdateJoseph VuralNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project Report Ratio Analysis of P&GDokument16 SeitenProject Report Ratio Analysis of P&Gvedprakashyadav5053100% (1)
- Accounting For Managers Question Paper PDFDokument4 SeitenAccounting For Managers Question Paper PDFSmruti Ranjan Nayak100% (1)
- Igcse Accounting Prepayments Accruals Questions AnswersDokument16 SeitenIgcse Accounting Prepayments Accruals Questions AnswersInnocent GwangwaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- JD Management Trainee-SalesDokument1 SeiteJD Management Trainee-SalesAnkita JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- AnnualReport2013 EDokument167 SeitenAnnualReport2013 EMohammad AldehneeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Retail Math: Talking The Talk of Retail Business!Dokument29 SeitenRetail Math: Talking The Talk of Retail Business!Furqan DxNoch keine Bewertungen
- ch01 Introduction Acounting & BusinessDokument37 Seitench01 Introduction Acounting & Businesskuncoroooo100% (1)
- Week 3Dokument60 SeitenWeek 3AJNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final AccountsDokument91 SeitenFinal AccountsKartikey swami0% (1)
- Case Spirit and Northwest Airlines IndustryDokument42 SeitenCase Spirit and Northwest Airlines IndustryTuan Anh NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cottle Taylor CaseDokument9 SeitenCottle Taylor CaseVignesshvar UmasankarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Commerce Paathshaala: Pu-Ii Annual Examination April-May-2022 Accountancy Key Answers Section A (1 Mark Answers)Dokument12 SeitenCommerce Paathshaala: Pu-Ii Annual Examination April-May-2022 Accountancy Key Answers Section A (1 Mark Answers)Ashok dore Ashok doreNoch keine Bewertungen
- FY19 NCAA Financial Report-Ohio StateDokument93 SeitenFY19 NCAA Financial Report-Ohio StateMatt BrownNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ara Asset Management: Analyst Research ReportDokument33 SeitenAra Asset Management: Analyst Research Reporthi_chrisleeNoch keine Bewertungen
- PWC TP Oecd Beps CBCR GuidanceDokument4 SeitenPWC TP Oecd Beps CBCR GuidanceIchbin BinNoch keine Bewertungen
- FA1 3y03aef4Dokument160 SeitenFA1 3y03aef4Akash LoiyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Combined Valuing Yahoo! in 2013Dokument15 SeitenCombined Valuing Yahoo! in 2013George Ng100% (1)
- Lobrigas Unit5 Topic4 AssessmentDokument5 SeitenLobrigas Unit5 Topic4 AssessmentClaudine LobrigasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Income TaxDokument292 SeitenIncome TaxynnadadenipNoch keine Bewertungen