Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Latih Excel Cookies Error
Hochgeladen von
Desy PurliantiOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Latih Excel Cookies Error
Hochgeladen von
Desy PurliantiCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Excelet
Investigating the Height of a Stack of Cookies and Exploring Measurement Errors
Analysis ToolPak must be loaded for this spreadsheet to function. Instructions are given on the last tab.
Click on the tabs below!
Sinex, Gage, & Beck (2007) The AMATYC Review 29 (1) click here
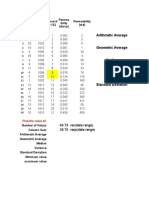
Investigating the height of a stack of cookies - Your measurements in centimeters!
Enter your data in the appropriate yellow cells in the table on the left. number of cookies 0 1 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 12.3 8.6 6.1 3.5 2 height of stack 0.0 2.4 14.0 -0.07812
12.0 1.157761 0.926209
y = 1.236x - 0.078 -0.06249 R = 1.000
1.914911 2.903613 3.892316 4.881018
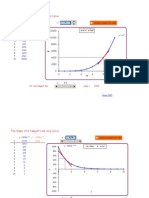
The regression line (blue), equation, and r2 will appear when data are entered. If you don't have data for a certain number of cookies, leave the cell blank.
height of stack, cm
2.393639 10.0 3.629517 8.0 4.865394 6.06.101272
5.86972 4.0 7.33715 8.573028 6.858422 2.0 9.808906 7.847125 0.011.04478 8.835827 0 2 9.824529 -2.012.28066
10
number of cookies change average thickness (the green line appears) new slope 0.8 increase 0.989 8 decrease
Using the regression equation from the graph, the following can be calculated: enter number of cookies = measured stack height = 20 50 predicted height of stack = predicted number of cookies = 24.6 40.5
Sinex, Gage, & Beck (2007)
Investigating the height of a stack of cookies
average cookie thickness = number 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 slope: intercept: r2: height 0.0 1.2 2.5 3.7 5.0 6.2 7.4 8.7 9.9 11.2 12.4 1.24 0.00 1.000 constant proportional error 1.2 2.5 3.7 5.0 6.2 7.4 8.7 9.9 11.2 12.4 13.6 1.24 1.24 -error 0.0 1.5 3.1 4.6 6.2 7.7 9.2 10.8 12.3 13.9 15.4 1.54 0.00 -random error 0.0 2.6 3.7 5.0 6.0 7.7 8.9 10.1 11.3 12.6 1.26 -0.03 0.999 Random Error 0.031 31 The actual errors or differences are plotted on the next tab. none some
height of stack, cm
1.24
of cookies of stack
18.0 16.0 14.0 12.0 10.0 8.0 6.0 4.0
1.2
2.0
0.0 0 2 4 6 number of cookies 8 10
extra cookie =
1.24
spacer thickness =
0.3
Values for regression lines fit to appropriate data.
Sinex, Gage, & Beck (2007)
Plotting the difference (this worksheet responses to changes from the error types worksheet)
number 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
height 0 1.2 2.5 3.7 5.0 6.2 7.4 8.7 9.9 11.2 12.4
constant error 1.24 2.5 3.7 5.0 6.2 7.4 8.7 9.9 11.2 12.4 13.6 difference 1.24 1.24 1.24 1.24 1.24 1.24 1.24 1.24 1.24 1.24 1.24
proportional error 0 1.5 3.1 4.6 6.2 7.7 9.2 10.8 12.3 13.9 15.4 0 0.3 0.6 0.9 1.2 1.5 1.8 2.1 2.4 2.7 3
random difference error difference 0 1.2 2.6 3.7 5.0 6.0 7.7 8.9 10.1 11.3 12.6 0 0.0 0.1 0.0 0.0 -0.2 0.2 0.2 0.2 0.1 0.2 0.000000
3 0.000000 2.5 0.124000 2 -0.031000 3.5
of cookies of stack
0.031000 1.5 -0.248000 1
0
0.217000 0.5 0.217000 0.186000 0.124000 0.155000
-0.5 0 2 4 6 8 10
difference
number of cookies
difference = constant error - height of stack
mean random error difference =
0.07
(should be zero or very close) difference = proportional error - height of stack difference = random error -height of stack
Sinex, Gage, & Beck (2007)
can be discovered and corrected or controlled, such as mis-calibrated measuring devices
error can be minimized by replicate measurements - no control over
systematic or determinant or commonly called bias
random or indeterminant
constant
proportional
causes scatter in the data r2 < 1
influences the intercept
influences the slope
Would this ruler cause any problems? If so, what?
10
Sinex, Gage, & Beck (2007)
Combination of errors (this worksheet responses to changes from the error types worksheet)
number 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
height 0 1.2 2.5 3.7 5.0 6.2 7.4 8.7 9.9 11.2 12.4 r2 =
constant error 1.2 2.5 3.7 5.0 6.2 7.4 8.7 9.9 11.2 12.4 13.6 1.000 difference 1.2 1.2 1.3 1.2 1.2 1.2 1.3 1.2 1.3 1.2 1.2 r2 =
proportional error 0.0 1.6 3.1 4.6 6.1 7.7 9.3 10.8 12.3 13.9 15.4 1.000 difference = constant error - height of stack difference = proportional error - height of stack difference 0.0 0.3 0.6 1.2 1.5 1.8 2.1 2.4 2.7 3.0 difference 0.9 4.0 3.0 2.0 1.0 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0 0.000000 4 2 6 0.000000 number of cookies 0.000000 8 10
of cookies of stack
0.0
-1.0
These r2 values are for the appropriate stack height as a function of the number of cookies graph (not shown).
Random Error 0.002 2 none some
This is a new random error generator connected to the constant and proportional errors.
Sinex, Gage, & Beck (2007)
Building a comparison graph
Enter data in yellow cells; points, x = y, and regression lines will appear. Device 1 Device 2
2 0
regression between devices slope = intercept = r2 = #DIV/0! #DIV/0! #N/A
0 0
Device 2
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Device 1
This plot allows you to identify the type of error between two
2
devices, methods, or analysts.
regression line
x = y line ----
You can relabel the device columns (green headings) and the axes labels by turning the protection off under Tools.
Sinex, Gage, & Beck (2007)
then select
close Excel and reopen!
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Latih Excel Cookies StackDokument3 SeitenLatih Excel Cookies StackDesy PurliantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Burning CandlesDokument11 SeitenBurning CandlesThivjhan KanaganayagamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applied Statistics Ans KeyDokument3 SeitenApplied Statistics Ans KeyJunaid SiddiqiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Method of Reporting Screen AnalysisDokument4 SeitenMethod of Reporting Screen AnalysisRose Lynn Anne BesaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dia Methods SetupDokument7 SeitenDia Methods SetupScoots LimeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 07a Linear Correlation & Regression (I)Dokument2 Seiten07a Linear Correlation & Regression (I)ng louisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Isen 614 HW1Dokument2 SeitenIsen 614 HW1Advendro ChandraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Statistical Analysis Using Microsoft ExcelDokument11 SeitenStatistical Analysis Using Microsoft ExcelNithi AyyaluNoch keine Bewertungen
- "Automatic" Determination of Particle Size Distribution: Analyze Set ScaleDokument6 Seiten"Automatic" Determination of Particle Size Distribution: Analyze Set ScaleIndalecio PrietoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Delsa™ Nano: (D) (NM) (P.I.) (D) (CM /sec)Dokument2 SeitenDelsa™ Nano: (D) (NM) (P.I.) (D) (CM /sec)Rahmah IdrisNoch keine Bewertungen
- ProblemSet 1 - (NEW2) Screening and Size ReductionDokument7 SeitenProblemSet 1 - (NEW2) Screening and Size ReductionSam Denielle Tugaoen0% (1)
- ProblemDokument25 SeitenProblemAshish BhardwajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unconfined Compression Test: Analysis of Obtained Results Should Include Answers To The Following PointsDokument3 SeitenUnconfined Compression Test: Analysis of Obtained Results Should Include Answers To The Following PointsShre BNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sistem Telemetri Radio: Eksperimen FisikaDokument22 SeitenSistem Telemetri Radio: Eksperimen FisikaMohamad Reza NurrahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stat Z-Test CompDokument1 SeiteStat Z-Test CompMackenzie Heart ObienNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reduccion de VarianzaDokument21 SeitenReduccion de VarianzaEugenia CapoulatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fault Detection Using Data Based ModelsDokument14 SeitenFault Detection Using Data Based ModelsPierpaolo VergatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gauss Seidel - Tabla FacilDokument4 SeitenGauss Seidel - Tabla FacilJohn Paul Bueno RizzoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7708 - MBA PredAnanBigDataNov21Dokument11 Seiten7708 - MBA PredAnanBigDataNov21Indian Lizard KingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control ChartDokument43 SeitenControl ChartSRI RAMNoch keine Bewertungen
- Item 17 MCMHR50V104M4X7Dokument3 SeitenItem 17 MCMHR50V104M4X7difa20061168Noch keine Bewertungen
- Particle Size DistributionDokument21 SeitenParticle Size DistributionNovianto JsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem Set 6Dokument4 SeitenProblem Set 6PeaceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mat Prob Pertemuan 4Dokument20 SeitenMat Prob Pertemuan 4Andi WijayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DAFM CIA-1 by Anand Krishnan G 2227210Dokument9 SeitenDAFM CIA-1 by Anand Krishnan G 2227210Prasath NagendraNoch keine Bewertungen
- C3 1 Exe Quality ToolsDokument9 SeitenC3 1 Exe Quality ToolsHy CaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture7appendixa 12thsep2009Dokument31 SeitenLecture7appendixa 12thsep2009Richa ShekharNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHEE3741 2016 Assignments PDFDokument16 SeitenCHEE3741 2016 Assignments PDFJoshua MitchellNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quality Costing M 41Dokument5 SeitenQuality Costing M 41sm munNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simulation Problems AnsDokument9 SeitenSimulation Problems AnsAnand Dharun100% (1)
- Supply & Demand 2Dokument27 SeitenSupply & Demand 2mgpchangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Bank For Absolute C 5th Edition Savitch Mock 013283071X 9780132830713Dokument36 SeitenTest Bank For Absolute C 5th Edition Savitch Mock 013283071X 9780132830713johnbellgienbqscjt100% (22)
- Statistiek 1920 HER ENG CovDokument8 SeitenStatistiek 1920 HER ENG CovThe PrankfellasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Don Don - S Tabling SkillsDokument6 SeitenDon Don - S Tabling Skillsfortnitegamerpro123451Noch keine Bewertungen
- 12 Getting CatfishedDokument16 Seiten12 Getting Catfishedkimmiej.gilbertNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ids Final SolDokument16 SeitenIds Final SolHumayun RazaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BusStat 2023 HW13 Chapter 13Dokument3 SeitenBusStat 2023 HW13 Chapter 13Friscilia OrlandoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Middle East Technical University Mechanical Engineering Department ME 485 CFD With Finite Volume Method Spring 2017 (Dr. Sert)Dokument34 SeitenMiddle East Technical University Mechanical Engineering Department ME 485 CFD With Finite Volume Method Spring 2017 (Dr. Sert)Kwanchai Choicharoen100% (1)
- Practice Problem 2Dokument7 SeitenPractice Problem 2Austin AzengaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tugas I UnivariateDokument4 SeitenTugas I UnivariateHamza AhsanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tugas I UnivariateDokument4 SeitenTugas I UnivariateHamza AhsanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 Number Systems and CodesDokument90 SeitenChapter 1 Number Systems and Codesfa iqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Esame Quality Data Analysis 2018+07+23Dokument18 SeitenEsame Quality Data Analysis 2018+07+23Giuseppe D'AngeloNoch keine Bewertungen
- WekaDokument22 SeitenWekavaibhav solankiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pratik Zanke Source CodesDokument20 SeitenPratik Zanke Source Codespratik zankeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sampling and Analysis ExamplesDokument53 SeitenSampling and Analysis ExamplesyromeroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advertising - Paulina Frigia Rante (34) - PPBP 1 - ColaboratoryDokument7 SeitenAdvertising - Paulina Frigia Rante (34) - PPBP 1 - ColaboratoryPaulina Frigia RanteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Estimate "Beta" Through MatrixDokument8 SeitenEstimate "Beta" Through MatrixAyeezha HazhmeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8.2a Calculating Normal ProbabilitiesDokument9 Seiten8.2a Calculating Normal ProbabilitiesJob PolvorizaNoch keine Bewertungen
- This Template Is Obtained From HTTP://WWW - Andypope.info Above Mentioned Website Has Great Worksheets Tutorials and Excellent SamplesDokument5 SeitenThis Template Is Obtained From HTTP://WWW - Andypope.info Above Mentioned Website Has Great Worksheets Tutorials and Excellent SamplesiPakistanNoch keine Bewertungen
- This Template Is Obtained From HTTP://WWW - Andypope.info Above Mentioned Website Has Great Worksheets Tutorials and Excellent SamplesDokument5 SeitenThis Template Is Obtained From HTTP://WWW - Andypope.info Above Mentioned Website Has Great Worksheets Tutorials and Excellent Samplesanon-13887Noch keine Bewertungen
- FDP Assignment 1Dokument22 SeitenFDP Assignment 1Muhammad Ikhsan HadisaputraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exam 1Dokument6 SeitenExam 1Danien LopesNoch keine Bewertungen
- H63CMS Jpeg Report JiaweeyoongDokument12 SeitenH63CMS Jpeg Report JiaweeyoongYoong Jia WeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter01 Solutions 10e SIDokument12 SeitenChapter01 Solutions 10e SIMarcos marinhoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oup 8Dokument36 SeitenOup 8TAMIZHAN ANoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture6 Chapter3 - Function Simplification Using Quine-MacCluskey MethodDokument15 SeitenLecture6 Chapter3 - Function Simplification Using Quine-MacCluskey MethodAyesha HussainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eclipse Tutorial 2 Jan 2018Dokument10 SeitenEclipse Tutorial 2 Jan 2018Konul AlizadehNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gradation Curve of The Aggregate Sample For Which Data Are Presented AboveDokument1 SeiteGradation Curve of The Aggregate Sample For Which Data Are Presented AboveSude FilizNoch keine Bewertungen
- WondershareDokument2 SeitenWondershareChoirurohman Bos FaisalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Knten Excel LagiDokument9 SeitenKnten Excel LagiDesy PurliantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Peralatan TIDokument5 SeitenPeralatan TIDesy PurliantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Contoh Excel 2Dokument17 SeitenContoh Excel 2Desy PurliantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Latihan ExcelDokument8 SeitenLatihan ExcelDesy PurliantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Investigating Types of ErrorDokument4 SeitenInvestigating Types of ErrorDesy PurliantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Konten Excel: Flipping PenniesDokument117 SeitenKonten Excel: Flipping PenniesDesy PurliantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Konten Dengan Excel: DerivativeDokument3 SeitenKonten Dengan Excel: DerivativeDesy PurliantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Praktek Excel: Counting - CoinsDokument3 SeitenPraktek Excel: Counting - CoinsDesy PurliantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lat Excel: Calorie - CalcDokument4 SeitenLat Excel: Calorie - CalcDesy PurliantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lat Excel: Calorie - CalcDokument4 SeitenLat Excel: Calorie - CalcDesy PurliantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exploring Area and Perimeter For The Square and RectangleDokument4 SeitenExploring Area and Perimeter For The Square and RectangleDesy PurliantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Latihan Excel-@temperature ScalesDokument7 SeitenLatihan Excel-@temperature ScalesDesy PurliantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Latihan Excel - @P - V - T - SurfaceDokument2 SeitenLatihan Excel - @P - V - T - SurfaceDesy PurliantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- LatihanDokument1 SeiteLatihanDesy PurliantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Latihan ExcelDokument24 SeitenLatihan ExcelDesy PurliantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Proficiency StageDokument10 SeitenProficiency StageFLORITA SERRANO50% (2)
- ALNAP Paper - Getting Remote M&E RightDokument37 SeitenALNAP Paper - Getting Remote M&E RightShahid NadeemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research ProjectDokument39 SeitenResearch ProjectShaira Mae VelascoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Consumer Preference Regarding Apple and Samsung SmartphonesDokument3 SeitenConsumer Preference Regarding Apple and Samsung SmartphonesCris Ezechial0% (1)
- Term Paper Hera PGDMMDokument117 SeitenTerm Paper Hera PGDMMMd. Arifur Rahman HeraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ayoub Jumanne Proposal MzumbeDokument36 SeitenAyoub Jumanne Proposal MzumbeGoodluck Savutu Lucumay50% (2)
- Cohesive Features in The Expository Writing of Undergraduates in Two Chinese UniversitiesDokument36 SeitenCohesive Features in The Expository Writing of Undergraduates in Two Chinese UniversitiesMuftah HamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hammer MillDokument4 SeitenHammer MillinstrutechNoch keine Bewertungen
- Disertasi AkuntansiDokument10 SeitenDisertasi AkuntansiEcko Ione PurwantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 7 EpidemiologyDokument68 SeitenWeek 7 EpidemiologyAngela Louise SmithsNoch keine Bewertungen
- SPH4U Course OutlineDokument3 SeitenSPH4U Course OutlineShakib FirouziNoch keine Bewertungen
- Recruitment and Selection Policy in NaharDokument23 SeitenRecruitment and Selection Policy in NaharSai PrintersNoch keine Bewertungen
- Griliches (1976) - Wages of Very Young MenDokument18 SeitenGriliches (1976) - Wages of Very Young MenAnonymous WFjMFHQNoch keine Bewertungen
- Controlling: Creation of SKF: SKF Represent Activities or Statistics. in CO, SKF Is Used in Assessment and DistributionDokument4 SeitenControlling: Creation of SKF: SKF Represent Activities or Statistics. in CO, SKF Is Used in Assessment and DistributionSundarKrishnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 To 3 For TOPIC DefenseDokument15 SeitenChapter 1 To 3 For TOPIC DefenseJesusa AmbrosioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Customer Profitability Analysis With Time-Driven Activity-Based Costing: A Case Study in A HotelDokument30 SeitenCustomer Profitability Analysis With Time-Driven Activity-Based Costing: A Case Study in A HotelSiva Krishna Reddy NallamilliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strategic Agility and PerformanceDokument11 SeitenStrategic Agility and PerformanceChiraz RosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Example of Critical Appraisal of Qualitative Research PaperDokument8 SeitenExample of Critical Appraisal of Qualitative Research Papergz8bjzmjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diff BW CBO and RBODokument2 SeitenDiff BW CBO and RBORamreddy BollaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strategic Plan DRAFTVolunteerDokument85 SeitenStrategic Plan DRAFTVolunteerLourdes SusaetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCSDokument3 SeitenMCSperky_khanNoch keine Bewertungen
- SacharDokument424 SeitenSacharRik ChowdhuryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stat 4091 Exercise1Dokument13 SeitenStat 4091 Exercise1Random ExistenceNoch keine Bewertungen
- q4-Wlp Math10 Week 3Dokument3 Seitenq4-Wlp Math10 Week 3nikka rose bautistaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Training and Development in HALDokument58 SeitenTraining and Development in HALyoganthmurthy100% (1)
- 2 Measuring Student Satisfaction in PDFDokument13 Seiten2 Measuring Student Satisfaction in PDFアミール イムランNoch keine Bewertungen
- Interventions To Improve The Preparedness To Care.98781Dokument17 SeitenInterventions To Improve The Preparedness To Care.98781shaznay delacruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 1 Front Sheet: Qualification BTEC Level 5 HND Diploma in ComputingDokument33 SeitenAssignment 1 Front Sheet: Qualification BTEC Level 5 HND Diploma in Computing(FG ĐN) Hoàng Minh HoànNoch keine Bewertungen
- NMIMS Semester 2 Assignment Solution June 2021 Call 9025810064Dokument8 SeitenNMIMS Semester 2 Assignment Solution June 2021 Call 9025810064Palaniappan NNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research IIDokument29 SeitenResearch IIIvan Sabado100% (1)