Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
22 Portal
Hochgeladen von
denis1808scribdOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
22 Portal
Hochgeladen von
denis1808scribdCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
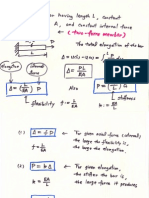
21 Portal Method Copyright G G Schierle, 2001-06 Press Esc to end, for next, for previous slide 1
Portal Method
21 Portal Method Copyright G G Schierle, 2001-06 Press Esc to end, for next, for previous slide 2
Portal Method
The Portal Method for approximate analysis
of moment frames is based on the following
assumptions:
Lateral forces resisted by frame action
Inflection points at mid-height of columns
Inflection points at mid-span of beams
Column shear is based on tributary area
Overturn is resisted by exterior columns only
1 Single moment frame (portal)
2 Multistory moment frame
3 Moment frame subject to total shear V
4 Column shear is proportional to tributary area:
Va = (V/B) L1/2
Vb = (V/B) (L1+L2)/2
Vc = (V/B) (L2+L3)/2
Vd = (V/B) L3/2
5 Column moment = shear x height to inflection point
Ma = Va h/2
Mb = Vb h/2
Mc = Vc h/2
Md = Vd h/2
21 Portal Method Copyright G G Schierle, 2001-06 Press Esc to end, for next, for previous slide 3
Column axial force N:
Overturn moment generates column axial force
1 Exterior columns resist most overturn
2 Portal method assumes exterior columns resist
all overturn
Column axial force = overturn / building width
N = M / B
3 Overturn moments per level are the sum of
forces above the level times lever arm of each
force to inflection point at respective level:
M2 = F2 h2/2 (level 2)
M1 = F2 (h2+h1/2) + F1 h1/2 (level 1)
Column axial force per level:
N2 = M2 / B (level 2)
N1 = M1 / B (level 1)
21 Portal Method Copyright G G Schierle, 2001-06 Press Esc to end, for next, for previous slide 4
1 Beam shear at any level is column axial force
below beam minus column axial force above beam
Level 1 beam shear:
V = N1 - N2
Roof beam:
V = N2 - 0 = N2
2 Beam bending moment is beam shear times
distance to beam inflection point
3 The beam inflection point is assumed at mid-span.
Hence beam bending is:
M = V L/2
Beam axial force is negligible and assumed 0
21 Portal Method Copyright G G Schierle, 2001-06 Press Esc to end, for next, for previous slide 5
Analyze 1st floor columns and beams
Column shear and bending
Base shear
V = F1+F2 = 8+12 V = 20 k
Column shear
Va = (L1/2) (V/B) = 15x20/80 Va = 3.75 k
Vb = (L1+L2)/2 (V/B)
Vb = (20+30)/2 (20/80) Vb = 6.25 k
Column bending
Ma = Va h/2 = 3.75 x 14/2 Ma = 26 k
Mb = Vb h/2 = 6.25 x 14/2 Mb = 44 k
Example: two-story building
Assume:
L1 = 30
L2 = 20
B = 30+20+30 B = 80
h = h1 = h2 h = 14
F1 = 8 k
F2 = 12 k
21 Portal Method Copyright G G Schierle, 2001-06 Press Esc to end, for next, for previous slide 6
Beam shear and bending
Overturn moments
M1 = F2 (h2+h1/2)+F1 h1/2
M1 = 12 (14+7)+8x7 M1 = 308 k
M2 = F2 h2/2 = 12x7 M2 = 84 k
Column axial load 1
st
floor
N1 = M1/B = 308/80 N1 = 3.9 k
Column axial load 2
nd
floor
N2 = M2/B = 84/80 N2 = 1.1 k
Beam shear
V1 = N1N2 = 3.9-1.1 V1 = 2.8 k
Beam bending
M1 = V1 L1/2 = 2.8x30/2 M1 = 42 k
M2 = V1 L2/2 = 2.8x20/2 M2 = 28 k
Example: two-story building
Assume:
L1 = 30
L2 = 20
B = 30+20+30 B = 80
h = h1 = h2 h = 14
F1 = 8k
F2 = 12k
21 Portal Method Copyright G G Schierle, 2001-06 Press Esc to end, for next, for previous slide 7
end
21 Portal Method Copyright G G Schierle, 2001-06 Press Esc to end, for next, for previous slide 8
Column shear and bending
V = F2 V = 12 k
Column a shear Va
Va = Va = k
Column b shear Vb
Vb = (L1+L2)/2 (V/B)
Vb = Vb = k
Column a bending Ma
Ma = Ma = k
Column b bending Mb
Mb = Mb = k
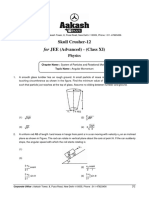
Exercise: 2-story building
Assume:
L1 = 30
L2 = 20
B = 30+20+30 B = 80
h = h1 = h2 h = 14
F1 = 8k
F2 = 12k
Analyze:
2
nd
floor columns and beams
21 Portal Method Copyright G G Schierle, 2001-06 Press Esc to end, for next, for previous slide 9
Beam shear and bending
Overturn moment M2
M2 = M2 = k
Column axial load N2
N2 = N2 = 1.0 k
Beam shear V2
V2 = V2 = k
Beam 1 bending M1
M1 = M1 = 15 k
Beam 2 bending M2
M2 = M2 = k
Exercise: 2-story building
Assume:
L1 = 30
L2 = 20
B = 30+20+30 B = 80
h = h1 = h2 h = 14
F1 = 8k
F2 = 12k
Analyze:
2
nd
floor columns and beams
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- IABSE IASS2011 Davis Rippmann Pawlofski BlockDokument8 SeitenIABSE IASS2011 Davis Rippmann Pawlofski Blockdenis1808scribdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Six Behavioral ObjectivesDokument4 SeitenSix Behavioral Objectivesapi-349767644Noch keine Bewertungen
- J IASS Tsuboi VanMele BlockDokument8 SeitenJ IASS Tsuboi VanMele Blockdenis1808scribdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 9 Generalized Hooke's Law: Objective: Derive Constitutive Relation in Three-Dimensional SpaceDokument10 SeitenLecture 9 Generalized Hooke's Law: Objective: Derive Constitutive Relation in Three-Dimensional Spacedenis1808scribdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 11 Torsion of Circular Shafts: Objective: Derive Elastic Torsion Formula Based On Kinematic AssumptionsDokument9 SeitenLecture 11 Torsion of Circular Shafts: Objective: Derive Elastic Torsion Formula Based On Kinematic Assumptionsdenis1808scribdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Saint-Venant Principle: Shaofan LiDokument7 SeitenSaint-Venant Principle: Shaofan Lidenis1808scribdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 4Dokument10 SeitenLecture 4denis1808scribdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 2Dokument28 SeitenLecture 2denis1808scribdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structural Mechanics Stiffness Method - One Dimensional Analyses ContinuedDokument6 SeitenStructural Mechanics Stiffness Method - One Dimensional Analyses Continueddenis1808scribdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tensegrity and Its ApplicationDokument9 SeitenTensegrity and Its Applicationdenis1808scribdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cec5 5Dokument0 SeitenCec5 5denis1808scribdNoch keine Bewertungen
- LAME Buckling ChecksDokument16 SeitenLAME Buckling ChecksBen ClackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Webinar 125 FlyerDokument2 SeitenWebinar 125 Flyereric_in_westyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Albert Einstein BiographyDokument1 SeiteAlbert Einstein BiographyfermrtechNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structural Dynamics (CE 661)Dokument25 SeitenStructural Dynamics (CE 661)santoshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 10 CW Waves PDFDokument2 SeitenGrade 10 CW Waves PDFAref Dahabrah0% (1)
- UB 203x102x23: Cross-Section PropertiesDokument2 SeitenUB 203x102x23: Cross-Section PropertiesRanjit S KashyapNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIPL - 30th LP List Wef 16.11.2021Dokument249 SeitenBIPL - 30th LP List Wef 16.11.2021Unfeatable GamerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pumps & CompressorsDokument32 SeitenPumps & CompressorssanjeevvangeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter Two Review of Related Literature and Studies 2.1 EarthquakesDokument8 SeitenChapter Two Review of Related Literature and Studies 2.1 EarthquakesJholo BuctonNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCQsDokument5 SeitenMCQs01ABHIGYAN MAJINoch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis of Double Wishbone Suspension System ComponentsDokument26 SeitenAnalysis of Double Wishbone Suspension System ComponentsDeepto BanerjeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Learning Objectives: at The End of This Chapter, You Should Be Able ToDokument26 SeitenLearning Objectives: at The End of This Chapter, You Should Be Able TotimunNoch keine Bewertungen
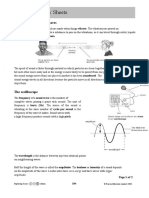
- Learning Activity Sheet in General Physics 1 Lesson 11: Mechanical Waves and SoundDokument10 SeitenLearning Activity Sheet in General Physics 1 Lesson 11: Mechanical Waves and SoundSenica Caydil Jay D.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Working Stress Method (WSM) and Limit State Method (LSM)Dokument5 SeitenWorking Stress Method (WSM) and Limit State Method (LSM)Mandar NadgaundiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Automatic Control, Basic Course FRTF05: ReglerteknikDokument6 SeitenAutomatic Control, Basic Course FRTF05: ReglerteknikAl-ShukaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Burt Goldman - New Moon ProgrammingDokument1 SeiteBurt Goldman - New Moon Programmingsigilum_dei0% (2)
- Summary Sheets: Sound Vibrations and WavesDokument2 SeitenSummary Sheets: Sound Vibrations and Waves박찬우Noch keine Bewertungen
- Laws of Motion Assignment 1 (JEE)Dokument8 SeitenLaws of Motion Assignment 1 (JEE)sdrgrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Determination of Metracentric HeightDokument5 SeitenDetermination of Metracentric HeightArbel AcurilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 Worksheet (F Ma)Dokument3 SeitenChapter 3 Worksheet (F Ma)Obsinet ObsinetNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phys101l A2 Group2 E103 E104 3Q2223Dokument9 SeitenPhys101l A2 Group2 E103 E104 3Q2223the blankNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Fuzzi-Pid Tracking Controller For IndustDokument8 SeitenDesign of Fuzzi-Pid Tracking Controller For IndustBernadetteNoch keine Bewertungen
- VIII Friction 1Dokument6 SeitenVIII Friction 1smi_santhoshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Science Lab Report 2 Question AnalysisDokument3 SeitenEngineering Science Lab Report 2 Question AnalysisKiddozesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flexibility Method - Temp. and Pre-StrainDokument32 SeitenFlexibility Method - Temp. and Pre-StrainSarah SullivanNoch keine Bewertungen
- SEW Compact Constant Speed Reducer MC SeriesDokument195 SeitenSEW Compact Constant Speed Reducer MC SeriesDênis DáyolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit - Iv: Limt State Design of ColumnsDokument26 SeitenUnit - Iv: Limt State Design of ColumnsTesfa HunderaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aashto M332-14Dokument8 SeitenAashto M332-14tony juarezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skull Crusher-12 - Class XI - JEE (Adv) - PhysicsDokument7 SeitenSkull Crusher-12 - Class XI - JEE (Adv) - Physicslootera715Noch keine Bewertungen