Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
A Rock Is A Naturally Occurring Solid Aggregate of One or More
Hochgeladen von
Mahesh TejaniOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
A Rock Is A Naturally Occurring Solid Aggregate of One or More
Hochgeladen von
Mahesh TejaniCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
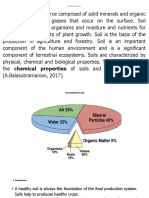
Soil is a natural body consisting of layers (soil horizons) that are primarily composed of minerals, mixed with at least
some organic matter, which differ from their parent materials in their texture, structure, consistency, color, chemical, biological and other characteristics. It is the loose covering of fine rock particles that covers the surface of the earth.[1] Soil is the end product of the influence of the climate, relief (slope), organisms, parent materials (original minerals), and time.[2] Soil is used in agriculture, where it serves as the primary nutrient base for the plants. The types of soil used in agriculture (among other things, such as the purported level of moisture in the soil) vary with respect to the species of plants that are cultivated
A Rock is a naturally occurring solid aggregate of one or more minerals or mineraloids. For example, the common rock granite is a combination of the quartz, feldspar and biotite minerals. The Earth's outer solid layer, the lithosphere, is made of rock. Rocks have been used by mankind throughout history. From the Stone Age rocks have been used for tools. The minerals and metals we find in rocks have been essential to human civilization.[1] Three major groups of rocks are defined: igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic. The scientific study of rocks is called petrology, which is an essential component of geology.
Used in road building materials Used in cements and mortars and the production of lime Used in scouring, scrubbing, and polishing materials
A mineral is a naturally occurring substance that is solid and stable at room temperature, representable by a chemical formula, usually abiogenic, and has an ordered atomic structure. It is different from a rock, which can be an aggregate of minerals or non-minerals, and does not have a specific chemical composition. The exact definition of a mineral is under debate, especially with respect to the requirement a valid species be abiogenic, and to a lesser extent with regards to it having an ordered atomic structure. The study of minerals is called mineralogy.
Aggregates Natural aggregates include sand, gravel, and crushed stone. Aggregates are composed of rock fragments that may be used in their natural state or after mechanical processing, such as crushing, washing, or sizing. Recycled aggregates consist mainly of crushed concrete and crushed asphalt pavement.
Aluminum Aluminum is the most abundant metallic element in the Earth's crust. Bauxite ore is the main source of aluminum. Aluminum is used in automobiles and airplanes (36%), bottling and canning industries (25%), building and electrical (14%) and in other applications (25%).
Antimony Antimony is a silvery-gray, brittle semi-metal. It rarely occurs in nature as a native element, but is found in a number of different minerals. Antimony is used principally for flame retardants as well as in ammunition and automotive batteries and as a decolorizing agent in glassmaking.
Water is a chemical compound with the chemical formula H 2O. A water molecule contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms connected by covalent bonds. Water is a liquid at standard ambient temperature and pressure, but it often co-exists on Earth with its solid state, ice, and gaseous state (water vapor or steam). Water also exists in a liquid crystal state near hydrophilic surfaces.[1][2]
Common household uses consume a lot of water for drinking and It may take between 30 and 40 gallons for one bath Much of our fresh water is also used outdoors for watering lawns, flower beds, and vegetable gardens, as well as washing cars and filling swimming pools.
Plants, also called green plants (Viridiplantae in Latin), are living multicellular organisms of the kingdom Plantae. They form a clade that includes the flowering plants, conifers and other gymnosperms, ferns, clubmosses, hornworts, liverworts and mosses, as well as, depending on definition, the green algae. Plants exclude the red and brown seaweeds such as kelp, the fungi and bacteria.
The uses of plants are: 1. Food & drink 2. Clothing 3. Heat/ fuel (wood, coal, bio-fuel etc.) 4. Structures and furniture 5. Oxygen 6. Paper 7. Medicines 8. Decoration 9. Soil stabilization 10. Aesthetics (landscaping/ cut flowers)
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms of the kingdom Animalia or Metazoa. Their body plan eventually becomes fixed as they develop, although some undergo a process of metamorphosis later on in their lives. Most animals are motile, meaning they can move spontaneously and independently. All animals must ingest other organisms or their products for sustenance (see Heterotroph). Most known animal phyla appeared in the fossil record as marine species during the Cambrian explosion, about 542 million years ago. Animals are divided into various sub-groups, including birds, mammals, amphibians, reptiles, fish and insects.
uses of animals
animals providing food animals provide material for clothes animals as sources of medicines animals used for transportation animals useful in agriculture animals helps in pollination and dispersal of seeds animals can be domesticated animals are used as beasts of burden. animal dung is used as fuel as well as fertilizer
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Barriers to the Promotion of Cross-Cultural Studies EcologyVon EverandBarriers to the Promotion of Cross-Cultural Studies EcologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical & Biological Properties of The SoilDokument122 SeitenChemical & Biological Properties of The SoilJoshua StevenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mini Research ReportDokument17 SeitenMini Research ReportadelinameidyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formation, Composition and PropertiesDokument13 SeitenFormation, Composition and PropertiesSamantha MillerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Natural Resources: Name-: Aniket Sanjay Ghodinde ROLL NO - : 906 STD-: Ix Subject-: ScienceDokument16 SeitenNatural Resources: Name-: Aniket Sanjay Ghodinde ROLL NO - : 906 STD-: Ix Subject-: ScienceAniketGhodindeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mona Sarastasi Tugas Pengantar Ilmu Dan Teknologi KebumianDokument10 SeitenMona Sarastasi Tugas Pengantar Ilmu Dan Teknologi KebumianAdrian MaratiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project Work - Biology (Class Ix)Dokument9 SeitenProject Work - Biology (Class Ix)Aarav VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture No. 6 Natural Resources Potential and Utilization For The Last Hundred Years and Its ImpactDokument3 SeitenLecture No. 6 Natural Resources Potential and Utilization For The Last Hundred Years and Its ImpactAnanda PreethiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Definition of Soil ?: MineralDokument5 SeitenDefinition of Soil ?: MineralGolam MasudNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soil PollutionDokument27 SeitenSoil PollutionShivam SrivastavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 NotesDokument8 SeitenChapter 2 Noteshtetminphyoiris1411Noch keine Bewertungen
- GEOGRAPHY A LEVEL (FORM SIX) NOTES - PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY 1.5 - STUDY OF SOIL - EcoleBooksDokument63 SeitenGEOGRAPHY A LEVEL (FORM SIX) NOTES - PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY 1.5 - STUDY OF SOIL - EcoleBooksMukasa NajibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soil ScienceDokument15 SeitenSoil ScienceAntonette FrondaNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is SoilDokument4 SeitenWhat Is SoilLiaw Wan TzeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Agricultural ScienceDokument4 SeitenAgricultural ScienceNadia HammondNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evs Notes Grade Xii 2022-23Dokument10 SeitenEvs Notes Grade Xii 2022-23Anoushka PradhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- LP 2 GEEC 1 Environmental ScienceDokument25 SeitenLP 2 GEEC 1 Environmental ScienceelieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Environmental Studies-1Dokument51 SeitenEnvironmental Studies-1Muskan NarulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The EcosystemDokument9 SeitenThe EcosystemLuz ManaloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study of SoilsDokument39 SeitenStudy of Soilsjumajumbe150Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4 - Natural ResocurcesDokument3 SeitenChapter 4 - Natural ResocurcesRajesh KrishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soil Sediment Slug DustDokument6 SeitenSoil Sediment Slug Dustsalman ahmed100% (1)
- Natural Resources - SOILDokument21 SeitenNatural Resources - SOILR.NiranjanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment - 1: What Are Renewable and Non-Renewable Resources?Dokument16 SeitenAssignment - 1: What Are Renewable and Non-Renewable Resources?ᏋᏒ ᎴᏋᏋᎮᏗᏦ ᏦᏬᎷᏗᏒ ᏕᎥᏁᎶᏂNoch keine Bewertungen
- Toddle-MYP2 Question and AnswersDokument6 SeitenToddle-MYP2 Question and Answersaditri anumandlaNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is SoilDokument3 SeitenWhat Is SoilHanzel Asuncion LopezNoch keine Bewertungen
- SoilSci Chapter 1Dokument16 SeitenSoilSci Chapter 1zs6ngbszm7Noch keine Bewertungen
- Plant and SoilDokument8 SeitenPlant and SoilAstitva VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Earth Science 1ST Quarter SummaryDokument9 SeitenEarth Science 1ST Quarter SummaryLeonard SalvacionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yr 10 WK 6 & 8 NoteDokument6 SeitenYr 10 WK 6 & 8 Notesedrick ocheNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 Soil As Natural and Dynamic BodyDokument4 SeitenChapter 1 Soil As Natural and Dynamic BodyAndre Martin NuñezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 1 Introduction To Soil ScienceDokument94 SeitenLesson 1 Introduction To Soil ScienceFranz Euriel CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project On Natural ResourcesDokument12 SeitenProject On Natural ResourcesMaridasrajanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4 Ecosystem GudDokument39 SeitenChapter 4 Ecosystem Gudshivam sharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 1Dokument5 SeitenLec 1Sri Ram.MNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECOLOGYDokument160 SeitenECOLOGYmichelle banacNoch keine Bewertungen
- DavongDokument4 SeitenDavongArthadian De PeraltaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1st Mid PartDokument13 Seiten1st Mid PartAbdullah Al Mamun100% (1)
- Abiotic and Biotic Components Free Essay ExampleDokument5 SeitenAbiotic and Biotic Components Free Essay ExampleEnash RidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Properties of Soil ColloidsDokument11 SeitenChemical Properties of Soil Colloidsgurpreet KaurNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.4 Ecology H 1.4.10, 1.4.11, 1.4.12Dokument41 Seiten1.4 Ecology H 1.4.10, 1.4.11, 1.4.12George Oswald Junior CarringtonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conserving and Protecting Natural Resources: Philippine BiodiversityDokument3 SeitenConserving and Protecting Natural Resources: Philippine BiodiversityMarileth CoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theory EnviornmentDokument132 SeitenTheory EnviornmentAnu Sandeep AggrawalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of Soil Science: NRMH 1.1 (2 + 1) First Semester B.Sc. (Hons.) HorticultureDokument38 SeitenFundamentals of Soil Science: NRMH 1.1 (2 + 1) First Semester B.Sc. (Hons.) HorticultureMakarim KhusnulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project P 1Dokument17 SeitenProject P 1Aqeel ShahzadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Saint Mary'S University School of Engineering, Architecture and Information TechnologyDokument1 SeiteSaint Mary'S University School of Engineering, Architecture and Information TechnologyJeje CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Land Pollution and SWMDokument126 SeitenLand Pollution and SWMShawn BaynoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1Dokument7 SeitenModule 1Jea AnimoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 15 Our EnvironmentDokument17 SeitenChapter 15 Our EnvironmentEnola DangNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6 - Chapter 6Dokument7 Seiten6 - Chapter 6Jonathan BaroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soils-Formation, Classification, Soil Profiles and Soils of KeralaDokument23 SeitenSoils-Formation, Classification, Soil Profiles and Soils of KeralaRA H ULNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 11: Life Sciences: Soil BiologyDokument31 SeitenGrade 11: Life Sciences: Soil BiologyBboatb PpbblNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 2-6 Environment Ecology and BiosphereDokument19 SeitenLecture 2-6 Environment Ecology and Biospherepriyamjoshi2022Noch keine Bewertungen
- Soil Science For BSC Forestry/environmental Science/agriculture StudentsDokument58 SeitenSoil Science For BSC Forestry/environmental Science/agriculture StudentsMadan ThapaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Environmental Science 3Dokument19 SeitenEnvironmental Science 3Tapas BanerjeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- EM Module 1 Intro & Def of EnvironmentDokument21 SeitenEM Module 1 Intro & Def of EnvironmentIshaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Every Soil Occupies Space. Soil Extends Down Into The Planet As Well As Over Its Surface. Soil Has Length, Breadth, and DepthDokument26 SeitenEvery Soil Occupies Space. Soil Extends Down Into The Planet As Well As Over Its Surface. Soil Has Length, Breadth, and DepthublehkogeniusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1: Introduction: Associate Professor Department of Environmental ScienceDokument20 SeitenChapter 1: Introduction: Associate Professor Department of Environmental ScienceDivesh ChandraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summary Per ModuleDokument8 SeitenSummary Per ModuleKinsey BugayongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deforestation in IndiaDokument4 SeitenDeforestation in IndiaMahesh TejaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impact of All Technology On EnvironmentDokument4 SeitenImpact of All Technology On EnvironmentMahesh TejaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- ResumeDokument1 SeiteResumeMahesh TejaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- GTA San Andreas CheatsDokument31 SeitenGTA San Andreas CheatsMahesh TejaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maths in Everyday LifeDokument4 SeitenMaths in Everyday LifeMahesh TejaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Honesty Is The Best PolicyDokument3 SeitenHonesty Is The Best PolicyMahesh TejaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Forms of PollutionDokument3 SeitenForms of PollutionMahesh TejaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Origin of The Word: Secured LoansDokument4 SeitenOrigin of The Word: Secured LoansMahesh TejaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mecklai Weekly Global Currency Report-230913Dokument3 SeitenMecklai Weekly Global Currency Report-230913Mahesh TejaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bees Radio Station Animals SoundsDokument2 SeitenBees Radio Station Animals SoundsMahesh TejaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- InventionsDokument1 SeiteInventionsMahesh TejaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Recruitment and Selection FrontDokument9 SeitenRecruitment and Selection FrontMahesh TejaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation 1Dokument1 SeitePresentation 1Mahesh TejaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types: GossypiumDokument12 SeitenTypes: GossypiumMahesh TejaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Demat AccountDokument2 SeitenDemat AccountMahesh TejaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Demat Account: VerificationDokument10 SeitenDemat Account: VerificationMahesh TejaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- +dehradun EXP: Y Y Y Y Y Y YDokument6 Seiten+dehradun EXP: Y Y Y Y Y Y YMahesh TejaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- SaharaDokument103 SeitenSaharaMahesh TejaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Attractive AdvertisingDokument6 SeitenAttractive AdvertisingMahesh TejaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Autobiography of A FlowerDokument1 SeiteAutobiography of A FlowerMahesh TejaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dangers Deforestration - Role of EnvironmentDokument3 SeitenDangers Deforestration - Role of EnvironmentMahesh TejaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Partnership DeedDokument7 SeitenPartnership DeedMahesh Tejani67% (3)
- Production ManagementDokument18 SeitenProduction ManagementMahesh TejaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Initial PaagesDokument3 SeitenInitial PaagesMahesh TejaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Production ManagementDokument18 SeitenProduction ManagementMahesh TejaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Production ManagementDokument18 SeitenProduction ManagementMahesh TejaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mobile Phone Repairing Courses MumbaiDokument2 SeitenMobile Phone Repairing Courses MumbaiMahesh TejaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Production ManagementDokument18 SeitenProduction ManagementMahesh TejaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flora at Sanjay Gandhi ParkDokument9 SeitenFlora at Sanjay Gandhi ParkMahesh TejaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Place of Faults in Petroleum Traps: Rasoul SorkhabiDokument32 SeitenThe Place of Faults in Petroleum Traps: Rasoul Sorkhabic_b_umashankarNoch keine Bewertungen
- ManghiDokument2 SeitenManghiJomelyn DawiNoch keine Bewertungen
- EL M/ Week 5 6Dokument20 SeitenEL M/ Week 5 6Mariels FernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jharkhand GKDokument4 SeitenJharkhand GKNirbhay KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ingleton Field ReportDokument5 SeitenIngleton Field Reportjosh0704Noch keine Bewertungen
- Q& A - StoneDokument11 SeitenQ& A - StoneAnonymous cQ13WWe100% (1)
- Non Metallic Minerals Available in Commercial Quantities in NigeriaDokument113 SeitenNon Metallic Minerals Available in Commercial Quantities in Nigeriafrikdensil474850% (2)
- Tungsten Exploration in IndiaDokument24 SeitenTungsten Exploration in IndiaAravind Kumaravelu100% (1)
- Reference Book: Exploration Drilling 2021Dokument120 SeitenReference Book: Exploration Drilling 2021ioanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Field Trip AssignmentDokument6 SeitenField Trip Assignmentapi-241268840Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sedimentology - Kuliah 1 - IntroductionDokument27 SeitenSedimentology - Kuliah 1 - IntroductionIrsan BahutalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Land ResourcesDokument4 SeitenLand ResourcesJennaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ZIMSEC Geography Notes Form 2Dokument93 SeitenZIMSEC Geography Notes Form 2violetcuchNoch keine Bewertungen
- DRI Vrtatelnosť Urcenie S20 Z Pevnosti Hornín Cez Is50 Mega DôležitéDokument27 SeitenDRI Vrtatelnosť Urcenie S20 Z Pevnosti Hornín Cez Is50 Mega DôležitéDaniel MoravanskýNoch keine Bewertungen
- Earth & Life Science: This Hypothesis Suggest That A Cloud of Gas and Dust, 10 Million KM in Diameter Rotated SlowlyDokument26 SeitenEarth & Life Science: This Hypothesis Suggest That A Cloud of Gas and Dust, 10 Million KM in Diameter Rotated SlowlyLjae NatinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Everyday Science Mcqs 5Dokument18 SeitenEveryday Science Mcqs 5Hina IftikharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Load-Bearing Tilt-Up Concrete Wall PanelsDokument149 SeitenLoad-Bearing Tilt-Up Concrete Wall PanelsxufafruitjuiceNoch keine Bewertungen
- CPV Ro enDokument509 SeitenCPV Ro enscumpik2805Noch keine Bewertungen
- Minerals and RocksDokument14 SeitenMinerals and RocksCésar LópezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rocks and Minerals WebquestDokument2 SeitenRocks and Minerals Webquestapi-264150929Noch keine Bewertungen
- Geologia de Engenharia em Tunel - Tese - Tunel Sao Gotardo - BomDokument122 SeitenGeologia de Engenharia em Tunel - Tese - Tunel Sao Gotardo - BomsanberteiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5e Lesson Plan Layers of The EarthDokument13 Seiten5e Lesson Plan Layers of The Earthapi-350178228100% (3)
- Classification of Igneous RocksDokument23 SeitenClassification of Igneous RocksAdit8450100% (1)
- 1 Stuck Pipe Hole Cleaning SectionDokument52 Seiten1 Stuck Pipe Hole Cleaning SectionjalalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review of Geology, Geochemistry and Origin of Gypsum Mineralization in Chad Basin (North Eastern Nigeria)Dokument81 SeitenReview of Geology, Geochemistry and Origin of Gypsum Mineralization in Chad Basin (North Eastern Nigeria)ATBU_Dr_Ahmed100% (1)
- Sample Exploration Work Plan Regular GrantDokument2 SeitenSample Exploration Work Plan Regular GrantImad SoutajiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reservoir Engineering NotesDokument270 SeitenReservoir Engineering Notesimogen200780% (15)
- Slope Stabilization Measures For The Kuala Lumpur - Karak Toll Highway, 1991, 9th ARC, ThailandDokument6 SeitenSlope Stabilization Measures For The Kuala Lumpur - Karak Toll Highway, 1991, 9th ARC, ThailandfreezefreezeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rock ExcavationDokument14 SeitenRock ExcavationRamanarayanSankritiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 'DiagenesisDokument342 Seiten'DiagenesisBen De Mol92% (13)