Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Contract Rules
Hochgeladen von
colin8790Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Contract Rules
Hochgeladen von
colin8790Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
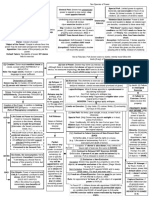
These are notes relating to the basics of contract law.
No responsibility is take n cfor the accuracy of any information contained here in. Nothing in this docume nt can be considered or constrewed as legal advice. This information is designed for educational and entertaiment purposes. You are encouraged to do your own re search and to familiarise yourself with contract law as it applies to the region or jurisdiction you are in. These notes are only a very rough guid to a very la rge subject. ----------------------------------------------------An acceptance is sufficient to evidence an agreement. ----------------------------------------------------Define Acceptance? What are the 2 requirements of Acceptance? Do you always need them? What is Unequivocal Acceptance? When do you need it? What is Communication when dealing with Acceptance? What kind of contract does Communication not work for when trying to prove Accep tance? when is a document effective when using the mailbox rule? What does it mean when you have to send something by Authorized means? If nothing is specified when trying to use authorized means what should you use? If you don't use authorized means to send a document. when is the document autho rized? What is Communication when dealing with Acceptance? a promise for an act. Can on ly accept by performing. Unilateral contract. (doesn't need Oral communication) What is Unequivocal Acceptance? When do you need it? you have to accept the entire offer. Must always have. -------------------------------------Define Agreement? Must have an offer and acceptance What are the 5 ways a contract can be voidable? 1. mistakes 2. Fraud 3. Misrepresentation 4. Undue Influence 5. Duress What are the 2 kinds of Mistakes when dealing with agreement? Mistake in Judgement. Mistake in fact. Out of the 2 mistakes which one can void a contract? Mistake in fact. what is mistake in fact?
Mistake must be something an ordinary person would have made under the same circ umstances. How can you prove fraud? -have to show intent. -misrepresentation -material fact -reasonable reliance -damages How do you prove intent in fraud? show someone is reckless with the truth. (difficult) What is Misrepresentation in fraud? a false statement of fact made by one party to another party, which has the effe ct of inducing that party into the contract. What is material fact in fraud? an important factor that is used to make the decision of entering into a contrac t. What is reasonable reliance in fraud? would a reasonable person have believed the false statement that made the decisi on to enter into a contract. What must you prove with damages in fraud. -must prove legal injury. -only in fraud can you resend the contract and sue for damages. What is the difference between fraud and misrepresentation? misrepresentation has all elements of fraud except intent. If you have fraud you have? misrepresentation What is Undue Influence? a person in a position of trust, pressures you into a contract you would other w ise not do. what is Duress? forcing a party to enter into a contract with threats of a wrongful act.(physica l harm, blackmail, extorsion) ---------------------------------------------what does consideration do to a promise? Its what takes a promise and moves it up to a contract. What makes it binding. What do you need to make a promise biding? consideration What is Consideration in a contract? Something of value that both parties get out of the exchange (motivation for goi ng into a contract) (Ex: buyer wants item and seller wants buyers money) (Consideration is an essential element for the formation of a contract, exept i n Scotland) what is value in consideration?
specific legal sufficiency If you make a promise based on a moral obligation are you held to that contract. no. it is not sufficient to hold you. is a Past Consideration able to hold a current contract? no. can't make a promise based on something that's already happened. When can a court enforce a promise without consideration? -Promise to pay a debt that's been discharged in bankruptcy. -promise that's prevented by the statute of limitations (Statute of limitations - time limit on when you have to bring a law suit.) -Charities- make a promise to a charity, you have to pay -illusory Promise- can't say exactly what the consideration is. What is legal sufficiency Something you didn't have to do and is beneficial. (legally detrimental and beneficial) What is adequacy? dosnt matter how unfair a contract is if you sign you are legaly bound to it. Fo cuses on the fairness of the bargain. -------------------------------------------------------------Common Law contract law Define contract? promise that are enforceable by law. why do we have contracts and contract law? 1. to make sure people follow through with a promise. (Regulate promises) 2. to make sure we have solutions when people break contracts. (Punishment for b roken promises) What is freedom of Contracts? Freedom OF choosing whatever contracts we want enter. What is freedom from Contracts? freedom FROM preforming that contract What are the basic requirements to meet Common Law Contracts? (need all 4) 1. Agreement- 2 parts Offer and Acceptance. 2. Consideration- (motivation for going into contract.) something of value that both parties get out of the exchange 3. Capacity- are we competent to enter into contract 4. Legality- must be legal What is Objective theory of contracts? courts deciding, would a reasonable person think they were entering into a contr act. (Example pepsi fighter jet ch 9) What are the classifications of Contracts? 1. Bilateral or Unilateral 2. Expressed or Implied 3. Quasi Contract 4. Formal or Informal 5. Executed and/or Executory
6. Valid, Void, Voaidable, Unenforceable What are Bilateral or Unilateral contracts? Focuses on what the other party is supposed to do to accept. Bilateral-(bi= 2) a promise for a promise Unilateral-(uni= 1) a promise for an act What is Expressed or Implied contracts? Expressed- terms are expressed orally or in writing. Implied- courts focus on the way the parties act. 4 elements not important when trying to use imply contracts. 3 substitutes. What are the 3 thing you need when using an Implied contract? 1. Plaintiff provided goods or services 2. Plaintiff expected payment and defendant knew it. 3. Defendant had an opportunity to reject goods or services and failed to do so . What is a Quasi Contract? Court is imposing a contract. People can't be unjustly enrichment. CAN'T FORCE B ENEFITS ON SOMEONE. What are Formal or Informal contracts? Formal- require special method for informing. (almost never happens) Informal- everything else What are Executed and/or Executory contracts? (focused on performance) Executed- fully preformed. Executory- not full performance. "I promise to pay him $50 if he mows my lawn." "I promise to pay him $50 if he mows my lawn." How can this example be preformed and not fully preformed contract? What kind of contract would that be? (Depends on point of view, can be both preformed and not fully preformed) Executed- (preformed) person who mowed the lawn. completed the task. Executory- (not fully preformed he mowed he is done. i haven't payed so I'm not done. What are Valid, Void, Voidable, Unenforceable contracts? Valid- good contract (all 4 elements exist) Void- missing 1 of the 4 elements. No good. Voidable- have all 4 elements, but something else is going on. focuses on actio ns of the parities. Unenforceable- has all 4 elements, but is illegal. 2 ways of this happening. What are the 2 ways a contract becomes Unenforceable? 1. statute of Fraud 2. statute of limitations- time limit with in which you can sue. 2 years (check your country's law} Which of the requirements for common law contracts are needed when using implied contracts? Non of the 4 elements are needed. Have 3 subsets instead. What is legality in a contract? Must be legal.
What is consideration in a contract? Something of value both parties get out of the exchange. (Motivation for going i nto a contract) (Ex: buyer wants sellers item and seller wants buyers money) What is agreement in a contract? Must have an offer and acceptance What is capacity in a contract? Are we competent to enter into this contract. Define Discharge, when talking about a contract? No breach of contract and no further obligations in a contract. What are the 4 ways to discharge contract parties without breach? 1. Discharged through conditions 2. Performance as Discharge 3. Discharge by Agreement of the parties 4. Discharge by Operation of Law What is condition when talking about discharged through conditions? a possible future event that may discharge the parties What are the 3 types of conditions? Which one is most/least common? 1. Condition precedent (most common) 2. Condition subsequent (least common) 3. Concurrent (same time) condition What is Condition precedent? before the contract. A condition that must be met before the other party has to perform (most common) Termite inspection on house not passed ~ you don't have to buy and it's not a br each in the contract. Which type of condition is this an example of? Condition precedent What is condition subsequent? after the contract. if the condition happens, it terminates the party's obligati on to perform (least common) What is concurrent condition? one party's performance is conditioned on the others simultaneous performance payment on delivery as soon as they deliver you must pay... when they drop off y ou pay ~ if they don't drop off you don't pay. Which type of condition is this a n example of? Concurrent (same time) condition What are the different degrees of performance (the minimum amount you must do to get a discharge)? Complete Performance Substantial Performance Anything below Substantial What is complete performance and how much payment is owed? performance is within reasonable expectations. Discharge with full payment owed What is Substantial performance and how much payment is owed? slightly below reasonable expectations. Almost, complete. Payment is reduced by the amount that wasn't finished
What is Anything below performance and how much payment is owed? is a material breach of contract. This time the discharge is switched and now I can sue for damages (non-breaching party owes nothing) A Docked for work not finished and get paid for only for what he completed, whic h degree of performance is this an example of? Substantial performance- Almost, complete. Payment is reduced by the amount that wasn't finished if you want to terminate an offer, but its already been accepted. How what would you look for to get out of it? see if its impossible to perform or complete. if a contract does not specify a time, when is it due according to the law? whatever is reasonable. what is ok if the contract isn't vital according to the courts? a slight delay is ok if its not vital. What is Anticipatory Breach of Contract? when your expecting a breach in contract. before performance is required one par ty refuses to perform. can an innocent party get out of the contract? yes. immediate discharge of the non-breaching party and can sue immediately what are the 3 types of Discharge by Agreement of the parties? Rescission (contract goes away, nothing ever happened) Novation (substituting a new party into the contract) Accord & Satisfaction (agreeing on alternative performance) What is Rescission in discharge by agreement? parties agree to undo the agreement as if nothing ever happened What is Novation in discharge by agreement? substituting a new party into the contract, by agreement of all parties What is Accord & Satisfaction in discharge by agreement? offering substitute performance. If that sub performance is accepted (delivered satisfactory substitute). Then the performing party is discharged. Can't sue for any remaining balance that is discharged. original agreement is $5000; you don't have $5000 so both agree to replace the $ 5000 with a car as payment instead. If the car is worth more than $5000, you can not sue for remainder. Which discharge by agreement is this an example of? Accord & Satisfaction What is Discharge by Operation of Law? courts will step in and automatically discharge What are the different types of Discharge by Operation of Law? 1. Bankruptcy- no longer have any obligations to pay 2. Statute of limitations- limits the time in which to sue 3. Alteration of the contract- if someone is changing the terms of the contract without permission, innocent party is completely discharged 4. Discharge by Impossibility or Impracticability.
when can a contract by Discharge by Impossibility or Impracticability? 1. Impossibility destruction of subject matter, death, and/or supervening illega lity after acceptance but before performance. 2. Impracticality means that performance is going to be EXTREMELY difficult or costly. If a reasonable person would have foreseen that difficulty, the court wo uldn't have allowed it. What is impossibility when trying to discharge a contract? destruction of subject matter death supervening illegality after acceptance but before performance. What is Impracticability when trying to discharge a contract? means that performance is going to be EXTREMELY difficult or costly. If a reason able person would have foreseen that difficulty, the court wouldn't have allowed it. Bilateral contains two promises. Contract any agreement enforceable by law. Express stated in words (oral or written). Implied comes about by actions with no words Unenforceable court will no uphold due to some rule of law. Unilateral contains one promise. ----------------------------------------------the purpose of tort law is to provide remedies when legally protected interests have been invaded.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Understanding Executor Office and Use of The Executor Letter 10.28.10Dokument24 SeitenUnderstanding Executor Office and Use of The Executor Letter 10.28.10colin879098% (44)
- Awesome Debt Validation LetterDokument27 SeitenAwesome Debt Validation Letterbalestrery85% (55)
- Two Types of Power of AppointmentDokument1 SeiteTwo Types of Power of AppointmentseabreezeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Possession SummaryDokument19 SeitenPossession SummaryAna WagnerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uniform Partnership Act (1997)Dokument162 SeitenUniform Partnership Act (1997)Mrudula V.100% (3)
- 14 08 04 Letter FiledDokument7 Seiten14 08 04 Letter FiledwarriorsevenNoch keine Bewertungen
- In The Matter of Miriam Carey v. United States of America, Et Al.Dokument131 SeitenIn The Matter of Miriam Carey v. United States of America, Et Al.Eric SandersNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wills Handout PDFDokument52 SeitenWills Handout PDFMichael CarrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lord Diplock in Att-Gen v. Times Newspapers Ltd. (1974) JusticeDokument1 SeiteLord Diplock in Att-Gen v. Times Newspapers Ltd. (1974) Justicecolin8790Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ue vs. JaderDokument3 SeitenUe vs. JaderKR ReborosoNoch keine Bewertungen
- People vs Naji Mock Trial ScriptDokument2 SeitenPeople vs Naji Mock Trial ScriptRussel SirotNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power of Eminent DomainDokument37 SeitenPower of Eminent DomainNoel Ephraim Antigua100% (1)
- 73 - Gov - Uscourts.ord.124749.73.0Dokument14 Seiten73 - Gov - Uscourts.ord.124749.73.0Freeman LawyerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Memo of Motion For Summary JudgmentDokument11 SeitenSample Memo of Motion For Summary Judgmentrifishman100% (1)
- Claim Against The StateDokument2 SeitenClaim Against The StateRon FerlingereNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tresspass To LandDokument9 SeitenTresspass To LandSharath KanzalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case 1:10-cv-01083-JFM Document 1 Filed 04/30/10 Page 1 of 4Dokument11 SeitenCase 1:10-cv-01083-JFM Document 1 Filed 04/30/10 Page 1 of 4winstons2311100% (1)
- Do Not File This Page: Affidavit of Death FormDokument4 SeitenDo Not File This Page: Affidavit of Death FormDaniel Cardenas RuizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Property 1L GuideDokument2 SeitenProperty 1L Guidevnord_1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Equitable Remedies PDFDokument2 SeitenEquitable Remedies PDFdgpNoch keine Bewertungen
- JDF 906 Instructions For Probate With A WillDokument6 SeitenJDF 906 Instructions For Probate With A WilltxkellerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Statute of FraudsDokument3 SeitenStatute of FraudsDebiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1921 Westerfield Banking Principles and Practice Vol 05 of 05Dokument308 Seiten1921 Westerfield Banking Principles and Practice Vol 05 of 05naturalvibesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Federal Habeas Corpus Petition 28 U S C 2254Dokument19 SeitenFederal Habeas Corpus Petition 28 U S C 2254Janeth Mejia Bautista AlvarezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diversity and Alienage Jurisdiction ExplainedDokument28 SeitenDiversity and Alienage Jurisdiction ExplainedCherifa Ben AouichaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 1st Notice of DemandDokument3 Seiten5 1st Notice of DemandKristin Cantley SnellNoch keine Bewertungen
- O A Case in Which State and Federal Courts Have Concurrent JurisdictionDokument2 SeitenO A Case in Which State and Federal Courts Have Concurrent JurisdictionAnjaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complaint-Affidavit Written OutputDokument6 SeitenComplaint-Affidavit Written OutputCyrus DaitNoch keine Bewertungen
- FLOW CHARTS - Debt Recovery Through The Courts - Claire SandbrookDokument13 SeitenFLOW CHARTS - Debt Recovery Through The Courts - Claire SandbrooknaturalvibesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Illinois Civil Procedure Code Section on Form of PleadingsDokument6 SeitenIllinois Civil Procedure Code Section on Form of Pleadingsjuliovargas6100% (1)
- American Court Structure and Jurisdiction OverviewDokument67 SeitenAmerican Court Structure and Jurisdiction Overviewmjwyatt01Noch keine Bewertungen
- Treaty of Peace 2020 Private Law Contract Vital History and Important Explanation - SOTN: Alternative News, Analysis & CommentaryDokument5 SeitenTreaty of Peace 2020 Private Law Contract Vital History and Important Explanation - SOTN: Alternative News, Analysis & Commentarynujahm1639100% (1)
- IndyStar Cease & Desist LetterDokument2 SeitenIndyStar Cease & Desist LetterIndiana Public Media NewsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trespass to Land CasesDokument30 SeitenTrespass to Land Casesrekha vasanthNoch keine Bewertungen
- Contracts Outline KarDokument22 SeitenContracts Outline KarchenyijingNoch keine Bewertungen
- IRS Complaint FormDokument3 SeitenIRS Complaint FormSteveManning100% (1)
- 40N Rosin.S2012 Agency OverviewDokument107 Seiten40N Rosin.S2012 Agency Overviewmason_lanham8143Noch keine Bewertungen
- Real Property I: Classification of PropertyDokument4 SeitenReal Property I: Classification of PropertyDutchsMoin Mohammad100% (1)
- Production of Financial Documents For IRS and FinCENDokument8 SeitenProduction of Financial Documents For IRS and FinCENJoshua Sygnal GutierrezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Charitable Trusts: Create An Inter Vivos OR Testamentary Charitable Trust?Dokument5 SeitenCharitable Trusts: Create An Inter Vivos OR Testamentary Charitable Trust?Kim BoSliceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Proprietary EstoppelDokument24 SeitenProprietary EstoppelMin Hee ParkNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10000016119Dokument7 Seiten10000016119Chapter 11 DocketsNoch keine Bewertungen
- F 13551Dokument2 SeitenF 13551IRSNoch keine Bewertungen
- CA Bar: Contracts (2009)Dokument20 SeitenCA Bar: Contracts (2009)The LawbraryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Passport InstructionDokument18 SeitenPassport InstructionBala SubramanianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Handout - Consideration, Promissory Estoppel and Intention To Create Legal RelationsDokument4 SeitenHandout - Consideration, Promissory Estoppel and Intention To Create Legal RelationsAdam 'Fez' Ferris100% (4)
- 74 1 The Long Story of Notice and Personal JurisdictionDokument82 Seiten74 1 The Long Story of Notice and Personal JurisdictionKevin YohburtNoch keine Bewertungen
- PJ Flow ChartDokument1 SeitePJ Flow ChartMalik DeanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Your Power To TrespassDokument2 SeitenYour Power To TrespassMaggie WikleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Instructions: Writing and Filing A Motion: ChecklistDokument12 SeitenInstructions: Writing and Filing A Motion: ChecklistNathaniel HudsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Irs Form 14039Dokument2 SeitenIrs Form 14039waterfordpoliceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Real PropertyDokument20 SeitenReal PropertyTiffany BrooksNoch keine Bewertungen
- Court denies wife's habeas corpus petition to compel husband's cohabitationDokument30 SeitenCourt denies wife's habeas corpus petition to compel husband's cohabitationMikhailFAbzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Replevin LawsuitDokument1 SeiteReplevin Lawsuitklg.consultant2366Noch keine Bewertungen
- Breach of TrustDokument18 SeitenBreach of TrustLouise MansuetoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reporting Agent Authorization Form 8655Dokument2 SeitenReporting Agent Authorization Form 8655bilalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Affiant Denied Statement for Court Bonds, Wins by Judicial RecusalDokument1 SeiteAffiant Denied Statement for Court Bonds, Wins by Judicial Recusalrhouse_1Noch keine Bewertungen
- How To Do A Summary JudgmentDokument10 SeitenHow To Do A Summary Judgmentchickie10Noch keine Bewertungen
- Contracts Final OutlineDokument41 SeitenContracts Final OutlineDiamonds875Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mortgage Drafting and Restatement (3d) of Property 1998Dokument41 SeitenMortgage Drafting and Restatement (3d) of Property 1998johngaultNoch keine Bewertungen
- Non-Probate Assets ChartDokument1 SeiteNon-Probate Assets ChartseabreezeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Foi A LetterDokument1 SeiteSample Foi A LetterSalaam Bey®Noch keine Bewertungen
- Civil Government of Virginia: A Text-book for Schools Based Upon the Constitution of 1902 and Conforming to the Laws Enacted in Accordance TherewithVon EverandCivil Government of Virginia: A Text-book for Schools Based Upon the Constitution of 1902 and Conforming to the Laws Enacted in Accordance TherewithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding Conditional SentencesDokument4 SeitenUnderstanding Conditional Sentencescolin8790Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1942 Clearfield DoctrineDokument4 Seiten1942 Clearfield Doctrinecolin8790Noch keine Bewertungen
- CollectivismDokument1 SeiteCollectivismcolin8790Noch keine Bewertungen
- Legal Clarified The Term VERIFICATIONDokument1 SeiteLegal Clarified The Term VERIFICATIONcolin8790Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1942 Clearfield DoctrineDokument4 Seiten1942 Clearfield Doctrinecolin8790Noch keine Bewertungen
- We Produce EverythingDokument2 SeitenWe Produce Everythingcolin8790Noch keine Bewertungen
- No Law, No Constitution No Sovereignty That Can Compel Two People To Agree.Dokument1 SeiteNo Law, No Constitution No Sovereignty That Can Compel Two People To Agree.colin8790Noch keine Bewertungen
- Family Bible As EvidenceDokument1 SeiteFamily Bible As Evidencecolin8790Noch keine Bewertungen
- Render To Caesar What Is Caesar'sDokument15 SeitenRender To Caesar What Is Caesar'scolin8790Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Jurisdiction Argument-For DummiesDokument9 SeitenThe Jurisdiction Argument-For Dummiescolin8790Noch keine Bewertungen
- Family Bible As EvidenceDokument1 SeiteFamily Bible As Evidencecolin8790Noch keine Bewertungen
- American Home Vs TantucoDokument3 SeitenAmerican Home Vs TantucoJoel MilanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pariso, Philip JamescpltDokument4 SeitenPariso, Philip Jamescpltamannix3112Noch keine Bewertungen
- MCIAA Vs Limbonhai G.R. No. 217956, November 16, 2016Dokument8 SeitenMCIAA Vs Limbonhai G.R. No. 217956, November 16, 2016Elimer EspinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project - Law of Torts 1: Topic - Novus Interveniens and Its ApplicationDokument21 SeitenProject - Law of Torts 1: Topic - Novus Interveniens and Its ApplicationRohan D'cruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Macalintal Vs TehDokument5 SeitenMacalintal Vs TehpyulovincentNoch keine Bewertungen
- FCIC Crim Book 1 First QuizDokument1 SeiteFCIC Crim Book 1 First QuizRex Lagunzad FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic Date Case Title GR No Doctrine: FactsDokument2 SeitenTopic Date Case Title GR No Doctrine: FactsJasenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Johnny Watkins, Jr. v. Edward Murray, Director, Virginia Department of Corrections, 493 U.S. 907 (1989)Dokument4 SeitenJohnny Watkins, Jr. v. Edward Murray, Director, Virginia Department of Corrections, 493 U.S. 907 (1989)Scribd Government DocsNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Golden Rule in Islam FINALDokument102 SeitenThe Golden Rule in Islam FINALAliyah DiponegoroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Limitation Act 1963Dokument24 SeitenLimitation Act 1963Dikshagoyal1230% (1)
- 32 Northern Mindanao vs. Iligan Cement DigestDokument2 Seiten32 Northern Mindanao vs. Iligan Cement DigestBay Nazareno100% (1)
- CA Final Law Penalties ChartDokument5 SeitenCA Final Law Penalties ChartPankaj PathakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rights of Accused PersonsDokument4 SeitenRights of Accused PersonsSanni KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- CASES EthicsDokument61 SeitenCASES EthicsLove Jirah JamandreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dilweg vs. PhilippsDokument4 SeitenDilweg vs. PhilippsLalaine FelixNoch keine Bewertungen
- Proper execution of tax waiverDokument2 SeitenProper execution of tax waiversmtm06Noch keine Bewertungen
- LABOR LAW DIGESTS SUMMARYDokument20 SeitenLABOR LAW DIGESTS SUMMARYJeng GacalNoch keine Bewertungen
- James Flanders v. Larry R. Meachum, Commissioner of Corrections, 22 F.3d 48, 2d Cir. (1994)Dokument6 SeitenJames Flanders v. Larry R. Meachum, Commissioner of Corrections, 22 F.3d 48, 2d Cir. (1994)Scribd Government DocsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aw On Environment and Natural Resources VS O AYDokument6 SeitenAw On Environment and Natural Resources VS O AYmmmmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zone 5 and 6 Seniority Circular MemoDokument2 SeitenZone 5 and 6 Seniority Circular MemoQC&ISD1 LMD COLONY100% (1)
- ESSENTIAL REQUISITES OF CONTRACTSDokument7 SeitenESSENTIAL REQUISITES OF CONTRACTSKim Alyssa100% (4)
- 07 Legaspi vs. CSCDokument1 Seite07 Legaspi vs. CSCAnonymous bOncqbp8yiNoch keine Bewertungen
- DCDN 082Dokument175 SeitenDCDN 082dklawofficeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abbott V AlcarazDokument6 SeitenAbbott V AlcarazErika Angela GalceranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Law 435 ShahDokument3 SeitenLaw 435 ShahUmar MahfuzNoch keine Bewertungen
- PNB v. PikeDokument2 SeitenPNB v. PikeTiffany AnnNoch keine Bewertungen