Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Pediatric DosaPediatric Dosages Based On Body Weightges Based On Body Weight
Hochgeladen von
djbhetaOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Pediatric DosaPediatric Dosages Based On Body Weightges Based On Body Weight
Hochgeladen von
djbhetaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
UNRS 314 Pediatric Dosages Based on Body Weight Converting pounds to kilograms is done by dividing body weight by 2.
2 Practice problems: change to kilograms - Chapter 13 Curren 58 3/4 lbs 63 1/2 lbs 98 lbs 6lbs 2 oz 8 lbs 10 oz __________ __________ __________ __________ __________
Remember you need to change ounces to a fraction to do the calculations (16 ounces in a pound) Calculating dosages: Calculating total daily dosage is calculated and then it is divided by the number of doses per day to obtain the actual dose administered at one time. Example: Polymox or Amoxicillin oral suspension Average dosage range is 20 40 mg / kg / day This dosage is to be given in divided doses every 8 hours, or a total of three doses (24 hr divided by 8 hours) The child weighs 18.2 kg To calculate average dosage range: 18.2 x 20 = 364 mg / kg / day 18.2 x 40 = 728 mg / kg / day The recommended dosage for an 18.2 kg child is 360 to 728 mg / kg / day Minimus dose is 360 mg / day or 121 mg per dose Maximum dose is 728 mg / kg / day or 243 mg per dose
Practice problems: If the order is to give 125 mg every 8 hours is this within the recommended range? If the order is to give 375 mg every 8 hours is this within the recommended range? If the order is to give 75 mg every 8 hours is this within the recommended range? If the order is to give 250 mg every 8 hours is this within the recommended range? If the order is to give 125 mg every 4 hours is this an accurate dosing? Clinical Pearl: The younger or more compromised by illness the patient, the more critical a discrepancy is likely to be. A po dosage may be rounded to 250 mg per dose versus an IV calculation would need to be within the range of 121 mg to 243 mg per dose. Practice Problem: The label on the medication Polymox reads: 125 mg per 5 mL To give 125 mg you would administer _____ mL or _____ tsp
To give 375 mg you would administer _____mL or _____ tsp
To give 75 mg you would administer _____ mL or
To give 250 mg you would administer ____ mL or _____ tsp
Practice Problem: Oral Medications Principen (ampicillin suspension) 250 mg per 5 mL Child weighs 20 pounds Usual dosage: 100 mg / kg per day (give q.i.d in equally divided doses) What is the childs body weight in kg t the nearest tenth kg? __________
What is the recommended dosage in mg per day for this child? _________ How many doses will this be divided into? _______________
How many mg will this be per dose? ____________________ How many mL would you need to administer to administer the dose? ________
IV Drug Calculations: Ampicillin is often given IV and is unstable is pre-mixed. It is often provided as a vial of powder to be mixed. Physician order is for IV Ampicillin 125 mg every 6 hours. The pharmacy sends you a vial of powdered ampicillin of 250 mg. Look up how to mix this in your drug book. Hint: you can mix this as an IM or IV dose to be given IV According to your drug manual: What solution would you use to mix the drug? __________ For an IM injection how much solution would you add? __________ For direct IV you would add how much solution_________ For Intermittent infusion how much solution would you dilute the drug in ________ What is the rate of administration? ____________________
Route and Dosage: Ampicillin Respiratory or soft tissue infections: PO (adults and children) > 20 kg: 250 mg q 6 hour PO (children) < 20 kg: 50 mg / kg / day divided q 6 8 hours IM, IV (adults and children) > 40 kg: 250 500 mg q 6 hours IM, IV (children) < 40 kg: 25 50 mg / kg / day in divided dose q 6 8 hours Bacterial Meningitis caused by H. influenzae, Staphylocossus pneumonia or N. Meningitidis or Septicemia IM, IV (adults and children): 150 200 mg / kg / day in divided doses q 3 -4 hours Prevention of Bacterial Endocarditis IM, IV (adults): 2 grams 30 minutes before procedure IM, IV (children) 50 mg / kg 30 minutes before procedure Practice problem: You are working in an outpatient surgical clinic and a 12-year-old child is being admitted for a tonsillectomy. The child has a history of heart surgery as an infant. The physician order is for 1.2 grams Ampicillin IV 30 minutes prior to surgery. The pharmacy sends up a vial of powdered Ampicillin containing 1.5 grams. The child weighs 56 pounds. _______________ kg
What would be the appropriate dosage for this child? _______________ How would you mix this medication? _________ mL of sterile water After you mix this medication how much would you draw up to administer the 1.2 grams? _______
Medication administration via Burette: Chapter 21 of Curren Volumetric pumps are used extensively to administer intermittent IV medications to infants and children Calibrated burette has a total capacity of 100 to 120 mL of fluid calibrated in 1 mL increment. Regardless of method of administration the medication infusion is routinely followed by a flush t make sure the mediation has cleared the tubing and the total dosage of medication has been administered Volume of the flush will vary depending on the length of the tubing usually 20 mL If primary line exists the medication my be administered by IV piggy-back If no IV is infusing, a saline or heparin lock (heplock) can be used for intermitted infusion or IV push medications The flush needs to be accounted for during administration of the medication in regards to flow rate or gtts/min and hourly fluid intake.
Example: I do differ a bit from the Curren Math for Meds in that I include the medication fluid and flush fluid in the total to be infused for a specific amount of time. I would expect that all IV fluid medication calculations on the quizzes would include the FLUSH. Example: An antibiotic dosage of 125 mg is in1 mL of solution and is to be further diluted in IV solution of dextrose 5% in normal saline to equal 20 mL. The 20 mL is to be infused over 30 minutes. A flush of 20 mL is to follow. A volumetric pump will be used. 20 mL of the fluid with the medication plus the 20 mL of flush is to be infused over 30 minutes (20 mL of medication + 20 mL of flush) Calculate the gtt / min flow __________________ 40 mL over 30 minutes with drip factor of 60 gtt/min = IV pump to be set at 80 gtts/min or 80 mL / hour to get the total mediation infused over 30 minutes. Steps involved in infusion:
Add medication and amount of fluid to equal 20 mL in the burette and close the clamp. Label the burette with a RED TAG indicating a medication is being infused. Set the IV at rate to infuse both the medication and flush in over 30 minutes. After the medication is infused open up the clamp and add the flush to finish the infusion of the IV medication Move the RED TAG to the IV line to indicate that the medication is now in the line and the flush is infusing After the flush is in remove the RED TAG from the line and re-set the IV fluid rate of gtts / min to the ordered IV rate.
Note: the physician will never tell you to add the FLUSH. A typical order may read: Physician order: Ancef 750 mg IV every 8 hours It is the nurse responsibility to: Calculate mg / mg dosage If the medication comes in a vial or in powder form you will need to draw up or mix the solution to appropriate dose Determine how much IV fluid the medication has to be further diluted in How fast to infuse the mediations: 1 to 5 minutes, 30 minutes, 1 hour Example: Ancef (Cefazolin) is provided at 1.5 grams in powdered form. The childs weight is 35 kg. According the drug manual (Davis Drug Guide): IM, IV (children and infants) > 1 mo 6.25 to 25 mg / kg q 6 hours 8.3 to 33.3 mg / kg q 8 hours Calculate the safe range __________to ____________ every 8 hours Dilute 1 g / 10 mL of sterile water Further dilute to 50 to 100 mL of IV solution Mixing 1.5 grams with 10 mL of sterile water how much medication would you draw up to equal 750 mg _____________________
You will add the Medication to IV solution to equal 50 mL to be infused over 60 minutes (you will need to include the FLUSH in the 60 minutes administration).
How fast will you set you IV at (gtts / min or mL / hour) to get the medication in over 60 minutes__________________
24 hour fluid Calculations (you will need to memorize this) 100 mg for 1st 10 kg of weight 50 mg for 2nd 10 kg of weight 20 mg for each additional kg of weight Calculate 14 hour fluid calculation for: 12 pound child:
6 pound child:
33 pound child:
64 pound child: This is for maintenance IV fluids only. The physician order may be for less or more fluids depending on the infant / child diagnosis or fluid needs. In some cases the order will be for 1 times maintenance or 2/3 maintenance.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Practice Test For Clinical Calculations - AnDokument5 SeitenPractice Test For Clinical Calculations - Anhv123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Math Pre-Test QuestionsDokument4 SeitenMath Pre-Test Questionsgok_addictedNoch keine Bewertungen
- IV Drip RatesDokument12 SeitenIV Drip RatesNikki802100% (1)
- 10 Golden Rules For Administering Drug SafelyDokument5 Seiten10 Golden Rules For Administering Drug SafelyAngel EsplenadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NR 324 Med Calculation Practice TestDokument3 SeitenNR 324 Med Calculation Practice TestHilarymaeBoldaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dosage Calculation 09.04.21Dokument24 SeitenDosage Calculation 09.04.21PHARMACOLOGY SMVMCNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCM 106 - Case Analysis - Nursing Care Plan of Heart FailureDokument2 SeitenNCM 106 - Case Analysis - Nursing Care Plan of Heart FailureMarisol Jane JomayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nitrates Comparison ChartDokument7 SeitenNitrates Comparison ChartModi Evana PutriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diabetes Management ATIDokument15 SeitenDiabetes Management ATIJessica ChirinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paediatric Drug ND DosesDokument5 SeitenPaediatric Drug ND Dosesanon_842593420Noch keine Bewertungen
- Drugs Affecting Blood PressureDokument54 SeitenDrugs Affecting Blood PressureJeremy VivitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study GuideDokument3 SeitenDrug Study GuideNicole CardenasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medication Calculation - Commonly Used FormulasDokument1 SeiteMedication Calculation - Commonly Used FormulasAaron AntonioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pediatric DosesDokument17 SeitenPediatric DosesIris MambuayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computation FormulasDokument1 SeiteComputation FormulasNicole cuencosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug CalculationsDokument8 SeitenDrug CalculationsakosipidroNoch keine Bewertungen
- ATI Flash Cards 05, Medications Affecting The Nervous SystemDokument110 SeitenATI Flash Cards 05, Medications Affecting The Nervous SystemGiovanni MictilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid GuidelinesDokument8 SeitenFluid GuidelinesAya SalahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pediatric Dosage CalculationsDokument1 SeitePediatric Dosage Calculationssmckenzie1964Noch keine Bewertungen
- Disease Mechanism of Action NoteDokument3 SeitenDisease Mechanism of Action Noteamoody95Noch keine Bewertungen
- ICE DrugsDokument2 SeitenICE DrugsRichelle FrondaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DRIPSDokument7 SeitenDRIPSKim Alvarez100% (2)
- Gestational DiabetesDokument51 SeitenGestational Diabeteskhadzx100% (2)
- Humalog - Uses, Dosage & Side Effects - DrugsDokument4 SeitenHumalog - Uses, Dosage & Side Effects - Drugsremyde07100% (1)
- Med Math Sample CalculationsDokument9 SeitenMed Math Sample Calculationsiamlx2100% (1)
- Grady EMS Drug List 2017 FINALDokument20 SeitenGrady EMS Drug List 2017 FINALThomas LeachNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 30 NotesDokument4 SeitenChapter 30 NotesMariah Jane TaladuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Appendix A: Sample Patient Profiles and Prescriptions: (For Pharmacist Use)Dokument6 SeitenAppendix A: Sample Patient Profiles and Prescriptions: (For Pharmacist Use)Cesly Jewel Acosta AvilesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abbreviations PDFDokument4 SeitenAbbreviations PDFLouie LacreNoch keine Bewertungen
- CardiopathophysiologyDokument63 SeitenCardiopathophysiologyapplesncoreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Labetalol Card#8Dokument1 SeiteLabetalol Card#8USMCDOC100% (1)
- ASN 11 Handout Case Study PDFDokument4 SeitenASN 11 Handout Case Study PDFania ojedaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diabetes Study GuideDokument4 SeitenDiabetes Study GuideNicole Brassington0% (1)
- The Dangers of SmokingDokument2 SeitenThe Dangers of SmokingEvi Febri RahmawatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Insulin ChartDokument1 SeiteInsulin ChartGabriel TaylorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Criticalcaredrugs PDFDokument2 SeitenCriticalcaredrugs PDFtomywekaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Heart of A NurseDokument2 SeitenThe Heart of A Nurseflex gyNoch keine Bewertungen
- DigoxinDokument18 SeitenDigoxinApril Mergelle LapuzNoch keine Bewertungen
- IVF ComputationDokument31 SeitenIVF ComputationDuran JustineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rle Neonate DrugsDokument13 SeitenRle Neonate DrugsLhara Vhaneza CuetoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paediatric DosesDokument2 SeitenPaediatric DosesEdio PathicNoch keine Bewertungen
- FormulaDokument5 SeitenFormulaEloiseBalasbasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug CalculationsDokument2 SeitenDrug CalculationsBern NerquitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Insulin ChartDokument1 SeiteInsulin ChartChristian BagaresNoch keine Bewertungen
- FurosemideDokument4 SeitenFurosemideapi-3797941100% (1)
- Date Performed: August 18, 2015 Group No. and Section: Group 5 WCDE-A Date Submitted: September 1, 2015 Group MembersDokument28 SeitenDate Performed: August 18, 2015 Group No. and Section: Group 5 WCDE-A Date Submitted: September 1, 2015 Group MembersCm MacaliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Myocardial Infarction QuestionsDokument10 SeitenMyocardial Infarction Questionsdsaitta108Noch keine Bewertungen
- Action Plan PICU FINALDokument2 SeitenAction Plan PICU FINALMark MacasadduNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concept Map Diagnosis and InterventionsDokument3 SeitenConcept Map Diagnosis and Interventionsmenickel3Noch keine Bewertungen
- EpinephrineDokument16 SeitenEpinephrineBrad Pitt-HongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adult Immediate Post Cardiac Arrest Care Algorithm 2015 UpdateDokument1 SeiteAdult Immediate Post Cardiac Arrest Care Algorithm 2015 UpdateRyggie Comelon0% (1)
- Electrolyte ReplacementDokument3 SeitenElectrolyte ReplacementRatih Dwi OctariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- HA-RLE-WS # 10 Assessing Nutritional StatusDokument4 SeitenHA-RLE-WS # 10 Assessing Nutritional StatusJULIE ANNE CORTEZNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug CalculationsDokument3 SeitenDrug Calculationsapi-3739910100% (4)
- CCT Practice ProblemsDokument13 SeitenCCT Practice Problemsbbianca1990Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tac Requirements/Skills Practice Guidelines N 122Dokument15 SeitenTac Requirements/Skills Practice Guidelines N 122bdollars123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pediatric Medication Calculations: UNRS 314 Jan Bazner-Chandler CPNP, CNS, MSN, RNDokument47 SeitenPediatric Medication Calculations: UNRS 314 Jan Bazner-Chandler CPNP, CNS, MSN, RNHunny BearstenNoch keine Bewertungen
- N - Lec4 - Pediatric Medication Calculations PDFDokument56 SeitenN - Lec4 - Pediatric Medication Calculations PDFgeng gengNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pediatric Pharmacology 07Dokument45 SeitenPediatric Pharmacology 07Nadz CyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pediatric Practice Problems 07Dokument6 SeitenPediatric Practice Problems 07sarah_stover_1Noch keine Bewertungen
- 28Dokument21 Seiten28djbheta100% (1)
- Care Plan PedsDokument7 SeitenCare Plan PedsdjbhetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 27Dokument18 Seiten27djbhetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dental HygieneDokument12 SeitenDental HygienedjbhetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Introduction To The Netherlands Healthcare SystemDokument12 SeitenAn Introduction To The Netherlands Healthcare SystemdjbhetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anemia-Careplan For AdultDokument29 SeitenAnemia-Careplan For AdultdjbhetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Preassignment Work-Careplan #2Dokument30 SeitenPreassignment Work-Careplan #2djbhetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trying To Pull A Boulder Up A Hill Working Vectors: W + F + N + P oDokument4 SeitenTrying To Pull A Boulder Up A Hill Working Vectors: W + F + N + P odjbhetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Preassignment Work-Careplan #2Dokument30 SeitenPreassignment Work-Careplan #2djbhetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Patient Care Plan-PhychologicalDokument2 SeitenPatient Care Plan-PhychologicaldjbhetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Patient Care Plan-EducationalDokument1 SeitePatient Care Plan-EducationaldjbhetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Allama Iqbal Open University, Islamabad: (Secondary Teacher Education Department) WarningDokument2 SeitenAllama Iqbal Open University, Islamabad: (Secondary Teacher Education Department) WarningAiNa KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neighbor'S Plot - : Sheet No Rev No R0Dokument1 SeiteNeighbor'S Plot - : Sheet No Rev No R0jibeesh cmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ap Government Imperial PresidencyDokument2 SeitenAp Government Imperial Presidencyapi-234443616Noch keine Bewertungen
- Emcee Script For CompetitionDokument2 SeitenEmcee Script For CompetitionArdini Izzati100% (3)
- Types of Media and Media ConvergenceDokument70 SeitenTypes of Media and Media ConvergenceYsmile De LaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- VA RESUME HelloracheDokument1 SeiteVA RESUME HelloracheJessa AbadianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Student Exam FormDokument4 SeitenStudent Exam FormRaj Kumar TeotiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- E5170s-22 LTE CPE - Quick Start Guide - 01 - English - ErP - C - LDokument24 SeitenE5170s-22 LTE CPE - Quick Start Guide - 01 - English - ErP - C - LNelsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- End-Of-Chapter Questions: CambridgeDokument17 SeitenEnd-Of-Chapter Questions: CambridgeMido MidoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deferred Tax QsDokument4 SeitenDeferred Tax QsDaood AbdullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Moatiz Riaz - Area Sales ManagerDokument1 SeiteMoatiz Riaz - Area Sales ManagerMoatiz RiazNoch keine Bewertungen
- WearebecausewebelongDokument3 SeitenWearebecausewebelongapi-269453634Noch keine Bewertungen
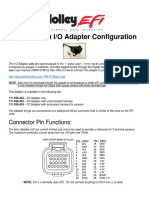
- Digital Dash I/O Adapter Configuration: Connector Pin FunctionsDokument8 SeitenDigital Dash I/O Adapter Configuration: Connector Pin FunctionsAfeef Ibn AlbraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Admission Sos 2013-14090513 PDFDokument21 SeitenAdmission Sos 2013-14090513 PDFmanoj31285manojNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reich 0001 PDFDokument87 SeitenReich 0001 PDFYordys Domínguez RodríguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2016 Lesson 9Dokument34 Seiten2016 Lesson 9Junas Jr LaputNoch keine Bewertungen
- Individual Ability in SoftwareDokument9 SeitenIndividual Ability in Softwaredhana0809100% (4)
- University of Physician V CIRDokument24 SeitenUniversity of Physician V CIROlivia JaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Installing Hyperledger Fabric and Composer: Ser/latest/installing/development-To Ols - HTMLDokument13 SeitenInstalling Hyperledger Fabric and Composer: Ser/latest/installing/development-To Ols - HTMLVidhi jainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Learning Module 4 - BARTENDINGDokument34 SeitenLearning Module 4 - BARTENDINGivy mae flores67% (3)
- How To Read Research PaperDokument7 SeitenHow To Read Research Papertuigauund100% (1)
- B.tech Cse Third Yr Syllabus 21-06-2018Dokument21 SeitenB.tech Cse Third Yr Syllabus 21-06-2018SuperdudeGauravNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strength of Materials Aug 5 2017Dokument16 SeitenStrength of Materials Aug 5 2017MikaellaTeniolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- GnatusDokument36 SeitenGnatusNacer Mezghiche100% (1)
- People Vs SB - Paredes - Ex Post FactoDokument2 SeitenPeople Vs SB - Paredes - Ex Post FactoMara Aleah CaoileNoch keine Bewertungen
- AtharvasheershamDokument5 SeitenAtharvasheershamforthegroupsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ksiidc and KssidcDokument13 SeitenKsiidc and KssidckasperNoch keine Bewertungen
- Title Toolbox 1 ADokument2 SeitenTitle Toolbox 1 AGet LiveHelpNoch keine Bewertungen
- QAS M001 SLPS Quality Assurance ManualDokument49 SeitenQAS M001 SLPS Quality Assurance ManualMHDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Mathematics 11 Q2 Week3 MELC20 MELC21 MOD Baloaloa, JeffersonDokument25 SeitenBusiness Mathematics 11 Q2 Week3 MELC20 MELC21 MOD Baloaloa, JeffersonJefferson BaloaloaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Love Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)Von EverandLove Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)Bewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (1)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedVon EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (82)
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDVon EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (3)
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionVon EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (404)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityVon EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (32)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeVon EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeBewertung: 2 von 5 Sternen2/5 (1)
- Manipulation: The Ultimate Guide To Influence People with Persuasion, Mind Control and NLP With Highly Effective Manipulation TechniquesVon EverandManipulation: The Ultimate Guide To Influence People with Persuasion, Mind Control and NLP With Highly Effective Manipulation TechniquesBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (1412)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsVon EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsVon EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (4)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsVon EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisVon EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (42)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaVon EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Comfort of Crows: A Backyard YearVon EverandThe Comfort of Crows: A Backyard YearBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (23)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossVon EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (6)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityVon EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (6)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisVon EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeVon EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (254)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Von EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (110)
- To Explain the World: The Discovery of Modern ScienceVon EverandTo Explain the World: The Discovery of Modern ScienceBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (51)
- Critical Thinking: How to Effectively Reason, Understand Irrationality, and Make Better DecisionsVon EverandCritical Thinking: How to Effectively Reason, Understand Irrationality, and Make Better DecisionsBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (39)
- The Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlVon EverandThe Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (60)
- Dark Psychology: Learn To Influence Anyone Using Mind Control, Manipulation And Deception With Secret Techniques Of Dark Persuasion, Undetected Mind Control, Mind Games, Hypnotism And BrainwashingVon EverandDark Psychology: Learn To Influence Anyone Using Mind Control, Manipulation And Deception With Secret Techniques Of Dark Persuasion, Undetected Mind Control, Mind Games, Hypnotism And BrainwashingBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1138)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessVon EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (328)