Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
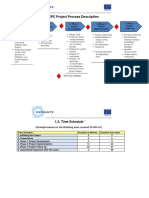
01b. - Design Phases & Information
Hochgeladen von
Ana Carrasco MartínezOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
01b. - Design Phases & Information
Hochgeladen von
Ana Carrasco MartínezCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Economic Model
Process Flow Diagram (PFD)
Stoichiometry
Plant Design Documents Piping and Instrument Diagram (PID) and Information Flow
Plot Plan (Plant Layout)
Accumulation of Value Delivered in Capital Projects
Contributing Activities
Client Case Conceptual Design Detail Design Construction Commissioning Production
Major Equipment Placement
Premium to Operate (Service Contract) Premium to Complete (Fixed Bid)
Major Pipe Routing
Piping Layout
Discount or Premium to Achieve Expected Value to Customer V i
Discount to Purchase (Prudent Buyer)
Copyright , 2008, William G. Beazley, PhD Fabrication ISOs Pipe Segment PFV Material All Rights Reserved Other Copyrights Apply as Noted Extracted Pipe Segments Piping Spool Sheets
From Turtons et. al. P. 2
Process Flow Diag & ROI
Design Concept & ROI
ROI with Fabricator / Suppier Bids
Plant Built
Production Begins
Value Assessments
Front-End Loading Process
(The Business Roundtable) Critical planning phases of the project Named from commitment of time and resources at FEL to dictate future success of project
FEL 1 Business Planning - opportunity is explored FEL 2 Facility Planning hones broad objectives into a particular project at a particular site with a particular technology configuration and schedule. FEL 3 Project Planning stage fills in details needed so detailed engineering can execute the project with little or no change.
http://www.ipainstitute.com/home/publications/pdf/ipa_business_stake.pdf
Three-Phase Gated Approval System (IPA Institute)
Idea Initiation
Business Planning
Gate 1
Gate 2
Gate 3
Turnover
Facility Planning
Project Planning
Execution Phase
Operations Phase
75% of the Ideas Do Not Pass Gate 1
50% of the Remaining Ideas Do Not Pass Gate 2
Only 1% of the Remaining Ideas Do Not Pass Gate 3
Decision Gates
Recycle Back Continue
Cancel/Shelve
The IPA Institutes Gatekeeper seminar will arm gatekeepers with the questions they need to ask to move a project forward or to kill it.
Engineering Design Phases
Conceptual designs
Sketchy or minimal information Abstract plot plan (equipment & piping layout)
Three Major Sources of Project Data
1. Project design data supplied by the client or project engineering.
Process and process materials Plant location and environmental features
Preliminary, or study phase
Unchecked or uncertified data Design a facility in sufficient detail so that:
Confirm purchased equipment costs & delivery Purchase Long Lead Time Bulk materials.
Detail phase
All designs are finalized Based on such checked data;
Steel, concrete, hydraulics drawings, Certified vendor drawings for equipment, valves, and instruments.
2. Vendor data pertaining to equipment and specialty bulk items. 3. Internally generated engineering data.
Layout designer impact in conceptual, study phases
FEED
EPC
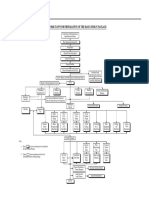
Plant Design Information Flow
Economics Owner Process Owner Materials Integrity Owner
The Flow of Information to Pipers
BFD
PFD
Matl SPEC
Piping Layout Owner
Piping Layout
Controls and Stability Owner
Equipment Vendors
Feedback
Equip Data
Fab ISOs, Spools, Etc. Structures, Foundations, etc.
P&ID
Process Information
Process description, including reactions, separations, mixing stages and their stability Operating/Extreme pressures, temperatures Likelihood and consequences of excursions and loss of control Process flow diagram (PFD) and stream data Required function and performance rate of each equipment item Physical properties of process materials
Arterial inventories Corrosion data and materials of construction.
Block Flow Diagram for Early Entrance Coproduction Plant
(US DoE)
http://www.osti.gov/bridge/servlets/purl/788122-TeVDrj/native/788122.pdf
Claus Plant: H2S to Sulphur
http://www.valero.com/AboutUs/Refineries/TexasCitySchematic.htm
http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Image%3AClausPlt.JPG
Block Flow Diagram
(Chevron Products Company)
Process Flow Diagram
(US OSHA)
http://www.aqmd.gov/ceqa/documents/2003/nonaqmd/chevron/chvFND.html
Process Flow Diagram
Shows Material Flows and Properties
Anchor Point Temperatures and Pressures Material Balances As Best Known
Typical Project PFD (KBR)
Shows Equipment that Changes State:
Major Pressure Vessels (Reactors, Columns, Drums) Major Pumps and Compressors Column Reboilers and Condensers Reactors, Furnaces, Heat Exchangers Valves If a Significant Pressure Drop
Sample Process Flow Diagram
(Source: Bausbacher and Hunt)
Data Normally Included on a Process Flowsheet
Process lines, but including only those bypasses essential to an understanding of the process All process equipment. Spares are indicated by letter symbols or notes Major instrumentation essential to process control and to understanding fIowsheet Valves essential to an understanding of the flowsheet Design basis, including stream factor Temperatures, pressures, flow quantities Weight and/or mol balance, showing compositions, amounts, and other properties of the principal streams Utilities requirements summary Equipment Data
Operators Viewing Process Details
(Chevron Phillips Chemical Company)
Information Developed from PFD
Piping and Instrumentation Diagram (P&ID) Equipment List (then Equipment Data) Process Material Hazards Material Specification
http://www.cpchem.com/enu/image_bank.asp
P&ID Example
(Source: DoE)
P&ID as Schematic for Layout
Piping and Instrumentation Diagrams
Schematic (connectivity only) Shows Items Needed to Control Process Conditions:
All process, utility, and auxiliary equipment Connecting piping, Valving, Specialty items, Instrumentation and Insulation, and heat tracing requirements.
Equipment List
Itemized accounting list by class of all equipment to be used on project Gives the equipment item numbers and descriptions Generally furnished by the client or project engineering
PIP P&ID Equipment Classes
CLASS A B C D E SUBJECT
Mixing Equipment Blowers Compressors Mechanical Drivers Heat Exchangers
P&ID Data Included for Particular Equipment
(James R. Couper)
Compressors SCFM (60F. 14.7 psia, P psi; HHP; number of stages; details of stages if important Drives type; connected HP; utilities such as kW. lb steam/ hr, or Btu/hr Drums and tanks- ID or OD. seam to seam length, important internals Exchangers: Sqft, KBtU/hr, temperatures, and flow quantities in and out, shell side and tube side indicated Furnaces: KBtU/hr, temperatures in and out, fuel Pumps: 6PM (60Ft, P psi, HHP, type, drive Towers Number and type of plates or height arid type of packing identification of all plates at which streams enter or leave: ID or OD seam to seam length; skirt height Other equipment: Sufficient data for identification of duty and size
DESCRIPTION
Agitators, Aerators, Mechanical Mixers Centrifugal Blowers, Positive Displacement Blowers, Fans Centrifugal, Reciprocating, Screw, Vacuum Electric and Pneumatic Motors, Diesel Engines, Steam and Gas Turbines Unfired Heat Exchangers, Condensers, Coolers, Reboilers, Vaporizers and Heating Coils, Double Pipe, Spiral, Plate & Frame, Air Coolers Fired Heaters, Furnaces, Boilers, Kilns Horizontal and Vertical Centrifugal, Positive Displacement, Vertical Canned, Screw, Gear, Sump
F P R T TK U V
Furnaces Pumps
Reactors Towers / Columns Tanks Misc Equipment Drums
API atmospheric and low pressure Filters, Bins, Silos Separators, Driers, Accumulators
Sample Equipment List
(Source: Bausbacher and Hunt)
Process Materials & Hazards
Hazardous properties, eg
Lower Flammability Limit (LFL) Upper Flammability Limit (UFL) Immediately Dangerous to Life or Health Concentrations (IDLH) Long Term Exposure Limit (LTEL)
Electrical classification practices Site climatic conditions & impacts Environmental effects and permitted discharge & release levels
Pipe Specs
Maximum Hydrostatic Test Pressure:
e.g. 450 psig
Changing Pipe Pressures in Oil Production
(Source: API RP 14E)
As Oil, Gas Moves Down Stream, Pressure, Temperature Changes Changing Pressure, Temperature Requirements Reflected in Pipe Spec
2500 PSIG (Well Head Press) 1420 PSIG 500 PSIG 125 PSIG
2500 PSIG (Well Head Press)
Allowed Service Types:
SW Seawater - Raw SH Sodium Hypochlorite FL Flare WP Water - Potable
Specified Pipe, Valves, Fittings (PVF) Specified Flanges, Blinds, etc.
Pipe Spec Can Change When Process Conditions Change
A FEED Process Document Schedule
(Puneet Sharma, Iris LLC)
http://www.irisllc.com/
Typical Deliverables
(Puneet Sharma, Iris LLC)
Conceptual Design
Estimate
Deterministic @ 30-40% Risk-Based for Base Case
Piping Design Documents
Economic Model Process Flow Diagram (PFD)
Front-End Design
Class A Package
Completed Pipeline Surveys Deck Layout with CG Facility Weights, Lift Plan & Structural Design Long-Lead Item POs Process Hazard Analysis Preliminary P&Ids
Stoichiometry
Piping and Instrument Diagram (PID)
Facilities (Process)
Heat & Material Balance Process Flow Sketch
Major Equipment Placement
Plot Plan (Plant Layout)
Flowlines & Pipelines
Route Definition
Structural
Design Concept
Estimate @ 15-20%
Major Pipe Routing
Piping Layout
Detail Design
Equipment & E&I Pos HAZOP P&IDs, UFDs Loop Diagrams, Piping ISOs Pipe Segment PFV Material Fabrication ISOs
Extracted Pipe Segments
Piping Spool Sheets
From Turtons et. al. P. 2
http://www.irisllc.com/
DESIGN DOCUMENTATION TYPICAL PER $100MM
FLOWSHEETS /PIDs PIPING ISOs INSTRUMENT LOOPS VESSEL/EQUIP DWGS 100 - 150 2500 - 3000 2000 - 3000 100
Piping Layout Information Flow
Plot Plan (Plant Layout) Piping and Instrument Diagram (PID) Equipment, Item Data Sheets Piping Spec
ROTATING EQUIP SPECS 150 - 200
Richard B. Pettigrew, Rohm & Haas Co, at EAC Systems 96
Piping Layout
From Turtons et. al. P. 2
Plant Layout Design
Conceptual and preliminary development of process unit plot plans Routing of major above and below grade piping Layout of equipment and its associated infrastructure
Good Layout Design and Engineering Affects plant cost and economy Can shorten construction schedules Affects operations and maintenance efficiency
Plot Plan Information
Pipe Racks Layout of the Equipment in the PFD Layout of Major Equipment
Tankage Other areas shown as blocks Access via roads, rail, waterway Plant perimeter
Sample Proposal Plot Plan
(Source: Bausbacher and Hunt)
Approx Layout & Grouping Major interfaces and flows Overall Dimensions
Sample Planning Plot Plan
(Source: Bausbacher and Hunt)
Defined Areas Tagged Equipment Critical Dimensions
Sample Construction Plot Plan
(Source: Bausbacher and Hunt)
Final Dimensions Foundation Locations
Plant Layout Plan
(Axis Point Design)
http://www.axispointdesign.com/
Pipe Layout Plan
(Axis Point Design)
http://www.axispointdesign.com/
Pipe Layout Elevation
(Axis Point Design)
http://www.axispointdesign.com/
Pipe Fab ISO & BOM
(Axis Point Design)
http://www.axispointdesign.com/
Typical Fabrication ISO
Single Line Isometric Spool Drawing
Spool Bill of Materials
Layout Interactions with Business Case and Design Baseline
Business Opportunity
Select Process Route
Process Design
Evaluate:Safety Environment Operability
Plant Layout
Evaluate Costs:Capital Operating
Good Practice guidance from:
Layout standards Published or company experience and guidance. Prior work
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Typical Piping DeliverablesDokument4 SeitenTypical Piping DeliverablesShyam Prasad K S100% (1)
- Project phases and deliverablesDokument1 SeiteProject phases and deliverablesEmmanuel Cervantes VelázquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Piping Drawings Guide: PFDs, P&IDs, Isometrics & GADsDokument89 SeitenPiping Drawings Guide: PFDs, P&IDs, Isometrics & GADsbey100% (2)
- Plant Design P&ID GuideDokument15 SeitenPlant Design P&ID Guideplanet123Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1 FEED Engineering Man Hour 산정 기준Dokument8 Seiten1 FEED Engineering Man Hour 산정 기준Mohsen HamdiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Weightage Factors For EPC ProjectsDokument10 SeitenWeightage Factors For EPC ProjectsManyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.1-1.3 - epc - project-Rev Project Proceess Owner's Procedure 节能项目 业主前期开发Dokument11 Seiten1.1-1.3 - epc - project-Rev Project Proceess Owner's Procedure 节能项目 业主前期开发zhangj5Noch keine Bewertungen
- Design Manhours EstimationDokument3 SeitenDesign Manhours Estimationpuru55980Noch keine Bewertungen
- Check List Piping Project Start Kick-Off Meeting DiscussionDokument5 SeitenCheck List Piping Project Start Kick-Off Meeting DiscussionAnonymous PsafDWSiOoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Piping ArticlesDokument187 SeitenPiping Articlesdhanu1308Noch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Design Data ListDokument2 SeitenEngineering Design Data ListThiruThirunavukkarasuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Definitions of Overall Engineering PhasesDokument12 SeitenBasic Definitions of Overall Engineering PhasesTamka76100% (1)
- OMECO Competitive Selection Process for Short-Term Power Supply 2019-2026Dokument139 SeitenOMECO Competitive Selection Process for Short-Term Power Supply 2019-2026Mellie MorcozoNoch keine Bewertungen
- DWP For Piping EngineeringDokument83 SeitenDWP For Piping Engineeringlin kin100% (3)
- Lecture 2 Process Engineering-1Dokument95 SeitenLecture 2 Process Engineering-1ahmed.ayoob.abdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Document Description Type Document Name (Client) Document Name (Terna) Issued by Project Management Documentation VENDOR Document ListDokument1 SeiteDocument Description Type Document Name (Client) Document Name (Terna) Issued by Project Management Documentation VENDOR Document ListXXXNoch keine Bewertungen
- List of DeliverablesDokument3 SeitenList of DeliverablesPrad1979Noch keine Bewertungen
- Deliverables List - EngineeringchecksDokument3 SeitenDeliverables List - EngineeringchecksKarthik NagendraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Approved Vendor ListDokument13 SeitenApproved Vendor Listhaniif mk100% (1)
- Pipeline FEED Package Executive SummaryDokument1 SeitePipeline FEED Package Executive SummarySamvendan JohnjacobNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineer ProcedureDokument7 SeitenEngineer ProcedureRadziel EngineeringNoch keine Bewertungen
- ScheduleDokument12 SeitenScheduleRic S. MalongaNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Get Costing of Labor?: Preparing Detailed EstimateDokument21 SeitenHow To Get Costing of Labor?: Preparing Detailed Estimatecass0608Noch keine Bewertungen
- FEED Deliverable List (Sample) - The Project Definition PDFDokument5 SeitenFEED Deliverable List (Sample) - The Project Definition PDFbecpavanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Project DeliverablesDokument18 SeitenEngineering Project DeliverablesLeman IbishovaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Deliverables for Chemical ProjectsDokument6 SeitenEngineering Deliverables for Chemical Projectskamala 123100% (1)
- FEED Deliverable List (Sample) - The Project Definition PDFDokument5 SeitenFEED Deliverable List (Sample) - The Project Definition PDFPeter BridgeNoch keine Bewertungen
- PT Synergy Engineering Proposal for Detailed Engineering Support of Kerendan Field DevelopmentDokument7 SeitenPT Synergy Engineering Proposal for Detailed Engineering Support of Kerendan Field DevelopmentmatsuruNoch keine Bewertungen
- PFD ChecklistDokument1 SeitePFD ChecklistNguyen Anh TungNoch keine Bewertungen
- Itb Part I - Instruction To BiddersDokument16 SeitenItb Part I - Instruction To BiddersilsaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering document delivery stagesDokument1 SeiteEngineering document delivery stagessyafiqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Feed - Piping StudyDokument8 SeitenFeed - Piping Studydriveamar21Noch keine Bewertungen
- Documents Required-Engineering-20210821Dokument133 SeitenDocuments Required-Engineering-20210821Abdelhay MarocainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Engineering PDFDokument17 SeitenBasic Engineering PDFvaradarajck893Noch keine Bewertungen
- Planningforengineering 12559824333307 Phpapp03Dokument12 SeitenPlanningforengineering 12559824333307 Phpapp03Prashant AgrawalNoch keine Bewertungen
- CTR-InPK Fertilizer Plant Project-FEED DesignDokument7 SeitenCTR-InPK Fertilizer Plant Project-FEED DesignNoman Abu-FarhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pistep Act ModDokument13 SeitenPistep Act ModkamlNoch keine Bewertungen
- RFQ - ATM (20110323) Tanks ManualDokument35 SeitenRFQ - ATM (20110323) Tanks ManualAlmario SagunNoch keine Bewertungen
- FEEDDokument6 SeitenFEEDxam marNoch keine Bewertungen
- EPC Epcm: The Best Delivery Method For Your ProjectDokument1 SeiteEPC Epcm: The Best Delivery Method For Your ProjectAbdessamad JannaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plot Plan and Equipment LayoutDokument23 SeitenPlot Plan and Equipment Layoutravirawat15Noch keine Bewertungen
- Process DeliverablesDokument6 SeitenProcess DeliverablesAnonymous QSfDsVxjZNoch keine Bewertungen
- MRT Phase 2Dokument47 SeitenMRT Phase 2hilmihilmi100% (1)
- PID Check ListDokument6 SeitenPID Check ListArunachalam KaliyaperumalNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Easily Estimate The Duration of An Oil & Gas EPC ProjectDokument2 SeitenHow To Easily Estimate The Duration of An Oil & Gas EPC ProjectdhaferjabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Detailed Design and Engineering Deliverable List (Sample) - The Project Definition PDFDokument7 SeitenDetailed Design and Engineering Deliverable List (Sample) - The Project Definition PDFPeter Bridge100% (1)
- Design of A Chemical Plant PDFDokument2 SeitenDesign of A Chemical Plant PDFAdarsh SvNoch keine Bewertungen
- ENGINEERING WORK FLOW FOR BASIC DESIGN PACKAGEDokument1 SeiteENGINEERING WORK FLOW FOR BASIC DESIGN PACKAGEMC ANoch keine Bewertungen
- Monitor Piping Construction Progress with WCS and ITPDokument8 SeitenMonitor Piping Construction Progress with WCS and ITPAsraf Ali100% (1)
- Introduction To Piping EngineeringDokument6 SeitenIntroduction To Piping EngineeringchaitraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project WBS ChartDokument4 SeitenProject WBS ChartMohit AroraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Detail Engineering Inquiry Specification RFQ - Rev. 2Dokument16 SeitenDetail Engineering Inquiry Specification RFQ - Rev. 2joseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Requirements for FEED Study and PTE PreparationDokument3 SeitenRequirements for FEED Study and PTE PreparationklmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dokumen - Tips - Epcprojectinterdepency and Work Flow 1pdfDokument103 SeitenDokumen - Tips - Epcprojectinterdepency and Work Flow 1pdfAhmed AggourNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rocess LOW Iagram: An OverviewDokument20 SeitenRocess LOW Iagram: An OverviewRajkumar ANoch keine Bewertungen
- New Automatic Test Bench for Pumps Streamlines Inspections Up to 75 Pumps DailyDokument6 SeitenNew Automatic Test Bench for Pumps Streamlines Inspections Up to 75 Pumps Dailysturbine100% (1)
- Fertilizer Project DeliverablesDokument28 SeitenFertilizer Project DeliverablesClément50% (2)
- Codes and Standards: Piping EngineeringDokument23 SeitenCodes and Standards: Piping EngineeringAnanto Yusuf WNoch keine Bewertungen
- LMS Network Asset Management Guidebook PDFDokument137 SeitenLMS Network Asset Management Guidebook PDFasawinrajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gasification Process ModelingDokument6 SeitenGasification Process ModelingRebeca Santamaria MedelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bases FEED EPC Parte 3viDokument229 SeitenBases FEED EPC Parte 3viAbdelhamid LaroussiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic and Detailed EngineeringDokument2 SeitenBasic and Detailed EngineeringSomnath LahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plant LayoutDokument8 SeitenPlant Layoutrsmallwood395895100% (1)
- Heat Exchanger Tube RuptureDokument3 SeitenHeat Exchanger Tube RuptureKarthik Sakthivel100% (1)
- Procurement Process in Larsen & Toubro Epc: by Deepak Bhatt 063015Dokument14 SeitenProcurement Process in Larsen & Toubro Epc: by Deepak Bhatt 063015Deepak BhattNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineered Packaging Center A Global ProviderDokument6 SeitenEngineered Packaging Center A Global ProviderLTE002Noch keine Bewertungen
- Meindo SAKA - MDR BEIDokument6 SeitenMeindo SAKA - MDR BEIperdana kusumaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Opgc Owners Engineer - CPPDokument18 SeitenOpgc Owners Engineer - CPPwas00266Noch keine Bewertungen
- Flow SheetsDokument23 SeitenFlow SheetsAmmar SaeedNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01c. - General Layout ConsiderationsDokument18 Seiten01c. - General Layout ConsiderationsAna Carrasco MartínezNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01a-Introduction To Process Plant DesignDokument8 Seiten01a-Introduction To Process Plant DesignChooi Jia HoongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hipac FolderDokument5 SeitenHipac FolderAna Carrasco MartínezNoch keine Bewertungen
- LISEGA Catalog 2010Dokument7 SeitenLISEGA Catalog 2010Olivier RioNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Catalogue - Equipment PDFDokument6 SeitenGeneral Catalogue - Equipment PDFDiegoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Volvo Group KPMG True Value Case StudyDokument8 SeitenVolvo Group KPMG True Value Case Studyaa1122Noch keine Bewertungen
- Abb Traction Motors Broschyr 12sDokument12 SeitenAbb Traction Motors Broschyr 12sJanmejay SaxenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2013 Trane High Wall R410aDokument4 Seiten2013 Trane High Wall R410aRonald ValenciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plant layout quiz answersDokument2 SeitenPlant layout quiz answersReyman RosalijosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Daily Report October 2013 Yde (4) RtttfrreDokument112 SeitenDaily Report October 2013 Yde (4) Rtttfrreguymanuel20025387Noch keine Bewertungen
- สูตรคำนวน KPI Rev0-110251 xls - สูตรคำนวนKPIRev0-110251 PDFDokument11 Seitenสูตรคำนวน KPI Rev0-110251 xls - สูตรคำนวนKPIRev0-110251 PDFkatfy1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ups 9355 EatonDokument108 SeitenUps 9355 EatonJoss Love Isra100% (1)
- Soldadora Linde GMDokument96 SeitenSoldadora Linde GMcamelod555Noch keine Bewertungen
- HVAC Patterson BrochureDokument9 SeitenHVAC Patterson BrochureAnonymous 5RhHmNmgJNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manuale Uso Trasformatori TA enDokument8 SeitenManuale Uso Trasformatori TA enhino_kaguNoch keine Bewertungen
- CS Steel Pipe Selection GuideDokument40 SeitenCS Steel Pipe Selection GuideImran HussainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Badger Daylighting PitchDokument16 SeitenBadger Daylighting PitchAnonymous Ht0MIJNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indian Wind Turbine Manufacturers AssociationDokument3 SeitenIndian Wind Turbine Manufacturers AssociationMAYANK CHHATWALNoch keine Bewertungen
- Consumer Switchgear CatalogueDokument128 SeitenConsumer Switchgear CatalogueYasir ArafatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kajaria Ceramics LTD PpaDokument37 SeitenKajaria Ceramics LTD PpaVinay GhuwalewalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hayaan Trading ProfileDokument18 SeitenHayaan Trading Profilerezzu_786Noch keine Bewertungen
- Rti Process Manual IntDokument183 SeitenRti Process Manual IntdlebreromNoch keine Bewertungen
- Punjab Power Boards Unbundling and DutiesDokument19 SeitenPunjab Power Boards Unbundling and DutiesSudhir AggarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summer Training ReportDokument43 SeitenSummer Training ReportVikalp SaxenaNoch keine Bewertungen