Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Ch.09 Center of Gravity and Centroid
Hochgeladen von
CK_85_3Originalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Ch.09 Center of Gravity and Centroid
Hochgeladen von
CK_85_3Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
3/25/2013
Engineering Mechanics Statics
9.01
Center of Gravity and Centroid
Engineering Mechanics Statics
9.02
Center of Gravity and Centroid
09. Center of Gravity and Centroid
Chapter Objectives To discuss the concept of the center of gravity, center of mass, and the centroid To show how to determine the location of the center of gravity and centroid for a system of discrete particles and a body of arbitrary shape To use the theorems of Pappus and Guldinus for finding the surface area and volume for a body having axial symmetry To present a method for finding the resultant of a general distributed loading and show how it applies to finding the resultant force of a pressure loading caused by a fluid
HCM City Univ. of Technology, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering
Nguyen Tan Tien
HCM City Univ. of Technology, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering
Nguyen Tan Tien
Engineering Mechanics Statics
9.03
Center of Gravity and Centroid
Engineering Mechanics Statics
9.04
Center of Gravity and Centroid
1. Center of Gravity, Center of Mass, and the Centroid of a Body - To design the structure for supporting a water tank, we will need to know the weights of the tank and water as well as the locations where the resultant forces representing these distributed loads are acting - How can we determine these weights and their locations?
1. Center of Gravity, Center of Mass, and the Centroid of a Body Center of Gravity - A body is composed of an infinite number of particles of differential size and each of these particles have a weight - These weights will form a parallel force system, and the resultant of this system is the total weight of the body, which passes through a single point called the center of gravity, - Center of gravity: the point at which the entire weight of a body may be considered as concentrated so that if supported at this point the body would remain in equilibrium in any position
HCM City Univ. of Technology, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering
Nguyen Tan Tien
HCM City Univ. of Technology, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering
Nguyen Tan Tien
Engineering Mechanics Statics
9.05
Center of Gravity and Centroid
Engineering Mechanics Statics
9.06
Center of Gravity and Centroid
1. Center of Gravity, Center of Mass, and the Centroid of a Body - The weight of the body: the sum of the weights of all of its particles = - The location (, , ) = = = of the center of gravity
1. Center of Gravity, Center of Mass, and the Centroid of a Body Center of Mass of a Body - The location of the center of mass with respect to the ,, axes Substitute = to = , = , = = , = , =
- The location of the center of gravity with respect to the ,, = , = , =
HCM City Univ. of Technology, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering Nguyen Tan Tien HCM City Univ. of Technology, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering Nguyen Tan Tien
3/25/2013
Engineering Mechanics Statics
9.07
Center of Gravity and Centroid
Engineering Mechanics Statics
9.08
Center of Gravity and Centroid
1. Center of Gravity, Center of Mass, and the Centroid of a Body Center of a Volume - The center of a volume or centroid or geometric center of the body with respect to the ,, axes Substitute = to = , = , = =
1. Center of Gravity, Center of Mass, and the Centroid of a Body Center of an Area
, =
, =
- If an area lies in the plane and is bounded by the curve = (), then its Centroid , = , = - These integrals can be evaluated by performing a single integration if we use a rectangular strip for the differential area element
HCM City Univ. of Technology, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering
Nguyen Tan Tien
HCM City Univ. of Technology, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering
Nguyen Tan Tien
Engineering Mechanics Statics
9.09
Center of Gravity and Centroid
Engineering Mechanics Statics
9.10
Center of Gravity and Centroid
1. Center of Gravity, Center of Mass, and the Centroid of a Body Center of a Line
1. Center of Gravity, Center of Mass, and the Centroid of a Body - Example 9.1 Locate the centroid of the rod bent into the shape of a parabolic arc Solution Differential Element: arbitrary point (,) Area: = 2 / = 2 = ()2 +()2 = Moment Arms: = , = Integrations =
+ 1
- If a line segment lies within the plane and it can be described by a thin curve = (), then its Centroid , = , =
=
HCM City Univ. of Technology, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering Nguyen Tan Tien
1 1 2 42 + 1 42 + 1 0.6063 0 = 01 = = 0.41 1 1.479 42 + 1 42 + 1 0 0 1 42 + 1 0.8484 = 01 = = 0.574 1.479 42 + 1 0
Nguyen Tan Tien
HCM City Univ. of Technology, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering
Engineering Mechanics Statics
9.11
Center of Gravity and Centroid
Engineering Mechanics Statics
9.12
Center of Gravity and Centroid
1. Center of Gravity, Center of Mass, and the Centroid of a Body - Example 9.2 Locate the centroid of the circular wire segment Solution Polar coordinates will be used to solve this problem since the arc is circular Differential Element: arbitrary point ( ,) Area: = Moment Arms: = , = Integrations =
/2 0 /2 0 /2 0 /2 0
/2 0 /2 0 /2 0 /2 0
2
Nguyen Tan Tien
1. Center of Gravity, Center of Mass, and the Centroid of a Body - Example 9.3 Determine the distance measured from the axis to the centroid of the area of the triangle Solution Differential Element Arbitrary element (,) at Area: = = ( ) Moment Arms: = Integrations 1 2 1 0 = = =6 = 1 3 0 2
HCM City Univ. of Technology, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering Nguyen Tan Tien
HCM City Univ. of Technology, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering
3/25/2013
Engineering Mechanics Statics
9.13
Center of Gravity and Centroid
Engineering Mechanics Statics
9.14
Center of Gravity and Centroid
1. Center of Gravity, Center of Mass, and the Centroid of a Body - Example 9.4 Locate the centroid for the area of a quarter circle Solution Polar coordinates will be used Differential Element (, ,) Area: = = 2
2 3 1 2 1 2 2 3
Moment Arms: = , = Integrations = = =
/2 0
1. Center of Gravity, Center of Mass, and the Centroid of a Body - Example 9.5 Locate the centroid for the area Solution 1 Differential Element Arbitrary element (, ) at Area: = Moment Arms: = , = /2 Integration =
/2 0
2 2 2 3 2 =3 2 /2 0 2 2 2 2 3 2 =3 2 /2 0 2
/2 0 /2 0 /2 0 /2 0
4 = 3 4 = 3
1 1 3 0.250 0 = 0 = = 0.75 1 1 2 0.333 0 0 1 1 2 (/2) ( /2) 2 0.100 0 = 0 1 = 1 0.333 2 0 0
= 0.3
HCM City Univ. of Technology, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering
Nguyen Tan Tien
HCM City Univ. of Technology, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering
Nguyen Tan Tien
Engineering Mechanics Statics
9.15
Center of Gravity and Centroid
Engineering Mechanics Statics
9.16
Center of Gravity and Centroid
1. Center of Gravity, Center of Mass, and the Centroid of a Body - Example 9.5 Locate the centroid for the area Solution 2 Differential Element Arbitrary element (1 ,) at (, ) Area: = (1 ) Moment Arms: = + Integration =
1 2
1+ 2
1 [ 0
1 + /2](1 )
1 (1 ) 0 1 1 (1 ) 0 0 = 1 1 (1 ) 0 0
=
3
0.250 = 0.75 0.333 = 0.100 = 0.3 0.333
Nguyen Tan Tien
2 1
1. Center of Gravity, Center of Mass, and the Centroid of a Body - Example 9.6 Locate the centroid of the semi-elliptical area Solution Differential Element Arbitrary element ( ,) Area: = Moment Arms: = , = /2 Integration = 0 2 2 2 1 4/3 (1 ) 2 4 2 2 = = = = = 0.424 2 2 2 2 1 2 4
HCM City Univ. of Technology, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering
HCM City Univ. of Technology, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering
Nguyen Tan Tien
Engineering Mechanics Statics
9.17
Center of Gravity and Centroid
Engineering Mechanics Statics
9.18
Center of Gravity and Centroid
1. Center of Gravity, Center of Mass, and the Centroid of a Body - Example 9.7 Locate the centroid for the paraboloid of revolution Solution Differential Element Arbitrary element: thin disk Volume: = 2 Moment Arms: = Integration = 0 =
100 (2 ) 0 100 (2 ) 0
100 100
100 2 0 100 0
1. Center of Gravity, Center of Mass, and the Centroid of a Body - Example 9.8 Determine the location of the center of mass of the cylinder if its density varies directly with the distance from its base, i.e., = 200/3 Solution Differential Element Arbitrary element: disk element thickness Volume: = 0.52 Moment Arms: = Integration = 0, = 0 =
= 66.7
1 200 [ 0.52 ] 0 1 200 [ 0.52 ] 0
1 2 0 1 0
= 0.667
HCM City Univ. of Technology, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering
Nguyen Tan Tien
HCM City Univ. of Technology, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering
Nguyen Tan Tien
3/25/2013
Engineering Mechanics Statics
9.19
Center of Gravity and Centroid
Engineering Mechanics Statics
9.20
Center of Gravity and Centroid
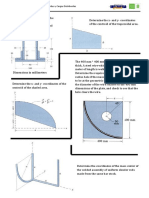
Fundamental Problems - F9.1 Determine the centroid ( , ) of the shaded area
Fundamental Problems - F9.2 Determine the centroid ( , ) of the shaded area
HCM City Univ. of Technology, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering
Nguyen Tan Tien
HCM City Univ. of Technology, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering
Nguyen Tan Tien
Engineering Mechanics Statics
9.21
Center of Gravity and Centroid
Engineering Mechanics Statics
9.22
Center of Gravity and Centroid
Fundamental Problems - F9.3 Determine the centroid of the shaded area
Fundamental Problems - F9.4 Locate the center mass of the straight rod if its mass per unit length is given by = 0 (1 + 2 /2 )
HCM City Univ. of Technology, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering
Nguyen Tan Tien
HCM City Univ. of Technology, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering
Nguyen Tan Tien
Engineering Mechanics Statics
9.23
Center of Gravity and Centroid
Engineering Mechanics Statics
9.24
Center of Gravity and Centroid
Fundamental Problems - F9.5 Locate the centroid of the homogeneous solid formed by revolving the shaded area about the axis
Fundamental Problems - F9.6 Locate the centroid of the homogeneous solid formed by revolving the shaded area about the axis
HCM City Univ. of Technology, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering
Nguyen Tan Tien
HCM City Univ. of Technology, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering
Nguyen Tan Tien
3/25/2013
Engineering Mechanics Statics
9.25
Center of Gravity and Centroid
Engineering Mechanics Statics
9.26
Center of Gravity and Centroid
2. Composite Body - A composite body consists of a series of connected simpler shaped bodies, which may be rectangular, triangular, semicircular, - Such a body can often be sectioned or divided into its composite parts and, provided the weight and location of the center of gravity of each of these parts are known - We can then eliminate the need for integration to determine the center of gravity for the entire body
2. Composite Body - The center of gravity of = , = , = , , : the coordinates of the center of gravity of the composite body : the weights of the composite parts of the body , , : the coordinates of the center of gravity of each composite part of the body - The Centroid for composite lines, areas and volumes can be found using relations analogous to the above one
HCM City Univ. of Technology, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering
Nguyen Tan Tien
HCM City Univ. of Technology, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering
Nguyen Tan Tien
Engineering Mechanics Statics
9.27
Center of Gravity and Centroid
Engineering Mechanics Statics
9.28
Center of Gravity and Centroid
2. Composite Body - Example 9.9 Locate the centroid of the wire
2. Composite Body - Example 9.9 Locate the centroid of the plate area
Solution
11310 5600 = = 45.5, = = = 22.5, 248.5 248.5 200 = = = 0.805 248.5 =
HCM City Univ. of Technology, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering Nguyen Tan Tien
Solution Composite Parts: divide the wire into 3 segments Moment Arms: the centroid are located as indicated Summary 4 = = = 0.348 11.5 14 = = = 1.22 11.5
HCM City Univ. of Technology, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering Nguyen Tan Tien
Engineering Mechanics Statics
9.29
Center of Gravity and Centroid
Engineering Mechanics Statics
9.30
Center of Gravity and Centroid
2. Composite Body - Example 9.10 Locate the center of mass of the assembly. The conical frustum has a density of and the hemisphere has a density of There is a 25-radius cylindrical hole in the center of the frustum Solution Composite Parts (1) + (2) (3) (4)
2. Composite Body Composite Parts: (1) + (2) (3) (4) Moment Arms: the centroid are located as indicated Summary
HCM City Univ. of Technology, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering
Nguyen Tan Tien
HCM City Univ. of Technology, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering
Nguyen Tan Tien
3/25/2013
Engineering Mechanics Statics
9.31
Center of Gravity and Centroid
Engineering Mechanics Statics
9.32
Center of Gravity and Centroid
2. Composite Body Composite Parts: (1) + (2) (3) (4) Moment Arms: the centroid are located as indicated Summary
Fundamental Problems - F9.7 Locate the centroid (, , ) of the wire bent in the shape
The center of mass = 0 = 0 45.815 = = = 14.6 3.142
HCM City Univ. of Technology, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering
Nguyen Tan Tien
HCM City Univ. of Technology, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering
Nguyen Tan Tien
Engineering Mechanics Statics
9.33
Center of Gravity and Centroid
Engineering Mechanics Statics
9.34
Center of Gravity and Centroid
Fundamental Problems - F9.8 Locate the centroid of the beams cross-sectional area
Fundamental Problems - F9.9 Locate the centroid of the beams cross sectional area
HCM City Univ. of Technology, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering
Nguyen Tan Tien
HCM City Univ. of Technology, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering
Nguyen Tan Tien
Engineering Mechanics Statics
9.35
Center of Gravity and Centroid
Engineering Mechanics Statics
9.36
Center of Gravity and Centroid
Fundamental Problems - F9.10 Locate the centroid (, ) of the cross-sectional area
Fundamental Problems - F9.11 Locate the center of mass (, , ) of the homogeneous solid block
HCM City Univ. of Technology, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering
Nguyen Tan Tien
HCM City Univ. of Technology, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering
Nguyen Tan Tien
3/25/2013
Engineering Mechanics Statics
9.37
Center of Gravity and Centroid
Fundamental Problems - F9.12 Locate the center of mass (, , ) of the homogeneous solid block
HCM City Univ. of Technology, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering
Nguyen Tan Tien
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- CN Chap10 - Moments of InertiaDokument25 SeitenCN Chap10 - Moments of Inertiaengineer_atulNoch keine Bewertungen
- SM 14Dokument78 SeitenSM 14zahidahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Method of JointsDokument17 SeitenMethod of Jointssunny sunflowerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Centroides PDFDokument7 SeitenCentroides PDFDavid FernandoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Double Integration SMATDokument12 SeitenDouble Integration SMATAndrew JoseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Centroid Centre of GravityDokument10 SeitenCentroid Centre of GravityAmeya1823Noch keine Bewertungen
- Analytic Geometry 1Dokument4 SeitenAnalytic Geometry 1Mj AquinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lemh106 PDFDokument53 SeitenLemh106 PDFA/C Kapil Dev MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- NUmerical SolutionsDokument76 SeitenNUmerical SolutionsLiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6.0 Static Friction and Belt FrictionDokument17 Seiten6.0 Static Friction and Belt FrictionStewart StevenNoch keine Bewertungen
- CentroidDokument18 SeitenCentroidedwin f. sampangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanics of Deformable Bodies M1 Post TestDokument3 SeitenMechanics of Deformable Bodies M1 Post TestBenmark JabayNoch keine Bewertungen
- PS1 Statics of Rigid BodiesDokument2 SeitenPS1 Statics of Rigid BodiesGillian AmbaNoch keine Bewertungen
- fw5 Ce121Dokument16 Seitenfw5 Ce121Jun-jun PaleroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acceleration Analysis of MechanismsDokument32 SeitenAcceleration Analysis of MechanismsThahir Shah100% (1)
- Centroids and Centers of GravityDokument29 SeitenCentroids and Centers of GravityDanzel C DayondonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 1 Surveying Concepts and Measurement of Distance by Tape PDFDokument6 SeitenLecture 1 Surveying Concepts and Measurement of Distance by Tape PDFJimbo PerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Statics of Rigid BodiesDokument15 SeitenStatics of Rigid BodiesKhawaz HossainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elasticity & Oscillations: Ut Tension, Sic Vis As Extension, So Force. Extension Is Directly Proportional To ForceDokument11 SeitenElasticity & Oscillations: Ut Tension, Sic Vis As Extension, So Force. Extension Is Directly Proportional To ForceJustin Paul VallinanNoch keine Bewertungen
- fw4 Ce121Dokument15 Seitenfw4 Ce121Jun-jun Palero100% (1)
- Bending Stress in BeamsDokument9 SeitenBending Stress in BeamscataiceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Upang Cea Common Bes025 p3Dokument69 SeitenUpang Cea Common Bes025 p3Jairo OntongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coplanar Parallel Force SystemDokument5 SeitenCoplanar Parallel Force Systemclarissa ordonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- AnalyticDokument8 SeitenAnalyticMark Neil Delgaco GastiloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principles of Dynamics Students Hand OutsDokument4 SeitenPrinciples of Dynamics Students Hand OutsPauline CreoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integral Calculus 3 - PPTXDokument15 SeitenIntegral Calculus 3 - PPTXJustine Ejay MoscosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Normal and Shear Stress PDFDokument25 SeitenNormal and Shear Stress PDFmohanadymtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Double Integration MethodDokument10 SeitenDouble Integration Methodmau_boi16100% (1)
- Chapter-1: Introduction To Dynamics Mechanics As The Origin of DynamicsDokument92 SeitenChapter-1: Introduction To Dynamics Mechanics As The Origin of DynamicsRoutine Of Nepal BandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- In-HOUSE REVIEW (De, Advance Math and Discrete Math)Dokument11 SeitenIn-HOUSE REVIEW (De, Advance Math and Discrete Math)anjoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theory of Error (Prelim)Dokument5 SeitenTheory of Error (Prelim)Athina Maricar CabaseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report Math2.1Dokument15 SeitenReport Math2.1Anonymous qOUo59FCNoch keine Bewertungen
- MODULE 2 Plane Surveying PDFDokument7 SeitenMODULE 2 Plane Surveying PDFJexther Pascua NazarNoch keine Bewertungen
- E106Dokument2 SeitenE106Ralph De Vera EstevesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Centroids by Composite Areas PDFDokument20 SeitenCentroids by Composite Areas PDFMarc Jason YuNoch keine Bewertungen
- CablesDokument47 SeitenCablesankit roy100% (1)
- A. Hydrostatic Force On Plane Surface: 1. FormulaDokument20 SeitenA. Hydrostatic Force On Plane Surface: 1. FormulaKim Kelley AngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem 325 - Equilibrium of Three-Force System - Engineering Mechanics ReviewDokument4 SeitenProblem 325 - Equilibrium of Three-Force System - Engineering Mechanics Reviewnavneetkpatil8409Noch keine Bewertungen
- 3.1 Differential Calculus - Integration Course 1 For CE PDFDokument11 Seiten3.1 Differential Calculus - Integration Course 1 For CE PDFKenAbejuelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integral Calculus: Engr. Anacleto M. Cortez JRDokument10 SeitenIntegral Calculus: Engr. Anacleto M. Cortez JRPanfilo Diaz LacsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Normal and Tangential ComponentsDokument19 SeitenNormal and Tangential ComponentsGarrey BrionesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Surveying Lecture 100620Dokument2 SeitenSurveying Lecture 100620John Dalton ValenciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.0 Intro Engineering Utilities 1Dokument59 Seiten1.0 Intro Engineering Utilities 1Miguel Is My NameNoch keine Bewertungen
- D - Horizontal Alignment and Super ElevationDokument22 SeitenD - Horizontal Alignment and Super ElevationAva CastilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ce 402 Expt 7-8Dokument16 SeitenCe 402 Expt 7-8veeveegarcia_Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Mechanics: Engr. Cheryll C. MalibiranDokument29 SeitenFluid Mechanics: Engr. Cheryll C. MalibiranYedda M IlaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sheet 4 Centroied and Moment of Inertia PDFDokument1 SeiteSheet 4 Centroied and Moment of Inertia PDFmohamed mahmoud abdelhafezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Force Vectors, Vector Operations & Addition of Forces 2D & 3DDokument51 SeitenForce Vectors, Vector Operations & Addition of Forces 2D & 3DparklNoch keine Bewertungen
- Highway and Railroad Engineering: Compound CurvesDokument9 SeitenHighway and Railroad Engineering: Compound CurvesDirect XNoch keine Bewertungen
- MATH 403 EDA Chapter 8Dokument19 SeitenMATH 403 EDA Chapter 8Marco YvanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 04 First Law of ThermodynamicsDokument33 Seiten04 First Law of ThermodynamicsLuthfiani Widyawati Dwi AntariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 9 - Centroid and CGDokument24 SeitenChapter 9 - Centroid and CGnishant361Noch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering DrawingDokument116 SeitenEngineering DrawingIonel RaveicaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Moments MechanicsDokument173 SeitenMoments MechanicsChicha WatersNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applications of Differential EquationsDokument34 SeitenApplications of Differential EquationsNguyễn Văn CườngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 9 emDokument2 SeitenAssignment 9 emoperationmanagerNoch keine Bewertungen
- LEARNING Module 8: Centroid Center of Mass and Center of GravityDokument20 SeitenLEARNING Module 8: Centroid Center of Mass and Center of GravityZoe Angel Mhae AnteolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AMT 3102 Module 06 - Centroids & Center of GravityDokument20 SeitenAMT 3102 Module 06 - Centroids & Center of GravityRovic LopezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch.07 Internal ForcesDokument13 SeitenCh.07 Internal ForcesCK_85_3100% (1)
- Ch.08 FrictionDokument9 SeitenCh.08 FrictionCK_85_3Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ch.07 Internal ForcesDokument13 SeitenCh.07 Internal ForcesCK_85_3100% (1)
- Ch.04 Force System ResultantsDokument16 SeitenCh.04 Force System ResultantsCK_85_3Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ch.04 Force System ResultantsDokument16 SeitenCh.04 Force System ResultantsCK_85_3Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ch.02 Force VectorsDokument14 SeitenCh.02 Force VectorsCK_85_3Noch keine Bewertungen
- Diprotic Acid Titration Calculation Worked Example Sulphuric Acid and Sodium Hydroxide - mp4Dokument2 SeitenDiprotic Acid Titration Calculation Worked Example Sulphuric Acid and Sodium Hydroxide - mp4tobiloba temiNoch keine Bewertungen
- SPEC SHEET 005 AeroGlass LensDokument1 SeiteSPEC SHEET 005 AeroGlass LensMarco GalindoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hitide 2i (BP)Dokument4 SeitenHitide 2i (BP)Biju_PottayilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inspection & Maintenance of Dams: Dam Safety GuidelinesDokument79 SeitenInspection & Maintenance of Dams: Dam Safety Guidelinesvishu1909100% (1)
- IGS-NT Application Guide 05-2013 PDFDokument104 SeitenIGS-NT Application Guide 05-2013 PDFNikitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Specification Sheets PDFDokument6 SeitenSpecification Sheets PDFVu TongNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Does A Blueprint Work?Dokument5 SeitenHow Does A Blueprint Work?Eumieh Jane AlfonsoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kroo Subsonic WingDokument8 SeitenKroo Subsonic WingRod ManserNoch keine Bewertungen
- b-737 - Rev 59 PDFDokument402 Seitenb-737 - Rev 59 PDFCatevario NegroNoch keine Bewertungen
- DST FingerprintDokument10 SeitenDST FingerprintAli DMNoch keine Bewertungen
- DsPIC33F - 01 - IntroductionDokument8 SeitenDsPIC33F - 01 - IntroductionLau SandovalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Epanet Vs Watergems (083011)Dokument9 SeitenEpanet Vs Watergems (083011)MABA02100% (1)
- B766Dokument9 SeitenB766marriolavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet # 7 - Free Body DiagramDokument2 SeitenWorksheet # 7 - Free Body DiagramyabalabahiyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MEMS-Based Uncooled Infrared Bolometer Arrays - A ReviewDokument15 SeitenMEMS-Based Uncooled Infrared Bolometer Arrays - A ReviewMarco LicofonteNoch keine Bewertungen
- 07 Power Voltage FeedthroughsDokument52 Seiten07 Power Voltage FeedthroughsDeepak SomanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Caterpillar 990H BrochureDokument20 SeitenCaterpillar 990H BrochureEugene MalinowskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teodoriu 2010Dokument13 SeitenTeodoriu 2010JhormanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operating Systems: Credits: 4 Credits Course Coordinator: V.V.SubrahmanyamDokument4 SeitenOperating Systems: Credits: 4 Credits Course Coordinator: V.V.SubrahmanyamHarendra KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Day 1 Borehole Geophysics WDokument21 SeitenDay 1 Borehole Geophysics Waliy2k4uNoch keine Bewertungen
- db12 HornDokument3 Seitendb12 HornGerman Andres GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Single Head Nest Detail: Turbonest F644-12Mm-S355-04Dokument5 SeitenSingle Head Nest Detail: Turbonest F644-12Mm-S355-04Vv ZzNoch keine Bewertungen
- SWOT Analysis of Viyellatex Spinning LimitedDokument81 SeitenSWOT Analysis of Viyellatex Spinning LimitedHossain RanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Catalogue For AutoDokument22 SeitenCatalogue For Autosentimiento azulNoch keine Bewertungen
- PeltonDokument7 SeitenPeltonKunal Kumar DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cables TheoryDokument15 SeitenCables TheorytceterexNoch keine Bewertungen
- Earthquake in TaguigDokument4 SeitenEarthquake in TaguigDianca Zyra Rodil-CabanelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- d8n Wiring HardnessDokument2 Seitend8n Wiring HardnessandraNoch keine Bewertungen
- HN1000 HN2000Dokument44 SeitenHN1000 HN2000Mose SodeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Subitec Info Industrial CultivationDokument4 SeitenSubitec Info Industrial CultivationUsamah ZakiNoch keine Bewertungen