Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Practice Test
Hochgeladen von
api-233668463Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Practice Test
Hochgeladen von
api-233668463Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Name: Class:
Teacher: Date:
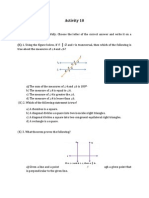
Task: This is a short answer test that will be conducted individually. Note: Standard geometric markings have been used to indicate the properties of shapes. Part A 1. Circle the correct definitions. a) Corresponding angles are equal in size. Corresponding angles are supplementary they add up to 180. b) Alternate angles are equal in size. Alternate angles are supplementary they add up to 180. c) Co-interior angles are equal in size. Co-interior angles are supplementary they add up to 180. d) Parallel lines are two straight lines that cross each other at a 90 angle. Parallel lines are two straight lines that are an equal distance apart for their entire length.
2. Draw over the dotted lines to illustrate the angles labelled below.
Corresponding
Alternate
Co-interior
3. In the diagram shown, angles 2 and 5 are ... a) vertically opposite angles b) complementary angles c) alternate angles d) corresponding angles e) co-interior angles
4. Draw a line to connect the definition on the right with the pairs of angles on the left: 2&8 5&1 8&2 2&5 4&2
alternate angles vertically opposite angles alternate angles corresponding angles co-interior angles
5.
35
Find the size of angle a.
Give a reason for your answer.
Find the size of angle b.
Give a reason for your answer.
6.
130
40
Find the size of angle c.
Give a reason for your answer.
Find the size of angle d.
Give a reason for your answer.
7. Imagine you are a building inspector checking walls for a company which sells prefabricated (already made) walls to builders. The technical words used for the parts of the framework are shown on the diagram below.
a. Why would it be important that the studs are perpendicular (at right angles) to both the top and bottom plates? b. Why would it be important that the alternate angles formed between the brace and the top and bottom plates are equal? c. The prefabricated walls are inspected for accurate construction before being sent to the building site. Complete the table below using the information given on the diagrams of prefabricated walls. (Note: Diagrams are not drawn to scale.)
Wall 1 2 3 4
Rejected/possibly accepted
Reason
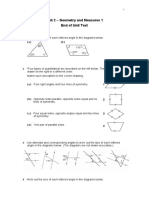
4. Mark the following angles and streets with the colour indicated. a) 1 pair of corresponding angles (red) b) 1 pair of alternate angles (blue) c) 1 pair of co-interior angles (black)
5. Find the value of the unknown angles in the diagram below. Show reasons for all answers.
a) Find the size of angle a.
Give a reason for your answer.
b) Find the size of angle c.
Give a reason for your answer.
c) Find the size of angle b.
Give a reason for your answer.
d) Find the size of angle e.
Give a reason for your answer.
Part B
1. A rule to describe the pattern shown above is m = 3s+ 1 (a) What is represented by the pronumeral s? (b) What is represented by the pronumeral m? (c) Use the rule to find how many matches are required to make 6 squares. Show all working.
(d) Use the rule (m = 3s + 1) to complete the missing y values in the table of values:
s m
1 4
2 7
3 10
4 13
10
(e) Plot the points from the table of values on the Cartesian plane.
(f) How many matchsticks are needed to make 8 squares? Explain how you would work this out.
(g) How many squares can be made from a box of 50 matchsticks? Show how you worked this out.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- 4q-Math8 V1-PTDokument7 Seiten4q-Math8 V1-PTAlessa LamesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Angles MeasurementDokument60 SeitenAngles Measurementsitaram_akella_1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Paper (Class 9) - SA2Dokument7 SeitenSample Paper (Class 9) - SA2vinod1577Noch keine Bewertungen
- Geometry QuizDokument2 SeitenGeometry QuizDarth KingofvNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4TH Grading Periodical Examination-Grade 8Dokument6 Seiten4TH Grading Periodical Examination-Grade 8Anthony Rey CaneteNoch keine Bewertungen
- TransformationsDokument42 SeitenTransformationsAbha SumanNoch keine Bewertungen
- WE1 Sample ExamDokument8 SeitenWE1 Sample ExamKritika27Noch keine Bewertungen
- Y7 Math RevisionDokument6 SeitenY7 Math RevisionAskiitians Education CentreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Q4 Summative Test Math 7 SY 2022-2023 (1sheet)Dokument4 SeitenQ4 Summative Test Math 7 SY 2022-2023 (1sheet)ICT CRMNHSNoch keine Bewertungen
- bk9 12Dokument18 Seitenbk9 12Rahique ShuaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- HKCEE Maths 2002 Paper 1Dokument33 SeitenHKCEE Maths 2002 Paper 1auau1997100% (1)
- Geometry EOC Practice TestDokument34 SeitenGeometry EOC Practice TestsujkubvsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Access NCERT Solutions For Class 6 Chapter 5 - UpDokument19 SeitenAccess NCERT Solutions For Class 6 Chapter 5 - UpKamjith PadinjareveeduNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Triangles Angles Scale 3d LsDokument5 SeitenTest Triangles Angles Scale 3d Lsapi-583528524Noch keine Bewertungen
- Joy Activity 10Dokument7 SeitenJoy Activity 10api-279213523Noch keine Bewertungen
- Geometry 3 PFDokument60 SeitenGeometry 3 PFAnwar HossainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Post Test in Mathematics 7Dokument8 SeitenPost Test in Mathematics 7zaldy mendozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Third Quarter Unit Test SY 2022-23 Direction: Choose The Letter Corresponding To The Correct Answer. 1Dokument5 SeitenThird Quarter Unit Test SY 2022-23 Direction: Choose The Letter Corresponding To The Correct Answer. 1Lacuata, Christine Joy LoisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Angles WorksheetDokument9 SeitenAngles WorksheetAyesha BaigNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Triangles Angles Scale 3dDokument7 SeitenTest Triangles Angles Scale 3dapi-583528524Noch keine Bewertungen
- AMC 8 Mock 2013 A FinalDokument4 SeitenAMC 8 Mock 2013 A FinalmanrongjiangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test 2007 Final VersionDokument12 SeitenTest 2007 Final Versionau auNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Drawing Questions and AnswersDokument449 SeitenEngineering Drawing Questions and AnswersVishalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2 - Geometry and Measures 1 End of Unit TestDokument4 SeitenUnit 2 - Geometry and Measures 1 End of Unit TestThaxter QubeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2015 WMI Grade 6 Questions Part 1 PDFDokument4 Seiten2015 WMI Grade 6 Questions Part 1 PDFสฮาบูดีน สาและ86% (7)
- Aryabhatta Question Paper Class VIII 2019Dokument15 SeitenAryabhatta Question Paper Class VIII 2019Easy peasy Coding100% (4)
- Texas Geometry Staar DiagnosticDokument29 SeitenTexas Geometry Staar DiagnosticJason MillerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ccgps CRCT Math 7th Grade Geometry Review PacketDokument9 SeitenCcgps CRCT Math 7th Grade Geometry Review PacketOishin MariscalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simple Equations & Lines & AnglesDokument2 SeitenSimple Equations & Lines & AnglesChhavi KhandujaNoch keine Bewertungen
- General SATDokument7 SeitenGeneral SATIddosa AsfawNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cayley Contest: Canadian Mathematics CompetitionDokument5 SeitenCayley Contest: Canadian Mathematics Competitionสฮาบูดีน สาและNoch keine Bewertungen
- All1st Year Engineering Drawing MCQ (Tgiti)Dokument348 SeitenAll1st Year Engineering Drawing MCQ (Tgiti)Ari HauntNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geometry PracticeDokument8 SeitenGeometry PracticeEddy R. VélezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Old Mutual South African Mathematics OlympiadDokument16 SeitenOld Mutual South African Mathematics OlympiadjoshlancelemmetjiesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class-9 Maths Summative Assessment - IIDokument6 SeitenClass-9 Maths Summative Assessment - IIApex InstituteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Roll No.: 28 Aryabhatta Inter-School Mathematics Competition - 2011Dokument12 SeitenRoll No.: 28 Aryabhatta Inter-School Mathematics Competition - 2011DgjjkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 6 Final MathsDokument3 SeitenClass 6 Final Mathssarthak06gNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3rd Monthly AssignmentDokument6 Seiten3rd Monthly AssignmentBanana Jr.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ab - Class Viii - Sample Paper-02Dokument15 SeitenAb - Class Viii - Sample Paper-02Bhakti AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Geometry GRE EdgeDokument40 SeitenBasic Geometry GRE EdgeKrishnendu Ghosh100% (1)
- Summ Math7 q3Dokument4 SeitenSumm Math7 q3Demuel Tenio LumpaanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exam Review Student Jan 2018 GeometryDokument4 SeitenExam Review Student Jan 2018 Geometryapi-286302284Noch keine Bewertungen
- 3rd Periodical Test in Mathematics 7Dokument5 Seiten3rd Periodical Test in Mathematics 7sineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Visualising Solid Shapes: Unit 6 Unit 6 Unit 6 Unit 6 Unit 6Dokument42 SeitenVisualising Solid Shapes: Unit 6 Unit 6 Unit 6 Unit 6 Unit 6AjiteshPaddaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Extra Exercises - Express and SpecialDokument26 SeitenExtra Exercises - Express and Specialdmal88Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mathlinks9 Final Review ch1-11 TextbookDokument9 SeitenMathlinks9 Final Review ch1-11 Textbookapi-171445363Noch keine Bewertungen
- MTRP Pyq JR 15Dokument4 SeitenMTRP Pyq JR 15bishwajitparamanik140Noch keine Bewertungen
- Math G9 HowsDokument4 SeitenMath G9 Howstae hyungNoch keine Bewertungen
- June 99 Paper 4Dokument8 SeitenJune 99 Paper 4Trishna Patel ŦNoch keine Bewertungen
- Long Quiz in Math 6Dokument8 SeitenLong Quiz in Math 6Joice Ann PolinarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Polygons Form 1Dokument38 SeitenPolygons Form 1graciezaynNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cayley Contest: Canadian Mathematics CompetitionDokument5 SeitenCayley Contest: Canadian Mathematics Competitionสฮาบูดีน สาและNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2 Geometry Study GuideDokument8 SeitenUnit 2 Geometry Study Guides9120362Noch keine Bewertungen
- Math Homwork 7Dokument87 SeitenMath Homwork 7abdul subhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Master Fundamental Concepts of Math Olympiad: Maths, #1Von EverandMaster Fundamental Concepts of Math Olympiad: Maths, #1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering DrawingDokument5 SeitenEngineering DrawingSainadhReddy100% (4)
- Basic Geometry STUDENTDokument15 SeitenBasic Geometry STUDENTJacky PoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Section A: Section A Consists of 20 Questions of 1 Mark EachDokument4 SeitenSection A: Section A Consists of 20 Questions of 1 Mark EachReet KaurNoch keine Bewertungen
- MathDokument13 SeitenMathVinod KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trigonometry - ThursdayDokument10 SeitenTrigonometry - Thursdayapi-233668463Noch keine Bewertungen
- Humphries J Etp310 Assignment 2Dokument28 SeitenHumphries J Etp310 Assignment 2api-233668463Noch keine Bewertungen
- Design Task Shogun JapanDokument5 SeitenDesign Task Shogun Japanapi-233668463Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mccloy LukeDokument1 SeiteMccloy Lukeapi-233668463Noch keine Bewertungen
- Shougun Japan PreDokument1 SeiteShougun Japan Preapi-233668463Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sorbello T Humphries J Etl329 Assignment 3Dokument34 SeitenSorbello T Humphries J Etl329 Assignment 3api-233668463Noch keine Bewertungen
- ElearningDokument5 SeitenElearningapi-233668463Noch keine Bewertungen
- Japanese CultureDokument12 SeitenJapanese Cultureapi-233668463Noch keine Bewertungen
- Monday 14 OctDokument17 SeitenMonday 14 Octapi-233668463Noch keine Bewertungen
- Etl121 Assignment 1 Humphries JoannaDokument6 SeitenEtl121 Assignment 1 Humphries Joannaapi-233668463Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mock Up Pamphlet - FinalDokument14 SeitenMock Up Pamphlet - Finalapi-233668463Noch keine Bewertungen
- English 8c Placemat Term 3Dokument4 SeitenEnglish 8c Placemat Term 3api-233668463Noch keine Bewertungen
- Class Rules2Dokument1 SeiteClass Rules2api-233668463Noch keine Bewertungen
- Humphries J 220647 Etl212 Assign 1Dokument12 SeitenHumphries J 220647 Etl212 Assign 1api-2336684630% (1)
- Facebook Assignment 2 CDokument1 SeiteFacebook Assignment 2 Capi-233668463Noch keine Bewertungen
- PLP Powerpoint 3Dokument11 SeitenPLP Powerpoint 3api-233668463Noch keine Bewertungen
- Humphries Joanna Etl301 Assignment 2 FinalDokument32 SeitenHumphries Joanna Etl301 Assignment 2 Finalapi-233668463Noch keine Bewertungen
- Facebook Wall Page For SamuraiDokument1 SeiteFacebook Wall Page For Samuraiapi-233668463Noch keine Bewertungen
- HisfbdamiyoooowallpgDokument1 SeiteHisfbdamiyoooowallpgapi-233668463Noch keine Bewertungen
- Shogun Facebook Assignment 2Dokument1 SeiteShogun Facebook Assignment 2api-233668463Noch keine Bewertungen
- Humphries Joanna s220647 Etl203 Assign 1Dokument6 SeitenHumphries Joanna s220647 Etl203 Assign 1api-233668463Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mock Up Pamphlet - FinalDokument14 SeitenMock Up Pamphlet - Finalapi-233668463Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mccloy LukeDokument1 SeiteMccloy Lukeapi-233668463Noch keine Bewertungen
- Personal Learning ProfileDokument1 SeitePersonal Learning Profileapi-233668463Noch keine Bewertungen
- Facebook Assignment 2casDokument1 SeiteFacebook Assignment 2casapi-233668463Noch keine Bewertungen
- Indigenous LearnersDokument18 SeitenIndigenous Learnersapi-233668463Noch keine Bewertungen
- Monday 14thDokument25 SeitenMonday 14thapi-233668463Noch keine Bewertungen
- Humphries Joanna Etl301 Assignment 2 FinalDokument32 SeitenHumphries Joanna Etl301 Assignment 2 Finalapi-233668463Noch keine Bewertungen
- Humphries J 220647 Etl212 Assign 1Dokument12 SeitenHumphries J 220647 Etl212 Assign 1api-2336684630% (1)
- Humphries Joanna Etl301 Assignment 2 FinalDokument32 SeitenHumphries Joanna Etl301 Assignment 2 Finalapi-233668463Noch keine Bewertungen
- Recalling Trigonometry: Property of STIDokument3 SeitenRecalling Trigonometry: Property of STIKetaks MooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geometry SamplerDokument30 SeitenGeometry SamplerSusanNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Level Math Paper 1 TrigonometryDokument40 SeitenA Level Math Paper 1 TrigonometryREMO MosesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geometry PostulatesTheorems-ListDokument11 SeitenGeometry PostulatesTheorems-ListGeorge FanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answer Sheet Grade 7 Properties of TriangleDokument5 SeitenAnswer Sheet Grade 7 Properties of TriangleNandini pilaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- 06.01.2021 - Grade 7 Maths QPDokument10 Seiten06.01.2021 - Grade 7 Maths QPMidhun Bhuvanesh.B 7ANoch keine Bewertungen
- MIT8 02SC Challenge Sol19Dokument12 SeitenMIT8 02SC Challenge Sol19enrnwrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Euler AnglesDokument18 SeitenEuler AnglesRamónNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geometry in Art: Symbols and LinesDokument1 SeiteGeometry in Art: Symbols and LinesChiew N PangNoch keine Bewertungen
- State of Technology and Design Guidelines For The Archimedes Screw TurbineDokument9 SeitenState of Technology and Design Guidelines For The Archimedes Screw TurbineAgung FauziNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measurement of Angles and DirectionsDokument73 SeitenMeasurement of Angles and DirectionsSHEAN GAYLE ANGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Procedure For Stimating Basic Friction Angle From A Tilt TestDokument7 SeitenProcedure For Stimating Basic Friction Angle From A Tilt TestBen AguilarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geometry Success in 20 Minutes A DayDokument223 SeitenGeometry Success in 20 Minutes A Daykeruiro100% (1)
- 2013 Incoming 8th Grade Summer Math PacketDokument13 Seiten2013 Incoming 8th Grade Summer Math Packetlinda_collins891100% (1)
- Answer Aerodynamics - Rotational Theory and Velocity Triangle PDFDokument2 SeitenAnswer Aerodynamics - Rotational Theory and Velocity Triangle PDFRickshit Buragohain0% (1)
- Introduction To GeogebraDokument3 SeitenIntroduction To GeogebraStefano FochesattoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revise 3Dokument88 SeitenRevise 3Aisha QasimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plane & Spherical Trigonometry: Engr. Marvin Y. Villorente, ECE, ECTDokument59 SeitenPlane & Spherical Trigonometry: Engr. Marvin Y. Villorente, ECE, ECTMira Alvarez100% (2)
- Lesson Plan in TrigonometryDokument4 SeitenLesson Plan in TrigonometryLianjieNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9a03101e Engineering DrawingDokument4 Seiten9a03101e Engineering DrawingsivabharathamurthyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introducing Differentiation: PrerequisitesDokument14 SeitenIntroducing Differentiation: PrerequisitesShrishail SambanniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Curve RangingDokument23 SeitenCurve RangingYounq KemoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Knowledge Skills Attitudes ValuesDokument4 SeitenKnowledge Skills Attitudes ValuesTherence UbasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment Two: 2. Angular MeasurementDokument4 SeitenExperiment Two: 2. Angular Measurementahmed jemalNoch keine Bewertungen
- CIE IGCSE 0580 - 2018 Hardest Questions CompilationDokument89 SeitenCIE IGCSE 0580 - 2018 Hardest Questions CompilationJiyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Baby Gie Tausa - Math-CG - G7 - 3QDokument1 SeiteBaby Gie Tausa - Math-CG - G7 - 3QBaby Gie TausaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11.CSEC Maths JUNE 2009 PDFDokument29 Seiten11.CSEC Maths JUNE 2009 PDFnatasha fNoch keine Bewertungen
- Schwarz-Christoffel TransformationsDokument11 SeitenSchwarz-Christoffel TransformationsjohnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4Dokument19 SeitenChapter 4Ifa AsratNoch keine Bewertungen