Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
76FAD0C345164EDAB3C955B33285D137
Hochgeladen von
Manoj Kumaran0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
89 Ansichten0 SeitenTerm End Examination - November 2012 Course : EEE540 - Embedded System Design Slot: F1 Class NBR : 4116 Time : Three Hours Max.Marks:100 Answer ALL the questions.
Originalbeschreibung:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenTerm End Examination - November 2012 Course : EEE540 - Embedded System Design Slot: F1 Class NBR : 4116 Time : Three Hours Max.Marks:100 Answer ALL the questions.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
89 Ansichten0 Seiten76FAD0C345164EDAB3C955B33285D137
Hochgeladen von
Manoj KumaranTerm End Examination - November 2012 Course : EEE540 - Embedded System Design Slot: F1 Class NBR : 4116 Time : Three Hours Max.Marks:100 Answer ALL the questions.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 0
Page 1 of 3
Term End Examination - November 2012
Course : EEE540 - Embedded System Design
Slot: F1
Class NBR :
4116
Time : Three Hours
Max.Marks:100
Answer ALL the Questions
1. Name the classification of Embedded Systems. [2]
2. What are the constraints we will meet while designing an embedded system? [4]
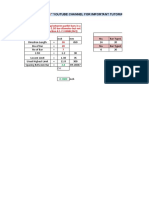
3. Calculate the revenue loss percentage for the following
[4]
4. Assume three technologies are available for developing a product of 1000 units.
Calculate total cost and per product cost.
Tech NRE
Cost
Unit cost
A 2000 100
B 30,000 30
C 100000 2
[4]
5. Apart from speed, distance, master-slave, no. of wires, size of the data frame,
Error/collision detection, voltage scheme, what is the major disadvantage of CAN
protocol from other protocols [USB, I
2
C, RS232, SPI]
[2]
6. Design a 4K X 16 bit SRAM system using 2K X 8 bit SRAMs. [5]
8 months 16 months 2 months
Peak revenue = Rs. 100
Revenue = Rs. 60
Page 2 of 3
7. Draw the circuit for interfacing processor, memory and I/O devices through DMA. [4]
8. Name the different packets and transfers in USB 2.0. [3]
9. With neat diagram explain the STACK organisation of a processor for an embedded
system.
[4]
10. Select the features you need in a processor and Memorys type, size to develop a
a) Intelligent traffic light controller b) Text to Speech converter
[4]
11. Explain the following IO devices.
(i) Timers (ii) counters (iii) Watch dog timers
[3]
12. How RS485 has less electromagnetic interference/noise when compared to RS232? [3]
13. In CAN communication no clock data is communicated in the network [True or False] [2]
14. Consider a 4bit ADC with a reference voltage of 8V, what is the digital value after
conversion by ADC if the input voltage to ADC is 5 V?
[5]
15. Elaborate on each term in a CAN NODE. [6]
16. Below shown are the scrambled blocks of a CAN data Format. Arrange it in a correct
order for a Standard CAN data format.
[5]
17. Assume the situation given in below and generate the sequence of action required if
microcontroller need to read from the sensor (assume the sensor data is 64h) and write
in display controller. Support your statements by drawing the data format.
[6]
I2C BUS
Master
Micro
Controller
Sensor Display
Controller
Address-7ah
Address-88h
Page 3 of 3
18. With neat diagram explain the different task states for an RTOS. [6]
19. With necessary diagram explain the function call mechanism which makes use of stack
frames.
[5]
20. Explain an embedded system application and model it using FSM. [3]
21. Differentiate General purpose and Real time operating system of an embedded system. [3]
22. Explain in detail the need of context switching. [4]
23. Define the States of a Task and explain when and between which states context
switching takes place.
[4]
24. Describe about priority inversion problem. How it can be avoided? [4]
25. Arrange the Data frames in the CAN bus in the sequential order based on the CAN
arbitration principles, justify it. The numbers in the diagram are the Value of the
Identifier field of a Data format.
[5]
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Resistors Module 01Dokument10 SeitenResistors Module 01Manoj KumaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7th SemDokument17 Seiten7th SemShankar MukalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Story of PhysicsDokument49 SeitenStory of Physicssukuya100% (1)
- A Survey On Clustering Techniques For Wireless Sensor NetworkDokument7 SeitenA Survey On Clustering Techniques For Wireless Sensor NetworkWhite Globe Publications (IJORCS)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Story of PhysicsDokument49 SeitenStory of Physicssukuya100% (1)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5782)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (72)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- E0642426 PDFDokument3 SeitenE0642426 PDFAyaz KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Low Cost Earthquake Resistant Housing Construction in India: I. Abstract & IntroductionDokument3 SeitenLow Cost Earthquake Resistant Housing Construction in India: I. Abstract & IntroductionArvind BajpaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Churches That Have Left RCCG 0722 PDFDokument2 SeitenChurches That Have Left RCCG 0722 PDFKadiri JohnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drill Pipe Performance SheetDokument3 SeitenDrill Pipe Performance Sheetjinyuan74Noch keine Bewertungen
- Drawing Checklist - An Integral Part of Your Construction ContractDokument4 SeitenDrawing Checklist - An Integral Part of Your Construction Contractamtris406Noch keine Bewertungen
- LNT - Ecc - InfoDokument5 SeitenLNT - Ecc - InfoJnanamNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0734net PDFDokument589 Seiten0734net PDFArturo PerdomoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mpls 04 Static LSPDokument12 SeitenMpls 04 Static LSPpkdor2008Noch keine Bewertungen
- How Fine Art Enhances Architecture.Dokument9 SeitenHow Fine Art Enhances Architecture.KomalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ig FreeSpace 2120 HZ-LZ AmpsDokument48 SeitenIg FreeSpace 2120 HZ-LZ AmpsohundperNoch keine Bewertungen
- Production of Expanded-Clay Aggregate For Lightweight Concrete From Non-Selfbloating Clays (Pioro 2004)Dokument5 SeitenProduction of Expanded-Clay Aggregate For Lightweight Concrete From Non-Selfbloating Clays (Pioro 2004)juan diazNoch keine Bewertungen
- BUILDING REGULATIONS SCHEDULES 1 TO 11 G.D.C.RDokument21 SeitenBUILDING REGULATIONS SCHEDULES 1 TO 11 G.D.C.Rriddhi patelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Space Saving Hostel TableDokument18 SeitenSpace Saving Hostel TablesadiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Using The FTD CLIDokument10 SeitenUsing The FTD CLIInderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Datasheet Scopus MPEG2 Encoder Model E 1000Dokument2 SeitenDatasheet Scopus MPEG2 Encoder Model E 1000acharlessNoch keine Bewertungen
- Military Golf Clubhouse Design GuideDokument68 SeitenMilitary Golf Clubhouse Design GuideCAP History LibraryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Edgecam Getting Started Guide - 2010 R1Dokument44 SeitenEdgecam Getting Started Guide - 2010 R1Alexandru DumitruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Refrigeration IIAR 4 PR1Dokument28 SeitenRefrigeration IIAR 4 PR1geverett2765100% (3)
- Mivan Technology Reasearch PaperDokument4 SeitenMivan Technology Reasearch PaperKushal Patil100% (8)
- Zip HydroTap warranty detailsDokument8 SeitenZip HydroTap warranty detailsstarchitectNoch keine Bewertungen
- Archmodels Vol.107 PDFDokument32 SeitenArchmodels Vol.107 PDFAlejandra Ximena MelendezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Game Proposal Document 3 With ContentsDokument14 SeitenGame Proposal Document 3 With ContentsSaif AminNoch keine Bewertungen
- KGDVSDokument19 SeitenKGDVSBrandi ReynoldsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modern Architecture: Chicago School and Early PioneersDokument75 SeitenModern Architecture: Chicago School and Early Pioneersgeethanjali jNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathcad - Final Version - Vertical Cantilever Retaining Wall - CTA 95th Street - Typical SE - Without Column Canopy PedestalDokument59 SeitenMathcad - Final Version - Vertical Cantilever Retaining Wall - CTA 95th Street - Typical SE - Without Column Canopy PedestalAnonymous rQKN6vV100% (3)
- Decode BD YouTube tutorialsDokument6 SeitenDecode BD YouTube tutorialsAnish KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Troubleshooting RPC Endpoint Mapper Errors Using The Windows Server 2003 Support Tools From The Product CDDokument17 SeitenTroubleshooting RPC Endpoint Mapper Errors Using The Windows Server 2003 Support Tools From The Product CDAnderson SilvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Configuring DC1Dokument58 SeitenConfiguring DC1jessenierinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Asigra TrueNAS Backup Appliance Built On Ixsystems Open Source Storage To Be Unveiled at VMWorld 2018Dokument4 SeitenAsigra TrueNAS Backup Appliance Built On Ixsystems Open Source Storage To Be Unveiled at VMWorld 2018PR.comNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comandos Consola ZimbraDokument12 SeitenComandos Consola ZimbraBryan Centeno GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen