Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
JS PH Temp Conc Rennin Enzyme Lab
Hochgeladen von
crazymax90Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
JS PH Temp Conc Rennin Enzyme Lab
Hochgeladen von
crazymax90Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Name: ___________ Rennin Enzyme Lab
Period: _____
Digestion is the breakdown of food into molecules useable by the body. Enzymes are chemicals that help digest food. Chymosin (rennin) is an enzyme that is found in the stomach of milk-producing animals. The enzyme leads to curd formation and aids in digestion. Procedures: Students will work in pairs. Each pair will test EITHER enzyme concentration, temperature OR pH. Part 1: Enzyme Concentration 1. Obtain six test tubes and label them 1 through 6. 2. Add 2 ml of whole milk to each tube. 3. Add the following amounts of enzyme to the test tubes using a calibrated plastic pipette. a. Tube 1 = 0 ml b. Tube 2 = 0.5 ml c. Tube 3 = 1 ml d. Tube 4 = 2 ml e. Tube 5 = 3 ml f. Tube 6 = 4 ml 4. Start timing as soon as the enzyme is added. 5. After adding the enzyme, put your thumb over the top of the test tube and mix. Do this approximately every 30 seconds. 6. Record the time it takes for the milk in each tube to begin to coagulate. Use the appropriate table provided. 7. Prepare a graph (X-axis amount of enzyme, Y-axis Minutes to coagulation). Part 2: Temperature 1. Obtain seven test tubes and label them 1 through 7. 2. Add 2 ml of whole milk to each tube 3. Add 1 ml of enzyme to each tube EXCEPT tube 1 4. After adding the enzyme, put your thumb over the top of the test tube and mix. Do this approximately every 30 seconds 5. Place the tubes at various temperatures as follows: a. Tubes 1 & 2 & 3 at room temperature b. Tubes 4 & 5 on ice c. Tubes 6 & 7 in a warm water bath. 6. Record the time for the milk in each tube to begin to coagulate. Use the appropriate table provided. 7. Prepare a graph (X axis = Temperature of milk, Y-axis = Minutes to coagulation).
Part 3: pH 1. Obtain eight test tubes and label them 1 through 8. 2. Add 2 ml of whole milk to each of eight test tubes. 3. Add 1 ml of each of the 7 vinegar solution to separate test tubes as follow: EX. Test tube 1 vinegar solution 1 pH=2.8 Test tube 2 vinegar solution 2 pH=3.0 Test tube 3 vinegar solution 3 pH=3.2 Test tube 4 - vinegar solution 4 pH=3.5 Test tube 5 - vinegar solution 5 pH=3.8 Test tube 6 - vinegar solution 6 pH=4.1 Test tube 7 - vinegar solution 7 pH=4.7 Test tube 8 distilled water pH=7.0 Test tube 9 distilled water pH=7.0 NO ENZYME Use ONLY the pipette that is in each solution. DO NOT mix the pipettes. 4. Add 1 ml of enzyme to test tubes 1-8. DO NOT ADD enzyme to test tube 9. 5. After adding the enzyme, put your thumb over the top of the test tube and mix. Do this approximately every 30 seconds 6. Record the time for the milk in each tube to begin to coagulate in the appropriate table provided. 7. Prepare a graph (X-axis = pH of milk, Y-axis = Minutes to coagulation) Clean Up: 1. Use a test tube brush to scrub out your test tubes. Rinse them well with water. Place them upside down in the test tube rack at your station. 2. Get data for the two sections your team did not do from other teams. 3. Graph the data on three separate graphs. Graph pH vs. time, enzyme concentration vs. time, and temperature vs. time.
Discussion questions 1. Describe the effect of Rennin on Milk.
2. Have you ever seen a baby spit up? Did it look anything like this? Why do you think it did?
3. Describe the effect of enzyme concentration on milk coagulation.
4. Describe the effect of temperature on milk coagulation.
5. Describe the effect of pH on milk coagulation.
6. What evidence do you have that the Rennin was responsible for the change in the milk? What do you call this element of the experiment?
7. Why would rennin be useful in making ice cream or cheese?
8. What is the difference between an enzyme and a catalyst?
9. Is rennin an enzyme or a catalyst? Why?
10) What other factors do you think could change the effect of the Rennin?
DATA TABLES Concentration Volume of Rennin (ml)
Tube 1 2 3 4 5 6
Coagulation Time (Minutes)
Tube 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
Temperature Temperature of Milk C
Coagulation Time (Minutes)
Tube 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
pH pH of Milk
Coagulation Time (Minutes)
GRAPHS
Name______________
Teacher Preparation Materials
Vinegar beakers roasters test tube racks rennet tablets Distilled Water plastic pipettes metal test tube racks test tubes test tube brushes pH probe aluminum foil test tube clamps labeling tape stop watches flasks Hot plates thermometers marker
Enzyme solution is made by mixing one rennet tablet with 50 ml of water. Need about 3 tablets per class of 26-30 students. Amount of shaking the test tube greatly influences rate of coagulation. If you are really going to use a class average, make sure method of shaking is established. Students work as a pair on only one of the tests, pH, concentration, or temperature. Students then get the data for the other two tests from other groups. I found it best to have students go into the lab and depending on where they were standing they were placed into their test groups.
Temperature Notes:
5 samples (one cold from the refrigerator, one room temperature, three warmed in water bath). Only warmed ones will coagulate within the class period.
Concentration Notes: pH Notes:
3 ml + will coagulate within the class period.
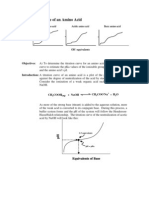
pH solutions of 2.8 and sometimes 3.0 coagulate milk without enzyme! Be sure to cover with aluminum foil to minimize evaporation. Also, it is important that the plastic pipettes are not transferred from one solution to another. The pH solution of 4.7 required only 0.1 ml of vinegar in 100 ml of water, so transferring even a small amount of vinegar can affect the pH greatly! Other substances that could be tried could be citric acid (ph ~2.4, baking soda, ammonia, etc.) pH solutions were prepared as follows: Volume of vinegar(ml) Volume of water(ml) pH (using probe) 0 100 7.0 0.1 100 4.7 0.25 100 4.1 1.0 100 3.8 3.0 100 3.5 8.0 100 3.2 30 100 3.0 100 0 2.8
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- DocxDokument12 SeitenDocxmutinda100% (4)
- Effect of Temperature On Enzyme Activity HSCDokument3 SeitenEffect of Temperature On Enzyme Activity HSCsamham9662% (13)
- Delta Pulse Metal Detector Practical GuideDokument0 SeitenDelta Pulse Metal Detector Practical Guidecrazymax9083% (6)
- Milk and Rennin PracDokument7 SeitenMilk and Rennin PracTherese Nguyen50% (2)
- Experiment 4 (Biology)Dokument11 SeitenExperiment 4 (Biology)言爱邦0% (1)
- Chemical Mechanisms of Digestion LabDokument9 SeitenChemical Mechanisms of Digestion Labapi-294622133Noch keine Bewertungen
- Blue Simple Illustration Science and Research Stationery A4 Page Border - 20231101 - 192225 - 0000Dokument16 SeitenBlue Simple Illustration Science and Research Stationery A4 Page Border - 20231101 - 192225 - 0000bhabak0024Noch keine Bewertungen
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDokument6 SeitenNew Microsoft Word Documentprinsuumrao3625Noch keine Bewertungen
- LAB EXERCISE: Enzymes II-AmylaseDokument6 SeitenLAB EXERCISE: Enzymes II-AmylaseBasem AbdelrahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- A ProjectDokument17 SeitenA ProjectDivya Yadav100% (1)
- Biology Practical GuideDokument29 SeitenBiology Practical GuidebekoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12TH Chem.Dokument13 Seiten12TH Chem.Tanu SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem Final - PrajithDokument13 SeitenChem Final - PrajithA PRAJITH ARWESMENTNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digestion of Starch by Salivary Amylase: Effects of pH and TemperatureDokument12 SeitenDigestion of Starch by Salivary Amylase: Effects of pH and TemperatureMAGMA GAMINGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lipase Reaction in Milk TypesDokument11 SeitenLipase Reaction in Milk TypesOscarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry - Investigatory - Project (1) .PPTX (Read-Only)Dokument14 SeitenChemistry - Investigatory - Project (1) .PPTX (Read-Only)djjeena619Noch keine Bewertungen
- Study of Digestion of Starch by Salivary Amylase and Effect of PH and Temperature On It.Dokument9 SeitenStudy of Digestion of Starch by Salivary Amylase and Effect of PH and Temperature On It.surya pratap charasiya66% (35)
- Chemistry Investigatory ProjectDokument16 SeitenChemistry Investigatory ProjectSriram .R100% (4)
- Investigate Effects of Environmental Factors on Enzyme ActivityDokument13 SeitenInvestigate Effects of Environmental Factors on Enzyme ActivityIsland VitalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study Digestion of Starch by Salivary AmylaseDokument4 SeitenStudy Digestion of Starch by Salivary AmylaseTanishq SainiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enzymes Lab ReportDokument7 SeitenEnzymes Lab ReportMemorie BrownNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 Spineappleenzymelabday 2Dokument2 Seiten10 Spineappleenzymelabday 2api-257187977Noch keine Bewertungen
- Digestion of Salivary GlandDokument12 SeitenDigestion of Salivary GlandJatin suthar100% (1)
- 6.5-6 Urinalysis Procedure-3Dokument1 Seite6.5-6 Urinalysis Procedure-3Nathan Jacob100% (1)
- Enzymes LolsDokument38 SeitenEnzymes LolsThon JustineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yeast LabDokument3 SeitenYeast LabAlex AlilingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Potato Enzyme Lab HonorsDokument2 SeitenPotato Enzyme Lab HonorsCrisa ChinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Investigatory File - 063557Dokument21 SeitenChemistry Investigatory File - 063557goelvinayak406Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry ProjectDokument19 SeitenChemistry ProjectKabeer Golechha100% (1)
- Revised Gcse Biol Revised Support 22589Dokument6 SeitenRevised Gcse Biol Revised Support 22589yoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prakhar Chemistry ProjectDokument12 SeitenPrakhar Chemistry ProjectVEDANT ONLYNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phyics ExtraDokument11 SeitenPhyics ExtraHimanshu Somkunwar0% (1)
- Salivary Amylase ProjectDokument14 SeitenSalivary Amylase ProjectTanmay SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- To Study The Digestion of Starch by SaliDokument12 SeitenTo Study The Digestion of Starch by SaliUthaya SurianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Investigating The Effect of PH On Amylase Activity: ProcedureDokument4 SeitenInvestigating The Effect of PH On Amylase Activity: ProcedureJohanna Marie GantalaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Project Report On To Study The Digestion of Starch by Salivary Amylase and Effect of PH and Temperature On ItDokument5 SeitenChemistry Project Report On To Study The Digestion of Starch by Salivary Amylase and Effect of PH and Temperature On ItGSI BHUBANESWARNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design Experiment SPM BiologyDokument32 SeitenDesign Experiment SPM BiologyEma94% (36)
- EnzymesDokument5 SeitenEnzymesboxz2258Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Investigatory Project (1) 3Dokument16 SeitenChemistry Investigatory Project (1) 3Manjushree .TNoch keine Bewertungen
- Harsh Singh Chemistry3Dokument10 SeitenHarsh Singh Chemistry3hateu1588Noch keine Bewertungen
- Objectives of The Project Repor1Dokument5 SeitenObjectives of The Project Repor1Sunny SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem Inves Proj FinalDokument13 SeitenChem Inves Proj FinalphychemgodNoch keine Bewertungen
- InvestigatoryProject Purnendu Jha XIIADokument17 SeitenInvestigatoryProject Purnendu Jha XIIAPurnendu JhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Harsh ChemistryDokument8 SeitenHarsh Chemistryhateu1588Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Exercise DigestionDokument14 SeitenLab Exercise DigestionPatricia GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- (A) To Show The Action of Amylase On StarchDokument3 Seiten(A) To Show The Action of Amylase On StarchMismah Binti Tassa YanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dissolving Eggs: The Power of EnzymesDokument4 SeitenDissolving Eggs: The Power of EnzymesDianne VillanuevaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Investigating The Effect of PH On Amylase Activity Ss 34Dokument4 SeitenInvestigating The Effect of PH On Amylase Activity Ss 34darren boesonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enzymes LolsDokument39 SeitenEnzymes LolsA FloraldeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enzyme Lab FinishedDokument7 SeitenEnzyme Lab Finishedjenna727Noch keine Bewertungen
- To Study The Digestion of Starch by Salivary Amylase and Effect of PH and Temperature On ItDokument4 SeitenTo Study The Digestion of Starch by Salivary Amylase and Effect of PH and Temperature On Itethirajmagesh5Noch keine Bewertungen
- Amylase Activity TestDokument14 SeitenAmylase Activity TestSanya chauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yeast and Temperature Experiment ANSWERSDokument4 SeitenYeast and Temperature Experiment ANSWERSrachelchristabelleleeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Noah's Fascinating World of STEAM Experiments: Chemical Reactions: A Junior Scientist's Lab Notebook for Learning Scientific MethodVon EverandNoah's Fascinating World of STEAM Experiments: Chemical Reactions: A Junior Scientist's Lab Notebook for Learning Scientific MethodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Explosive Science Experiments for Little Chemists - Science Project | Children's Science Experiment BooksVon EverandExplosive Science Experiments for Little Chemists - Science Project | Children's Science Experiment BooksNoch keine Bewertungen
- 30 Mason Jar Experiments To Do With Your Kids: Fun and Easy Science Experiments You Can Do at HomeVon Everand30 Mason Jar Experiments To Do With Your Kids: Fun and Easy Science Experiments You Can Do at HomeNoch keine Bewertungen
- A 2.4Ghz Vertical Collinear Antenna For 802.11 Applications: Brian Oblivion Capt - Kaboom Richard A WennerDokument8 SeitenA 2.4Ghz Vertical Collinear Antenna For 802.11 Applications: Brian Oblivion Capt - Kaboom Richard A WennerNikola PetkovićNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wireless Intro StudyDokument47 SeitenWireless Intro StudyEmmanuel O. AyeniNoch keine Bewertungen
- 102003BGA Reballing Instruction ManualDokument31 Seiten102003BGA Reballing Instruction ManualMassimo LizzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- TversityguideDokument72 SeitenTversityguidetiolindyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Valentina Semen Cenk o Refer at TM FDokument12 SeitenValentina Semen Cenk o Refer at TM Fcrazymax90Noch keine Bewertungen
- User ManualDokument193 SeitenUser Manualcrazymax90Noch keine Bewertungen
- Selection and Application of Autochthonous Functional Starter Cultures in Traditional Croatian Fermented SausagesDokument6 SeitenSelection and Application of Autochthonous Functional Starter Cultures in Traditional Croatian Fermented Sausagescrazymax90Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Application of Biotechnological Methods For The Synthesis of BiodieselDokument14 SeitenThe Application of Biotechnological Methods For The Synthesis of Biodieselcrazymax90Noch keine Bewertungen
- Resent Devolpment in Indigo Dyeing.Dokument5 SeitenResent Devolpment in Indigo Dyeing.vasucristalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Install Windows 8 On Tablet PDFDokument4 SeitenInstall Windows 8 On Tablet PDFcrazymax90Noch keine Bewertungen
- Us20070144036a1 PDFDokument9 SeitenUs20070144036a1 PDFcrazymax90Noch keine Bewertungen
- EnzymeDokument25 SeitenEnzymecrazymax90Noch keine Bewertungen
- Optiplex-Xe Service Manual3 Sr-YuDokument43 SeitenOptiplex-Xe Service Manual3 Sr-Yucrazymax90Noch keine Bewertungen
- EnzymesDokument17 SeitenEnzymesakshaymoga0% (1)
- EnzymeDokument13 SeitenEnzymecrazymax90Noch keine Bewertungen
- Additive 133Dokument1 SeiteAdditive 133crazymax90Noch keine Bewertungen
- Enzyme FactorsDokument19 SeitenEnzyme FactorsAriana Hernández RamírezNoch keine Bewertungen
- 51012119Dokument7 Seiten51012119crazymax90Noch keine Bewertungen
- Maelgwyn Imhoflot (Chile)Dokument0 SeitenMaelgwyn Imhoflot (Chile)crazymax90Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cikloidni OptDokument8 SeitenCikloidni Optcrazymax90Noch keine Bewertungen
- Q 5Dokument1 SeiteQ 5crazymax90Noch keine Bewertungen
- DesulfatorDokument5 SeitenDesulfatormad659Noch keine Bewertungen
- Surf PIProDokument1 SeiteSurf PIProcrazymax90Noch keine Bewertungen
- Quick Controller InstructionsDokument1 SeiteQuick Controller Instructionscrazymax90Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pic-P8-X Prototype Board For 8 Pin Pic Microcontrollers: Features: EEPROM Memory InterfaceDokument2 SeitenPic-P8-X Prototype Board For 8 Pin Pic Microcontrollers: Features: EEPROM Memory Interfacecrazymax90Noch keine Bewertungen
- MbedGWEmeter1 0SCHDokument1 SeiteMbedGWEmeter1 0SCHcrazymax90Noch keine Bewertungen
- Q 5Dokument1 SeiteQ 5crazymax90Noch keine Bewertungen
- MbedGWEmeter1 0SCHDokument1 SeiteMbedGWEmeter1 0SCHcrazymax90Noch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet # 5 On Forces and MotionDokument1 SeiteWorksheet # 5 On Forces and MotionlinlinycNoch keine Bewertungen
- DP Chem Unit 3 PerodicityDokument5 SeitenDP Chem Unit 3 PerodicityPatrick AbidraNoch keine Bewertungen
- FINISHINGDokument32 SeitenFINISHINGdyuti singhNoch keine Bewertungen
- 06 PenetrexDokument13 Seiten06 PenetrexMari WellNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electro Cat Alys Is 101Dokument29 SeitenElectro Cat Alys Is 101Vu LeNoch keine Bewertungen
- O Level Physics Pressure NotesDokument28 SeitenO Level Physics Pressure NotesMarvel ComicsNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Astronet Infraestructure RoadmapDokument178 SeitenThe Astronet Infraestructure RoadmapALNoch keine Bewertungen
- Titration CurveDokument12 SeitenTitration Curveoguztop10Noch keine Bewertungen
- Atividade 8º - Inglês - Semana 22Dokument3 SeitenAtividade 8º - Inglês - Semana 22Maria ClaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mariner 910 S - ENGDokument2 SeitenMariner 910 S - ENGNindi Widia Devi RahmasariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flexure Formula Stresses in BeamsDokument18 SeitenFlexure Formula Stresses in BeamsAthena YoungNoch keine Bewertungen
- MeteorologyDokument2 SeitenMeteorologyIoniță AndreeaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 02 Diffusivity - PPT (Read Only)Dokument20 Seiten02 Diffusivity - PPT (Read Only)dxdiag97Noch keine Bewertungen
- G.6 Q.1 SCIENCE Lesson 2 Homogeneous MixtureDokument35 SeitenG.6 Q.1 SCIENCE Lesson 2 Homogeneous MixturemeguiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Space DynamicsDokument37 SeitenSpace Dynamicspurushottam KashyapNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concrete Aggregates: Standard Specification ForDokument15 SeitenConcrete Aggregates: Standard Specification ForHasanalmahmudNoch keine Bewertungen
- 07 01 2024 JR Super60 NUCLEUS BT Jee Adv2021 P1 CTA 23 Q PaperDokument20 Seiten07 01 2024 JR Super60 NUCLEUS BT Jee Adv2021 P1 CTA 23 Q Paperzaid khanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbon Dioxide As CatalystDokument7 SeitenCarbon Dioxide As CatalystNaubeqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Safari - 6 Sep 2022 at 2:40 PMDokument1 SeiteSafari - 6 Sep 2022 at 2:40 PMTerrence AzariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yemigeba DocumentDokument78 SeitenYemigeba DocumentDemelashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spin Valve TransistorDokument19 SeitenSpin Valve Transistorajayg2020Noch keine Bewertungen
- Substance Chemistry Lesson 2Dokument16 SeitenSubstance Chemistry Lesson 2samsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Makalah-Work Energy PowerDokument29 SeitenMakalah-Work Energy PowerSastri DwisariniNoch keine Bewertungen
- 23 - High Temperature Materials - Torralba PDFDokument70 Seiten23 - High Temperature Materials - Torralba PDFAnish MahajanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cambridge International AS and A Level PhysicsDokument2 SeitenCambridge International AS and A Level PhysicsnaylinaungNoch keine Bewertungen
- EMPC2015 - Wire Bonding of Au-Coated Ag Wire Bondwire Properties, Bondability andDokument4 SeitenEMPC2015 - Wire Bonding of Au-Coated Ag Wire Bondwire Properties, Bondability andChong Leong GanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Mechanics PDFDokument65 SeitenFluid Mechanics PDFSiddharth GargNoch keine Bewertungen
- Claus Plants Prove FlexibleDokument3 SeitenClaus Plants Prove Flexiblebakhtiari_afNoch keine Bewertungen
- SuspensionDokument31 SeitenSuspensionSakandar TalibNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Otto Schmidt's Inter-Stellar Dust TheoremDokument1 SeiteThe Otto Schmidt's Inter-Stellar Dust TheoremKC CampilanNoch keine Bewertungen