Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Lesson Plan or
Hochgeladen von
sumikannuOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Lesson Plan or
Hochgeladen von
sumikannuCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
LESSON PLAN
Sub Name : OPERATIONS RESEARCH Sub Code : 11ME 501 Branch: MechanicalEngg. Semester : V Hours and Credit: L-T-P-C (3 1 0 4)
UNIT I LINEAR PROGRAMMING
12(L)
Introduction - Formulation of linear programming models Assumptions-Graphical solution procedure solving LPP using simplex algorithm Degeneracy, Revised Simplex Method Duality theory - Interpretation of dual variables- Primal Dual Relationships Role of duality in sensitivity analysis - Dual simplex method Objective: To understand and apply operations research techniques to industrial operations.
Session No
Topics to be covered
Time (min) 55 55 55 55 55
Ref
Teaching Method BB BB BB BB BB
Introduction
1
Formulation of linear programming models
2
Graphical solution procedure
3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
solving LPP using simplex algorithm solving LPP using simplex algorithm Degeneracy Revised Simplex Method Duality theory Interpretation of dual variables Primal Dual Relationships Primal Dual Relationships Role of duality in sensitivity analysis Dual simplex method
1,2 55 55 55 55 55 55 55 BB BB BB BB BB BB BB
UNIT II TRANSPORTATION & ASSIGNMENT MODEL
12(L)
Transportation problems, transportation simplex method Assignment problems, Hungarian method- LP formulation of transportation and Assignment networks- Traveling sales man problem Objective: To create awareness about utilization of resources through various optimization techniques.
Session No 1
Topics to be covered
Time (min) 55 55 55 55 55
Ref
Teaching Method BB BB BB BB BB
Transportation problems Transportation simplex method
2
Transportation simplex method
3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
Assignment problems -Hungarian method Assignment problems -Hungarian method Assignment problems -Hungarian method LP formulation of transportation LP formulation of transportation LP formulation of Assignment networks LP formulation of Assignment networks Traveling sales man problem Traveling sales man problem
2 55 55 55 55 55 55 55 BB BB BB BB BB BB BB
UNIT III INVENTORY MODELS
12(L)
Purchase model with no shortages manufacturing model with no shortage Purchase model with shortage Manufacturing model with shortages model with price breaks Objective: To create awareness about utilization of resources through various optimization techniques.
Session No 1
Topics to be covered
Time (min) 55 55 55 55 55 55 55 55 55 55 55 55
Ref
Teaching Method BB BB BB BB
Purchase model with no shortages Purchase model with no shortages
2
Manufacturing model with no shortage
3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
Manufacturing model with no shortage Purchase model with shortage Purchase model with shortage Manufacturing model with shortages Manufacturing model with shortages Manufacturing model with shortages Model with price breaks Model with price breaks Revision
BB BB BB BB BB BB BB BB
UNIT IV NETWORK MODELS
12(L)
Maximal flow problem Shortest route problem Minimal spanning tree problem - Project networks, CPM, PERT, Crashing of networks, L P model for crashing project costing and control. Objective: To create awareness about utilization of resources through various optimization techniques.
Session No 1
Topics to be covered
Time (min) 55 55 55 55 55 55 55 55 55 55 55 55
Ref
Teaching Method BB BB BB BB
Maximal flow problem Shortest route problem
2
Minimal spanning tree problem
3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
Project networks introduction CPM Continuation of CPM Continuation of CPM PERT Continuation of PERT Continuation of PERT Crashing of networks L P model for crashing project costing and control.
BB BB BB BB BB BB BB BB
UNIT V QUEUING AND REPLACEMENT MODELS
12(L)
Queuing theory terminology Single server, multi server, Limited queue capacity applications Markov chains.Replacement models Money value, present worth factor and discount rate.
Objective: To develop the basic of Metaheuristics techniques in different fields.
Session No 1
Topics to be covered
Time (min) 55 55 55 55 55 55 55 55 55 55 55 55
Ref
Teaching Method BB BB BB BB
Queuing theory terminology Single server
2
multi server
3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
Continuation of Single server & multi server Limited queue capacity applications Markov chains Replacement models Money value Replacement models Money value Replacement models present worth factor Replacement models present worth factor Replacement models discount rate Revision
4,5
BB BB BB BB BB BB BB BB
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (894)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- Labview Core 2 Exercises: Instruments Not For DistributionDokument102 SeitenLabview Core 2 Exercises: Instruments Not For DistributionAmín ACNoch keine Bewertungen
- Schedule Review ChecklistDokument3 SeitenSchedule Review Checklistsampath_priyashanthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cisco Intelligent WANDokument878 SeitenCisco Intelligent WANHernán Conrado Krause LeytonNoch keine Bewertungen
- AspenFlareSysAnalyzerV8 0 RefDokument228 SeitenAspenFlareSysAnalyzerV8 0 RefrandimakmurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conversion ChartDokument1 SeiteConversion ChartLibinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Create Excel Files CDokument29 SeitenCreate Excel Files CSaka Kely100% (1)
- 1.what Is BDC and Explain The Real Time Scenarios Where We Need To Write The BDC Programs ?Dokument15 Seiten1.what Is BDC and Explain The Real Time Scenarios Where We Need To Write The BDC Programs ?api-19817778100% (1)
- H1B Resume TemplateDokument5 SeitenH1B Resume TemplateSuresh ParaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lease Agreement or Rental Agreement FormatDokument3 SeitenLease Agreement or Rental Agreement Formatyuvashreesharmi60% (5)
- Integrated Product and Process Development Unit I A. IntroductionDokument19 SeitenIntegrated Product and Process Development Unit I A. IntroductionsumikannuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7541 1462 5100 1 SyllabusDokument8 Seiten7541 1462 5100 1 SyllabussumikannuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dr. Mahalingam College of Engineering and Technology, Pollachi - 642 003Dokument1 SeiteDr. Mahalingam College of Engineering and Technology, Pollachi - 642 003sumikannuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Explain Briefly How The ChipDokument4 SeitenExplain Briefly How The ChipsumikannuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11EC801Dokument1 Seite11EC801sumikannuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ivyeara&b Hostel Stdnts DataDokument2 SeitenIvyeara&b Hostel Stdnts DatasumikannuNoch keine Bewertungen
- DV03PUB7 Study GuideDokument4 SeitenDV03PUB7 Study GuidesumikannuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 - 8th BoG Agenda NotesDokument20 Seiten1 - 8th BoG Agenda NotessumikannuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2013 BE Mechanical Engineering A Section Student Name ListDokument6 Seiten2013 BE Mechanical Engineering A Section Student Name ListsumikannuNoch keine Bewertungen
- PT II SyllabusDokument1 SeitePT II SyllabussumikannuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hints 1Dokument19 SeitenHints 1sumikannuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Agenda: Team Orientation DayDokument3 SeitenAgenda: Team Orientation DaysumikannuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dr. Mahalingam College of Engineering and Technology, PollachiDokument1 SeiteDr. Mahalingam College of Engineering and Technology, PollachisumikannuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 28Dokument13 SeitenLec 28sumikannuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Apt I NumbersDokument2 SeitenApt I NumberssumikannuNoch keine Bewertungen
- WWW WWW WWWWDokument1 SeiteWWW WWW WWWWsumikannuNoch keine Bewertungen
- BE SW EEE Opting - List 2010 2015Dokument5 SeitenBE SW EEE Opting - List 2010 2015sumikannuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Non-Conventional Energy SystemsDokument2 SeitenNon-Conventional Energy SystemsJAMESJANUSGENIUS5678Noch keine Bewertungen
- 3306 7730 1 PBDokument6 Seiten3306 7730 1 PBsumikannuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calendar of Activies For14-15 CTDokument1 SeiteCalendar of Activies For14-15 CTsumikannuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Itc LTD Interview QuestionsDokument2 SeitenItc LTD Interview QuestionssumikannuNoch keine Bewertungen
- MTS Prepaid Mobile Top Up, MTS Data Card Recharge With Credit Cards & Net BankingDokument1 SeiteMTS Prepaid Mobile Top Up, MTS Data Card Recharge With Credit Cards & Net BankingsumikannuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Course 9Dokument2 SeitenCourse 9faster123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Maximising Energy Performance and Productivity With Solar ShadingDokument28 SeitenMaximising Energy Performance and Productivity With Solar ShadingsumikannuNoch keine Bewertungen
- DR - Mahalingam College of Engineering & Technology, Pollachi - 3Dokument12 SeitenDR - Mahalingam College of Engineering & Technology, Pollachi - 3sumikannuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calendar of Activies For14-15 CTDokument1 SeiteCalendar of Activies For14-15 CTsumikannuNoch keine Bewertungen
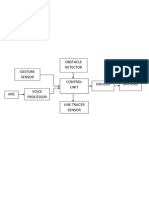
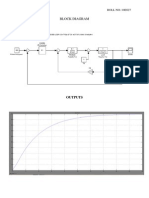
- Student block diagram and output reportDokument3 SeitenStudent block diagram and output reportsumikannuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Student Project Block Diagram and OutputDokument3 SeitenStudent Project Block Diagram and OutputsumikannuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summer Internship Report 2022 - 19EC452Dokument41 SeitenSummer Internship Report 2022 - 19EC452ParthNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cakephp TestDokument22 SeitenCakephp Testhathanh13Noch keine Bewertungen
- E Learning in Health Education - Feasibility, Pros and Cons: S.HemalathaDokument18 SeitenE Learning in Health Education - Feasibility, Pros and Cons: S.HemalathaHemalatha sNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 MalikDokument15 SeitenChapter 1 MalikPutra Makmur BoangmanaluNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principles of Scalable Performance and Parallelism MetricsDokument41 SeitenPrinciples of Scalable Performance and Parallelism MetricsHarminder SokhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux-5-SystemTap Beginners Guide-En-USDokument76 SeitenRed Hat Enterprise Linux-5-SystemTap Beginners Guide-En-USBuland Kumar SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- SafeQ4 - Quick Start GuideDokument21 SeitenSafeQ4 - Quick Start GuideLuki LeviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Java Language Fundamental by Druga SirDokument48 SeitenJava Language Fundamental by Druga SirSheikhShoaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- WebGIS-Coastal Database Management SystemDokument7 SeitenWebGIS-Coastal Database Management SystemChinna RamaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- PM Compatibility Change LogDokument10 SeitenPM Compatibility Change LogSyed SuhailNoch keine Bewertungen
- REMOTE WORK PLANDokument19 SeitenREMOTE WORK PLANAzbul EnterpriseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 LoadersDokument47 SeitenChapter 3 LoadersSky J0% (1)
- 489 Genator Management Relay PDFDokument322 Seiten489 Genator Management Relay PDFEugene MababaNoch keine Bewertungen
- StarCaster ATIS Technical OverviewDokument42 SeitenStarCaster ATIS Technical OverviewhurantiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- fx-CG50 Soft EN PDFDokument662 Seitenfx-CG50 Soft EN PDFSaksham RanjanNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Keep Journal Entry Approval HistoryDokument8 SeitenHow To Keep Journal Entry Approval HistoryKriez NamuhujaNoch keine Bewertungen
- QC Video & Labelling Training DocumentsDokument13 SeitenQC Video & Labelling Training DocumentsAhmad Miqdad AljabaNoch keine Bewertungen
- It6006 Da Iq Nov - Dec 2018 RejinpaulDokument1 SeiteIt6006 Da Iq Nov - Dec 2018 RejinpaulVanathi AnandavelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Window Air ConditionerDokument8 SeitenWindow Air ConditionerHimanshu UpadhyayNoch keine Bewertungen
- SAINIK SCHOOL SUMMER TASK FILE HANDLING AND BOOLEAN ALGEBRADokument8 SeitenSAINIK SCHOOL SUMMER TASK FILE HANDLING AND BOOLEAN ALGEBRAKanish KannaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Generations and Applications GuideDokument20 SeitenComputer Generations and Applications Guideirfanahmed.dbaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIS User Manual For CAPFDokument9 SeitenBIS User Manual For CAPFilyas bagliNoch keine Bewertungen
- NotesDokument303 SeitenNotesDaniel EcheverriaNoch keine Bewertungen