Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Edexcel 6679 Mechanics M3 January 2004 Provisional Mark Scheme
Hochgeladen von
metalmaniacmandarkOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Edexcel 6679 Mechanics M3 January 2004 Provisional Mark Scheme
Hochgeladen von
metalmaniacmandarkCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
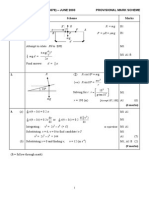
EDEXCEL 6679 MECHANICS M3 JANUARY 2004 PROVISIONAL MARK SCHEME
1.
(a) (b) T P mg
(b)
T cos60 = mg T = 2mg *
B1 M1A1
(1)
( ) T sin60 = mr 2 [Omission of m is M0] Attempt at r = Lsin60 (T sin60 = m Lsin60 2) 2g = L
M1
A1
(4)
(c) Applying Hookes Law: 2mg = [L in denominator is M0]
( L)
5 3
(L
2 5
L) ;
= 3m g
M1;A1 (2)
[7] 2.
(a) Integration of 4e 2t w.r.t. t to give v = 2e 2t (+c) Using initial conditions to find c (1) or v 1 = [ f (t )] t0 v = 2e 2t 1 ms1 (b) Integrating v w.r.t t ; x = e 2t t (+c)
B1 M1 A1
(3)
M1;A1 M1 M1;A1
Using t =0, x = 0 and finding value for c ( c = 1) Finding t when v = 0; t = ln 2 or equiv., 0.347
[both f.t. marks dependent on v of form ae 2t b] x = (1 ln 2) m or 0.153 m(awrt) [For A1, exact form must be two termed answer] A1
(6) [9]
EDEXCEL 6679 MECHANICS M3 JANUARY 2004 PROVISIONAL MARK SCHEME
3.
(a)
F=
k x2
[k may be seen as Gm1m2 , for example] [mg =
k ] R2
mgR 2 x2
M1 M1 * A1 (3)
Equating F to mg at x = R ,
Convincing completion [k = mgR2 ] to give F =
[Note: r may be used instead of x throughout, then r x at end.] (b) Equation of motion: ( m) a = ( ) Integrating: v2 =
( m) gR 2 ; x2 ( m )v dv ( m) gR 2 = dx x2
M1;M1 M1A1
gR 2 ( + c) or equivalent x [S.C: Allow A1 if A0 earlier due to + only]
Use of v 2 =
3gR , x = R to find c [ c = gR] or use in def. int. 2 2 gR 2 gR [ v2 = ] [Using x = 0 is M0] x 2 gR Substituting x = 3R and finding V ; V = 6 [Using x = 2R is M0] Alternative in (b) a mgR 2 Work/energy () dx ; = mv2 m u 2 2 x R
mgR 2 mgR 2 3gR ] = mv2 m 2 x R Final 2 marks as scheme
M1
M1;A1 (7)
[10]
M1;M1 M1A1M1 M1A1
Integrating:
[Conservation of energy scores 0]
EDEXCEL 6679 MECHANICS M3 JANUARY 2004 PROVISIONAL MARK SCHEME
4.
(a) Length of string =
A
1
10 3
B1
2a
EPE =
mg 2a
49 36
( L a) 2
M1
R P mg
T =
1
mga
A1 (3)
(b)
Energy equation: mv
mg 2a a2 = (
2 3
49 36
mga )C
M1A1
v =
5 ga or equivalent
A1 (3)
(c) When string at angle to horizontal, length of string = Vert. Comp. of T, TV, = T sin =
2a sin
M1A1
mg 2a a) sin ( 2a sin mg (2 sin ) = 2
(b) R + T V = mg and find R = .
M1
R = mg
mg mg (2 sin ) = sin 2 2
A1 A1 (5)
R > 0 (as sin > 0), so stays on table [Alternative final 3 marks: As increases so TV decreases Initial TV (string at to hor.) = TV
7 10 7 10
M1
mg A1
mg < mg, so stays on table A1]
[11]
EDEXCEL 6679 MECHANICS M3 JANUARY 2004 PROVISIONAL MARK SCHEME
5.
(a)
R
= 48N
B
0.6m
A 0.2g
A0
BA0 = 0.9 m
Applying Hookes Law correctly : e.g. T =
48 x 0.6
M1 M1 A1 A1 A1
(5)
& x Equation of motion: () T = 0.2 & 48 x & x Correct equation of motion: e.g. = 0.2 & 0.6 & = 2 x, and stating motion is SHM x Writing in form & 2 2 = * (no incorrect working seen) Period = = 20 10
[If measure x from B or A, final 2 marks only available if equation && = 2 X] of motion is reduced to X (b) max v = aw with values substituted; = 0.3 x 20 = 6 ms1 (c) Using x = 0.3 cos 20t or x = 0.3 sin 20T Using x = 0.15 to give either cos 20t = or sin 20T = Either t =
M1A1(2) M1 M1 A1
60
5 60
or
T=
120
Complete method for time:
t2 t1 ,
Time =
or
10
2t1 , or 2(
40
+ T)
M1 A1 (5)
[12]
15
s ( must be in terms of )
EDEXCEL 6679 MECHANICS M3 JANUARY 2004 PROVISIONAL MARK SCHEME
6.
(a) Masses
Cylinder ( ) (2a ) 2 ( 3 a )
2
Hemisphere ( ) a 3
3 2
S
( )( 16 a 3 )
3
M1A1
[6 a 3 ] [18] Distance of CM from O Moments equation: 6 a 3 ( a)
2 3
[2]
3 8
[16]
B1B1
a 3 (
3 8
a) =
51 64
16 3
a 3 x
M1 A1 (6)
x =
(b)
X A
G above A seen or implied or mg sin (GX) = mg cos (AX)
tan =
M1
AX = XG
2a
3 2
ax
M1
[GX =
3 2
51 64
a=
45 64
a , tan =
128 ] 45
= 70.6
A1 (3) M1 M1 A1
(3) [12]
(c) Finding F and R : R = mg cos , F = mg sin Using F = R and finding tan [= 0.8]
= 38.7
EDEXCEL 6679 MECHANICS M3 JANUARY 2004 PROVISIONAL MARK SCHEME
7.
(a) Energy: mv2 mu2 = mga sin
v2 =
3 2
M1 A1
(2)
ga + 2 ga sin
v2 a
(b) Radial equation: T mg sin = m
M1A1
T=
3mg (1 + 2sin) any form 2
A1 (3) M1;A1(2) M1 A1
(2)
(c) Setting T = 0 and solving trig. equation; (sin = ) = 210 * (d) Setting v = 0 in (a) and solving for sin = so not complete circle OR Substituting = 270 in (a); v 2 < 0 so not possible to complete (e) No change in PE no change in KE (Cof E) so v = u (f) When string becomes slack, V 2 = ga [sin = in (a)] Using fact that horizontal component of velocity is unchanged
B1 B1 M1
(1)
ga cos 60 o = 2
cos
3ga cos 2 1 = 73.2 12 M1A1 (4)
[14]
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Edexcel GCE Mechanics M2 (6678) : J Anuary 2006Dokument5 SeitenEdexcel GCE Mechanics M2 (6678) : J Anuary 2006Mk D. AssassinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mark Scheme (Results) January 2009: GCE Mathematics (6679/01)Dokument7 SeitenMark Scheme (Results) January 2009: GCE Mathematics (6679/01)Guruprasath BalakrishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vibration and Control: Associate Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Y.T.UDokument82 SeitenVibration and Control: Associate Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Y.T.Udora901Noch keine Bewertungen
- UntitledDokument11 SeitenUntitledapi-108235015Noch keine Bewertungen
- Edexcel GCE Mechanics M1 (6677) : Summer 2005Dokument5 SeitenEdexcel GCE Mechanics M1 (6677) : Summer 2005medja2233Noch keine Bewertungen
- M1 Jun 04 MSDokument7 SeitenM1 Jun 04 MSAnwer JalilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Communications 5th Ed SolutionsChap3Dokument33 SeitenDigital Communications 5th Ed SolutionsChap3Top StudentNoch keine Bewertungen
- 795 - 16 M2 Mock Paper Mark SchemeDokument6 Seiten795 - 16 M2 Mock Paper Mark SchemeTaqsim RajonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mark Scheme (Results) January 2008: GCE Mathematics (6678/01)Dokument6 SeitenMark Scheme (Results) January 2008: GCE Mathematics (6678/01)dasha962Noch keine Bewertungen
- Edexcel Mechanics M3 (6679) - June 2003 Provisional Mark Scheme Number Scheme Marks 1Dokument4 SeitenEdexcel Mechanics M3 (6679) - June 2003 Provisional Mark Scheme Number Scheme Marks 1Margarita SatrakiNoch keine Bewertungen
- M2 Jun 03 MSDokument4 SeitenM2 Jun 03 MSHykalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mark Scheme January 2007 6679 Mechanics M3Dokument7 SeitenMark Scheme January 2007 6679 Mechanics M3Amjed NizamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mark Scheme (Results) January 2007: GCE Mathematics Mechanics M1 (6677)Dokument5 SeitenMark Scheme (Results) January 2007: GCE Mathematics Mechanics M1 (6677)Sharmeen HelalNoch keine Bewertungen
- M2 Jan 04 MSDokument4 SeitenM2 Jan 04 MSHykalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solucionario Segundo Quimestre DPDokument16 SeitenSolucionario Segundo Quimestre DPAndres FernandoNoch keine Bewertungen
- M3Jan08A PDFDokument12 SeitenM3Jan08A PDFmetalmaniacmandarkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bab 1Dokument37 SeitenBab 1Ben Yudha SatriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- M1 January 2003 Mark SchemeDokument4 SeitenM1 January 2003 Mark SchemeAshique FarhadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math 1ZC3 Custom Courseware 2012Dokument121 SeitenMath 1ZC3 Custom Courseware 2012Vytautas StasiuleviciusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kunci Jawaban Fisika Klas X Bab 1 Martin Kanginan1Dokument37 SeitenKunci Jawaban Fisika Klas X Bab 1 Martin Kanginan1Yogastio Esadimmarca100% (4)
- Hints/Solutions: Leap ForwardDokument8 SeitenHints/Solutions: Leap ForwardOggy22Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanics Module M3: Marking GuideDokument4 SeitenMechanics Module M3: Marking GuideazsxdfghjklNoch keine Bewertungen
- Major Test - 2 - Main - SolutionDokument20 SeitenMajor Test - 2 - Main - SolutionPunit Singh SahniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Continuum Mech ProblemsDokument85 SeitenContinuum Mech ProblemsDeepak Verma100% (1)
- EE351 ProblemSet3 E Field Line SolutionDokument10 SeitenEE351 ProblemSet3 E Field Line Solutionomarsiddiqui8Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2004 Jan MS - m1Dokument4 Seiten2004 Jan MS - m1dasha962Noch keine Bewertungen
- ALP Solutions RBD Physics EngDokument27 SeitenALP Solutions RBD Physics EngShubhamDubeysubhashNoch keine Bewertungen
- 69 75Dokument10 Seiten69 75Carlos Moran CepedaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Section 12.6: C12S06.001: We First ComputeDokument24 SeitenSection 12.6: C12S06.001: We First ComputedifameNoch keine Bewertungen
- Edexcel GCE Mathematics Mechanics 2 M2 (6678) : Final Mark SchemeDokument7 SeitenEdexcel GCE Mathematics Mechanics 2 M2 (6678) : Final Mark SchemeMk D. AssassinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CV2015 - Tut 4 Soln - Vel Dist in OC & Most Efficient X-SectionDokument3 SeitenCV2015 - Tut 4 Soln - Vel Dist in OC & Most Efficient X-SectionleemariosanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phys (Main) SolutionsDokument9 SeitenPhys (Main) SolutionsSaurav MeherNoch keine Bewertungen
- FP2 Practice Paper A Mark SchemeDokument4 SeitenFP2 Practice Paper A Mark Schemejimbolina92100% (1)
- 6677 01 Rms 20080807Dokument7 Seiten6677 01 Rms 20080807Ashique FarhadNoch keine Bewertungen
- M1 January 2006 Mark SchemeDokument5 SeitenM1 January 2006 Mark SchemeAshique FarhadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mark Scheme January 2007 6677 Mecfhanics M1Dokument4 SeitenMark Scheme January 2007 6677 Mecfhanics M1dinosauroftheeastNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ispravci - Cvrstoca 2Dokument10 SeitenIspravci - Cvrstoca 2Mile Konfuzije JunglistNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mark SchemeDokument4 SeitenMark Schemebluebeary123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Solutions To Home Work Test/Physics: Dynamics of A Particle HWT - 1Dokument13 SeitenSolutions To Home Work Test/Physics: Dynamics of A Particle HWT - 1varunkohliinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mark Scheme (Results) Summer 2007: Mathematics Mecha Ic GCE N S M2 (6678)Dokument9 SeitenMark Scheme (Results) Summer 2007: Mathematics Mecha Ic GCE N S M2 (6678)dasha962Noch keine Bewertungen
- Trigo 1 Class Test (MS)Dokument5 SeitenTrigo 1 Class Test (MS)Madhu SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Core Mathematics C3: GCE Examinations Advanced SubsidiaryDokument4 SeitenCore Mathematics C3: GCE Examinations Advanced SubsidiaryHanna Kozak-KingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scheme Sem II 20082009Dokument12 SeitenScheme Sem II 20082009Sharifah Shahida Syed IdrusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analisis AtwoodDokument2 SeitenAnalisis AtwoodAde PriantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solomon A MSDokument4 SeitenSolomon A MSgranadeclamoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 16 M4 January 2003 Mark SchemeDokument5 Seiten16 M4 January 2003 Mark SchemeraaaaaawrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vectors IB Problems Mark SchemeDokument47 SeitenVectors IB Problems Mark Schememaryyam24Noch keine Bewertungen
- Iit - Jee Model Grand Test - Ii Paper - 2: Solutions KEY PhysicsDokument8 SeitenIit - Jee Model Grand Test - Ii Paper - 2: Solutions KEY PhysicsSayan Kumar KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2013 Vcaa Specialist Mathematics Exam 2 SolutionsDokument4 Seiten2013 Vcaa Specialist Mathematics Exam 2 SolutionsGarrison LiuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marking Guide: Mechanics Module M1Dokument4 SeitenMarking Guide: Mechanics Module M1Ghaith AdnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Merton Jump - Diffusion.modelDokument7 SeitenMerton Jump - Diffusion.modelIoannis MilasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Companion-Soln bk5Dokument6 SeitenCompanion-Soln bk5samthegofNoch keine Bewertungen
- IspitOtpornost 03-09-2007Dokument6 SeitenIspitOtpornost 03-09-2007Anonymous uJffWRZnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solution Manual - Control Systems by GopalDokument0 SeitenSolution Manual - Control Systems by Gopalsaggu199185% (27)
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageVon EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesVon EverandAnswers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesBewertung: 1.5 von 5 Sternen1.5/5 (2)
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesVon EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Edexcel GCE: Mechanic M3Dokument24 SeitenEdexcel GCE: Mechanic M3metalmaniacmandarkNoch keine Bewertungen
- M3Jan08A PDFDokument12 SeitenM3Jan08A PDFmetalmaniacmandarkNoch keine Bewertungen
- DDDokument21 SeitenDDSyed HaiderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dice Half Life ExperimentDokument1 SeiteDice Half Life ExperimentEsmond TangNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Option) P: Nahian Islam Rahat Nazrul Islam Sultana ParveenDokument1 Seite(Option) P: Nahian Islam Rahat Nazrul Islam Sultana ParveenmetalmaniacmandarkNoch keine Bewertungen
- A-Level Practical Support BookletDokument3 SeitenA-Level Practical Support Bookletforum4physics100% (6)
- Our T-ShirtDokument1 SeiteOur T-ShirtmetalmaniacmandarkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evsjv 'K Cö KŠKJ Wek We' VJQ, XVKV: Cö - G DCW 'WZ: MB'C Îi MZ ZV HVPVB, Wefvm Wbe©Vp Bi Ackb Cö'Vb I V ' CixÿvDokument3 SeitenEvsjv 'K Cö KŠKJ Wek We' VJQ, XVKV: Cö - G DCW 'WZ: MB'C Îi MZ ZV HVPVB, Wefvm Wbe©Vp Bi Ackb Cö'Vb I V ' CixÿvmetalmaniacmandarkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sam Gce MathematicsDokument97 SeitenSam Gce MathematicsShareef UddinNoch keine Bewertungen
- EarthquakeDokument14 SeitenEarthquakemetalmaniacmandarkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Khulna University of Engineering & Technology: Main Merit List of Selected Candidates (According To Roll)Dokument4 SeitenKhulna University of Engineering & Technology: Main Merit List of Selected Candidates (According To Roll)metalmaniacmandarkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Excitation of Plasmons and Interband Transitions by Electrons PDFDokument2 SeitenExcitation of Plasmons and Interband Transitions by Electrons PDFRobNoch keine Bewertungen
- SSCF StainlessSteel Shell and TubeDokument7 SeitenSSCF StainlessSteel Shell and TubeTom GuyetteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Asme B16.34Dokument16 SeitenAsme B16.34Thomas Martin100% (1)
- Report Radiation Exchange Between SurfacesDokument52 SeitenReport Radiation Exchange Between SurfacesStephen TabiarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analogies and Dimensionless NumbersDokument27 SeitenAnalogies and Dimensionless NumbersShahla GondalNoch keine Bewertungen
- AReviewOnGeopolymerConcrete (214 217)Dokument4 SeitenAReviewOnGeopolymerConcrete (214 217)anupamrcNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Thermochemistry of Fuel-Air MixturesDokument86 Seiten3 Thermochemistry of Fuel-Air MixturesArsalan Ahmad100% (1)
- Fisher - Surface.tensiometer - Manual Escuela ViejoDokument16 SeitenFisher - Surface.tensiometer - Manual Escuela ViejoLuis Angel SalcedoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maache Rezzoug Et Al.1998Dokument20 SeitenMaache Rezzoug Et Al.1998Mădălina ȘtefanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gold Cyanidation PresentationDokument25 SeitenGold Cyanidation Presentationsatrioherbirowo100% (3)
- Che 381 N 2011915200Dokument3 SeitenChe 381 N 2011915200trienphatphanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Continuum Electromechanics Cem - 811Dokument637 SeitenContinuum Electromechanics Cem - 811kgrhoads100% (1)
- Gorki 3Dokument26 SeitenGorki 3Shushay GebreyesusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Photosynthesis in PlantsDokument5 SeitenPhotosynthesis in Plantskay69max47Noch keine Bewertungen
- Daftar Pustaka: Reactor Design, John Wiley & Sons Inc., USADokument4 SeitenDaftar Pustaka: Reactor Design, John Wiley & Sons Inc., USASyariful Maliki NejstaršíNoch keine Bewertungen
- Benzene Hydrogenation Over Ni/Al O Catalysts Prepared by Conventional and Sol-Gel TechniquesDokument9 SeitenBenzene Hydrogenation Over Ni/Al O Catalysts Prepared by Conventional and Sol-Gel TechniquesHarun AydınNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stireno 1Dokument2 SeitenStireno 1jhonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Temperature Dependence and ZTC Bias Point Evaluation of Sub 20nm Bulk Multigate DevicesDokument16 SeitenTemperature Dependence and ZTC Bias Point Evaluation of Sub 20nm Bulk Multigate DevicesYgor AguiarNoch keine Bewertungen
- MME 3518-Powder Metallurgy-1-2Dokument80 SeitenMME 3518-Powder Metallurgy-1-2Mohammed GhisheerNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.1. Fossils: Picture 3.1 Cast and Mold FossilDokument6 Seiten1.1. Fossils: Picture 3.1 Cast and Mold Fossilsushan19Noch keine Bewertungen
- Incorporation of Waste Plastic in Asphalt Binders To Improve TheirDokument9 SeitenIncorporation of Waste Plastic in Asphalt Binders To Improve TheirSandor ManesesNoch keine Bewertungen
- COA + MSDS Formic Acid PDFDokument7 SeitenCOA + MSDS Formic Acid PDFindra suryanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antimicrobial Activity and Chemical Composition of Essential Oil FromDokument9 SeitenAntimicrobial Activity and Chemical Composition of Essential Oil FromTrần Thuý QuỳnhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shjohntec 2008218115733800771Dokument36 SeitenShjohntec 2008218115733800771Kristin NgoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lightning ProtectionDokument20 SeitenLightning Protectionsofyan_shah50% (2)
- SynopsisDokument4 SeitenSynopsisyashaahmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- IGSCE Reviewer Multiple Choice PDFDokument52 SeitenIGSCE Reviewer Multiple Choice PDFAlan Peter50% (2)
- Elce221 Lab 1Dokument6 SeitenElce221 Lab 1Little VoiceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Statistical and Optimization Techniques For Laundry Portfolio Optimization at Procter GambleDokument19 SeitenStatistical and Optimization Techniques For Laundry Portfolio Optimization at Procter GambletyabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Combiglide Quick Start ManualDokument52 SeitenCombiglide Quick Start Manuala_singhal007Noch keine Bewertungen