Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Optocoupler
Hochgeladen von
Sindhuja JsOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Optocoupler
Hochgeladen von
Sindhuja JsCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
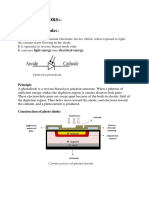
Optocoupler In electronics, an opto-isolator (or optical isolator, optocoupler, photocoupler, or photoMOS) is a device that uses a short optical transmission
path to transfer a signal between elements of a circuit, typically a transmitter and a receiver, while keeping them electrically isolated since the signal goes from an electrical signal to an optical signal back to an electrical signal, electrical contact along the path is broken.
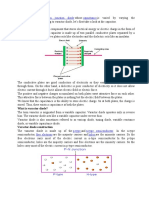
Configurations A common implementation involves a LED and a phototransistor, separated so that light may travel across a barrier but electrical current may not. When an electrical signal is applied to the input of the opto-isolator, its LED lights, its light sensor then activates, and a corresponding electrical signal is generated at the output. Unlike a transformer, the opto-isolator allows for DC coupling and generally provides significant protection from serious overvoltage conditions in one circuit affecting the other. With a photodiode as the detector, the output current is proportional to the amount of incident light supplied by the emitter. The diode can be used in a photovoltaic mode or a photoconductive mode. In photovoltaic mode, the diode acts like a current source in parallel with a forward-biased diode. The output current and voltage are dependent on the load impedance and light intensity. In photoconductive mode, the diode is connected to a supply voltage, and the magnitude of the current conducted is directly proportional to the intensity of light. An opto-isolator can also be constructed using a small incandescent lamp in place of the LED; such a device, because the lamp has a much slower response time than an LED, will filter out noise or half-wave power in the input signal. In so doing, it will also filter out any audio- or higherfrequency signals in the input. It has the further disadvantage, of course, (an overwhelming disadvantage in most applications) that incandescent lamps have finite life spans. Thus, such an unconventional device is of extremely limited usefulness, suitable only for applications such as science projects. The optical path may be air or a dielectric waveguide. The transmitting and receiving elements of an optical isolator may be contained within a single compact module, for mounting, for example, on a circuit board; in this case, the module is often called an optoisolator or opto-isolator. The photosensor may be a photocell, phototransistor, or an optically triggered SCR or Triac. Occasionally, this device will in turn operate a power relay or contactor.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Optocoupler Devices and ApplicationDokument4 SeitenOptocoupler Devices and ApplicationvijeeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optical CouplersDokument36 SeitenOptical CouplersSyed muhammad zaidiNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Semiconductor Device Is An Electronic Component That Exploits The Electronic Properties of Semiconductor MaterialDokument10 SeitenA Semiconductor Device Is An Electronic Component That Exploits The Electronic Properties of Semiconductor MaterialPrakhar Pratap SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optocoupler TutorialDokument4 SeitenOptocoupler TutorialAnonymous HXFi2kJRUvNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optocoupler Tutorial: Home Miscellaneous CircuitsDokument5 SeitenOptocoupler Tutorial: Home Miscellaneous CircuitsMoh OkoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Photo DidodeDokument4 SeitenPhoto Didodejagadeeshkumar116Noch keine Bewertungen
- More On TransducersDokument18 SeitenMore On TransducersRand Ahmed BushnaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Swagata Deb BurmanDokument9 SeitenSwagata Deb Burmanvincent GamingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Photodiode - WikipediaDokument15 SeitenPhotodiode - WikipediaIKENNANoch keine Bewertungen
- From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDokument7 SeitenFrom Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaratannsNoch keine Bewertungen
- IR Transmitter: Ir LedDokument14 SeitenIR Transmitter: Ir LedPragna ThatipelliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Photo DiodeDokument3 SeitenPhoto DiodeAngga Wijaya KusumaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optocoupler or Optoisolator PDFDokument10 SeitenOptocoupler or Optoisolator PDFpiyushpandeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optocouplers: Muskan Mittal 08104033Dokument15 SeitenOptocouplers: Muskan Mittal 08104033Muskan MittalNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Photo Diode Is A Type of Photo Detector Capable of Converting Light Into Either Current or Voltage Repaired)Dokument14 SeitenA Photo Diode Is A Type of Photo Detector Capable of Converting Light Into Either Current or Voltage Repaired)vikassist1024Noch keine Bewertungen
- Untitled PresentationDokument9 SeitenUntitled Presentationvarshavaralakshmi83Noch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 3 Opto-IsolationDokument8 SeitenExperiment 3 Opto-IsolationasdfsafdasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fiber Optic CouplerDokument3 SeitenFiber Optic CouplerAkshay KakkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optoelectronics I:: Element14 Learning CenterDokument13 SeitenOptoelectronics I:: Element14 Learning CenterAjay VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Opto-Electronics Devices: Opto-Electronic Devices Light Emitting Diode (LED) (A) TheoryDokument7 SeitenOpto-Electronics Devices: Opto-Electronic Devices Light Emitting Diode (LED) (A) Theoryves vegasNoch keine Bewertungen
- PhotoconductivityDokument12 SeitenPhotoconductivitySarathy Kannan100% (1)
- Photodiode Are Semiconductor Light Sensor That Generate A Current or Voltage When The P-NDokument4 SeitenPhotodiode Are Semiconductor Light Sensor That Generate A Current or Voltage When The P-NMohamed A SbaihNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optical Detectors in Fiber Optic ReceiversDokument83 SeitenOptical Detectors in Fiber Optic Receiversali ghalibNoch keine Bewertungen
- ? ? ? 6/PERO ? ? ? RqvwuxfwlrqDokument7 Seiten? ? ? 6/PERO ? ? ? RqvwuxfwlrqLasam CagayanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Q. 11. Draw The Block Diagram of A Fiber Optic Communications System and Describe Function of Each Component. AnsDokument4 SeitenQ. 11. Draw The Block Diagram of A Fiber Optic Communications System and Describe Function of Each Component. AnsNurQaseh AmaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sensors - FinalDokument13 SeitenSensors - Finalbob123Noch keine Bewertungen
- The "Ins" and "Outs": Signal Isolators, Converters and InterfacesDokument1 SeiteThe "Ins" and "Outs": Signal Isolators, Converters and InterfacesazrinoordinNoch keine Bewertungen
- SynopsisDokument12 SeitenSynopsisGhazalpreet KaurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Varactor Diode DefinitionDokument6 SeitenVaractor Diode DefinitionMohit BhavsarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 3 MidDokument56 SeitenModule 3 MidZylah NorberteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transformer and Optical IsolationDokument18 SeitenTransformer and Optical IsolationAman MalikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ali AsignmentDokument10 SeitenAli AsignmentMuhammad Zain YousafNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation 4Dokument17 SeitenPresentation 4xoranek474Noch keine Bewertungen
- PhotodiodesDokument20 SeitenPhotodiodesRavindra Kumar100% (1)
- Experiment-5: Optocouplers and Their CharacteristicsDokument7 SeitenExperiment-5: Optocouplers and Their CharacteristicsKainat MalikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation 4Dokument17 SeitenPresentation 4xoranek474Noch keine Bewertungen
- What Is LDRDokument5 SeitenWhat Is LDRPrAkhar VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Op ToDokument2 SeitenOp ToSantosh PatilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group 9 PresantationDokument15 SeitenGroup 9 PresantationCollins OtienoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Galvanic IsolationDokument3 SeitenGalvanic IsolationDijith JhansiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Opto - Electronic Vts Final 2-1-1Dokument15 SeitenOpto - Electronic Vts Final 2-1-1Vincent GamliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Photodiode: Principle of OperationDokument6 SeitenPhotodiode: Principle of OperationRahul SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optical SC Photo DiodeDokument3 SeitenOptical SC Photo DiodeAnonymous mlYYLRe7HNoch keine Bewertungen
- Opto-Isolator: HistoryDokument9 SeitenOpto-Isolator: HistoryNavneet HoodaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Light Emmiting Diode Laser Diode: Semiconductor PhysicsDokument7 SeitenLight Emmiting Diode Laser Diode: Semiconductor PhysicsLa JiejaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation 4Dokument21 SeitenPresentation 4xoranek474Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fibre Optic CommunicationsDokument11 SeitenFibre Optic CommunicationsmycatalystsNoch keine Bewertungen
- AU-222-Automobile Instrumentation: Lecture No:15 DR - Saqib Jamshed RindDokument19 SeitenAU-222-Automobile Instrumentation: Lecture No:15 DR - Saqib Jamshed RindAkber AnwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- AssignmentDokument9 SeitenAssignmentKshitij DudheNoch keine Bewertungen
- Photo-Coupler and Touch Alarm SwitchDokument9 SeitenPhoto-Coupler and Touch Alarm SwitchZeeshan RafiqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Detectors and Storage DevicesDokument32 SeitenDetectors and Storage Devices7t854s6wd2Noch keine Bewertungen
- DiodeDokument10 SeitenDiodefewpew LumanglasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Part 2Dokument14 SeitenPart 2raedprimNoch keine Bewertungen
- IR ReceiverDokument8 SeitenIR ReceiverCoroiuStefanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ref1 Characteristics of SensorsDokument8 SeitenRef1 Characteristics of Sensorsosama.20en714Noch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation 4Dokument21 SeitenPresentation 4xoranek474Noch keine Bewertungen
- Resistors: PotentiometerDokument48 SeitenResistors: PotentiometerjojoNoch keine Bewertungen
- A PhototransistorDokument9 SeitenA PhototransistorGur PreetNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Tamilnadu Dr. M.G.R. Medical University, Chennai - 32: Methodology Examination Paper I - Research MethodologyDokument10 SeitenThe Tamilnadu Dr. M.G.R. Medical University, Chennai - 32: Methodology Examination Paper I - Research MethodologySindhuja JsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fulltext PHDDokument142 SeitenFulltext PHDSindhuja JsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Statement of Teaching InterestDokument1 SeiteStatement of Teaching InterestSindhuja JsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lag RangeDokument1 SeiteLag RangeSindhuja JsNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4th Sept - Marathon Series Lecture 8 - General AwarenessDokument208 Seiten4th Sept - Marathon Series Lecture 8 - General AwarenessManbir ArinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Note!: Rear Shock Absorber For YAMAHA N-MAXDokument4 SeitenNote!: Rear Shock Absorber For YAMAHA N-MAXAdityaArnas0% (1)
- Victor 2Dokument30 SeitenVictor 2EmmanuelNoch keine Bewertungen
- I. Learning Objectives / Learning Outcomes: Esson LANDokument3 SeitenI. Learning Objectives / Learning Outcomes: Esson LANWilliams M. Gamarra ArateaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2Dokument8 Seiten2Eduardo Antonio Comaru Gouveia75% (4)
- AE Notification 2015 NPDCLDokument24 SeitenAE Notification 2015 NPDCLSuresh DoosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enlightened ExperimentationDokument8 SeitenEnlightened ExperimentationRaeed HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tuma Research ManualDokument57 SeitenTuma Research ManualKashinde Learner Centered Mandari100% (1)
- PDFDokument3 SeitenPDFAhmedraza123 NagdaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PM Jobs Comp Ir RandDokument9 SeitenPM Jobs Comp Ir Randandri putrantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zomato Restaurant Clustering & Sentiment Analysis - Ipynb - ColaboratoryDokument27 SeitenZomato Restaurant Clustering & Sentiment Analysis - Ipynb - Colaboratorybilal nagoriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Continuing Professional Development PlanDokument4 SeitenContinuing Professional Development Planvviki50% (2)
- The Effect of Co-Op Approach in Improving Visual Motor Integration Skills in Children With Learning DisabilityDokument7 SeitenThe Effect of Co-Op Approach in Improving Visual Motor Integration Skills in Children With Learning DisabilityIJAR JOURNALNoch keine Bewertungen
- De Thi Hoc Ki 1 Lop 11 Mon Tieng Anh Co File Nghe Nam 2020Dokument11 SeitenDe Thi Hoc Ki 1 Lop 11 Mon Tieng Anh Co File Nghe Nam 2020HiềnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modular Q1 WK3-4Dokument3 SeitenModular Q1 WK3-4JENIFFER DE LEONNoch keine Bewertungen
- CA21159 MG 8 Digital BookletDokument5 SeitenCA21159 MG 8 Digital BookletcantaloupemusicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lacey Robertson Resume 3-6-20Dokument1 SeiteLacey Robertson Resume 3-6-20api-410771996Noch keine Bewertungen
- Saiva Dharma ShastrasDokument379 SeitenSaiva Dharma ShastrasfunnybizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Contoh Exposition TextDokument1 SeiteContoh Exposition TextKristin SeranNoch keine Bewertungen
- DCS800ServiceManual RevADokument96 SeitenDCS800ServiceManual RevAElinplastNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applying For A Job: Pre-ReadingDokument5 SeitenApplying For A Job: Pre-ReadingDianitta MaciasNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8 A - 1615864446 - 1605148379 - 1579835163 - Topic - 8.A.EffectiveSchoolsDokument9 Seiten8 A - 1615864446 - 1605148379 - 1579835163 - Topic - 8.A.EffectiveSchoolsYasodhara ArawwawelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- John DrydenDokument3 SeitenJohn DrydenDunas SvetlanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pediatrics: The Journal ofDokument11 SeitenPediatrics: The Journal ofRohini TondaNoch keine Bewertungen
- EMD Question Bank II 2Dokument4 SeitenEMD Question Bank II 2Soham MisalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yetta Company ProfileDokument6 SeitenYetta Company ProfileAfizi GhazaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- ADokument54 SeitenActyvteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Img 20150510 0001Dokument2 SeitenImg 20150510 0001api-284663984Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mecha World Compendium Playbooks BWDokument12 SeitenMecha World Compendium Playbooks BWRobson Alves MacielNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH-5 Further Percentages AnswersDokument5 SeitenCH-5 Further Percentages AnswersMaram MohanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Programming the Raspberry Pi, Third Edition: Getting Started with PythonVon EverandProgramming the Raspberry Pi, Third Edition: Getting Started with PythonBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (2)
- The Journeyman Electrician Exam Study Guide: Proven Methods for Successfully Passing the Journeyman Electrician Exam with ConfidenceVon EverandThe Journeyman Electrician Exam Study Guide: Proven Methods for Successfully Passing the Journeyman Electrician Exam with ConfidenceNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionVon EverandThe Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (543)
- Electrical Engineering 101: Everything You Should Have Learned in School...but Probably Didn'tVon EverandElectrical Engineering 101: Everything You Should Have Learned in School...but Probably Didn'tBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (27)
- Retro Gaming with Raspberry Pi: Nearly 200 Pages of Video Game ProjectsVon EverandRetro Gaming with Raspberry Pi: Nearly 200 Pages of Video Game ProjectsNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionVon EverandThe Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (331)
- Multiplexed Networks for Embedded Systems: CAN, LIN, FlexRay, Safe-by-Wire...Von EverandMultiplexed Networks for Embedded Systems: CAN, LIN, FlexRay, Safe-by-Wire...Noch keine Bewertungen
- Conquering the Electron: The Geniuses, Visionaries, Egomaniacs, and Scoundrels Who Built Our Electronic AgeVon EverandConquering the Electron: The Geniuses, Visionaries, Egomaniacs, and Scoundrels Who Built Our Electronic AgeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (10)
- Digital Filmmaking: The Ultimate Guide to Web Video Production for Beginners and Non-Professionals, Learn Useful Tips and Advice on How You Can Create, Film and Edit Your VideosVon EverandDigital Filmmaking: The Ultimate Guide to Web Video Production for Beginners and Non-Professionals, Learn Useful Tips and Advice on How You Can Create, Film and Edit Your VideosBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- 2022 Adobe® Premiere Pro Guide For Filmmakers and YouTubersVon Everand2022 Adobe® Premiere Pro Guide For Filmmakers and YouTubersBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Power System Control and ProtectionVon EverandPower System Control and ProtectionB. Don RussellBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (11)
- INCOSE Systems Engineering Handbook: A Guide for System Life Cycle Processes and ActivitiesVon EverandINCOSE Systems Engineering Handbook: A Guide for System Life Cycle Processes and ActivitiesBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Guide to the IET Wiring Regulations: IET Wiring Regulations (BS 7671:2008 incorporating Amendment No 1:2011)Von EverandGuide to the IET Wiring Regulations: IET Wiring Regulations (BS 7671:2008 incorporating Amendment No 1:2011)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (2)
- Build Your Own Electronics WorkshopVon EverandBuild Your Own Electronics WorkshopBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (3)
- Hacking Electronics: An Illustrated DIY Guide for Makers and HobbyistsVon EverandHacking Electronics: An Illustrated DIY Guide for Makers and HobbyistsBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2)
- Teach Yourself Electricity and Electronics, 6th EditionVon EverandTeach Yourself Electricity and Electronics, 6th EditionBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (15)
- Practical Troubleshooting of Electrical Equipment and Control CircuitsVon EverandPractical Troubleshooting of Electrical Equipment and Control CircuitsBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5)
- Digital Transformation: Survive and Thrive in an Era of Mass ExtinctionVon EverandDigital Transformation: Survive and Thrive in an Era of Mass ExtinctionBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (9)
- Empires of Light: Edison, Tesla, Westinghouse, and the Race to Electrify the WorldVon EverandEmpires of Light: Edison, Tesla, Westinghouse, and the Race to Electrify the WorldBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (87)