Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Reproduction in Plants
Hochgeladen von
anjupalCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Reproduction in Plants
Hochgeladen von
anjupalCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
REPRODUCTION IN PLANTS Asexual reproduction Only one parent organism is involved New organisms are genetically identical to the
o the parent(clones) No gamete formation and fusion Cell division involved mitosis
Types of asexual reproduction Fission Fragmentation Regeneration Budding Vegetative propagation
Fission
Many bacteria and protozoa simply split into two equal halves during cell division. In Amoeba, the splitting of the two cells during division can take place in any plane. In Leishmania (which cause kala-azar),, binary fission occurs in a definite orientation The malaria parasite, Plasmodium, divide into many daughter cells simultaneously by multiple fission.
Fragmentation Spirogyra simply breaks up into smaller pieces upon maturation. These pieces or fragments grow into new individual. Reproduction in such organisms is function of stem cells (a single cell type in the organism that is capable of growing, proliferating and making other cell types under the right circumstances).
Regeneration Ability of a living organism to regrow the lost parts of the body Hydra and Planaria can be cut into any number of pieces and each piece grows into a complete organism. regeneration is not the same as reproduction Budding In Hydra, a bud develops as an outgrowth due to repeated cell division at on specific site.
These buds develop into tiny individuals and when fully mature, detach from the parent body and become new independent
Vegetative propagation The root, stem and leaves develop into new plants under appropriate conditions.
Advantage of vegetative propagation Plants raised by vegetative propagation can bear flowers and fruits earlier than those produced from seeds. make possible the propagation of plants such as banana, orange, Rose and jasmine that have lost the capacity to produce seeds. all plants produced are genetically similar
Spore formation Spores are unicellular structure , thick walled, present in sporangia The blobs are sporangia, which contain cells, or spores, that can eventually develop into new Rhizopus individuals.
Spore formation in Rhizobium
Tissue culture
Advantage of Tissue culture many plants can be grown from one parent in disease-free conditions. SEXUAL REPRODUCTION In sexual reproduction, two individuals produce offspring that have genetic characteristics from both parents. Sexual reproduction introduces new gene combinations in a population.
New organisms are NOT genetically identical to the parent Gamete formation and fusion takes place Cell division involved meiosis for gamete formation Germ cells have half the amount of DNA as compared to the non reproductive body cells. Male gamete Female gamete Small in size Motile Do not store food Large in size Non-motile Store food
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN FLOWERING PLANTS The reproductive parts of Angiosperms are located in the flower. Types of flowers i) Unisexual flower-it contains either stamen or carpels. Example; papaya ,watermelon.
ii) Bisexual flower-it contains both stamen and carpel. Example; Hibiscus, mustard.
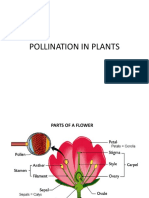
PARTS OF FLOWER
(1) Male reproductive part a) Stamen b) Anther c) Filament (2) Female reproductive partpistil a) Stigma b) Style c) Ovary
GAMETES MALE GAMETE- Pollen grains FEMALE GAMETE- Egg
POLLINATION: transfer of pollen grains from anther to stigma Self pollination- transfer of pollen occurs in the same flower
Cross pollination-The transfer of pollen grains from anther of flower of a plant to the stigma of flower of another plant (of the same species) is called cross-pollination.
AGENTS OF POLLINATION
FERTILISATION After pollen lands on a suitable stigma, a tube grows out of the pollen grain and travels through the style to reach the ovary. The nucleus of pollen grain fusses with the nucleus of egg and fertilization takes place. After fertilization, the zygote divides several times to form an embryo within the ovule. The ovule develops a tough coat and is gradually converted into a seed. The ovary grows rapidly and ripens to form a fruit. Meanwhile, the petals, sepals, stamens, style and stigma may shrivel and fall off. The seed contains the future plant or embryo which develops into a seedling under appropriate conditions. This process is known as germination.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Modes of Reproduction in PlantsDokument15 SeitenModes of Reproduction in Plantsjudy andrade100% (1)
- 5 Kingdom ClassificationDokument36 Seiten5 Kingdom ClassificationMichelle Arienza100% (1)
- How plants transport materialsDokument26 SeitenHow plants transport materialsliban100% (1)
- Pollination, Fertilisation and GerminationDokument25 SeitenPollination, Fertilisation and GerminationAsad RazaNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Upper Block) Reproduction in PlantsDokument18 Seiten(Upper Block) Reproduction in PlantsManoo JoshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plant ReproductionDokument5 SeitenPlant ReproductionFaizan ElahiNoch keine Bewertungen
- IGCSE - Bio - Lesson Plan 13 - Reproduction in PlantsDokument3 SeitenIGCSE - Bio - Lesson Plan 13 - Reproduction in PlantsHisokagenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 11 Biology Chapter 1 - Revision NotesDokument13 SeitenClass 11 Biology Chapter 1 - Revision NotesAyush JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flowering PlantsDokument43 SeitenFlowering Plantskingbanakon100% (1)
- All About FlowersDokument43 SeitenAll About FlowersjeffinjoffiNoch keine Bewertungen
- IGCSE Biology Chapter 1Dokument42 SeitenIGCSE Biology Chapter 1Eric Chew100% (2)
- The Characteristics of Living ThingsDokument8 SeitenThe Characteristics of Living ThingsMiy El NinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Short NotesDokument7 SeitenBiology Short NotesyusufNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pollination in PlantsDokument214 SeitenPollination in PlantsAbraham SekyiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cells: by - NatalieDokument24 SeitenCells: by - NatalieNatalie JaiswalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basis For Animal Kingdom ClassificationDokument31 SeitenBasis For Animal Kingdom ClassificationIan AlpaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell and Cell TheoryDokument13 SeitenCell and Cell TheoryAnaJeanJumawidMarananNoch keine Bewertungen
- iGCSE Biology Revision Quiz: Biological Molecules and Cell TransportDokument2 SeiteniGCSE Biology Revision Quiz: Biological Molecules and Cell TransportddddddffdfdfNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 7 Science Chapter 2 NotesDokument41 SeitenGrade 7 Science Chapter 2 Notesapi-238589602100% (2)
- How Organisms Reproduce: Asexual vs SexualDokument4 SeitenHow Organisms Reproduce: Asexual vs SexualNilkanth PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12 Reproduction Biology Notes IGCSE PDFDokument51 Seiten12 Reproduction Biology Notes IGCSE PDFUmair Khan Marwat100% (1)
- 01 Living ThingsDokument32 Seiten01 Living Thingsapi-632307358Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDokument12 SeitenSexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsSubrata SarkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Myp Quiz 4 - PhotosynthesisDokument2 SeitenMyp Quiz 4 - Photosynthesisapi-257190713Noch keine Bewertungen
- Characteristics of Plants NotesDokument5 SeitenCharacteristics of Plants Notesiamoliver_31100% (1)
- Plant Reproduction: Seed Dispersal and Germination ExplainedDokument3 SeitenPlant Reproduction: Seed Dispersal and Germination ExplainedSunil Nagar100% (1)
- Classification NOTESDokument8 SeitenClassification NOTESShahadMahmoud100% (1)
- O Level Biology 17 Reproduction in PlantsDokument45 SeitenO Level Biology 17 Reproduction in PlantsHamzu GamingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic chemistry concepts under 40 charactersDokument4 SeitenBasic chemistry concepts under 40 charactersHamzah AbdullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plant Nutrition Chapter-1: Review QuestionsDokument17 SeitenPlant Nutrition Chapter-1: Review QuestionsRajeevSangam100% (1)
- Chapter 8 Transport in Mammals - Lecture NotesDokument10 SeitenChapter 8 Transport in Mammals - Lecture Notesapi-3728508100% (2)
- Biology: By: Melis Doğu BAYAZITDokument39 SeitenBiology: By: Melis Doğu BAYAZITMelis Doğu BayazıtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Food WebDokument8 SeitenFood Webapi-4558008020% (2)
- Acids Bases Salts ExplainedDokument5 SeitenAcids Bases Salts ExplainedSANDEEP SINGH100% (1)
- Igcse Chemistry NotesDokument46 SeitenIgcse Chemistry Notesapi-1811760180% (1)
- P5 Respiratory System NotesDokument3 SeitenP5 Respiratory System NotesAlidiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Animal Circulation and RespirationDokument56 SeitenAnimal Circulation and Respirationacooper6Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Digestive Process of A Bowl of Banku and Okro Stew With FishDokument2 SeitenThe Digestive Process of A Bowl of Banku and Okro Stew With FishStefan Baimbill Johnson100% (2)
- Class 11 Biology Chapter 3 - Revision NotesDokument34 SeitenClass 11 Biology Chapter 3 - Revision NotesAnubhav MamgainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Igcse Biology - Transport in AnimalsDokument67 SeitenIgcse Biology - Transport in AnimalsYoshitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology PracticalsDokument40 SeitenBiology Practicalsabdulrehman999Noch keine Bewertungen
- Syllabus: Cambridge IGCSE Combined Science 0653Dokument65 SeitenSyllabus: Cambridge IGCSE Combined Science 0653Epicmaster27Noch keine Bewertungen
- IGCSE Biology Section 4 Lesson 1Dokument49 SeitenIGCSE Biology Section 4 Lesson 1arystaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology 1sec SB E 2014 PDFDokument156 SeitenBiology 1sec SB E 2014 PDFAnonymous tdtTl8KypNoch keine Bewertungen
- Animal Kingdom Notes: Vertebrates vs InvertebratesDokument5 SeitenAnimal Kingdom Notes: Vertebrates vs InvertebratesJacquiline Santiago100% (1)
- Cell Structure and Functions PDFDokument5 SeitenCell Structure and Functions PDFViswasriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Organelles WorksheetDokument8 SeitenCell Organelles WorksheetJohn OsborneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comparing Transpiration Rates in Coleus and Muntingia PlantsDokument4 SeitenComparing Transpiration Rates in Coleus and Muntingia PlantsLenard MerlinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDokument16 SeitenReproduction in Flowering PlantsAliDarimiKRNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study Guide BiologyDokument95 SeitenStudy Guide BiologyAnanyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teaching & Learning BiologyDokument178 SeitenTeaching & Learning BiologyobsrvrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Living TogetherDokument5 SeitenLiving TogetherJohn John AppleseedNoch keine Bewertungen
- IGCSE Excretion in HumansDokument15 SeitenIGCSE Excretion in HumansYashodhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Prelim NotesDokument47 SeitenBiology Prelim NotesAmanie SidawiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human Reproduction Question BankDokument23 SeitenHuman Reproduction Question Bankkaustubhchoudhary2005Noch keine Bewertungen
- Study Material Ix Science - 2Dokument150 SeitenStudy Material Ix Science - 2Tantra Path100% (1)
- Science Strategies to Increase Student Learning and Motivation in Biology and Life Science Grades 7 Through 12Von EverandScience Strategies to Increase Student Learning and Motivation in Biology and Life Science Grades 7 Through 12Noch keine Bewertungen
- Reproduction in Animals Notes For Class 8Dokument8 SeitenReproduction in Animals Notes For Class 8anjupalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control & Coordination - Class XDokument7 SeitenControl & Coordination - Class XanjupalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Matter in Our SurroundingsDokument12 SeitenMatter in Our SurroundingsanjupalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sources of Energy - Class XDokument9 SeitenSources of Energy - Class XanjupalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Improvement in Food ResourcesDokument11 SeitenImprovement in Food Resourcesanjupal100% (2)
- Heredity and EvolutionDokument16 SeitenHeredity and EvolutionanjupalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Periodic Classification of Elements PDFDokument8 SeitenPeriodic Classification of Elements PDFanjupal80% (5)
- Reproduction in Human BeingsDokument6 SeitenReproduction in Human BeingsanjupalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Main 1 & 2 (ClassGÇôIX) Open Book Exam Sample PDFDokument13 SeitenScience Main 1 & 2 (ClassGÇôIX) Open Book Exam Sample PDFanjupalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Improvement in Food REsources - Class IX Mind MappingDokument12 SeitenImprovement in Food REsources - Class IX Mind Mappinganjupal83% (6)
- Control and CoordinationDokument17 SeitenControl and Coordinationanjupal100% (1)
- Carbon Footprint - Vivek - X-ADokument33 SeitenCarbon Footprint - Vivek - X-AanjupalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nutrition in AnimalsDokument19 SeitenNutrition in AnimalsanjupalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Force and Laws of MotionDokument20 SeitenForce and Laws of MotionanjupalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Magnetic Effect of Electric CurrentDokument13 SeitenMagnetic Effect of Electric Currentanjupal100% (4)
- L-8 Motion: List of ConceptsDokument11 SeitenL-8 Motion: List of ConceptsanjupalNoch keine Bewertungen
- HeatDokument11 SeitenHeatanjupalNoch keine Bewertungen
- TissuesDokument16 SeitenTissuesanjupalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Life ProcessesDokument28 SeitenLife Processesanjupal100% (1)
- Nutrition in PlantsDokument8 SeitenNutrition in PlantsanjupalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell, The Fundamental Unit of LifeDokument12 SeitenCell, The Fundamental Unit of LifeanjupalNoch keine Bewertungen
- The BAR - Philippine Digested Cases - Landmark Case - RH BILL CASE - Imbong Vs Ochoa Et - Al. G.R. No. 204819 April 8, 2014 (Digested Case)Dokument8 SeitenThe BAR - Philippine Digested Cases - Landmark Case - RH BILL CASE - Imbong Vs Ochoa Et - Al. G.R. No. 204819 April 8, 2014 (Digested Case)Patronus GoldenNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1-The Human Life Cycle and Sexual ReproductionDokument12 Seiten1-The Human Life Cycle and Sexual ReproductionMary Joy ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Do Organisms Reproduce Class 10 Notes Science Chapter 8 - Learn CBSEDokument3 SeitenHow Do Organisms Reproduce Class 10 Notes Science Chapter 8 - Learn CBSEFantasy Anime WorldNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cot 4Dokument7 SeitenCot 4Jerwin Sarcia RemocalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Meiosis: Chromatids (The Two Halves of A Duplicated Chromosome), As inDokument29 SeitenMeiosis: Chromatids (The Two Halves of A Duplicated Chromosome), As inyamamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Apbd 1203 Topic 3Dokument56 SeitenApbd 1203 Topic 3Anonymous wsqFdcNoch keine Bewertungen
- PandaDokument5 SeitenPandaAzzahra RamadhaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ob-Gyne 1&2Dokument609 SeitenOb-Gyne 1&2Barron KlaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hatchery Business PlanDokument20 SeitenHatchery Business Planalutiiq67% (3)
- Grade-11: Life Science Achievement TestDokument14 SeitenGrade-11: Life Science Achievement TestBayani VicencioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flowering plant life cycleDokument3 SeitenFlowering plant life cycleAnonymous HMlygCCNoch keine Bewertungen
- Developmental Biology: Types of Eggs - Silk Moth, Frog, ChickDokument21 SeitenDevelopmental Biology: Types of Eggs - Silk Moth, Frog, ChickHoney krishnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Ethical Comparison - Vitro Fertilization: Rev. Juan R. VélezDokument11 SeitenAn Ethical Comparison - Vitro Fertilization: Rev. Juan R. VélezMica BongalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Angiosperm Reproduction: Parts of A FlowerDokument3 SeitenAngiosperm Reproduction: Parts of A FlowerfoodlastNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pollen Germination LabDokument6 SeitenPollen Germination LabJustyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seed Plants PDFDokument60 SeitenSeed Plants PDFMeena HaikondaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principles of Human DevelopmentDokument67 SeitenPrinciples of Human DevelopmentJaishenne CastuloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan Science Rep of BatterflyDokument4 SeitenLesson Plan Science Rep of BatterflyAinon Mardiya DiatorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sargassumfish ReproductionDokument3 SeitenSargassumfish ReproductionBinu VargheseNoch keine Bewertungen
- GenEd Science PART 1Dokument5 SeitenGenEd Science PART 1Ralph Tama Mangacop BenitoNoch keine Bewertungen
- All Combined Gpb201Dokument741 SeitenAll Combined Gpb201Abhinav K GNoch keine Bewertungen
- Q2 Earth and Life Module 10Dokument26 SeitenQ2 Earth and Life Module 10Jomar CarabotNoch keine Bewertungen
- Female Reproductive System StructuresDokument2 SeitenFemale Reproductive System StructuresMarian FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Module 4Dokument16 SeitenScience Module 4Prince Mhar SurioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abortion Is The Practice of Terminating A Pregnancy Resulting In, or CloselyDokument2 SeitenAbortion Is The Practice of Terminating A Pregnancy Resulting In, or CloselyAlejandra BenjumeaNoch keine Bewertungen
- D0838364 Chapter 24 Workbook A Teacher Notes PDFDokument16 SeitenD0838364 Chapter 24 Workbook A Teacher Notes PDFdeez IINoch keine Bewertungen
- P6 Science SA2 2017 Nanyang Exam PapersDokument52 SeitenP6 Science SA2 2017 Nanyang Exam PapersKui LiuNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCQS Human Reproduction Class 12Dokument13 SeitenMCQS Human Reproduction Class 12Shaashwati TandonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Preparing For KS3 Tests - BiologyDokument24 SeitenPreparing For KS3 Tests - Biologysam mirisonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activate 1 Biology Chapter3 AnswersDokument6 SeitenActivate 1 Biology Chapter3 AnswersJohn LebizNoch keine Bewertungen