Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
PracticeExam2 Blank
Hochgeladen von
lestyouforgetCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
PracticeExam2 Blank
Hochgeladen von
lestyouforgetCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Physics 220 Spring 2013 Exam #2
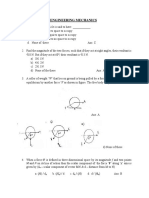
1) #1 - #10 [1 point each] Multiple Choice. Circle the letter of the correct answer. A refrigerator of mass 100kg has coefficients of friction with the floor of s= 0.60 and k= 0.40. A workman pushes the refrigerator with a horizontal force Fw in three different cases. Case 1: Fw = 300N. Case 2: Fw = 500N. Case 3: Fw = 700N. Rank the three cases in order of greatest frictional force to least frictional force created between the refrigerator and floor. Use g = 10 m/s2. Case 1 > Case 2 > Case 3 Case 3 > Case 2 > Case 1 Case 2 > Case 3 > Case 1 Case 1 > Case 3 > Case 2 All cases generate an equal force of friction
A) B) C) D) E)
2) A block of mass m is lowered along a 30 incline at constant speed by gradually letting out a length of rope as shown. The block-incline interface has a coefficient of kinetic friction k= 0.25 What is the tension in the rope? Use g = 10 m/s/s. A) 0.50mg B) 0.35mg C) 0.28mg D) 0.19mg E) This type of motion is not possible with this coefficient. 30 3) In problem #2 above, if k= s= 0, what would the tension in the rope be while the block is lowered at constant speed? A) 0.87mg B) 0.58mg C) 0.50mg D) 0.25mg E) None of the above 4) A car of mass M travels in a straight line at constant speed on a level road with a coefficient of friction and a drag force D. The magnitude of the net force on the car is: A) Mg B) (Mg)(D) C) Mg / D D) ( Mg)2 + D 2 E) Zero 5) A horizontal amusement park ride, when spinning at a constant rate, makes 20 revolutions in one minute. What is the Period of the uniform circular motion? A) B) C) D) E) 0.005s 0.333s 3.0s 40s The radius needs to be given in order to determine the Period.
Physics 220 Spring 2013 Exam #2
6) A woman stands on a bathroom scale that indicates her weight is W. The woman is standing on the scale inside an elevator when it is at rest. What will the scale read when the elevator is accelerating upward? The scale will read the same value W. The scale will read a value that is much less than W. The scale will read a value that is slightly less than W. The scale will read a value that is greater than W. The scale will read zero Newtons. In the diagram an incline is gradually tipped at greater angles until at a critical angle c, the block resting on it begins to slide. What is s for the block/incline interface? s = cos(c) m s = sin(c) s = tan(c) s = cot(c) More information is necessary to determine s.
A) B) C) D) E) 7) A) B) C) D) E)
8) What is k if the block of mass 3m is sliding at a constant speed down the incline? A) B) C) D) E) 3mgcos(3) 3mgsin(3) 3mgtan(3) tan(3) 3
3m
9) A 1.0 kg block is placed against a wall and is held stationary by a force of 30.0 N applied at a 30 angle below the horizontal as shown in the drawing. What is the magnitude and direction of the force of static friction that acts on the block? Note: use g = 10 m/s/s A) B) C) D) E) 5 N downwards 10 N upwards 20 N downwards 25 N upwards the scenario shown is impossible wall
30
1.0 kg
side view
10) In terms of m, what must the mass of block A be in order to keep blocks B and C stationary? The circular objects are frictionless pulleys suspended securely from the ceiling. A) (1/7)m B) 1.0m C) 3.5m D) 5.0m E) Insufficient information given ? block A 4m block B
3m block C
Physics 220 Spring 2013 Exam #2
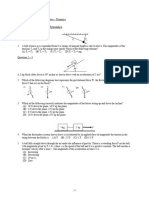
11. [10 pts] In the figure shown, the incline/block interface is frictionless, but the block/floor interface has a coefficient of friction s > 0. The block/block contact point is also frictionless. Block A has mass m and block B has a different mass M. These blocks remain stationary throughout the problem. Block A Block B mass m Mass M
s = k = 0
s > 0
(a) [4 pts] Draw the free-body diagrams for Block A and Block B. Make sure the forces you draw have the correct directions. Label your forces with understandable labels such as WA, WB, NA, NB, FA,B, FB,A, fs, etc. You may want to also sketch the components of any forces that do not lie directly along the coordinate axes shown. Use the coordinate system given here for both blocks. Hint: consider the 3rd law force pair generated at the mutual point of contact of the blocks.
y Block B
Block A x
(b) [4 pts] Using the coordinate system shown above, write the force equations F = ma for the free body diagrams you drew in part (a). You should have a horizontal and vertical force equation for Block A and a horizontal and vertical force equation for Block B (4 total equations). DO NOT SOLVE THEM YET.
Block A x-direction F=ma equation: y-direction F=ma equation: Block B x-direction F=ma equation: y-direction F=ma equation:
(c) [2 pts] If the blocks were to remain stationary, and if the contact force between the two blocks was known to be 25.0 Newtons, what would the direction and magnitude of fs be?
fs = ____________ in the direction:
(magnitude) (draw an arrow)
Physics 220 Spring 2013 Exam #2
12. [10 pts] A person in a sled (total mass m) slides from rest beginning at point A. Eventually the person+sled object compresses the spring on the right. The hills are frictionless. Fill out the table. Your answers must be written in terms of m, h, g, k. Note: Point C has height = 0.
A
h k
1 3
D C
1 4
h
h=0
Speed at A: _________________ Speed at B: _________________ Speed at C: _________________ Speed at D: _________________ Acceleration at C: _____________ Normal force at C: _____________ Potential Energy at D: ____________ Kinetic Energy at D: _____________ Energy Stored in spring at maximum Compression (in terms of m, g, h): _____________________ Maximum compression distance of spring, xmax (in terms of m, g, h, k) : ______________________
Physics 220 Spring 2013 Exam #2
13. [10 pts] A little girl whirls a ball of mass m around her waist in uniform circular motion (in a conical pendulum). The string has length L and makes an constant angle with respect to the vertical as shown. Fill out the table in terms of m, g, , L, . Draw the free body diagram for the ball at the instant drawn (label forces):
Ball
Radius of the circle the ball moves on: ______________________ Total distance the ball travels during one full revolution: ____________________ Tension in the string: ___________________ Speed of the ball: ____________________ Period of the ball (hard: calculate last): ____________________ Centripetal Force magnitude: ____________________ Centripetal Force direction at the instant shown: _____________________ Net force on the ball at every instant: ______________________
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- BB 2.0 - NLMDokument142 SeitenBB 2.0 - NLMParthMaluNoch keine Bewertungen
- BB 2.0 - Friction & Circular MotionDokument108 SeitenBB 2.0 - Friction & Circular MotionSunil DahaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice 3 Summer 2016Dokument9 SeitenPractice 3 Summer 2016Gloria LamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fiitjee Phase Test 1 (Class 11th), Jee Advance Paper 1Dokument12 SeitenFiitjee Phase Test 1 (Class 11th), Jee Advance Paper 1Shlok Sah71% (77)
- Jee 2014 Booklet3 HWT Energy & MomentumDokument19 SeitenJee 2014 Booklet3 HWT Energy & MomentumvarunkohliinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Force and Motion CalculationsDokument21 SeitenForce and Motion CalculationsStella MariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment#1Dokument4 SeitenAssignment#1Anoosha ArshadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Paper Physics Class XiDokument6 SeitenSample Paper Physics Class XiBhaskar JhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics 2. Exam 2 AnswersDokument7 SeitenPhysics 2. Exam 2 AnswersWino PazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering MechanicsDokument57 SeitenEngineering Mechanicsleah joylinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exam 2012 PDFDokument12 SeitenExam 2012 PDFYuChenQianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Friction and Forces in Mechanics ProblemsDokument11 SeitenFriction and Forces in Mechanics Problemsprem19999Noch keine Bewertungen
- Laws of Motion DPP For JEE Mains by Ajitlulla SirDokument16 SeitenLaws of Motion DPP For JEE Mains by Ajitlulla SirVardhan AmanapuNoch keine Bewertungen
- End Sem PaperDokument13 SeitenEnd Sem PaperKasani Tirumala tejaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Friction Level1Dokument6 SeitenFriction Level1BNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dynamics Practice Problems-2011!09!28Dokument21 SeitenDynamics Practice Problems-2011!09!28Lester CabungcalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Old Exam With Solutions 051Dokument11 SeitenPhysics Old Exam With Solutions 051poker100% (1)
- KrovvidyAPPhysicsCSummerWork Motion TestDokument13 SeitenKrovvidyAPPhysicsCSummerWork Motion Testgrace_lo_1Noch keine Bewertungen
- ap-physb_dynamics-multiple-choice-questions_2014-01-05Dokument10 Seitenap-physb_dynamics-multiple-choice-questions_2014-01-05Asma FarooquiNoch keine Bewertungen
- UP Physics ExamDokument12 SeitenUP Physics Examjerard999Noch keine Bewertungen
- Physics 211 Exam 1 ReviewDokument14 SeitenPhysics 211 Exam 1 ReviewGeorge KongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Int Mech Practice Exam 2Dokument9 SeitenInt Mech Practice Exam 2Kevin ApodacaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SpringerDokument10 SeitenSpringerMonico AlejoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phy10 DiagnosticDokument96 SeitenPhy10 DiagnosticMarc AlamoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solving Statics Problems Involving Tension, Forces, Torques and StressesDokument6 SeitenSolving Statics Problems Involving Tension, Forces, Torques and StressesBradley NartowtNoch keine Bewertungen
- PSI AP Physics I Dynamics Multiple-Choice QuestionsDokument10 SeitenPSI AP Physics I Dynamics Multiple-Choice QuestionsKarla PereraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Problems and SolutionsDokument7 SeitenPhysics Problems and Solutionsnailia eliasNoch keine Bewertungen
- India Outgoing SR (Y Programme) (2012 PAPER - 1 MODEL) Iitjee Model Exam Date: Time: 3:00 Max Marks: 210 Id - NoDokument9 SeitenIndia Outgoing SR (Y Programme) (2012 PAPER - 1 MODEL) Iitjee Model Exam Date: Time: 3:00 Max Marks: 210 Id - Nojagan9912342495Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lows of MotionDokument20 SeitenLows of MotionSaswata Sundar LagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Newton's Laws Chapter ApplicationsDokument12 SeitenNewton's Laws Chapter ApplicationsmultimainNoch keine Bewertungen
- STPM 2014 Physics Trial 2Dokument17 SeitenSTPM 2014 Physics Trial 2choichiang100% (1)
- Question 1Dokument12 SeitenQuestion 1eka123Noch keine Bewertungen
- McqsDokument12 SeitenMcqsjoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Linear DynamicsDokument11 SeitenLinear DynamicsInfrion MatiqueonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quest Forces 1 KeyDokument7 SeitenQuest Forces 1 KeyCarlos OrtizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Test 2Dokument7 SeitenPractice Test 2Maria YurlovaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ex3mech 2023Dokument9 SeitenEx3mech 2023Nasim RazaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stress Transformation: Chapter EightDokument0 SeitenStress Transformation: Chapter EightPurushottam KrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phys 204 Final Exam MechanicsDokument5 SeitenPhys 204 Final Exam MechanicsMalik ANoch keine Bewertungen
- 2a Dynamics MCNDokument17 Seiten2a Dynamics MCNSnowy JiangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paul FrictionDokument5 SeitenPaul FrictionPaul Aldrin OlvezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exam Review 3Dokument24 SeitenExam Review 3api-223793512Noch keine Bewertungen
- Multiple Choice Review - DynamicsDokument10 SeitenMultiple Choice Review - DynamicsPremkumar NaikarNoch keine Bewertungen
- G-11 Physics FinalDokument6 SeitenG-11 Physics FinalAlok DubeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wolfson Eup3 ch06 Test BankDokument22 SeitenWolfson Eup3 ch06 Test Bank陳禹誌Noch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Physics TestDokument7 SeitenPractice Physics Testthey12Noch keine Bewertungen
- Physics MCQ PDFDokument13 SeitenPhysics MCQ PDFSyed Mairaj Ul HaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phys 201 Practice Questions For Exam 2Dokument19 SeitenPhys 201 Practice Questions For Exam 2SawarSagwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Work Energy Power DPP Iitians Tapasya Akash GoyalDokument2 SeitenWork Energy Power DPP Iitians Tapasya Akash GoyalAkash Goyal100% (1)
- MIT Physics 8.01 Exam SolutionsDokument11 SeitenMIT Physics 8.01 Exam SolutionsAli RostamiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Problem With Recommended Format For Written SolutionDokument2 SeitenSample Problem With Recommended Format For Written Solutionsoumengoswami10Noch keine Bewertungen
- Block On Wedge PDFDokument2 SeitenBlock On Wedge PDFsoumengoswami10Noch keine Bewertungen
- DPP NLM and FrictionDokument3 SeitenDPP NLM and FrictionMy Moto G2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Physics 1Dokument6 SeitenPhysics 1iitiansrd2025Noch keine Bewertungen
- Trial 1 Term1 STPM 2015 Lengkap SMK MantinDokument10 SeitenTrial 1 Term1 STPM 2015 Lengkap SMK MantinSouseiseki ChromeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics For Scientists and Engineers A Strategic Approach With Modern Physics 4Th Edition Knight Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDokument37 SeitenPhysics For Scientists and Engineers A Strategic Approach With Modern Physics 4Th Edition Knight Test Bank Full Chapter PDFwadeperlid9d98k86% (7)
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Von EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Bewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- 797B Commissioning Guidebook 07 (Procesos)Dokument65 Seiten797B Commissioning Guidebook 07 (Procesos)wilmerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Schedule For Semester III, Class of 2021Dokument7 SeitenSchedule For Semester III, Class of 2021Jay PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Instruction Manual PC Interface RSM 100: TOSHIBA Corporation 1999 All Rights ReservedDokument173 SeitenInstruction Manual PC Interface RSM 100: TOSHIBA Corporation 1999 All Rights ReservedFarid HakikiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laptop repair messageDokument3 SeitenLaptop repair messagePonpes Manbaul MaarifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Personality, Movie Preferences, and RecommendationsDokument2 SeitenPersonality, Movie Preferences, and RecommendationsAA0809Noch keine Bewertungen
- Or Medallist Results WorldSkills Scale and 100 ScaleDokument39 SeitenOr Medallist Results WorldSkills Scale and 100 ScaleJoseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Express VPN Activation CodeDokument5 SeitenExpress VPN Activation CodeButler49JuulNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSIR AnalysisDokument1 SeiteCSIR Analysisசெபா செல்வாNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHCDokument1 SeitePHCsinh24X7Noch keine Bewertungen
- Audi A3 Audi A3 Audi A3 Audi A3 No. 2 / 1 No. 2 / 1 No. 2 / 1 No. 2 / 1Dokument18 SeitenAudi A3 Audi A3 Audi A3 Audi A3 No. 2 / 1 No. 2 / 1 No. 2 / 1 No. 2 / 1Crisedu VasriNoch keine Bewertungen
- CV. Anderson Hario Pangestiaji (English Version)Dokument5 SeitenCV. Anderson Hario Pangestiaji (English Version)Anderson PangestiajiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Barker-Choucalas, Vida PDFDokument176 SeitenBarker-Choucalas, Vida PDFAnn GarbinNoch keine Bewertungen
- V Ships Appln FormDokument6 SeitenV Ships Appln Formkaushikbasu2010Noch keine Bewertungen
- Linear Circuit Analysis (ELEN-1100) : Lecture # 13: More On Mesh Current AnalysisDokument11 SeitenLinear Circuit Analysis (ELEN-1100) : Lecture # 13: More On Mesh Current AnalysisPhD EENoch keine Bewertungen
- First Aid Emergency Action PrinciplesDokument7 SeitenFirst Aid Emergency Action PrinciplesJosellLim67% (3)
- Chapter 5Dokument11 SeitenChapter 5XDXDXDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Product 243: Technical Data SheetDokument3 SeitenProduct 243: Technical Data SheetRuiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oxyacetylene Welding (OAW)Dokument26 SeitenOxyacetylene Welding (OAW)athyrahNoch keine Bewertungen
- India's 1991 Economic ReformsDokument5 SeitenIndia's 1991 Economic ReformsLive AspireNoch keine Bewertungen
- ReadingDokument6 SeitenReadingakhyar sanchiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The English Center Articulation AgreementDokument9 SeitenThe English Center Articulation AgreementJose CabreraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To South Korean History, Cultures, Traditions, & BeliefsDokument8 SeitenIntroduction To South Korean History, Cultures, Traditions, & BeliefsKatriceNoch keine Bewertungen
- On-Chip ESD Protection Design For IcsDokument14 SeitenOn-Chip ESD Protection Design For IcsMK BricksNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sensors 18 02175Dokument15 SeitenSensors 18 02175Deepak D MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- GUEST MAIL HANDLINGDokument17 SeitenGUEST MAIL HANDLINGJoelThambi0% (1)
- Site AnalysisDokument15 SeitenSite Analysismaanik005Noch keine Bewertungen
- VNACS Final Case ReportDokument9 SeitenVNACS Final Case ReportVikram Singh TomarNoch keine Bewertungen
- TD EGGER Eurospan E1E05 TSCA Hydro P3 (Rec 224) enDokument2 SeitenTD EGGER Eurospan E1E05 TSCA Hydro P3 (Rec 224) enClarencegiNoch keine Bewertungen
- PuppetsDokument11 SeitenPuppetsShar Nur JeanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Law & TaxationDokument3 SeitenBusiness Law & TaxationD J Ben UzeeNoch keine Bewertungen