Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Class: Xii Max. Marks: 50 Subject: Chemistry. TIME: 2 Hours
Hochgeladen von
Prerak Kumar SharmaOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Class: Xii Max. Marks: 50 Subject: Chemistry. TIME: 2 Hours
Hochgeladen von
Prerak Kumar SharmaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
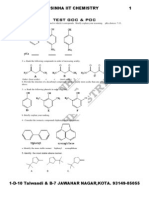
UNIT TEST PAPER CLASS : XII MAX. MARKS : 50 SUBJECT : CHEMISTRY.
TIME : 2 hours Haloalkanes & Haloarenes, Alcohols, phenols & ethers, Aldehydes, ketones & Carboxylic acids General Instructions: 1. All questions are compulsory. 2.There will be no overall options. 3. Internal choice is given in all three 5 marks questions.
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7.
16.
Explain why the dipole moment of chloroform is lower than that of cyclohexyl chloride? Which of the following 2 compounds would react faster by SN2 pathway:1-bromobutane or 2-bromobutane and why? Out of bezene and phenol which is more easily Nitrated and why? Di-tert-butyl ether cannot be made by williamsons synthesis. Explain why? Write the IUPAC name of the following organic compound. CH 3-O-CH2-CH(OH)-CH2 -CH 3 Identify the following name reactions and write the reagents used: CH3CHO CH3-CH3 + H 2O Fluorine is more electronegative than Chlorine even then P-Fluorobenzoic acid is weaker acid than P-Chlorobenzoic acid. State the reason for this. 8. Propanal is more reactive than propanone. Give reason. 9. Account for the following: i) Haloalkanes undergo nucleophilic substitutions while haloarenes undergo electrophilic substitution reaction ii) Haloalkanes react with KCN form alkylcyanides while isocyanides are formed with AgCN. 10. How the following conversions can be carried out ? i) Toluene to benzyl alcohol ii) Ethanol to but-1-yne. 11. Write the equations of the reactions which takes place when i) Thionyl chloride is treated with 2-propanol. ii) Cumene hydroperoxide is treated with dil. H2SO4. 12. When toluene is chlorinated: i) in presence of sunlight ii) in dark, in the presence of lewis acid, two separate compounds are obtained. Explain with suitable mechanism. 13. Write the steps involved in the mechanism of acid catalysed hydration of propene 14. Arrange the following compounds in an increasing order of the property mentioned CH3CH2CH(Br)COOH, CH3CH(Br)CH2COOH, (CH3)2CHCOOH, CH3CH2CH2COOH.. acidic strength. CH3CHO, CH3CH2OH, CH3OCH3, CH3 CH2 CH3 ------- boiling point. 15. The decreasing order of acidity of a few carboxylic acids is given below: C6H5COOH > C6H5CH2COOH > CH3COOH > CH3CH 2COOH Explain plausible reason for the order of acidity followed. Distinguish between: i) Acetaldehyde and Acetone (ii) Phenol and Aniline 17. Give reasons: i) The - hydrogen atoms of carbonyl compounds are acidic. ii) Benzaldehyde is less reactive in Nucleophilic addition reactions. 18. Write equations for i) Cross aldol condensation between propanal and ethanal in the presence of dil. NaOH. i) Disproportionation of Benzaldehyde in conc. NaOH. 19. Compound (A) reacts with SOCl2 to give compound (B). B reacts with Mg to form Grignard reagent which is treated with acetone and the product is hydrolyzed to give 2-methylbutan-2-ol. Identify A and B compounds? 20. How will you bring about the following conversions in more than two steps? i) Propanone to Propene ii) Benzoic acid to Benzaldehyde. Or// Account for the following: i) P-nitro phenol is a stronger acid than phenol. ii) Phenols undergo substitution at ortho and para positions iii) During preparation of an ester from carboxylic acid and alcohol the ester is distilled as soon as it is formed. 21. Write the equation involved in the following reactions: i) Reimer Tiemann Reaction. ii) Kolbes Reaction iii) Williamson ether synthesis. Or// Name the reagents for the following i) Oxidation of primary alcohol to aldehyde. ii) Oxidation of primary alcohol to carboxylic acid.
iii) Dehydration of prapan-2-ol to propene. An organic compound (A) having molecular formula C6H6O gives a characteristic colour with aqueous FeCl3 solution. (A) on treatment with CO 2 and NaOH at 400 K under high pressure gives (B) which on acidification gives a compound (C). C reacts with acetyl chloride to give (D), which is a popular Pain killer. Deduce the structures of (A), (B), (C) and (D). Or// Explain the following: (i) Wolf Kishner reduction (ii) Haloform reaction (iii) HVZ reaction 23. How do the following react i) Acetyl chloride and toluene in the presence of anhydrous AlCl3 ii) Semicarbazide and formaldehyde iii) Ethyl benzene and alkaline KMnO 4 Or// A compound X (C 2H4O) on oxidation gives Y (C2H4O2 ). X undergoes haloform reaction. On treatment with HCN, X forms a product Z which on hydrolysis gives 2-hydroxy propanoic acid. i) Write down the structures of X and Y. ii) Name the product when X reacts with dil. NaOH. iii) Write down the equations for the reactions involved. 24. Account for the following: i) C -OH bond angle in alcohol is less than tetrahedral angle of 109.50 ii) Alcohol reacts with SOCl2 to give pure halo alkane. iii) Methyl phenyl ether reacts with HI to give phenol and methyl iodide and not methanol and iodo benzene. iv) In the reaction between acid chloride and alcohol a small amount of pyridine is added. v) Water is a stronger acid than alcohol. OR a) Explain the mechanism of the following reactions: i) CH 3CH2OH CH2= CH2 + H 2O ii) (CH3)3CO C 2H5 + HI (CH3)3CI + C2H5OH b) Carry out the following conversions: i) Chloro benzene to phenol. ii) Tert butyl alcohol to 2-methyl prop-1-ene. 25. a) Describe the following reactions with one example of each i) Friedal- Craft reaction ii) Cannizzaro Reaction b) Compound A (C6H12O2) on reduction with LiAlH 4 yields two compounds B and C. The compound B On oxidation gave D which on treatment with aqueous alkali and subsequent heating furnished E. The latter on catalytic hydrogenation gave C. The compound D on further oxidation gave CH3COOH Deduce the structure of A,B,C,D and E. OR// a) Write the chemical reaction to illustrate the following: i) Rosenmund reduction ii) Aldol condensation. b) Distinguish between the following pairs : i) Propanal and propanone ii) Acetophenone and Benzophenone iii) Phenol and Benzoic acid. Or// a) Convert i) Acetophenone to 2-phenyl-2-butanol. ii) Propene to acetone. b) An organic compound A contains 69.77% carbon, 11.63% hydrogen and the rest is oxygen. The molecular mass of A is 86. It does not reduce Tollens reagent but forms an addition compound with sodium hydrogen sulphite. A gives a positive iodoform test. On vigorous oxidation Agives ethanoic and propanoic acids. Deduce the possible structure of molecule A. OR a) How do you separate the following mixtures? i) o-Nitrophenol & p-Nitrophenol ii) Aldehyde & Ketone b) An unknown aldehyde A, C7H6O on reaction with KOH gives B and C. A reacts with Zn-Hg and conc. HCl to give D which changes to A by CrO2Cl2. B on heating with soda lime gives E. identify A to E and write all reactions.
22.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Model Questions On U-12, 13 & 14Dokument12 SeitenModel Questions On U-12, 13 & 14kadedoxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assertion Reason - BiomoleculesDokument2 SeitenAssertion Reason - Biomoleculessteevejan541Noch keine Bewertungen
- Reasoning On Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDokument3 SeitenReasoning On Haloalkanes and Haloarenesjashwanth kumar58Noch keine Bewertungen
- Question Based On Name ReactionDokument4 SeitenQuestion Based On Name ReactionSelcouth elysianNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1chemical Reactions & Equations Top 25 Questions Prashant KiradDokument12 Seiten1chemical Reactions & Equations Top 25 Questions Prashant KiradKshitiz sharma100% (1)
- Reasoning Qns With Answers - Haloalkanes&Haloarenes 2Dokument8 SeitenReasoning Qns With Answers - Haloalkanes&Haloarenes 2tanishka0307Noch keine Bewertungen
- Holiday Homework Class XII Chemistry: ITL Public SchoolDokument14 SeitenHoliday Homework Class XII Chemistry: ITL Public SchoolNisith Kr DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10th Carbon and Its Compounds Test Paper-1Dokument1 Seite10th Carbon and Its Compounds Test Paper-1Kushal SarkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE Class 10 Chemistry Worksheet - Carbon and Its CompoundDokument4 SeitenCBSE Class 10 Chemistry Worksheet - Carbon and Its CompoundRaghav GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and EquationsDokument3 SeitenChapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations༄ɪɴd᭄乂Sɳιρҽɾ乂100% (1)
- Coordination Compounds Revision 2022Dokument2 SeitenCoordination Compounds Revision 2022Dêêpák Sîñgh Ñîtwál100% (1)
- NEET - Halo Alkanes and Halo Arenes Practice PaperDokument3 SeitenNEET - Halo Alkanes and Halo Arenes Practice PaperGanga DharaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 10 CH 1 Assertion Reason QuestionsDokument4 SeitenGrade 10 CH 1 Assertion Reason QuestionsVidhun 8ANoch keine Bewertungen
- Competency Based QuestionsDokument2 SeitenCompetency Based QuestionsMind On You tube100% (1)
- Reasoning Organic ChemDokument12 SeitenReasoning Organic ChemUtkarsh BajpaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHEMISTRY Ch2 Solved Assignment Class 9 CBSEDokument5 SeitenCHEMISTRY Ch2 Solved Assignment Class 9 CBSEgurdeepsarora8738100% (1)
- Chemistry Important QuestionsDokument20 SeitenChemistry Important QuestionsArjun Ramesh0% (1)
- Test1 Goc & Poc Tough by S.K.sinha See Chemistry Animations atDokument3 SeitenTest1 Goc & Poc Tough by S.K.sinha See Chemistry Animations atmyiitchemistry100% (1)
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry WorksheetDokument2 SeitenCBSE Class 12 Chemistry WorksheetSanthosh Siva KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alkyl HalideDokument8 SeitenAlkyl HalideMegh Raj BhattNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mock Examination 2007 Physics Paper 2Dokument20 SeitenMock Examination 2007 Physics Paper 2api-19650882Noch keine Bewertungen
- D and F Block ElementsDokument18 SeitenD and F Block ElementsLakshmi SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids QuestionsDokument5 SeitenAldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids QuestionssingamroopaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic Practice 3: Very Short Answer Type Questions - 1 MarkDokument7 SeitenTopic Practice 3: Very Short Answer Type Questions - 1 MarkDebasis GhosalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbon and It's Compounds Assignment + WorksheetDokument34 SeitenCarbon and It's Compounds Assignment + WorksheetDishant KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCQ Halo Alkanes and ArenesDokument27 SeitenMCQ Halo Alkanes and ArenessarahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids - Practice SheetDokument4 SeitenAldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids - Practice Sheetsameeryad72Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mole Concept - DPP 01 - Yakeen NEET 2024 PDFDokument3 SeitenMole Concept - DPP 01 - Yakeen NEET 2024 PDFKhushi PathakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atomic StructureDokument22 SeitenAtomic StructureYash AkhauriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbonyl Compounds 12thDokument24 SeitenCarbonyl Compounds 12thRaju SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coordination Chemistry TestDokument3 SeitenCoordination Chemistry TestSabitra Rudra100% (1)
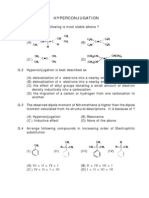
- Hyper ConjugationDokument3 SeitenHyper ConjugationKeval MaldeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Bonding Advance (Micro)Dokument28 SeitenChemical Bonding Advance (Micro)Anant JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 7 Physical and Chemical Changes WorksheetDokument6 SeitenGrade 7 Physical and Chemical Changes WorksheetProdigy GameplaysNoch keine Bewertungen
- Important-Question-ICSE-2010-Class-10th - Acids-Bases-Salts-CDokument5 SeitenImportant-Question-ICSE-2010-Class-10th - Acids-Bases-Salts-CYash KapoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- RIVISION TEST PAPER - Class 9Dokument4 SeitenRIVISION TEST PAPER - Class 9Teja RajarameshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sarvodaya.2puc - Mid-Term. IMPORTANT QUESTIONS IN CHEMISTRYDokument4 SeitenSarvodaya.2puc - Mid-Term. IMPORTANT QUESTIONS IN CHEMISTRYRavindar PurohitNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8-d and - F Block Elements (New) .Dokument16 Seiten8-d and - F Block Elements (New) .Shesha krishnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE Class 9 Chemistry Worksheet - Atoms and MoleculesDokument2 SeitenCBSE Class 9 Chemistry Worksheet - Atoms and MoleculesShweta100% (1)
- Alcohol Phenol Ether PDFDokument38 SeitenAlcohol Phenol Ether PDFsjahsnjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet Chemistry 12Dokument5 SeitenWorksheet Chemistry 12mohit kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Important Question ICSE 2010 Class 10th PhysicsDokument3 SeitenImportant Question ICSE 2010 Class 10th Physicspavan kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- XII - Physics - Preboard 1 - Set A 2023Dokument6 SeitenXII - Physics - Preboard 1 - Set A 2023Anuradha MukherjeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter # 12: Electrostatics: Practice Sheet # 12: Compiled By: Engr. M. Bilal ZiaDokument16 SeitenChapter # 12: Electrostatics: Practice Sheet # 12: Compiled By: Engr. M. Bilal ZiaMinhal KukdaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical EquilibriumDokument27 SeitenChemical EquilibriumYatharth ManchandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 12 Chemistry 2020Dokument16 SeitenCBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 12 Chemistry 2020Emtiaz AnsariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem PaperDokument4 SeitenChem PaperKeertana SN100% (1)
- Science: Fully Solved (Question-Answer)Dokument5 SeitenScience: Fully Solved (Question-Answer)First DriveNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHEMISTRY Assignment Class 9 CBSEDokument3 SeitenCHEMISTRY Assignment Class 9 CBSEgurdeepsarora8738100% (1)
- Chapter 20: Electrochemistry: Homework QuestionsDokument2 SeitenChapter 20: Electrochemistry: Homework Questionservaldi0% (1)
- Alkyl Halides and Amines Mcqs KeyDokument3 SeitenAlkyl Halides and Amines Mcqs KeySameer HussainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acids, Bases and Salts MCQDokument16 SeitenAcids, Bases and Salts MCQprayas thakreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Paper For ChemistryDokument23 SeitenSample Paper For ChemistryAmit joshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- D and F Block Elements Final RevisionDokument4 SeitenD and F Block Elements Final RevisionROWA new year CelebrationNoch keine Bewertungen
- BAHUBALI Notes Chemical Bonding by VT SirDokument19 SeitenBAHUBALI Notes Chemical Bonding by VT SirPixelTinker010% (1)
- 3B-HYDROCARBON Assignment - FinalDokument49 Seiten3B-HYDROCARBON Assignment - Finalkraken monsterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coordination Compound - Ex. Module-3-2Dokument18 SeitenCoordination Compound - Ex. Module-3-2Raju SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit-12 Aldehyde Ketone Carboxylic AcidDokument5 SeitenUnit-12 Aldehyde Ketone Carboxylic AcidVIDHI CHORDIANoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry 12Dokument3 SeitenChemistry 12Anonymous WxtxTR2Noch keine Bewertungen
- HelpDokument1 SeiteHelpPrerak Kumar SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CS-trainee Pilot FormDokument3 SeitenCS-trainee Pilot FormPrerak Kumar SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- R.k.Bali 20 Q.P PDFDokument124 SeitenR.k.Bali 20 Q.P PDFPrerak Kumar SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCS-012 Soved Assignment 2015-16-056-068 PDFDokument13 SeitenMCS-012 Soved Assignment 2015-16-056-068 PDFPrerak Kumar SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CodeDokument8 SeitenCodePrerak Kumar SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Untitled DocumentDokument1 SeiteUntitled DocumentPrerak Kumar SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Igknowuhelper in Wp-Content Uploads 2019 11 BCS-42 PDFDokument25 SeitenIgknowuhelper in Wp-Content Uploads 2019 11 BCS-42 PDFPrerak Kumar SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- RegsssDokument44 SeitenRegsssPrerak Kumar SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bcs 54 2016Dokument6 SeitenBcs 54 2016Prerak Kumar SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCS 011 June 2015 PDFDokument4 SeitenMCS 011 June 2015 PDFPrerak Kumar SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Secondary Coil, and This Induces Within It An EHT VoltageDokument3 SeitenSecondary Coil, and This Induces Within It An EHT VoltagePrerak Kumar SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCA (Revised) / BCA (Revised) Term-End Examination December, 2016Dokument2 SeitenMCA (Revised) / BCA (Revised) Term-End Examination December, 2016Prerak Kumar SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Character CertificateDokument1 SeiteCharacter CertificateShailesh KadamNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCS 022june 10 PDFDokument2 SeitenMCS 022june 10 PDFPrerak Kumar SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BCSL 061 S1 S2 S3 S4 June 2014Dokument4 SeitenBCSL 061 S1 S2 S3 S4 June 2014Yogesh HoodaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCS 011june 13Dokument3 SeitenMCS 011june 13Prerak Kumar SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCA (Revised) / BCA (Revised) Term-End Examination June, 2016Dokument4 SeitenMCA (Revised) / BCA (Revised) Term-End Examination June, 2016Prerak Kumar SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCS 022dec 13 PDFDokument2 SeitenMCS 022dec 13 PDFPrerak Kumar SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BCSL 022 PDFDokument20 SeitenBCSL 022 PDFPrerak Kumar SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCA (Revised) Term-End Examination June, 2010 Operating System Concepts and Networking ManagementDokument2 SeitenMCA (Revised) Term-End Examination June, 2010 Operating System Concepts and Networking ManagementPrerak Kumar SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bachelor of Computer Applications (Revised) (BCA) Term-End Practical Examination December, 2016 BCSL 063 (P) /S3Dokument1 SeiteBachelor of Computer Applications (Revised) (BCA) Term-End Practical Examination December, 2016 BCSL 063 (P) /S3Prerak Kumar SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bachelor of Computer: BCSL 063 (P) /S3Dokument1 SeiteBachelor of Computer: BCSL 063 (P) /S3Prerak Kumar SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bachelor of Computer Applications (Revised) (BCA) Term-End Practical Examination December, 2016Dokument1 SeiteBachelor of Computer Applications (Revised) (BCA) Term-End Practical Examination December, 2016Prerak Kumar SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guruignou pROJECTDokument2 SeitenGuruignou pROJECTPrerak Kumar SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01 Read Me First !!!!Dokument1 Seite01 Read Me First !!!!shahrooz siddiquiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bcs 54 2016Dokument6 SeitenBcs 54 2016Prerak Kumar SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Block 1 ECO 02 Unit 1Dokument20 SeitenBlock 1 ECO 02 Unit 1HozefadahodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Block 1 ECO 02 Unit 1Dokument24 SeitenBlock 1 ECO 02 Unit 1Akhilesh SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Terms and Condition PDFDokument2 SeitenTerms and Condition PDFPrerak Kumar SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BCSL 022 PDFDokument20 SeitenBCSL 022 PDFPrerak Kumar SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemquest 2018 c11 2018 p1 JawapanDokument2 SeitenChemquest 2018 c11 2018 p1 JawapanAiman JuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alkena / Alkene: H H C H C HDokument7 SeitenAlkena / Alkene: H H C H C HMOHAMAD REDUAN BIN IBRAHIM MoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amino Acids: Complete Protein Multi-Purposed DIGESTIVE ENZYMESDokument8 SeitenAmino Acids: Complete Protein Multi-Purposed DIGESTIVE ENZYMESPal_inNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group AssignmentDokument9 SeitenGroup AssignmentRenee Dwi Permata MessakaraengNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aldehyde and Ketones McMurryDokument43 SeitenAldehyde and Ketones McMurryShamira100% (1)
- Proteins PDFDokument20 SeitenProteins PDFDOMADO EBTISHAMNoch keine Bewertungen
- Photometer 4010: No. Parameter Vol. Sampel Vol - Reagen Program Pengukuran Terhadap Faktor Panj - GelDokument2 SeitenPhotometer 4010: No. Parameter Vol. Sampel Vol - Reagen Program Pengukuran Terhadap Faktor Panj - GelElga Yunus100% (2)
- Di-Pi Methane RearrangementDokument8 SeitenDi-Pi Methane RearrangementSengottaiyan M MuruganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes On "ORGANIC CHEMISTRY" CBSE Class XIIDokument52 SeitenNotes On "ORGANIC CHEMISTRY" CBSE Class XIIMahesh AdhikariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 2Dokument2 SeitenTutorial 2sylvieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture Notes: Carbohydrates: Topics CoveredDokument26 SeitenLecture Notes: Carbohydrates: Topics CoveredElumalaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- US6489384Stabilized UV-crosslinkable Hot-Melt Pressure Sensitive AdhesivesDokument6 SeitenUS6489384Stabilized UV-crosslinkable Hot-Melt Pressure Sensitive Adhesivespeter shiNoch keine Bewertungen
- PolymeDokument13 SeitenPolymeTu Dao NgocNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity 3 - Amino Acids and PeptidesDokument7 SeitenActivity 3 - Amino Acids and PeptidesKate MendozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stoker Chapter19 (Lipids) - 2 PDFDokument85 SeitenStoker Chapter19 (Lipids) - 2 PDFAsther Mantua86% (7)
- S.P.P.M. MasterDokument126 SeitenS.P.P.M. MasterwahyuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integration of MetabolismDokument10 SeitenIntegration of MetabolismAditya NayakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laporan Hasil Penelitian Korelasi Rasio Kolesterol Total Terhadap HDL Dengan Prediksi Outcome Stroke Iskemik AkutDokument13 SeitenLaporan Hasil Penelitian Korelasi Rasio Kolesterol Total Terhadap HDL Dengan Prediksi Outcome Stroke Iskemik AkutRay HannaNoch keine Bewertungen
- J. Biol. Chem.-1998-Uchida-16058-66 PDFDokument10 SeitenJ. Biol. Chem.-1998-Uchida-16058-66 PDFanchizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simple and Complex CarbohydratesDokument78 SeitenSimple and Complex CarbohydratesRonald GyezahoNoch keine Bewertungen
- NOMENCLATURE AROMATIC COMPOUNDS (Answer)Dokument4 SeitenNOMENCLATURE AROMATIC COMPOUNDS (Answer)Nurain azmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors As Alzheimer Therapy From Nerve Toxins To NeuroprotectionDokument24 SeitenAcetylcholinesterase Inhibitors As Alzheimer Therapy From Nerve Toxins To NeuroprotectionLucasBritoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Act 2 PDFDokument6 SeitenAct 2 PDFKhara TeanoTanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Daftar Dosis ObatDokument3 SeitenDaftar Dosis ObatFia putriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advances in Clinical Chemistry PDFDokument227 SeitenAdvances in Clinical Chemistry PDFMohammedAjebli0% (1)
- Bala Blood Report Ca, Uric, B12, D3Dokument3 SeitenBala Blood Report Ca, Uric, B12, D3BALANoch keine Bewertungen
- NSAIDsDokument3 SeitenNSAIDsMarco Anselmo C. AldepollaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 6 Amides and AminesDokument69 SeitenLecture 6 Amides and AminesJowayriyyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vitamin E StructureDokument3 SeitenVitamin E StructureWestern SunriseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carboxylic Acid Derivatives: Organic Chemistry, 5Dokument62 SeitenCarboxylic Acid Derivatives: Organic Chemistry, 5CV Sumber Mutiara AbadiNoch keine Bewertungen