Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
SCH 07
Hochgeladen von
Richelle Joy Reyes BenitoOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
SCH 07
Hochgeladen von
Richelle Joy Reyes BenitoCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
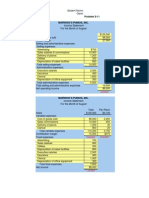
Student Name: Instructor Class: McGraw-Hill/Irwin Problem 07-20A 1. PHOTOTEC, INC.
Schedule of cash receipts: Cash sales-June Collections on accounts receivable: May 31 balance June Total cash receipts Schedule of cash payments for purchases: May 31 accounts payable balance June purchases Total cash payments
60,000
72,000 95,000 $ 227,000 Correct! $ 90,000 80,000 $ 170,000 Correct!
PHOTOTEC, INC. Cash Budget For the Month of June Cash balance, beginning Add receipts from customers Total cash available Less disbursements: Purchase of inventory Selling and administrative expenses Purchases of equipment Total cash disbursements Excess of receipts over disbursements Financing: Borrowings-note Repayments-note Interest Total financing Cash balance, ending $ 8,000 227,000 235,000 170,000 51,000 9,000 230,000 5,000 18,000 (15,000) (500) 2,500 $ 7,500 Correct!
Student Name: Instructor Class: McGraw-Hill/Irwin Problem 07-20A
2. PHOTOTEC, INC. Budgeted Income Statement For the Month of June Sales Cost of goods sold: Beginning inventory Purchases Goods available for sale Ending inventory Cost of goods sold Gross margin Selling and administrative expenses Net operating income Interest expense Net income $ $ 30,000 200,000 230,000 40,000 190,000 60,000 53,000 7,000 500 $ 6,500 Correct! 250,000
3. PHOTOTEC, INC. Budgeted Balance Sheet June 30 Assets Cash Accounts receivable Inventory Buildings and equipment, net of depreciation Total assets Liabilities and Equity Accounts payable Note payable Capital stock Retained earnings Total liabilities and equity $ 7,500 95,000 40,000 507,000 649,500
120,000 18,000 420,000 91,500 $ 649,500 Correct!
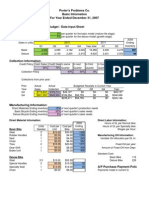
Given Data P07-20A: PHOTOTEC, INC. Balance Sheet May 31 Assets Cash Accounts receivable Inventory Buildings and equipment, net of depreciation Total assets Liabilities and Stockholders' Equity Accounts payable Note payable Capital stock Retained earnings Total liabilities and stockholders' equity Budgeted Data relating to June: Budgeted sales Budgeted sales in cash (remainder credit) Percent of credit sales collected in same month May accounts receivable collected Expected inventory purchases Purchases paid for in cash in month purchased May accounts payable paid Budgeted inventory balance, June 30 Budgeted selling and administrative expenses Budgeted depreciation Existing note payable paid Interest expense Equipment purchases New note
8,000 72,000 30,000 500,000 610,000
90,000 15,000 420,000 85,000 610,000
$ $
$ $ $ $ $ $
250,000 60,000 50% 100% 200,000 40% 100% 40,000 51,000 2,000 100% 500 9,000 18,000
Student Name: Instructor Class: McGraw-Hill/Irwin Problem 07-23A UNIVAX, INC. 1a. Schedule of expected cash collections: Year 2 Quarter Second Third $ 260,000 165,000
Year 1 - Fourth quarter sales: Year 2 - First quarter sales: Year 2 - Second quarter sales: Year 2 - Third quarter sales: Year 2 - Fourth quarter sales: Total cash collections
First 195,000 132,000
Fourth
325,000 198,000 523,000 Correct!
327,000 Correct!
425,000 Correct!
390,000 158,400 $ 548,400 Correct!
Total 195,000 392,000 490,000 588,000 158,400 $ 1,823,400 Correct! $
1b. Schedule of budgeted cash disbursements for merchandise purchases: Year 2 Quarter Second Third $ 208,000 62,000
Year 1 - Fourth quarter purchases: Year 2 - First quarter purchases: Year 2 - Second quarter purchases: Year 2 - Third quarter purchases: Year 2 - Fourth quarter purchases: Total cash disbursements
First 144,000 52,000
Fourth
248,000 74,000 322,000 Correct!
196,000 Correct!
270,000 Correct!
296,000 48,000 $ 344,000 Correct!
Total 144,000 260,000 310,000 370,000 48,000 $ 1,132,000 Correct! $
2. Budgeted selling and administrative expenses: Year 2 Quarter First Second Third Fourth Year $ 400,000 $ 500,000 $ 600,000 $ 480,000 $ 1,980,000 12% 12% 12% 12% 12% $ 48,000 $ 60,000 $ 72,000 $ 57,600 $ 237,600 90,000 90,000 90,000 90,000 360,000 138,000 150,000 162,000 147,600 597,600 20,000 20,000 20,000 20,000 80,000 $ 118,000 $ 130,000 $ 142,000 $ 127,600 $ 517,600 Correct! Correct! Correct! Correct! Correct!
Budgeted sales Variable expense rate Variable expenses Fixed expenses Total expenses Less depreciation Cash disbursements
3. Cash budget for Year 2: Year 2 Quarter Second Third $ 23,000 $ 18,000 425,000 523,000 448,000 541,000 270,000 130,000 10,000 80,000 490,000 (42,000) 60,000 60,000 $ 18,000 Correct! 322,000 142,000 10,000 48,500 522,500 18,500
Cash balance, beginning Add collections from sales Total cash available Less disbursements: Merchandise purchases Operating expenses Dividends Land Total disbursements Excess (deficiency) of receipts over disbursements Financing: Borrowings Repayments Interest Total financing Cash balance, ending
First 20,000 327,000 347,000 196,000 118,000 10,000 324,000 23,000
Fourth 18,500 548,400 566,900 344,000 127,600 10,000 481,600 85,300
Year 20,000 1,823,400 1,843,400 1,132,000 517,600 40,000 128,500 1,818,100 25,300
$ 23,000 Correct!
18,500 Correct!
60,000 (60,000) (60,000) (5,400) (5,400) (65,400) (5,400) $ 19,900 $ 19,900 Correct! Correct!
Given Data P07-23A: UNIVAX, INC. Budgeted Sales and Merchandise Purchases: Merchandise Purchases $ $ $ $ $ 180,000 260,000 310,000 370,000 240,000
Sales Year 1: Fourth quarter actual Year 2: First quarter estimated Second quarter estimated Third quarter estimated Fourth quarter estimated $ $ $ $ $ 300,000 400,000 500,000 600,000 480,000
Additional information: Percentage of sales collected in same quarter Percentage of sales collected in quarter following sales Percentage of sales deemed uncollectible Percentage of merchandise purchases paid in same quarter Percentage of merchandise purchases pain in following quarter Budgeted quarterly operating expenses for Year 2 plus percentage of sales Amount of depreciation budgeted each quarter Dividends to be paid each quarter Cash purchase of land in second quarter Cash purchase of land in third quarter Cash account balance at end of Year 1 Minimum cash balance required Bank loan borrowing increments Maximum loan balance allowed Interest rate per month on bank loans Current outstanding loan balance
$ $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $
33% 65% 2% 20% 80% 90,000 12% 20,000 10,000 80,000 48,500 20,000 18,000 10,000 100,000 1.0% -
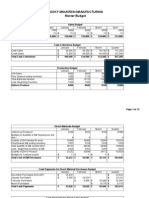
Student Name: Instructor Class: McGraw-Hill/Irwin 07-Case CRAVAT SALES COMPANY Budgets April 1a. Sales budget: Budgeted sales in units Selling price per unit Total sales 1b. Schedule of expected cash collections: February sales March sales April sales May sales June sales Total cash collections 1c. Merchandise purchases budget: Budgeted sales in units Add budgeted ending inventory Total needs Less beginning inventory Required unit purchases Unit cost Required dollar purchases 35,000 8 280,000 Correct! 48,000 112,000 70,000 May 45,000 8 360,000 Correct! June 60,000 8 480,000 Correct! Quarter 140,000 $ 8 $ 1,120,000 Correct! $ 56,000 140,000 90,000 $ 286,000 Correct! $ 70,000 180,000 120,000 $ 370,000 Correct! 60,000 36,000 96,000 54,000 42,000 $ 5 $ 210,000 Correct! 48,000 168,000 280,000 270,000 120,000 $ 886,000 Correct! 140,000 36,000 176,000 31,500 144,500 $ 5 $ 722,500 Correct! $ $ 110,000 146,250 256,250 Correct! $ 146,250 105,000 $ 251,250 Correct! 85,750 220,000 292,500 105,000 $ 703,250 Correct!
$ $
$ $
$ $
230,000 Correct!
35,000 40,500 75,500 31,500 44,000 $ 5 $ 220,000 Correct! 1d. Budgeted cash disbursements for merchandise purchases: March purchases $ 85,750 April purchases 110,000 May purchases June purchases Total cash payments $ 195,750 Correct! 2.
45,000 54,000 99,000 40,500 58,500 $ 5 $ 292,500 Correct!
CRAVAT SALES COMPANY Cash Budget For the Three Months Ending June 30 April 14,000 230,000 244,000 195,750 35,000 22,000 14,000 3,000 12,000 281,750 (37,750) 48,000 May 10,250 286,000 296,250 256,250 45,000 22,000 14,000 3,000 25,000 365,250 (69,000) 79,000 June 10,000 370,000 380,000 251,250 60,000 22,000 14,000 3,000 350,250 29,750 Quarter 14,000 886,000 900,000 703,250 140,000 66,000 42,000 9,000 12,000 25,000 997,250 (97,250)
Cash balance, beginning Add receipts from customers Total cash available Less disbursements: Purchase of inventory Sales commissions Salaries and wages Utilities Miscellaneous Dividends paid Land purchases Total disbursements Excess (deficiency) of receipts over disbursements Financing: Borrowings Repayments Interest Total financing Cash balance, ending
48,000 10,250 Correct!
79,000 10,000 Correct!
127,000 (16,000) (16,000) (3,020) (3,020) (19,020) 107,980 $ 10,730 $ 10,730 Correct! Correct!
Student Name: Instructor Class: McGraw-Hill/Irwin 07-Case
3. CRAVAT SALES COMPANY Budgeted Income Statement For the Three Months Ended June 30 Sales in units Sales revenue Variable expenses: Cost of goods sold Commissions Contribution margin Fixed expenses: Wages and salaries Utilities Insurance expired Depreciation Miscellaneous Net operating income Less interest expense Net income 140,000 $ 1,120,000 $ 700,000 140,000
840,000 280,000
66,000 42,000 3,600 4,500 9,000
125,100 154,900 3,020 $ 151,880 Correct!
4. CRAVAT SALES COMPANY Budgeted Balance Sheet June 30 Assets Cash Accounts receivable Inventory Unexpired insurance Fixed assets, net of depreciation Total assets Liabilities and Stockholders' Equity Accounts payable, purchases Dividends payable Loans payable, bank Capital stock, no par Retained earnings Total liabilities and equity Accounts receivable at June 30: May sales June sales Total Retained earnings at June 30: Balance, March 31 Add net income Total Less dividends declared Balance, June 30 $ 10,730 450,000 180,000 10,800 193,200 $ 844,730 Correct! $ 105,000 12,000 111,000 300,000 316,730 $ 844,730 Correct! $ 90,000 360,000 $ 450,000 Correct! $ 176,850 151,880 328,730 12,000 $ 316,730 Correct!
Given Data 07-Case: CRAVAT SALES COMPANY Minimum ending monthly cash balance Selling price Recent and forecast sales (in units): January (actual) February (actual) March (actual) April May June July August September Desired ending inventories (percentage of next month's sales) Cost of earrings Purchases paid as follows: In month of purchase In following month Collection on sales: Sales collected current month Sales collected following month Sales collected 2nd month following Monthly selling and administrative expenses: Variable: Sales commissions (per tie) Fixed: Wages and salaries Utilities Insurance Depreciation Miscellaneous Land purchased in May Dividends declared each quarter $ $ 10,000 8
20,000 24,000 28,000 35,000 45,000 60,000 40,000 36,000 32,000
90% 5
50% 50%
25% 50% 25%
1.00
$ $ $ $ $ $ $
22,000 14,000 1,200 1,500 3,000 25,000 12,000
Given Data 07-Case: Balance sheet at March 31: Assets Cash Accounts receivable February sales March sales Inventory (31,500 units) Prepaid insurance Fixed assets, net of depreciation Total assets $ $ 48,000 168,000 14,000
216,000 157,500 14,400 172,700 574,600
Liabilities and Stockholders' Equity Accounts payable Dividends payable Common stock Retained earnings Total liabilities and stockholders' equity Agreement with Bank: Borrowing increments Maximum borrowing amount Interest rate per month Repayment increments Total of interest paid each quarter Required minimum cash balance
85,750 12,000 300,000 176,850 574,600
$ $ $ $
1,000 140,000 1% 1,000 100% 10,000
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Computerised Accounting Practice Set Using MYOB AccountRight - Advanced Level: Australian EditionVon EverandComputerised Accounting Practice Set Using MYOB AccountRight - Advanced Level: Australian EditionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case 08-29 Cravat Sales CompanyDokument5 SeitenCase 08-29 Cravat Sales Companysubash1111@gmail.comNoch keine Bewertungen
- TestDokument14 SeitenTesthonest0988Noch keine Bewertungen
- How to Read a Financial Report: Wringing Vital Signs Out of the NumbersVon EverandHow to Read a Financial Report: Wringing Vital Signs Out of the NumbersNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 PhototecDokument3 Seiten1 Phototecalice horanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Economic & Budget Forecast Workbook: Economic workbook with worksheetVon EverandEconomic & Budget Forecast Workbook: Economic workbook with worksheetNoch keine Bewertungen
- Material BudgetDokument37 SeitenMaterial BudgetRahul SardaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Comprehensive Guide on How to Read a Financial Report: Wringing Vital Signs Out of the NumbersVon EverandThe Comprehensive Guide on How to Read a Financial Report: Wringing Vital Signs Out of the NumbersBewertung: 2 von 5 Sternen2/5 (1)
- 1 PhototecDokument3 Seiten1 PhototecKaishe RamosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem 07-18 Requirement 1: Minden Company: Correct!Dokument3 SeitenProblem 07-18 Requirement 1: Minden Company: Correct!foxstupidfoxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Given:: Problem 6 - 21: Prepare & Reconcile Variable Costing StatementsDokument13 SeitenGiven:: Problem 6 - 21: Prepare & Reconcile Variable Costing StatementsimjiyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case 08 29 Cravat Sales CompanyDokument5 SeitenCase 08 29 Cravat Sales CompanyDianaSafaryan0% (1)
- Bob's Bicycles - Master Budget 2010Dokument28 SeitenBob's Bicycles - Master Budget 2010Jonathan Slonim100% (2)
- 202E06Dokument21 Seiten202E06foxstupidfoxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Managerial Budget Master ProjectDokument2 SeitenManagerial Budget Master Projectapi-340156713Noch keine Bewertungen
- 202E08Dokument22 Seiten202E08David David100% (1)
- Profit Planning, Activity-Based Budgeting and E-Budgeting: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinDokument78 SeitenProfit Planning, Activity-Based Budgeting and E-Budgeting: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinSi HarisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accy 517 HW PB Set 1Dokument30 SeitenAccy 517 HW PB Set 1YonghoChoNoch keine Bewertungen
- TuyjDokument51 SeitenTuyjagnesNoch keine Bewertungen
- FileDokument5 SeitenFileRonnel RosalesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Required: Using The Data Above, Complete The Following Statements and Schedules For The First QuarterDokument6 SeitenRequired: Using The Data Above, Complete The Following Statements and Schedules For The First QuarterNomunzul GanpurevNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture-7 Overhead (Part 1)Dokument22 SeitenLecture-7 Overhead (Part 1)Nazmul-Hassan Sumon100% (2)
- Master BudgetingDokument11 SeitenMaster BudgetingsulavnepalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Required: Using The Data Above, Complete The Following Statements and Schedules For The First QuarterDokument6 SeitenRequired: Using The Data Above, Complete The Following Statements and Schedules For The First QuarterteferiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 10 BudgetingDokument83 SeitenCH 10 BudgetingShannon BánañasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cash Flow TutorialDokument6 SeitenCash Flow TutorialEric Chambers100% (1)
- 1101AFE Final Exam Practice Paper SEM 1Dokument10 Seiten1101AFE Final Exam Practice Paper SEM 1张兆宇Noch keine Bewertungen
- Nordic CompanyDokument6 SeitenNordic CompanySally ZansNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seminar 11answer Group 10Dokument75 SeitenSeminar 11answer Group 10Shweta Sridhar40% (5)
- Cash Budgeting TutorialDokument4 SeitenCash Budgeting Tutorialmichellebaileylindsa100% (1)
- Accounting For Merchandising BusinessesDokument73 SeitenAccounting For Merchandising BusinessesYustamar Ramatsuy100% (1)
- Exercises Budgeting ACCT2105 3s2010Dokument7 SeitenExercises Budgeting ACCT2105 3s2010Hanh Bui0% (1)
- Working Capital ManagementDokument67 SeitenWorking Capital ManagementAam aadmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 10 Assignment 4Dokument4 SeitenLesson 10 Assignment 4marcied357Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 04 - 12thDokument16 SeitenChapter 04 - 12thSarah JamesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Budgeted Cash Disbursements For Merchandise PurchasesDokument27 SeitenBudgeted Cash Disbursements For Merchandise PurchasesMavis LiuNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 07Dokument29 SeitenCH 07varunragav85Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hillyard CompanyDokument18 SeitenHillyard CompanyShellyn Erespe Gomez100% (4)
- Purposes of Budgeting Systems: BudgetDokument42 SeitenPurposes of Budgeting Systems: BudgetJohn Joseph CambaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abigail Foss - Comprehensive Problem - Master BudgetDokument15 SeitenAbigail Foss - Comprehensive Problem - Master Budgetapi-325954956Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ex06 - Comprehensive BudgetingDokument14 SeitenEx06 - Comprehensive BudgetingANa Cruz100% (2)
- Asignación 4 LSFPDokument6 SeitenAsignación 4 LSFPElia SantanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wasatch Manufacturing Master BudgetDokument6 SeitenWasatch Manufacturing Master Budgetapi-255137286Noch keine Bewertungen
- EportfolioDokument8 SeitenEportfolioapi-220792970Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2009-10-28 225356 SouthcoastDokument17 Seiten2009-10-28 225356 Southcoastjas02h1100% (1)
- Financial Accounting11Dokument14 SeitenFinancial Accounting11AleciafyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comp Problem 3Dokument3 SeitenComp Problem 3cjnegrette80% (5)
- Acct 2020 Excel Budget Problem Student TemplateDokument12 SeitenAcct 2020 Excel Budget Problem Student Templateapi-278341046Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chap 015Dokument31 SeitenChap 015magic1111Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 13Dokument9 SeitenChapter 13RBNoch keine Bewertungen
- BudgetDokument6 SeitenBudgetshobuzfeni100% (1)
- Prepare A Cash Budget - by Quarter and in Total ... - GlobalExperts4UDokument31 SeitenPrepare A Cash Budget - by Quarter and in Total ... - GlobalExperts4USaiful IslamNoch keine Bewertungen
- HorngrenIMA14eSM ch07Dokument57 SeitenHorngrenIMA14eSM ch07Aries Siringoringo50% (2)
- Financial Accounting ProblemsDokument20 SeitenFinancial Accounting Problemsmobinil1Noch keine Bewertungen
- HorngrenIMA14eSM ch07Dokument57 SeitenHorngrenIMA14eSM ch07manunited83100% (3)
- 9 45Dokument7 Seiten9 45René Morel0% (1)
- Budgeted Cash Disbursements For Merchandise Purchases Course Project ADokument19 SeitenBudgeted Cash Disbursements For Merchandise Purchases Course Project AitlnkickerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seminar 11answer Group 11Dokument115 SeitenSeminar 11answer Group 11Shweta SridharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap 007Dokument16 SeitenChap 007dbjn100% (1)
- Sowing Planting Equipments DescriptionsDokument1 SeiteSowing Planting Equipments DescriptionsRichelle Joy Reyes BenitoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tillage Equipments DescriptionDokument2 SeitenTillage Equipments DescriptionRichelle Joy Reyes BenitoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tillage Equipment ImagesDokument2 SeitenTillage Equipment ImagesRichelle Joy Reyes Benito100% (1)
- Journal Part 3Dokument3 SeitenJournal Part 3Richelle Joy Reyes BenitoNoch keine Bewertungen
- AaaaamascpaDokument12 SeitenAaaaamascpaRichelle Joy Reyes BenitoNoch keine Bewertungen
- OtesvatDokument18 SeitenOtesvatRichelle Joy Reyes BenitoNoch keine Bewertungen
- MAS BrewerDokument3 SeitenMAS BrewerRichelle Joy Reyes BenitoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summary of TVMDokument1 SeiteSummary of TVMRichelle Joy Reyes BenitoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Taxation Law ReviewerDokument48 SeitenTaxation Law ReviewerYen Yen NicolasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management Advisory Services - PreboardDokument13 SeitenManagement Advisory Services - PreboardAngelica Estrada100% (4)
- 0204 Part A DCHB Kullu PDFDokument362 Seiten0204 Part A DCHB Kullu PDFsoumi mitraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.1 AFM - Time Value of Money - 181223Dokument7 Seiten3.1 AFM - Time Value of Money - 181223Kushagra BhandariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Functions of State Bank of IndiaDokument7 SeitenFunctions of State Bank of IndiaMitali Pardhiye64% (11)
- Bank QuestionsDokument2 SeitenBank Questionsd_ochoa04Noch keine Bewertungen
- Jones Finac Ce ch02 PDFDokument32 SeitenJones Finac Ce ch02 PDFAnonymous HumanNoch keine Bewertungen
- UPPGMEE Information BrochureDokument27 SeitenUPPGMEE Information BrochureAnweshaBoseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Td112 FormDokument15 SeitenTd112 Formcisse_672868225Noch keine Bewertungen
- Loan AgreementDokument4 SeitenLoan AgreementTrishia Jane JavierNoch keine Bewertungen
- HR Manager Full Report 50kDokument6 SeitenHR Manager Full Report 50kfassNoch keine Bewertungen
- STRBI Table No. 02 Earnings and Expenses of Scheduled Commercial BanksDokument466 SeitenSTRBI Table No. 02 Earnings and Expenses of Scheduled Commercial BanksSai KishoreNoch keine Bewertungen
- HDFCDokument18 SeitenHDFCMiral VadhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- DWB Fintext-1 1Dokument372 SeitenDWB Fintext-1 1taibiscuteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Warring Ton Apartments MIPv1Dokument7 SeitenWarring Ton Apartments MIPv1Mark I'AnsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cash Accounting SAPDokument0 SeitenCash Accounting SAPKauam SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aircraft Leasing and Financing Into IndiaDokument9 SeitenAircraft Leasing and Financing Into Indiajayshree.kariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cengage Eco Dev Chapter 8 - Savings and The Financial System - 32804569Dokument50 SeitenCengage Eco Dev Chapter 8 - Savings and The Financial System - 32804569Wonwoo JeonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financing Mining Projects PDFDokument7 SeitenFinancing Mining Projects PDFEmil AzhibayevNoch keine Bewertungen
- CEZA CharterDokument5 SeitenCEZA CharterChristine C. ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Accounting ADokument137 SeitenFinancial Accounting AlordNoch keine Bewertungen
- Disbursement Voucher CacadiranDokument8 SeitenDisbursement Voucher CacadiranApril Joy Sumagit Hidalgo100% (1)
- Part 1 The Philipine Financial SystemDokument17 SeitenPart 1 The Philipine Financial SystemRona MaglahusNoch keine Bewertungen
- G.R. No. 187769 (Digest)Dokument6 SeitenG.R. No. 187769 (Digest)Davy Pats100% (1)
- People Soft Bundle Release Note 9 Bundle21Dokument21 SeitenPeople Soft Bundle Release Note 9 Bundle21rajiv_xguysNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECGCDokument46 SeitenECGCtrinath1100% (1)
- 1321612987financial AnalysisDokument15 Seiten1321612987financial AnalysisMuhammad Arslan UsmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Banks DataDokument3.429 SeitenBanks DatabharthiaeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Commercial Banking Assignment - 1Dokument7 SeitenCommercial Banking Assignment - 1kismat yadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Analysis & InterpretationDokument4 SeitenData Analysis & Interpretationprincessrox91Noch keine Bewertungen
- Easy Guide - Maker Checker Payment OnlyDokument34 SeitenEasy Guide - Maker Checker Payment Onlyooi woei songNoch keine Bewertungen
- Automated Teller MachineDokument21 SeitenAutomated Teller MachineAhmed SharifNoch keine Bewertungen