Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Waves and Oscillations
Hochgeladen von
Chamila SumathiratnaOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Waves and Oscillations
Hochgeladen von
Chamila SumathiratnaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Chamila Sumathiratna - FIVT
A wave is a disturbance that travels through a medium from one location to another, accompanied by a transfer of energy. Oscillation is the repetitive variation, typically in time, of some measure about a central value or between two or more different states.
Object repeats the same motion over and over again in a cyclic pattern is called periodic motion or oscillation. Starts with equilibrium point when disturbed. Restoring forces The objects are at stable equilibrium only under go oscillations Examples are the pendulum of a grandfathers clock, the vibrating strings of a musical instrument, the pistons in a engine, a child playing on a swing.
Consists of travelling oscillations Are important because it carries energy from one place to other. Also waves are harmful when enormous energy is carried. Natural disasters like tsunami and earthquakes happened because a energy at one place is propagated in the form of waves If the wave is simple harmonic then the wave is sinusoidal
distance between any two consecutive points in the wave shape is call the wavelength of the wave, denoted by . Time taken to travel one wave length is called periodic time.
.
Mechanical waves
Waves
Electromagnetic waves
Matter waves
Transverse waves
Longitudinal waves
Needs a medium to travel Can be transverse or longitudinal progressive
Time
Travelled distance %
Energy in the wave is in the form of potential energy and kinetic energy. There is a constant exchange of energy from potential energy to kinetic energy The amplitude of Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) becomes smaller. It is called damping Damping is due to loss of energy
Reflection
Refraction
Diffraction
Interference
All types of waves subjected to reflection at a fixed boundary.
Resulting wave front depends on the shape of the boundary
This process is called refraction. . Causes the speeds difference of the boundaries. Wave length changes Helpful in various applications like cameras, Ultrasound imaging etc.
property of waves that allows a wave to bend around an obstacle.
Diffraction around a corner Diffraction through an opening
Since radio waves have long wave lengths they get diffracted but waves that are used in cellular phones do not diffract much
Through small apertures diffraction is greater Through large apertures diffraction is negligible
total amplitude at any point in space and time is equal to the sum of the amplitudes of all waves that occur at the same point in space and time
Wave 1(red) has a single wavelength and frequency, as does wave 2( blue). Wave 3 contains two different frequencies
Interference is a special case of the superposition principle. Happens when two or more waves of same frequency overlap.
Wave length and frequency of resulting wave is same
If the two waves are same total destruction can happen
Constructive Interference
Destructive Interference
Microphone samples the noises The microphones are connected to a powerful computer chip Sound made destructively interfere with noise
With respect to blue wave Red wave is lagging Green wave is lagging With respect to green wave red wave is leading
Why certain musical instruments have chambers? Resonance in waves occurs when boundaries reflect a wave back on itself. Formed due to theory of super position
The wave profile doesnt move.
Stationary waves are found in musical instruments
Also the size of a system should match with the wavelength of a wave. Resonance preserves the energy of waves of certain frequencies Applications-micro waves, MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Fundamental frequency depends on the tension length and mass of the string
vibrator
When two frequencies of sound are close, but not the same, the sound waves drift in and out of phase and make beats.
When a source of sound is in motion relative to listener, the frequency of the sound heard by the listener is not the same as the source frequency. This is known as dopplers effect
Is the rate at which energy is transported by the wave, per unit area, across a surface perpendicular to the direction of propagation. The intensity of the faintest sound wave that can be heard by a person with normal hearing is about 10-12 W/m2. total power carried by the wave=intensity x perpendicular area
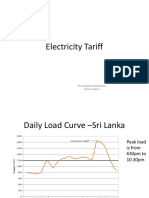
For a sound system for a 2000-seat auditorium, suppose we want the sound intensity over the surface of a hemisphere 20 m in radius to be 1 W/m2. What acoustic power output would be needed from an array of speakers at the center of the sphere?
Loudness describes the perception of sound by your ear and brain. Logarithmic scale vs linear scale
Logarithmic intensity scale is usually used.
The intensity level (or sound level) of a sound wave is defined by the equation
intensity level () = 10
I
0=
10-12 W/m
10 0
Find out the powerfulness of waves having following intensity levels 50dB, 30dB, 3dB, -3dB
The frequency spectrum breaks a complex wave down into its component frequencies and shows the amplitude.
Single frequency
Multi frequency
This theorem says any repetitive wave can be reproduced exactly by single frequency waves with different amplitudes. There is an equation to find the frequency and the amplitude of component waves
Graphical interpretation
equation
Electromagnetic (EM) waves do not need a physical medium. They are vibrations of electric and magnetic fields. Examples include radio waves, microwaves, and Xrays etc.
In empty space, all EM waves travel at the same speed, called the speed of light.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Universal Motor Operation & ApplicationsDokument10 SeitenUniversal Motor Operation & ApplicationsChamila SumathiratnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Universal Motor Operation & ApplicationsDokument10 SeitenUniversal Motor Operation & ApplicationsChamila SumathiratnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- TG Sinhala GD 7Dokument99 SeitenTG Sinhala GD 7Sahitya Nirmanakaranaya Sahitya NirmanakaranayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Introduction To Power Electronics2Dokument14 Seiten1 Introduction To Power Electronics2Chamila SumathiratnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electricity Tariff: Ms Chamila Sumathiratna Senior LeturerDokument11 SeitenElectricity Tariff: Ms Chamila Sumathiratna Senior LeturerChamila SumathiratnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1Dokument33 SeitenChapter 1Chamila SumathiratnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transformers: Ms. Chamila Sumathiratna Senior LecturerDokument59 SeitenTransformers: Ms. Chamila Sumathiratna Senior LecturerChamila SumathiratnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Factor ImprovementDokument25 SeitenPower Factor ImprovementChamila SumathiratnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lighting: Chamila Sumathiratna Senior LecturerDokument17 SeitenLighting: Chamila Sumathiratna Senior LecturerChamila SumathiratnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NPSH SimplifiedDokument4 SeitenNPSH Simplifiedtexwan_Noch keine Bewertungen
- Conduction in The Cylindrical Geometry PDFDokument12 SeitenConduction in The Cylindrical Geometry PDFNabhan RusydiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blooms TaxonomyDokument1 SeiteBlooms TaxonomysivaeeinfoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energy Work and Linear MomentumDokument33 SeitenEnergy Work and Linear MomentumChamila SumathiratnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energy Work and Linear MomentumDokument33 SeitenEnergy Work and Linear MomentumChamila SumathiratnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- GeneratorsDokument22 SeitenGeneratorsChamila SumathiratnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lectures Synchronous MachinesDokument47 SeitenLectures Synchronous MachinesChamila SumathiratnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bipolar Junction TransistorDokument18 SeitenBipolar Junction TransistorChamila SumathiratnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Starting Methods of IMDokument24 SeitenStarting Methods of IMChamila SumathiratnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diodes EstDokument2 SeitenDiodes EstChamila SumathiratnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 07 - DC MotorsDokument9 SeitenLab 07 - DC MotorsChamila SumathiratnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diode RectifiersDokument22 SeitenDiode RectifiersChamila SumathiratnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 07 - DC MotorsDokument9 SeitenLab 07 - DC MotorsChamila SumathiratnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Government College Of Technology, Coimbatore- 641 013. Applied Mathematics and Power Electronics CoursesDokument47 SeitenGovernment College Of Technology, Coimbatore- 641 013. Applied Mathematics and Power Electronics CoursesChamila SumathiratnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Relative Velocity Along Straight Lines ExplainedDokument4 SeitenRelative Velocity Along Straight Lines ExplainedChamila SumathiratnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJT) : NPN PNPDokument44 SeitenBipolar Junction Transistors (BJT) : NPN PNPAli AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- DiodeDokument24 SeitenDiodeChamila SumathiratnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6 Operating Characteristics Od Induction MotorDokument24 Seiten6 Operating Characteristics Od Induction MotorChamila SumathiratnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Asics OF Agnetism Lectromagnetism: Chamila Sumathiratna-Senior Lecturer Faculty of Industrial and Vocational TechnologyDokument29 SeitenAsics OF Agnetism Lectromagnetism: Chamila Sumathiratna-Senior Lecturer Faculty of Industrial and Vocational TechnologyChamila SumathiratnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effects of rotor resistance on induction motor torqueDokument31 SeitenEffects of rotor resistance on induction motor torquenovyjicinNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- 02 - MEE10603 - Fourier Series and Power Computations in Nonsinusoidally Driven CircuitsDokument33 Seiten02 - MEE10603 - Fourier Series and Power Computations in Nonsinusoidally Driven CircuitsMohammad HayazieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Partition WallDokument24 SeitenPartition WallSHRADDHA GHUGENoch keine Bewertungen
- Ejercicio para CompararDokument4 SeitenEjercicio para CompararCamila SarabiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- M103C 10/11 Meter Maximum Beam AntennaDokument9 SeitenM103C 10/11 Meter Maximum Beam AntennaRádio Técnica AuroraNoch keine Bewertungen
- pd1185 Fire CodeDokument3 Seitenpd1185 Fire CodeCamille MangaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- PBM and PBZ Crown Techniques ComparedDokument6 SeitenPBM and PBZ Crown Techniques ComparedDonanguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Air Sentry Guardian-BreathersDokument14 SeitenAir Sentry Guardian-BreathersNelson PeraltaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Interior Latex Semi-Gloss GL64XX: PremiumDokument2 SeitenInterior Latex Semi-Gloss GL64XX: PremiumVenkatesh SridharanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ijso 2012Dokument5 SeitenIjso 2012bhaskarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Silo Fluidizer: Keep Dry Bulk Materials MovingDokument2 SeitenSilo Fluidizer: Keep Dry Bulk Materials MovingHùng Thanh NguyễnNoch keine Bewertungen
- EJB 3.0 Final PreparedDokument243 SeitenEJB 3.0 Final PreparedjayavardhankotiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aniosyme DD1 SDSDokument6 SeitenAniosyme DD1 SDSSherwin CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kinematics Horizontal KinematicsDokument5 SeitenKinematics Horizontal KinematicsBaiJPNoch keine Bewertungen
- Squeeze Cementing TechniquesDokument22 SeitenSqueeze Cementing TechniquesDoni KurniawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reading 03 - Iron Lady The Eiffel TowerDokument2 SeitenReading 03 - Iron Lady The Eiffel TowerFernando Elías Valderrama GómezNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECE Lab ManualDokument95 SeitenECE Lab ManualranjithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diesel Engine: Service Parts List ForDokument49 SeitenDiesel Engine: Service Parts List ForIgnacio OsorioNoch keine Bewertungen
- 92v Parts List ViperDokument194 Seiten92v Parts List Viperreltih18Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud Radio Access Network Architecture Towards 5G NetworkDokument171 SeitenCloud Radio Access Network Architecture Towards 5G NetworkwobblegobbleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Capitulos 10 y 11Dokument34 SeitenCapitulos 10 y 11mlpz188669Noch keine Bewertungen
- Effect of Crystallinity On Electrical Properties of ElectronDokument4 SeitenEffect of Crystallinity On Electrical Properties of Electronapi-3837841Noch keine Bewertungen
- NHA 2430 Design Analysis Reporting FEADokument7 SeitenNHA 2430 Design Analysis Reporting FEAASIM RIAZNoch keine Bewertungen
- PM IS - 12818 June2021Dokument10 SeitenPM IS - 12818 June2021Mahendra AhirwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Physical GeologyDokument25 SeitenWhat Is Physical GeologyMelanyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Technical Information HANSA-FLEX Hose ConnectionsDokument75 SeitenTechnical Information HANSA-FLEX Hose ConnectionshorsanicuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Data Sheet: 49187073 E 1145842 1 of 1 October 21, 2016 60HzDokument1 SeiteEngineering Data Sheet: 49187073 E 1145842 1 of 1 October 21, 2016 60HzGustavo VillarrealNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oil GasDokument72 SeitenOil Gastony6868100% (1)
- System ConfigurationDokument13 SeitenSystem ConfigurationEdlyn Estopa BuenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2016 Popsicle Stick Bridge RulesDokument6 Seiten2016 Popsicle Stick Bridge RulesMahendra DewasiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acopos User's ManualDokument171 SeitenAcopos User's ManualKonstantin Gavrilov100% (1)