Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
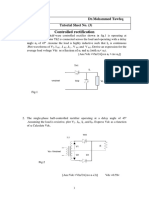
R and RC Firing Circuits
Hochgeladen von
Deepa Mary SobhaOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
R and RC Firing Circuits
Hochgeladen von
Deepa Mary SobhaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
RESISTANCE FIRING CIRUIT The resistance firing circuit is shown in figure. Here the gate current is supplied by an a.c.
source of voltage Vs through load, Rmin, R2, D and gate to cathode.R2 is a variable resistance used to vary the gate current and peak gate voltage Vgp.
The circuit operates as follows: As Vs goes positive, the SCR becomes forward biased from anode to cathode; however it starts conducting only when its gate current exceeds Ig(min) or when gate voltage Vg becomes Vgt. The positive voltage Vs also forward biases the diode D and the gate cathode junction of SCR. The gate current Ig starts to flow. The potentiometer setting R2 determines the gate voltage amplitude. When R2 is large, current Ig is small and the voltage across R, ie; Vg=IgR is also small as shown in figure. As peak gate voltage Vgp is less than gate trigger voltage Vgt SCR will not turn on. Therefore load voltage Vo=0, io=0and supply voltage appears across SCR (VT) as shown in figure. By decreasing the value of R2 the magnitude of gate current can be increased and when Vgp=Vgt the SCR will turn ON. As soon as Vg becomes equal to Vgt for first time SCR is turned on at a firing angle of 900. If R2 is decreased further gate current Ig will increase and Vg will increase above Vgt. This causes SCR triggerring at angles less than 900. When the SCR is on the voltage VT across it will reduce to almost zero. The load voltage will increase to the supply voltage. The SCR remains ON and Vo=Vs until Vs decreases to a point where the load current is below the SCR holding current. This usually occurs at wt=. The SCR now turns OFF and remains in OFF position as its anode to cathode is reverse biased when Vs is negative. SCR acts like a closed switch and load voltage will be zero.
The purpose of diode in the gate circuit is to prevent the gate-cathode reverse bias from exceeding peak reverse gate voltage during the negative half cycle of Vs. The diode is chosen to have peak reverse voltage rating greater than the input voltage Vmax. The same sequence is repeated when Vs again goes positive. Thus by varying R2 the firing angle() can be controlled from 00-900. As R increases increases. Design: Rmin: While varying R2 it should be taken care that the gate current should not exceed the maximum permissible gate current Igm. In the worst case, that is when supply voltage has reached its peak Vmax,
Stabilizing Resistance R: Resistance R should be such that maximum voltage drop across it does not exceed maximum permissible gate voltage Vgm.
( (
) )
The SCR will turn on only when the instantaneous anode voltage Vs is
( )(
Where ( ) = minimum gate current to turn on thyristor VD = voltage drop across diode Vgt= minimum gate voltage to trigger, it corresponds to Ig(min) Advantages: 1. It is the simplest and economical SCR triggering ciruit Disadvantages: 1. Firing angle range is limited in 0-900. 2. It is not possible to have zero degree firing angle, it can be brought near (20 40).
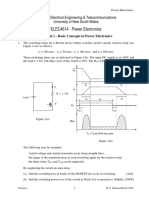
R-C TRIGGERRING CIRCUIT Figure shows a RC half wave trigger circuit. In this triggering circuit firing angle can be controlled from 00 1800 by changing the amplitude and phase of gate current. The circuit operates as follows: In the negative half cycle, capacitor C charges through diode D2 with lower plate positive to the peak supply voltage Vmax at wt=-900. After wt=900, source voltage Vs decreases from Vm to zero at wt=00.This causes the capacitor voltage Vc to fall from Vc= Vm to some lower value Vc=-oa at wt=00. Now as SCR anode voltage passes through zero and becomes positive, capacitor C begins to charge through variable resistance R from initial voltage Vc=-oa. When the capacitor charges to positive voltage equal to equal to gate trigger voltage Vgt(=Vgmin+Vd), SCR is triggered and after this ,capacitor holds to a mall positive voltage as shown in figure. The gate current flows through R, D1 and gate cathode. Diode D1 is used to prevent the breakdown of gate to cathode junction during the negative half cycle. Design: In the range of power frequencies it can be empirically shown that, RC for zero output voltage is given by
where
= period of ac line frequency in seconds.
The SCR will trigger when capacitor voltage Vc= Vgt+ Vd where Vd is the voltage drop across diode D1. With this voltage, gate current should be equal to Igmin. Therefore the maximum value of R can be obtained as
( )
By using this circuit firing angle can be varied from 00 to 1800.
UJT TRIGGERRING UJT Working:
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Power Electronics PPT by Atul Kumar PrajapatiDokument13 SeitenPower Electronics PPT by Atul Kumar Prajapatishadan alamNoch keine Bewertungen
- R RC Triggering of SCRDokument8 SeitenR RC Triggering of SCRRahulDas100% (2)
- 3) RC Half & Full Wave Firing Circuit - RFCDokument8 Seiten3) RC Half & Full Wave Firing Circuit - RFCPradeep KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gate Firing Circuits For SCR'S R-C Triggering CircuitDokument3 SeitenGate Firing Circuits For SCR'S R-C Triggering CircuitB ANIL KUMARNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment:-7 Aim: To Study The Operation of Resistance Firing Circuit Using R, RC & UJT Firing Module. ApparatusDokument6 SeitenExperiment:-7 Aim: To Study The Operation of Resistance Firing Circuit Using R, RC & UJT Firing Module. ApparatusNikhil BindalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Triangular Wave Generator Using Op Amp - WaveformsDokument6 SeitenTriangular Wave Generator Using Op Amp - WaveformsNagendrababu VasaNoch keine Bewertungen
- EXP17 Class A Power AmplifierDokument3 SeitenEXP17 Class A Power AmplifierMohammed Dyhia AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Submitted By: Rameshkumar Lakshmi Prabha Abirami R LoganandhiniDokument22 SeitenSubmitted By: Rameshkumar Lakshmi Prabha Abirami R LoganandhiniAbirami RajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indus Lab Exp 1Dokument12 SeitenIndus Lab Exp 1plokplokplokNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 3 Tuned AmplifierDokument89 SeitenUnit 3 Tuned Amplifiermohan100% (1)
- RC Phase Shift OscillatorDokument8 SeitenRC Phase Shift OscillatorSiva Narayanan67% (3)
- RC Phase Shift OscillatorDokument3 SeitenRC Phase Shift Oscillatoreseses100% (1)
- Exp No 06 Controlled HWER and FWRDokument4 SeitenExp No 06 Controlled HWER and FWRManjuanth100% (1)
- 1.RC CircuitsDokument7 Seiten1.RC CircuitsNaveen ChNoch keine Bewertungen
- IC 723 Voltage RegulatorsDokument16 SeitenIC 723 Voltage RegulatorsAtheessh .B0% (1)
- 3 Phase Fully Controlled RectifierDokument4 Seiten3 Phase Fully Controlled RectifierSpk Sudhin100% (1)
- Single Phase Series and Parallel Inverter FinalDokument19 SeitenSingle Phase Series and Parallel Inverter Finalmazza23467% (3)
- Network AnalysisDokument22 SeitenNetwork AnalysisShravan Kumar NamdeoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Square Wave GeneratorDokument6 SeitenSquare Wave GeneratorRahul KunduNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trransistor Switching TimesDokument6 SeitenTrransistor Switching TimesManjot KaurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment No:9: Op-Amp As A DifferentiatorDokument2 SeitenExperiment No:9: Op-Amp As A DifferentiatorBhadresh Renuka100% (1)
- TEE3211 DrivesDokument126 SeitenTEE3211 DrivesWebster Fungirai100% (1)
- 8251A USART - Programmable Communication InterfaceDokument15 Seiten8251A USART - Programmable Communication InterfaceselvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- RC Time ConstantDokument2 SeitenRC Time ConstantJunaid AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pe Tutorial 3 - 2 PDFDokument13 SeitenPe Tutorial 3 - 2 PDFkibrom atsbhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Single Phase and Three Phase Rectifiers NumericalsDokument71 SeitenSingle Phase and Three Phase Rectifiers Numericalsaryan singhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diode Clippers: 1. Positive Clipper and Negative ClipperDokument6 SeitenDiode Clippers: 1. Positive Clipper and Negative ClipperBibek ThapaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zero Crossing Detector and Window DetectorDokument7 SeitenZero Crossing Detector and Window DetectorTimoth Dev50% (2)
- AEC Lab ManualDokument75 SeitenAEC Lab Manualphalanetra100% (1)
- AC DC Analysis BJT Diffrential Amp PDFDokument8 SeitenAC DC Analysis BJT Diffrential Amp PDFtanishk jainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Precision Rectifier CircuitsDokument13 SeitenPrecision Rectifier CircuitsWaqas PervaizNoch keine Bewertungen
- AE08 SolDokument175 SeitenAE08 SolDilpalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 180 & 120 Degree Conduction Mode InverterDokument27 Seiten180 & 120 Degree Conduction Mode Invertersuriyamariappan80% (5)
- Name of The Experiment-Design & Simulation of Differentiator Amplifier Using 741 Op-Amp IC. Instrument/ Components Required - Proteus Simulator. TheoryDokument3 SeitenName of The Experiment-Design & Simulation of Differentiator Amplifier Using 741 Op-Amp IC. Instrument/ Components Required - Proteus Simulator. TheoryBidyut Prasad dalai100% (1)
- BJTDokument6 SeitenBJTengineerluvNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8051 Microcontroller Module 5 NotesDokument27 Seiten8051 Microcontroller Module 5 Notesrakesh rakiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circular Loop AntennaDokument23 SeitenCircular Loop AntennaEC19B1042- Pendurthy Bhavana100% (1)
- Expt No: 1 Mode Characteristics of Reflex Klystron 1.1 ObjectiveDokument6 SeitenExpt No: 1 Mode Characteristics of Reflex Klystron 1.1 ObjectivePriya DarshuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 2 - Iduction Motor Drive Using Slip Power RecoveryDokument6 SeitenExperiment 2 - Iduction Motor Drive Using Slip Power RecoveryDeepak BansalNoch keine Bewertungen
- EEM328 Electronics Laboratory - Experiment 6 - FET and FET BiasingDokument4 SeitenEEM328 Electronics Laboratory - Experiment 6 - FET and FET Biasingdonatello84100% (1)
- Analog Electronics Module-2Dokument15 SeitenAnalog Electronics Module-2Sourabh HalagekarNoch keine Bewertungen
- TWO STAGE RC Coupled AmplifierDokument3 SeitenTWO STAGE RC Coupled Amplifierfarzana kousar100% (1)
- Power Electronics & Drives: Unit: 1 Power Semiconductor DevicesDokument24 SeitenPower Electronics & Drives: Unit: 1 Power Semiconductor DevicesTapobroto ChatterjeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture ThyristorsDokument38 SeitenLecture ThyristorsHamza Saeed AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Questions On Small Signal Model of AmpDokument2 SeitenQuestions On Small Signal Model of AmpdevsrivastavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Half Wave and Full Wave RectifierDokument8 SeitenHalf Wave and Full Wave Rectifierbolbo naNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 12 Assignment SolutionsDokument5 SeitenWeek 12 Assignment SolutionsDeep Gandhi100% (1)
- Single Tuned Amplifier: Experiment:5Dokument2 SeitenSingle Tuned Amplifier: Experiment:5hari007kmrNoch keine Bewertungen
- IntegratorDokument38 SeitenIntegratorSyed AshmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment# 10: Measure The Power and Power Factor by Three Ammeter MethodDokument10 SeitenExperiment# 10: Measure The Power and Power Factor by Three Ammeter MethodFarwa MunirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment - 05Dokument17 SeitenExperiment - 05Sagar SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parallel Capacitor Inverter With Feedback DiodesDokument9 SeitenParallel Capacitor Inverter With Feedback DiodesJayant Kirpekar100% (1)
- Tutorial 1 - Basic Concepts in Power ElectronicsDokument7 SeitenTutorial 1 - Basic Concepts in Power ElectronicsJohn Appleseed100% (1)
- Diode Limiters and Clampers ReportDokument19 SeitenDiode Limiters and Clampers ReportMG Acdal PagulonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Light Intensity ControlDokument8 SeitenLight Intensity ControlRaman GargNoch keine Bewertungen
- Frequency and Phase Measurement With Lissajous Patterns .Dokument9 SeitenFrequency and Phase Measurement With Lissajous Patterns .Ali Naseeb67% (3)
- Eee-III-Analog Electronic Circuits (15ee34) - SolutionDokument48 SeitenEee-III-Analog Electronic Circuits (15ee34) - SolutionchaitanyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Firing Circuits of Thyristor or SCRDokument10 SeitenFiring Circuits of Thyristor or SCRdivakar r vlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Electronics Lab Demo NADokument155 SeitenPower Electronics Lab Demo NAsoumyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Idoc - Pub - R RC Triggering of SCR PDFDokument8 SeitenIdoc - Pub - R RC Triggering of SCR PDFPratik SarkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microcontroller Based Water Level IndicatorDokument46 SeitenMicrocontroller Based Water Level IndicatorSurabhi Sadavat0% (1)
- Ds Asi A2si Lite Rev2Dokument22 SeitenDs Asi A2si Lite Rev2api-3725139Noch keine Bewertungen
- Free Energy, Gravity and The Aether 101897Dokument17 SeitenFree Energy, Gravity and The Aether 101897Auro Tanaka100% (3)
- Difference Between Unearthed CableDokument14 SeitenDifference Between Unearthed CableArnab GhoshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emergency LightDokument46 SeitenEmergency Lightfunkisanju1Noch keine Bewertungen
- (Electrochemical) Impedance SpectrosDokument37 Seiten(Electrochemical) Impedance Spectrosamlandas08Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fuel Cell 10 KW Inverter SystemDokument60 SeitenFuel Cell 10 KW Inverter Systemismailbej100% (1)
- Av74 0008Dokument23 SeitenAv74 0008Franco PugaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sams Understanding Capacitors and Their Uses 1964 MullinDokument95 SeitenSams Understanding Capacitors and Their Uses 1964 MullinWasim KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2010 Me 105Dokument11 Seiten2010 Me 105Omer NadeemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mini Project Synopsis On: "Geyser Timer Circuit"Dokument13 SeitenMini Project Synopsis On: "Geyser Timer Circuit"Shikhar BajpaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- AlepDokument10 SeitenAlepMiz AelyfhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Service Manual: IndexDokument20 SeitenService Manual: IndexJose Luis AparicioNoch keine Bewertungen
- EC6401 Electronics Circuits II - Notes - AnnaunivupdatesDokument96 SeitenEC6401 Electronics Circuits II - Notes - Annaunivupdatesmanimangai100% (2)
- Application Note 106 February 2007 Instrumentation Circuitry Using RMS-to-DC ConvertersDokument20 SeitenApplication Note 106 February 2007 Instrumentation Circuitry Using RMS-to-DC ConvertersHahdNoch keine Bewertungen
- LonWorks FTT-10A Free Topology Transceiver User's GuideDokument91 SeitenLonWorks FTT-10A Free Topology Transceiver User's GuideGabor KomuvesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sensor KapasitifDokument5 SeitenSensor KapasitifMuizzuddin RosliNoch keine Bewertungen
- SFF1001G THRU SFF1008G: Isolation 10.0 AMPS. Glass Passivated Super Fast RectifiersDokument2 SeitenSFF1001G THRU SFF1008G: Isolation 10.0 AMPS. Glass Passivated Super Fast RectifiersSamvel KhachatryanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Keeley CompressorDokument2 SeitenKeeley Compressorpyreal100% (3)
- Power Quality Solution Key ComponentsDokument56 SeitenPower Quality Solution Key ComponentsMNSanthoshKumarRajuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elec 321 - 3Dokument6 SeitenElec 321 - 3Nur Alam ChowdhuryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Generation of High Voltage and CurrentDokument14 SeitenGeneration of High Voltage and CurrentpriyadarshniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Catalogo Contatores MTDokument56 SeitenCatalogo Contatores MTwillvinNoch keine Bewertungen
- IC318VNUDokument4 SeitenIC318VNUlachitprojectsalesNoch keine Bewertungen
- As 60044.5-2004 Instrument Transformers Capacitor Voltage TransformersDokument10 SeitenAs 60044.5-2004 Instrument Transformers Capacitor Voltage TransformersSAI Global - APAC100% (1)
- CP CR500 User ManualDokument44 SeitenCP CR500 User ManualRaúl MendozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ijireeice 21Dokument5 SeitenIjireeice 21Mufid SyedNoch keine Bewertungen
- 00001334B PDFDokument30 Seiten00001334B PDFJly JlyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Concepts of Linear Regulator and Switching Mode Power Supplies PDFDokument16 SeitenBasic Concepts of Linear Regulator and Switching Mode Power Supplies PDFmjam100Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fire on the Horizon: The Untold Story of the Gulf Oil DisasterVon EverandFire on the Horizon: The Untold Story of the Gulf Oil DisasterNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Journeyman Electrician Exam Study Guide: Proven Methods for Successfully Passing the Journeyman Electrician Exam with ConfidenceVon EverandThe Journeyman Electrician Exam Study Guide: Proven Methods for Successfully Passing the Journeyman Electrician Exam with ConfidenceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electric Motor Control: DC, AC, and BLDC MotorsVon EverandElectric Motor Control: DC, AC, and BLDC MotorsBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (19)
- Well Integrity for Workovers and RecompletionsVon EverandWell Integrity for Workovers and RecompletionsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (3)
- Air Cooled Heat Exchanger Handbook: Fundamentals, Calculations, Design and Q&AVon EverandAir Cooled Heat Exchanger Handbook: Fundamentals, Calculations, Design and Q&ANoch keine Bewertungen
- Building Energy Management Systems and Techniques: Principles, Methods, and ModellingVon EverandBuilding Energy Management Systems and Techniques: Principles, Methods, and ModellingNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Complete HVAC BIBLE for Beginners: The Most Practical & Updated Guide to Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning Systems | Installation, Troubleshooting and Repair | Residential & CommercialVon EverandThe Complete HVAC BIBLE for Beginners: The Most Practical & Updated Guide to Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning Systems | Installation, Troubleshooting and Repair | Residential & CommercialNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionVon EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Power of Habit: The Ultimate Guide to Forming Positive Daily Habits, Learn How to Effectively Break Your Bad Habits For Good and Start Creating Good OnesVon EverandPower of Habit: The Ultimate Guide to Forming Positive Daily Habits, Learn How to Effectively Break Your Bad Habits For Good and Start Creating Good OnesBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (21)
- Idaho Falls: The Untold Story of America's First Nuclear AccidentVon EverandIdaho Falls: The Untold Story of America's First Nuclear AccidentBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (21)
- Electric Motors and Drives: Fundamentals, Types and ApplicationsVon EverandElectric Motors and Drives: Fundamentals, Types and ApplicationsBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (12)
- Shorting the Grid: The Hidden Fragility of Our Electric GridVon EverandShorting the Grid: The Hidden Fragility of Our Electric GridBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (2)
- Well Control for Completions and InterventionsVon EverandWell Control for Completions and InterventionsBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (10)
- Oil companies and the energy transitionVon EverandOil companies and the energy transitionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Renewable Energy Finance: Theory and PracticeVon EverandRenewable Energy Finance: Theory and PracticeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- Solar Energy: Survive Easily on Solar Power Off the GridVon EverandSolar Energy: Survive Easily on Solar Power Off the GridNoch keine Bewertungen
- Global Landscape of Renewable Energy FinanceVon EverandGlobal Landscape of Renewable Energy FinanceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermal Power Plant: Design and OperationVon EverandThermal Power Plant: Design and OperationBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (23)
- Handbook on Battery Energy Storage SystemVon EverandHandbook on Battery Energy Storage SystemBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (2)
- Flow Analysis for Hydrocarbon Pipeline EngineeringVon EverandFlow Analysis for Hydrocarbon Pipeline EngineeringNoch keine Bewertungen
- Life Cycle Assessment: Principles, Practice and ProspectsVon EverandLife Cycle Assessment: Principles, Practice and ProspectsNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Homeowner's DIY Guide to Electrical WiringVon EverandThe Homeowner's DIY Guide to Electrical WiringBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (2)
- Electric Powertrain: Energy Systems, Power Electronics and Drives for Hybrid, Electric and Fuel Cell VehiclesVon EverandElectric Powertrain: Energy Systems, Power Electronics and Drives for Hybrid, Electric and Fuel Cell VehiclesNoch keine Bewertungen