Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
f5c4 Exer
Hochgeladen von
jalrizal7Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
f5c4 Exer
Hochgeladen von
jalrizal7Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
1.
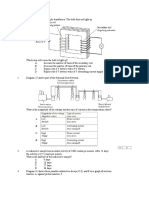
Which of the following is not a property of cathode rays? A. It is positively charged. B. It travels in a straight line. C. It can be deflected by magnetic field. D. It can be deflected by electric field. Cathode rays consists of A. Fluorescent particles B. Light rays from a screen C. Beams of fast moving particles D. Light rays from hot filament
8.
B. The semiconductor becomes an n-type. C. The majority charge carrier is electron. D. Atom P is a trivalent atom. The figure 9.36 shows a rectifier circuit. Which of the following statements is true?
2.
P Q
3.
A beam of electrons is being deflected due to a potential difference between plates P and Q.
A. B. C. D. 9.
A rectifier changes d.c to a.c. Device P allows current to flow in any directions. Device Q acts as a rectifier. The rectifier circuit would still work if device P is reversed.
Which of the following statements is not true? A. B. C. D. The potential at plate P is positive. The deflection would be greater if the potential difference is greater. The deflection would be greater if the electrons are moving faster. The electron beam will return to straight line if a suitable magnetic field is applied between the plates.
The figure 9.37 shows a circuit consisting of two diodes and a bulb. When the switch is on, the bulb does not light up. What needs to be done to light up the bulb?
4.
The figure below shows the trace displayed on a CRO with the Y-gain control is turned to 3.75 V/div. What is the maximum value of the potential difference being measured?
A. B. C. D. 10.
Replace the diode with a new one. Reverse the connection of the diode. Increase the number of bulbs. Connect a resistor in series with the bulb.
A. B. C. D. E. 5.
2.5 V 5.5 V 7.5 V 12.5 V 15.0 V
Figure 9.38 shows four identical bulbs, P, Q, R and S, and four electronic components connected in a circuit. Which of the following bulbs will light up continuously when the switch is on? A. B. C. D. P and Q only P, Q and R only R and S only P, Q and S only
In p-type semiconductor A. The number of holes is equal to the number of electrons. B. The number of the holes is more than the number of electrons. C. The number of the holes is less than the number of electrons.
6.
Which of the following is not true about diode? A. It can be used to rectify alternating current. B. It can only conduct electricity when it is connected in forward in forward bias in a circuit. C. It is formed by joining an n-type and a p-type semiconductor. D. The majority charge carriers in the diode are electrons.
11. Which of the following circuits shows the connect directions of the base current IB, emitter current, IE and collector current, IC?
7.
The figure below shows the arrangement of silicon atoms after an atom P is doped to form an extrinsic semiconductor.
Which of the following is not true? A. The conductivity of the semiconductor increases.
Page | 1
12. Which of the following statements about a transistor is not true? A. A transistor can act as an amplifier B. A transistor can act as a relay switch. C. The function of a transistor is the same as that of two diodes. D. A transistor is a combination of two types of semiconductors.
M- Microphone C- Capacitor
Which of the following is not correct about the circuit? Figure 9.39 A. B. C. D. T is an npn transistor The capacitor prevents d.c current but allows a.c current to pass through it. Speaker amplifies the sound. R1 and R2 act as potential divider.
13. What is the function of the transistor circuit shown in figure 9.39? A. As an amplifier B. As a rectifier C. As a switch device D. As a modulator 14. The figure 9.40 shows a transistor being used as a current amplifier.
17. The figure below shows a logic gate circuit with input signals, X and Y.
IB
IC
Which of the following is the output signal?
Figure 9.40 Which of the following is correct? A. B. C. IB > IC IB = IC IB < IC 18. The figure below shows a logic gate circuit.
15. Figure 9.41 shows a circuit consisting of a transistor which acts as an automatic switch. When the potential difference across the thermistor is 3 V and the resistance of the thermistor is 1000 , the resistance value of resistor, R is ..
Which of the following is the output signal Z? A. B. C. D. 0110 1010 1110 0101
19. The figure below shows the combination of three logic gates.
A. B. C. D. E.
3 4 5 6 7
k k k k k
The truth table for the combination of tree logic gates is as follows. What is gate X? A. B. C. D. AND NOR OR NAND
16. The figure below show a transistor circuit being used to amplify sound.
20. The figure below show a combination of three logic gates in a logic circuit. When inputs P and Q are both 1 output Y is 1.
Page | 2
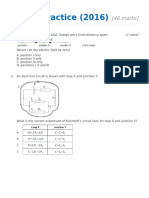
2. Which of the following logic gates can be used to represent J and K?
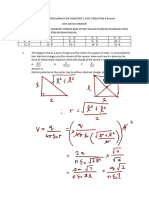
Figure 9. 47 show a full wave bridge rectifier. The a.c supply has a frequency of 50 Hz.
1.
Figure 9.46 shows a trace obtained on an oscilloscope screen when an a.c voltage is connected to the Y-plates of an oscilloscope. Scale: 1 division = 1 cm The Y-gain is set at 3 V/cm The time base is set at 5 ms/cm
(a) When the polarity of the a.c supply voltage is positive at
A, state the two diodes which are forward biased.
(b) When the polarity of the a.c supply voltage is negative at
A, state the two diodes which are forward biased.
(c)
Using the axes in figure 9.48, sketch the voltage-time graph across the resistor, R.
(a) Explain what is meant by thermionic emission.
(b) Determine the peak voltage of a.c voltage.
(c) Determine the time for one complete oscillation on the screen.
(d) What is the frequency of the a.c voltage?
(e) With the same a.c voltage applied to the oscilloscope, the time-base setting is altered to 2.5 ms/cm and the Y-gain setting is altered to 2 V/cm. On the space below, sketch the new trace would appear on the oscilloscope.
Page | 3
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- 2223 - Physics-Level M-CHAPTER5-Term 2Dokument10 Seiten2223 - Physics-Level M-CHAPTER5-Term 2MyNameIsYeetNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial Chapter 4: Electronics: A. B. C. D. EDokument8 SeitenTutorial Chapter 4: Electronics: A. B. C. D. EMohamad Rizal MukhtarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9702 p1 Current Electricity All MCQDokument35 Seiten9702 p1 Current Electricity All MCQNafi Ul Kaysar50% (2)
- Paper 1 Final Raw Source & MsDokument13 SeitenPaper 1 Final Raw Source & MsDewan Olin ChotepadaeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trialstpm 2022 Pahang P2 QuestionDokument13 SeitenTrialstpm 2022 Pahang P2 QuestionASANAMMAH NACHIAR A/P PAKEER MOHAMED MoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trial STPM Physics Term 2 - Module 1Dokument12 SeitenTrial STPM Physics Term 2 - Module 1annahiaz0% (1)
- Electric Circuits and Electron Devices Unit I Circuit Analysis Techniques Part-ADokument8 SeitenElectric Circuits and Electron Devices Unit I Circuit Analysis Techniques Part-ASalai Kishwar JahanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Questions Physics 2 Lab 22-23Dokument17 SeitenSample Questions Physics 2 Lab 22-23Tany TurkiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electricity 1Dokument12 SeitenElectricity 1saeed akhtarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lat2 2013Dokument11 SeitenLat2 2013Faizah Nur ZaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SSC Je Paper 2016 Electrical EnggDokument10 SeitenSSC Je Paper 2016 Electrical EnggrvrsantoshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 9: Electronic Devices: Question BankDokument4 SeitenUnit 9: Electronic Devices: Question BankNathanianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trialstpm 2022 Dato Mansor P2 AnswerDokument16 SeitenTrialstpm 2022 Dato Mansor P2 AnswerASANAMMAH NACHIAR A/P PAKEER MOHAMED MoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- NAS QuizDokument11 SeitenNAS QuizsubodhNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCQN M1Dokument45 SeitenMCQN M1Max HudgenesNoch keine Bewertungen
- TRIAL STPM P2 2016 With AnswerDokument16 SeitenTRIAL STPM P2 2016 With AnswerdarwishmajidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ice Elecs 8 QueDokument4 SeitenIce Elecs 8 QueJojo TakatoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electricity 12-01Dokument13 SeitenElectricity 12-01nguyentrongtinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Benchmark Exam #4 2010-2011Dokument11 SeitenPhysics Benchmark Exam #4 2010-2011Claudia HuoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Questions On LCR CircuitDokument2 SeitenQuestions On LCR CircuitKRISHNA PARIHARNoch keine Bewertungen
- Previous Year Board Exam Questions (2007-2016) : Semiconductor DevicesDokument13 SeitenPrevious Year Board Exam Questions (2007-2016) : Semiconductor DevicesRishabh AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- SemiconductorsDokument11 SeitenSemiconductorsKoyal GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronic Devices and Circuits Part 2Dokument9 SeitenElectronic Devices and Circuits Part 2Renz Benhar Ocon BobadillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Test 02-02-12 Final 12Dokument13 SeitenPhysics Test 02-02-12 Final 12Dewan Olin ChotepadaeNoch keine Bewertungen
- G-Cakna Kelantan 2015 - Physics Term 2 - Module 2Dokument12 SeitenG-Cakna Kelantan 2015 - Physics Term 2 - Module 2annahiazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronic Devices and Circuits3 PDFDokument9 SeitenElectronic Devices and Circuits3 PDFRenz Benhar Ocon BobadillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12 Physics SP CbseDokument20 Seiten12 Physics SP CbsePrachi DwivediNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trial P2 2018Dokument9 SeitenTrial P2 2018danialNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12th Physics B-5Dokument10 Seiten12th Physics B-5Riya KakaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- JM Coaching: Pre Mock TestDokument14 SeitenJM Coaching: Pre Mock TestDewan Olin ChotepadaeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elec Exam StandDokument14 SeitenElec Exam StandDaveyNoch keine Bewertungen
- trialstpm2017SMKTSKL P2 SoalanDokument10 Seitentrialstpm2017SMKTSKL P2 SoalanNurul BalkhisNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE Online SAEx 2 1 PDFDokument6 SeitenEE Online SAEx 2 1 PDFJunnar Jay AbañoNoch keine Bewertungen
- SPM Physics Summative Test 2 - Form 5 Chapter 2 and 3Dokument8 SeitenSPM Physics Summative Test 2 - Form 5 Chapter 2 and 3Winnie Lim Li Sze0% (1)
- Electrician TestDokument39 SeitenElectrician TestSaroh Lim92% (78)
- Test 5 - Potential and Circuits - BlankDokument8 SeitenTest 5 - Potential and Circuits - Blankandrey pradoNoch keine Bewertungen
- IT Phy F5 Topical Test 2 (BL)Dokument12 SeitenIT Phy F5 Topical Test 2 (BL)Jeemion JealiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic-Model For Communication StreamDokument19 SeitenBasic-Model For Communication StreamERMIAS AmanuelNoch keine Bewertungen
- AP EM FRQ-2aDokument7 SeitenAP EM FRQ-2aHansom boyzNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECE Mock Board Exam April 2022 ElectronicsDokument7 SeitenECE Mock Board Exam April 2022 Electronicsx8t2w5ngjcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 5 Practice (2016) : (46 Marks)Dokument13 SeitenTopic 5 Practice (2016) : (46 Marks)Palaash GoyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 7 Ac Worksheet 2022Dokument5 SeitenCH 7 Ac Worksheet 2022Hamad FarooqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- E-Note 12425 Content Document 20231105014816AMDokument6 SeitenE-Note 12425 Content Document 20231105014816AMkartik.doye2005Noch keine Bewertungen
- AEC Objective Question and AnswerDokument35 SeitenAEC Objective Question and AnswerGanesan KandasamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- PQ - Current Electricty 150Dokument18 SeitenPQ - Current Electricty 150dongoke2019Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ee1 Ece 500Dokument7 SeitenEe1 Ece 500Karen Gale A. Lodia - AlarconNoch keine Bewertungen
- Apllied Electric Circuit Objective Question and AnswerDokument42 SeitenApllied Electric Circuit Objective Question and AnswerGanesan KandasamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Semiconductor Electronics: Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits 1 Marks QuestionsDokument17 SeitenSemiconductor Electronics: Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits 1 Marks QuestionsTuition MasterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronics MCQ'sDokument66 SeitenElectronics MCQ'shassan0% (2)
- 1 Nov, David 9 Penabur 7Dokument5 Seiten1 Nov, David 9 Penabur 7Faber O.MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5 Past Paper (2017-2022)Dokument76 SeitenChapter 5 Past Paper (2017-2022)saba falahNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12 Physics sp02 PDFDokument25 Seiten12 Physics sp02 PDFaditya prabhakerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analog, Digital and Power Electronics 100 Important MCQsDokument13 SeitenAnalog, Digital and Power Electronics 100 Important MCQsHamdam NazarovNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ib Physics SL - Unit 4 ReviewDokument46 SeitenIb Physics SL - Unit 4 ReviewMax HudgenesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Majorship TLE ElectronicsDokument12 SeitenMajorship TLE ElectronicsAnonymous gijMJlwS6Noch keine Bewertungen
- 12th FileDokument3 Seiten12th FileshiviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2019-2023)Von EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2019-2023)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Set K2Dokument2 SeitenSet K2jalrizal7Noch keine Bewertungen
- Nature of MatterDokument1 SeiteNature of Matterjalrizal7Noch keine Bewertungen
- Trra,: Fgns+rn+fi. ($KLRNDokument17 SeitenTrra,: Fgns+rn+fi. ($KLRNjalrizal7Noch keine Bewertungen
- F 5 C 2Dokument14 SeitenF 5 C 2jalrizal7Noch keine Bewertungen
- F 4 C 3Dokument19 SeitenF 4 C 3jalrizal7Noch keine Bewertungen
- F 4 C 4Dokument3 SeitenF 4 C 4jalrizal7Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chem c2 Exer1Dokument3 SeitenChem c2 Exer1jalrizal7Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chai Sing4Dokument4 SeitenChai Sing4jalrizal7Noch keine Bewertungen
- c4c8 Exer1Dokument2 Seitenc4c8 Exer1jalrizal7Noch keine Bewertungen
- KPMT - Bi - 2013Dokument3 SeitenKPMT - Bi - 2013jalrizal7Noch keine Bewertungen
- 4 Simultaneous Equations MajuDokument3 Seiten4 Simultaneous Equations Majujalrizal7Noch keine Bewertungen
- Brushless Excitation SystemDokument27 SeitenBrushless Excitation SystemSam100% (2)
- Pub20 PDFDokument402 SeitenPub20 PDFfaridNoch keine Bewertungen
- MST 2Dokument4 SeitenMST 2Neha Prashant VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Practicals 1 and 2Dokument184 SeitenPhysics Practicals 1 and 2Zahid ArainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Porter GovernorDokument36 SeitenPorter GovernorAnnish Stanly Dhas50% (2)
- 07915a0208 - BBTDokument20 Seiten07915a0208 - BBTvenky123456789Noch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Engineering: MSC Full-Time CourseDokument17 SeitenElectrical Engineering: MSC Full-Time CourseFabiano Bezerra BezerraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter-II-Resultant-of-a-Force-2.6-2.7-2.8 (1) B273 LrcturesDokument6 SeitenChapter-II-Resultant-of-a-Force-2.6-2.7-2.8 (1) B273 LrcturesMickyleee ChannelNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Resistance and Resistivity - 1Dokument9 Seiten2 Resistance and Resistivity - 1Genesis MenesesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abstract Book PDFDokument252 SeitenAbstract Book PDFPABLO MAURONoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Current Electricity MCQDokument7 SeitenPhysics Current Electricity MCQHimanshu VasisthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design and Simulation of Flyback Converter in MATLAB Using PID ControllerDokument6 SeitenDesign and Simulation of Flyback Converter in MATLAB Using PID ControllerSkp FANoch keine Bewertungen
- Suction Cups/grippers: BFF40P, BFF60P, BFF80P, BFF110PDokument2 SeitenSuction Cups/grippers: BFF40P, BFF60P, BFF80P, BFF110PBe HappyNoch keine Bewertungen
- ALL QB's PDFDokument36 SeitenALL QB's PDFanimesh0gargNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integrator Information V2.8.2-131-Gf324cd6e2, 2022-05-28Dokument17 SeitenIntegrator Information V2.8.2-131-Gf324cd6e2, 2022-05-28Juan Carlos LesmasNoch keine Bewertungen
- H2 Physics J2 CT1 2013 Paper 2 SolutionsDokument10 SeitenH2 Physics J2 CT1 2013 Paper 2 SolutionsMichael LeungNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project ReportDokument53 SeitenProject ReportMUDAM ALEKYANoch keine Bewertungen
- ECT2000 English+MANUAL PDFDokument27 SeitenECT2000 English+MANUAL PDFHector DiazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Connector: 1.2mm Pitch/disconnectable Crimp Style ConnectorsDokument2 SeitenConnector: 1.2mm Pitch/disconnectable Crimp Style ConnectorsTrần Long VũNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of HVDC and FACTS Devices: Lecture NotesDokument22 SeitenFundamentals of HVDC and FACTS Devices: Lecture NotesKiran KunchamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Statement Manufacturer and Authorization Regarding ApplicationDokument19 SeitenStatement Manufacturer and Authorization Regarding Application200607807100% (1)
- An Intelligent Control Method For Performance Improvement of PMSMDokument59 SeitenAn Intelligent Control Method For Performance Improvement of PMSMDivyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- General ScienceDokument46 SeitenGeneral ScienceJosepino JosepinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- B503D Series: Sensorless Vector Control Controller Instruction ManualDokument108 SeitenB503D Series: Sensorless Vector Control Controller Instruction Manualnofal ali0% (1)
- IEEE ReclosingDokument55 SeitenIEEE ReclosinglearningalotNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Question Paper - Acadecraft !Dokument8 SeitenPhysics Question Paper - Acadecraft !Amit Shrivastava100% (1)
- 2 - Low-Speed CommissioningDokument20 Seiten2 - Low-Speed CommissioningQuang Pham DuyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fanning Friction FactorDokument1 SeiteFanning Friction Factorrelicario25Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gek ManualDokument36 SeitenGek Manualicaro100% (1)
- Lab Report Series and Parallel Circuits by Praewa 1108 4Dokument13 SeitenLab Report Series and Parallel Circuits by Praewa 1108 4api-439639600Noch keine Bewertungen