Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Trig Sum Difference
Hochgeladen von
aaoneOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Trig Sum Difference
Hochgeladen von
aaoneCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
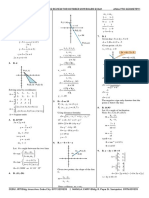
Trigonometric Sum and Difference Theorems 1.
Prove the Basic Formula (The Formula for Cosine of a Difference)
(cos, sin ) A A O (0, 0) B (cos , sin )
Consider any 2 points, A and B, on the unit circle. The radius segments to these points form angles of measure and measure as shown in the figure. Point O(0, 0) is at the origin and the center of the unit circle. Since points A and B are on the unit circle, we know their coordinates to be: A(cos , sin ) and B(cos , sin ) In the triangle OB = OA = 1, since the radius of the unit circle is 1. By the Distance Formula: AB = (cos - cos )2 + (sin - sin )2
(AB)2 = (cos - cos )2 + (sin - sin )2 (AB)2 = cos2 - 2 cos cos + cos2 + sin2 - 2 sin sin + sin2 (AB)2 = 2 - 2(cos cos + sin sin ) By the Law of Cosines: (AB)2 = (OA)2 + (OB)2 - 2(OA)(OB) cos( - ) (AB)2 = 1 + 1 - 2 1 1 cos( - ) (AB)2 = 2 - 2 cos( - ) Since both of the above equations have (AB)2 on the left, then we can say: 2 - 2 cos( - ) = 2 - 2(cos cos + sin sin ) Subtracting 2 from both sides, then dividing both sides by -2, we get: cos( - ) = cos cos + sin sin Q.E.D.
2. Prove that cosine is an even function: ie cos(-x) = cos x
cos(-x) = cos(0 - x) = cos 0 cos x + sin 0 sin x = 1 * cos x + 0 * sin x = cos x + 0 = cos x Q.E.D.
3. Prove the formula regarding the cosine cos ( /2 - x) = cos ( /2) cos x + sin ( /2) sin x of a compliment. = 0 * cos x + 1 * sin x = 0 + sin x = sin x Q.E.D. 4. Prove the formula regarding the sine of a complement. sin ( /2 - x) = cos [ /2 - ( /2 - x)] = cos [( /2 - /2) + x] = cos x Q. E. D. sin (-x) = cos [ /2 - (-x)] = cos ( /2 + x) = cos (- /2 - x) = cos (- /2) cos x + sin (- /2) sin x = 0 cos x - 1 sin x = - sin x Q. E. D. cos (x + y) = cos (x - -y) = cos x cos (-y) + sin x sin (-y) = cos x cos y - sin x sin y Q. E. D. 7. Prove the formula for sine of a sum. sin (x + y) = cos [ /2 - (x + y)] = cos [( /2 - x) - y] = cos ( /2 - x) cos y + sin ( /2 - x) sin y = sin x cos y + cos x sin y Q. E. D. 8. Prove the formula for the sine of a difference. sin (x - y) = sin [x + (-y)] = sin x cos (-y) + cos x sin (-y) = sin x cos y - cos x sin y Q. E. D.
5. Prove that sine is an odd function.
6. Prove the formula for cosine of a sum.
9. Prove the formula for tangent of a sum.
10 Prove the formula for tangent of a . difference.
sin(x + y) tan(x + y) = cos(x + y) sin x cos y + cos x sin y = cos x cos y - sin x sin y sin x cos y + cos x sin y cos x cos y = cos x cos y - sin x sin y cos x cos y tan x + tan y = 1 - tan x tan y Q.E.D. sin(x - y) tan(x - y) = cos(x - y) sin x cos y - cos x sin y = cos x cos y + sin x sin y sin x cos y - cos x sin y cos x cos y = cos x cos y + sin x sin y cos x cos y tan x - tan y = 1 + tan x tan y Q.E.D. sin(-x) tan(-x) = cos(-x) - sin x = cos x = -tan x Q.E.D.
11 Prove that tangent is an odd . function.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- 2020-06-01 Woodworker's JournalDokument68 Seiten2020-06-01 Woodworker's JournalaaoneNoch keine Bewertungen
- CABETEC Cat Jan16 PDFDokument388 SeitenCABETEC Cat Jan16 PDFaaoneNoch keine Bewertungen
- WoodcraftJune July 2020Dokument68 SeitenWoodcraftJune July 2020aaone100% (1)
- MGT-400 SyllabusDokument7 SeitenMGT-400 SyllabusaaoneNoch keine Bewertungen
- MS Mei C2Dokument65 SeitenMS Mei C2aaoneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 3 Mathematics: Unit 1, Activities 1 and 2, Tickets SoldDokument49 SeitenGrade 3 Mathematics: Unit 1, Activities 1 and 2, Tickets SoldaaoneNoch keine Bewertungen
- A12 Logarithms BP 9-22-14Dokument7 SeitenA12 Logarithms BP 9-22-14aaoneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transformations of Sin and Cos See Applet:: X A X X BX CDokument3 SeitenTransformations of Sin and Cos See Applet:: X A X X BX CaaoneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maths DictionaryDokument24 SeitenMaths DictionaryaaoneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Systems of Equations Lesson Notes: LESSON TWO - Substitution MethodDokument0 SeitenSystems of Equations Lesson Notes: LESSON TWO - Substitution MethodaaoneNoch keine Bewertungen
- 95mat2 3Dokument12 Seiten95mat2 3aaoneNoch keine Bewertungen
- 00 Mathematics 34 UDokument12 Seiten00 Mathematics 34 UaaoneNoch keine Bewertungen
- C2 May 2006 Mark SchemeDokument4 SeitenC2 May 2006 Mark SchemeaaoneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Algebra Revision 1 With Sound BitesDokument33 SeitenAlgebra Revision 1 With Sound BitesaaoneNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2007 HSC MathematicsDokument5 Seiten2007 HSC MathematicsaaoneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- 11 Angles RevisitDokument8 Seiten11 Angles Revisitflameplay2234Noch keine Bewertungen
- How Many Degrees Is 1 15 of A Complete RevolutionDokument5 SeitenHow Many Degrees Is 1 15 of A Complete RevolutionRhislee Pabriga67% (3)
- Trigonometry - An Overview of Important TopicsDokument65 SeitenTrigonometry - An Overview of Important TopicsChristJohn HalopNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 6 Plane GeometryDokument2 SeitenModule 6 Plane GeometryGlenn Frey LayugNoch keine Bewertungen
- Take Down - Right TrianglesDokument45 SeitenTake Down - Right TrianglesFonNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Trigo ABDokument5 Seiten1 Trigo ABEzzee YenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Makeup Assignment CH 2 AnswersDokument3 SeitenMakeup Assignment CH 2 AnswersMs YousufNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12-1 Trigonometric Functions in Right TrianglesDokument58 Seiten12-1 Trigonometric Functions in Right TriangleswhizzerschesspieceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trigonometric Functions: Extreme Values of Trigonometric Expressions and PeriodicityDokument23 SeitenTrigonometric Functions: Extreme Values of Trigonometric Expressions and Periodicityshubham kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inverse Trigonometric FunctionsDokument12 SeitenInverse Trigonometric FunctionsHéctorValleNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Trigonometry) Introduction, Types of Questions, Shortcut For Memorizing 30,45,60 For SSC CGL CDS Mrunal PDFDokument7 Seiten(Trigonometry) Introduction, Types of Questions, Shortcut For Memorizing 30,45,60 For SSC CGL CDS Mrunal PDFTiken TakhellambamNoch keine Bewertungen
- ch-3 (RM Khan)Dokument24 Seitench-3 (RM Khan)satanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 2 - Simplifying ExpressionsDokument8 SeitenLesson 2 - Simplifying Expressionsiminathi ndlovuNoch keine Bewertungen
- AQA Higher Answers PDFDokument71 SeitenAQA Higher Answers PDFSindi Dallashi100% (1)
- Arcs and Sectors WorksheetDokument3 SeitenArcs and Sectors WorksheetKaren OakleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Excel Review Center Ece Review For October 2019 Board Exam Analytic Geometry 1Dokument3 SeitenExcel Review Center Ece Review For October 2019 Board Exam Analytic Geometry 1Darlene Jasmae TiñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tech Class-Special Right TrianglesDokument3 SeitenTech Class-Special Right Trianglesapi-251820803Noch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise 13.1 (Solutions) : Solution Are Given Below Question # 1 (I) SupposeDokument6 SeitenExercise 13.1 (Solutions) : Solution Are Given Below Question # 1 (I) Supposerehmania78644Noch keine Bewertungen
- Plane & SphericalDokument28 SeitenPlane & SphericalMarcelo AbreraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2019 Hustle Geometry SolutionsDokument3 Seiten2019 Hustle Geometry SolutionsSimon SiregarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Catatan Matematika - TrigonometriDokument1 SeiteCatatan Matematika - Trigonometri33 SHARA FEBRIANA ANGGRAINI100% (1)
- Indian RMO 2000-11, CRMO 2012-18 With SolutionsDokument135 SeitenIndian RMO 2000-11, CRMO 2012-18 With SolutionsMuhammad Abdullah KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment Unit 8 GeometryDokument12 SeitenAssignment Unit 8 GeometrysunshineboxiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geometry and Measurement Unit TestDokument9 SeitenGeometry and Measurement Unit Testapi-287376685Noch keine Bewertungen
- Circular MeasureDokument2 SeitenCircular MeasureMeor Nizam0% (1)
- 7 - Trigonometric Equations and IdentitesDokument64 Seiten7 - Trigonometric Equations and IdentitesMath 30-1 EDGE Study Guide Workbook - by RTD LearningNoch keine Bewertungen
- Law of SinesDokument22 SeitenLaw of Sineskemsy 02Noch keine Bewertungen
- TrianglesDokument62 SeitenTrianglesFatya EyvazovaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Std08 Maths EM 2 PDFDokument152 SeitenStd08 Maths EM 2 PDFPrem Anand100% (1)
- Nme File: Experiment 1 (A) CLC Clear All Close AllDokument23 SeitenNme File: Experiment 1 (A) CLC Clear All Close AllReetta Sara GeomyNoch keine Bewertungen