Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
F 01114147
Hochgeladen von
Ashish KumarOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
F 01114147
Hochgeladen von
Ashish KumarCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
IOSR Journal of Business and Management (IOSR-JBM) e-ISSN: 2278-487X, p-ISSN: 2319-7668. Volume 11, Issue 1 (May. - Jun.
2013), PP 41-47 www.iosrjournals.org
An Analysis of the Impact of Merger and Acquisition of Corus by Tata Steel
Manoj Kumara N V 1, Dr. Satyanarayana2
(Doctoral Student, Department of Post Graduate Studies in Management Sciences,Maharaja Research foundation. University of Mysore, India) 2 (HOD and Professor, Department of Post Graduate Studies in Management Sciences,Maharaja Institute of Technology. Mysore, India)
1
Abstract: Merger and Acquisition have became exclusive trend in steel industry globally since the beginning of the 21st century. Corporate integration in the corporate world is accomplishing significance and concentration especially with an exciting undertaking of intense globalization. This is the clear evidence from the importance and increasing growth of deal values and resulted with more corporate integration in recent times. These studies examine the key motive drivers and evaluate the impact of mergers and acquisition in steel industry on event study approach. This event study focused on Tata steel Corus Acquisition during the year 2007. The study used a published financial statement which consists of secondary data. The financial statements are analysed and tested by using correlation co-efficient and t- test. The outcome of the analysis disclosed that there is a significant difference between pre post merger and acquisition in capital base and level of returns. There is a significant difference between pre post merger and acquisition EPS. The finding of this study evolves those synergies, increased capitalization with the proof of changes in returns, profitability based on the research findings. It can be summarized that the corporate integration has increase the organizational performance also contributed to the growth of the steel industry. Keywords Mergers and Acquisitions, Profitability, EPS, Steel Industry, Key drivers I. INTRODUCTION
Tata being the winner. As driven by slow growth and substantial profits in the steel industry. Corus asset sale may lift the Tata steel earnings. Tata steel had acquired British largest steel maker Corus for 608 pence per share. It is one of the striking acquisition in 2006, to propose Tata steel from the 56 th to the 6th largest steel maker in the world. A long term gap between their delivered performance of the firm and the strategic plan projected gap was in terms of size, sales and Income. Acquisition could fill the gap (J Fred Weston and Samuel C. Weaver 2002). However, companies can seek for genuine synergies through financial engineering. Figure: 1 outbound acquisition since2005-dec2006 (USD Million)
The merger of Tata steel and Corus will result to a saving of $400 million to the company after 3 years of corporate integration. Long term strategy Strong base in India De integrated manufacturing Technology advantage Economies of scale www.iosrjournals.org 41 | Page
An Analysis Of The Impact Of Merger And Acquisition Of Corus By Tata Steel
To enter European mature market Cost of acquisition is less than setting up a new industry Acquiring the holding of Corus through patents and R & D facilities The main reasons for Corus to be sold Increase in cost of production Corus revenue was $18.06 billion, profit was only just $626 million but incase of Tata , the total revenue is $4.84 billion and profit was $824 million Target with low cost high quality raw material from India. A chance to bailout of debt and financial distress(chapter 11) Figure: 2
Source: Thomson DataStream To a large extent, corporate integration is based on a belief that earnings accrued through reduction cost, increase market share, reduction in earning volatility, and sale of economies. However, the main features of the compassionate of reforms inductive mergers and acquisitions of Tata and Corus industry creates potential of realizing efficient gains The total value of the Tata Corus acquisition amounted to 6.2 billion (US $ 12 billion). Tata steel declares a bid of 608 pence per share to go beyond the final bid from Brazilian steel maker Compuhia siderurgica Nacional (CSN) of 603 pence per share. Proceeding of the deal negotiations, both the Tata and Corus were interested to create a corporate bondage by entering into an merger and acquisition deal due to the diversified reasons. Table no: 1 Comparison of Tata and Corus in pre acquisition period
Particulars Years Assets Debt Liabilities Revenue Net income 2006 582.7 98.1 231.3 760.5 33.9 Corus(in Rs billions) 2005 533.9 105 178.4 699.9 33.5 2004 487.8 96 155.5 596.5 -22.9 2006 205.5 45.9 30.5 202.4 37.2 Tata steel (in Rs billions) 2005 117.0 42 33.1 159.9 36.03 2004 147.9 39.9 32.7 111.2 17.8
Table No: 2
Particulars Sales($mill) EBITDA($mill) Net profit ($mill) Crude steel Production ($mill) Market Capitalisation ($mill)
Economies of Corus Acquisition
Tata Steel 5007 1480 840 5.3 6510 Corus 19367 1962 861 18.2 8227 Combined 24374 3442 1701 23.5 14737
Tata steel acquires Corus completely in April 2007; Tata steel manages to win the acquisition to CSN and has the voting right support from the Corus share holders
www.iosrjournals.org
42 | Page
An Analysis Of The Impact Of Merger And Acquisition Of Corus By Tata Steel
Figure No: 3 Deal combined group structure of Tata financed
II.
THEORITICAL BACKGROUND
Cornell and Tehranian (1992); Switzer (1996); Ghosh (2001) found merger and acquisition firms shows significantly increase in operating performance. Pawaskar (2001) found that the share holders of the acquirers companies increased their liquidity performance after the mergers and acquisitions. A mergers and acquisitions occur when two or more companies connect together, often to share and reduce cost, increase the efficiency or market share. Merger and acquisition frequently assigned to as a tool for exploring and expanding ones business or get around different legal framework such as tax or monopoly regulations. Ross and Westerfield(2002).id debatable issue for all state holders, academicians and for researchers. The purpose of this research paper is to find the rational for merger and acquisition in terms of management incentives, post merger and acquisition value creation and steel industry position of the entity merger and acquisition between Tata steel and European steel giant Corus. Many studies have been done made on the effects of corporate integration on their share prices, share holders wealth. There is no conclusive evidence of life after acquisition. So the study helps to understand and evaluate the performance by analyzing the value creation through pre and post merger and acquisition study.
III.
REVIEW OF LITERATURE
A deal that dies at the due diligence stage almost always dies for the right reason. In most of the merger and acquisition, the target has a choice, and negotiations may even be taking place in the context of structured action. Before deciding on tactics, therefore, acquires should assess their advantages and disadvantages relative to their potential bidder HBR (2001).Rao and Sankar (1997)examine that a positive effect on the liquidity, leverage, and profitability of the bidder firms. Other studies have also showed a positive impact on financial performance Hitt, Harrison and Best (1998) In accordance with empire building theory (The Hubris Theory), managers may derive both financial and non financial benefits in proportion to the size of the business units they manage; this provides a strong intensive to increase firm size by merger and acquisition and places managers in conflicts with shareholders interest. Rau and Vermalen (1997) has investigated that the determinants of poor performance of the bidding firm after acquisition and concluding that firms having low boo to market ratio in general make poor decisions regarding merger and acquisition. However, higher profitability of the firm being acquired is found to be existing pre and post merger and acquisition Acharys (2000). Clear and factual communication among the employees of the acquiring and acquired firms is very crucial to increase their productivity which will resultantly have positive impact on performance of firms during or even after merger and acquisition Appelbaum etal (2000)
IV.
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
The approach for examination of value creation of both bidder and target around the announcement of an offer and includes both successful and unsuccessful merger and acquisition. The three hypothesized statements tested using correlation co-efficient and T- test. Hypothesis Based on the research gap areas from literature review, the following hypothesis is tested. H0: there is no significant difference between pre merger and acquisition equity capital base and Profit after Tax. H0: there is no significant difference between post merger and acquisition equity capital base and Profit after Tax. H0: there is no significant difference between pre and post merger and acquisition earning per share. Mode Specifications Correlation co-efficient = r= N(xy) (x) (y) [N(x2) (x)2] [N (y2) (y)2] The T- test is used to determine the prior and post performance of an activity. t = d N(d2) (d)2 N-1 www.iosrjournals.org 43 | Page
An Analysis Of The Impact Of Merger And Acquisition Of Corus By Tata Steel
Decision Rule If the profitability (the level of significance) of the t calculated is less than 5%, we accept the alternative hypothesis and otherwise, we should accept the null hypothesis.
V. DATA ANALYSIS Hypothesis: 1 Table No-3 There is significant difference between pre merger and acquisition equity capital base and Profit after
Tax.
Pre-Merger and Acquisition
1 2 3 4 5 Capital(X) 3184.81 4515.86 7059.92 9755.3 13949.04 x =38464.93 PAT(Y) 1012.31 1746.22 3474.16 3506.38 4222.15 y = 13961.22 x2 10143014.73 20392991.53 49842470.4 95165878.09 194575716 x2 = 128737719.77 y2 10247714.54 3049284.29 12069787.7 12294700.7 17826550.62 y2 =370120071.65 Xy 3224015.01 7885685.05 24527291.66 34205788.81 58894939.24 xy =46265094.85
Correlation co-efficient =
r=
N(xy) (x) (y) [N(x2) (x)2] [N (y2) (y)2]
5(46265094.85) (38464.93) (13961.22) [5(128737719.77) (38464.93)2] [5 (370120071.65) (13961.22)2] 643688598.85 537017350.014 [1850600358.25 1479550839.9] [231325474.25 194915663.88] 106671248.836 [371049518.35] [36409810.37]
106671248.836 116231848.5 Hypothesis: 2 R2= 0.918
Table No-4 There is significant difference between post merger and acquisition equity capital base and Profit after
Tax.
Post- Merger and Acquisition
Capital(X) 1 2 3 4 5 27300.73 29704.65 37168.75 48266.43 52216.46 x =194657.02 PAT(Y) 4687.03 5201.74 5046.80 6865.69 6696.42 y = 28497.68 x2 745329858.53 882366231.62 1381515976.56 2329648264.94 2726558694.93 x2 = 8065419026.58 y2 21968250.22 27058099.03 25470190.24 47137699.18 44842040.82 y2 =166476279.49 Xy 127959340.53 154515866.09 187583247.50 331382345.79 349663347.07 xy =1151104146.98
N(xy) (x) (y) [N(x2) (x)2][N (y2) (y)2] 5(1151104146.98) (194657.02) (28497.68) [5(8065419026.58) (194657.02)2] [5 (166476279.49) (28497.68)2] 5755520734.9 5547273465.71 [40327095132.9 37591355435.2] [832381397.45 812117765.38] 208247269.19 [2435739697.7][20263632.07] Correlation co-efficient = r= www.iosrjournals.org 44 | Page
An Analysis Of The Impact Of Merger And Acquisition Of Corus By Tata Steel 208247269.19 222164202.9 R2= 0.937
Hypothesis: 3 Table No-5 There is significant difference between pre and post merger and acquisition Earning per Share T-Test Pre EPS 27.53 47.48 62.77 63.35 72.74 Post EPS 63.85 69.70 56.37 71.58 68.95 D 36.32 22.22 -6.4 8.23 -3.79 D=56.58 D2 1319.14 493.73 40.96 67.73 14.36 D2=1935.92
1 2 3 4 5
d = 56.58 /5 =11.32 t = d N(d2) (d)2 N2(N-1) t = 11.32 5(1935.92) (11.32)2 52(52-1) 11.32 5(1935.92) (11.32)2 25(24) 11.32 9679.6 128.14 25(24) 11.32 9551.46 600 11.32 15.9191 11.32 3.99 2.84
t =
Degree of freedom = N-1 = 5-1 = 4 at 5% level of significance The tabulated values 2.776, since this value is lesser than the computed value above 2.84, therefore reject the null hypothesis and accept the alternative hypothesis.
www.iosrjournals.org
45 | Page
An Analysis Of The Impact Of Merger And Acquisition Of Corus By Tata Steel
Figure No: 4 Return on capital employed post period performance
Figure No: 5 Interest coverage ratios based on capital base
Figure No: 5 Interest coverage ratios based on capital base
VI.
Findings And Suggesstions
The study findings are reviewed as follows i. Corporate integration of Tata and Corus has consequently increased the capital base. ii. Aggregate steel industry capacity of around 28.1 million tones. iii. In May 07 earning before interest tax and depreciation of 13%, 25 million tones of production also ranked 5th. iv. 2012 earning before interest tax and depreciation of 25%, 40 million tones of production and ranked 2nd. v. Recapitalization was made possible as a result of corporate integration. vi. Mergers and acquisitions , has significantly affected 5the earning per share of investors
VII.
CONLUSION
The results of the study shows that evident hypothesis, the research study conclude that merger and acquisition of Tata and Corus with respect of profitability, performance, turnover, capacity, economies of scale www.iosrjournals.org 46 | Page
An Analysis Of The Impact Of Merger And Acquisition Of Corus By Tata Steel
and enhanced control. This study of impact of merger and acquisition on value matters resulted with positive influenced in profitability, capital base, dividends and earnings for share holders. This is a positive characteristics for strong future. There will be a lot of potential synergies in terms of sharing of best practices across the companies
REFERENCES Journal Papers:
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] [7] [8] [9] Acharya,Ram,C, the impacts of merger and acquisition on firms profitability, a case study of Canadian firms. Journal of Finance ,, volume 4, 2000, 1605-1621. Appelbaum, etal,Atonomy of a merger ; behavior of organizational factors and processes throughout the pre during post- stages. Management decision. Ghosh, A, Does operating performance really improve following corporate acquisitions? Journal of Corporate Finance, 7(2), June 2001, 151-178. Harbir.S and Montgomery.C, corporate acquisition strategies and economic performance, Strategic Management Journal,8(4),1987,377-386 . Hitt.M, Harrison.J and Best.A, attributes of successful and unsuccessful acquisition of US firms, British Journal of Management,9(2, 1998, 91-114). Jarrell.A, Brickely.J and Netter.J, The market for corporate control; the empirical evidence since1980, Journal of Economic perspectives,2(1),1988, 49-68. Pawaskar.V, Effect of merger on corporate performance in India, Vikalpa, Vol. 26(1), Jan Mar-2001. Rao.K and Sankar, Takeover as a strategy of turn around, Mumbai,UTI,1997. Rau and Vermaelen, glamour, value and the post acquisition performance of acquiring firms , Journal of Financial Economics, Vol.49,1997,222-253 Note that the journal title, volume number and issue number are set in italics. Ross, Westerfield and Jaffee, Corporate finance (6th edition, Boston: Mcgraw-Hill/Ervin, 2002). Harward Business Reviews , mergers and acquisitions(Boston, HB SchoolPress,MA02163)
Books:
[10] [11]
www.iosrjournals.org
47 | Page
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Dollar General Case StudyDokument26 SeitenDollar General Case StudyNermin Nerko Ahmić100% (1)
- EEM MOD003477 Module GuideDokument24 SeitenEEM MOD003477 Module GuideSamar SalahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Four Fold TestDokument19 SeitenFour Fold TestNeil John CallanganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ingles Cuestionario Quimestre 2-1Dokument3 SeitenIngles Cuestionario Quimestre 2-1Ana AlvaradoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Urban Cooperative Banking SummitDokument78 SeitenUrban Cooperative Banking Summitashish srivastavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Write UpDokument5 SeitenWrite UpAli Tariq ButtNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Alpha StrategiesDokument189 SeitenThe Alpha StrategiesRenante RodrigoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intdiff Ltot Ldisrat Lusdisrat Lusprod LrexrDokument4 SeitenIntdiff Ltot Ldisrat Lusdisrat Lusprod LrexrsrieconomistNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shipping Doc Late SubmissionDokument29 SeitenShipping Doc Late SubmissionAbdullah QureshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Key Attributes of The World-Class Information Technology OrganizationDokument7 SeitenKey Attributes of The World-Class Information Technology OrganizationMichael Esposito100% (1)
- Do CC CadburyDokument42 SeitenDo CC CadburySaahil LedwaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lowrider - June 2018Dokument92 SeitenLowrider - June 2018Big Flores100% (2)
- Walmart Analyst ReportDokument29 SeitenWalmart Analyst ReportAlexander Mauricio BarretoNoch keine Bewertungen
- DBSV - Asian Consumer DigestDokument119 SeitenDBSV - Asian Consumer DigesteasyunittrustNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structural Consultants Registered With Dda Sl. No. Name & Address of The Agency ValidityDokument4 SeitenStructural Consultants Registered With Dda Sl. No. Name & Address of The Agency ValidityRupali ChadhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- EY Capital Markets Innovation and The FinTech Landscape Executive SummaryDokument9 SeitenEY Capital Markets Innovation and The FinTech Landscape Executive SummaryCrowdfundInsider100% (1)
- Starbucks PowerPointDokument20 SeitenStarbucks PowerPointAdarsh BhoirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Retail BankingDokument11 SeitenRetail Banking8095844822Noch keine Bewertungen
- L&T Infotech Announces Appointment of Sudhir Chaturvedi As President - Sales (Company Update)Dokument3 SeitenL&T Infotech Announces Appointment of Sudhir Chaturvedi As President - Sales (Company Update)Shyam SunderNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACCT3004Dokument8 SeitenACCT3004visio2004Noch keine Bewertungen
- IIT TenderDokument10 SeitenIIT TenderB DroidanNoch keine Bewertungen
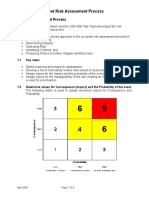
- 4 Fleet Risk Assessment ProcessDokument4 Seiten4 Fleet Risk Assessment ProcessHaymanAHMEDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Feasibility and Business Planning: Back To Table of ContentsDokument55 SeitenFeasibility and Business Planning: Back To Table of ContentsJK 9752Noch keine Bewertungen
- Presented By:: Pranav V Shenoy Gairik Chatterjee Kripa Shankar JhaDokument20 SeitenPresented By:: Pranav V Shenoy Gairik Chatterjee Kripa Shankar JhaPranav ShenoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Audit & Reporting ProvisionsDokument6 SeitenAudit & Reporting Provisionsdmk.murthyNoch keine Bewertungen
- (July 2019) - OT - AccomplishmentDokument2 Seiten(July 2019) - OT - AccomplishmentMark Kristoffer HilarionNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7 P'sDokument14 Seiten7 P'sReena RialubinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case SummaryDokument3 SeitenCase SummaryWilliam WeilieNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNACEMDokument246 SeitenUNACEMAlexandra Guzman BurgaNoch keine Bewertungen
- POM TopicsDokument2 SeitenPOM TopicsAnkit SankheNoch keine Bewertungen