Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Network: Chapter 2: Types of Network
Hochgeladen von
sweetashusOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Network: Chapter 2: Types of Network
Hochgeladen von
sweetashusCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Chapter 2: Types Of Network Network
A network is interconnection of resource that organization owns. It is a technology solution that helps organization to interconnect its hardware, software, databases and various media to achieve interconnectivity between its employees and stakeholders.
Types of Network
LAN - Local Area Networks A local area network (LAN) interconnects two or more computer or device within a relatively small well defined area such as room, building, cluster of building using physical wires, infrared links, or wireless systems.LAN connects networking devices with in short spam of area, i.e. small offices, home, internet cafes etc. LAN uses TCP/IP network protocol for communication between computers. It is often but not always implemented as a single IP subnet. Since LAN is operated in short area so It can be control and administrate by single person or organization. WAN - Wide Area Network As word Wide implies, WAN, wide area network cover large distance for communication between computers. The Internet itself is the biggest example of Wide area network, WAN, which is covering the entire earth. WAN is distributed collection of geographically LANs. A network connecting device router connects LANs to WANs. WAN used network protocols like ATM, X.25, and Frame Relay for long distance connectivity. Organizations That wants to share internet connection with its LAN user will need to connect their LAN to a public Communication service provider called Internet Service Provider (ISP). This interconnection of LAN with ISP qualifies to be WAN. VAN Virtual Private Network A virtual private network is a network that uses a public telecommunication, infrastructure, such as internet, to provide remote offices or individual user with secure access to their organizational networks. A virtual private network can be contrasted with an expensive system of owned or leased lines that can only be used by one organization. The goal of VPN is to provide the organization with the same capabilities but at a much lower cost.
1|Page
Chapter 2: Types Of Network Network Topology
A network consists of multiple computers connected using some type of interface, each having one or more interface devices such as a Network Interface Card (NIC) and/or a serial device for PPP networking. Each computer is supported by network software that provides the server or client functionality. The hardware used to transmit data across the network is called the media. It may include copper cable, fiber optic, or wireless transmission. The standard cabling used for the purposes of this document is 10Base-T category 5 Ethernet cable. This is twisted copper cabling which appears at the surface to look similar to TV coaxial cable. It is terminated on each end by a connector that looks much like a phone connector. Its maximum segment length is 100 meters. The physical topology of a network refers to the configuration of cables, computers, and other peripherals. Physical topology should not be confused with logical topology which is the method used to pass information between workstations. Logical topology was discussed in the Protocol chapter.
Main Types of Network Topologies :
In networking, the term "topology" refers to the layout of connected devices on a network. This article introduces the standard topologies of computer networking. One can think of a topology as a network's virtual shape or structure. This shape does not necessarily correspond to the actual physical layout of the devices on the network. For example, the computers on a home LAN may be arranged in a circle in a family room, but it would be highly unlikely to find an actual ring topology there. Network topologies are categorized into the following basic types:
Star Topology Ring Topology Bus Topology Tree Topology Mesh Topology Hybrid Topology
More complex networks can be built as hybrids of two or more of the above basic topologies.
2|Page
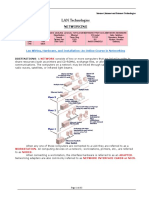
Chapter 2: Types Of Network Star Topology
Many home networks use the star topology. A star network features a central connection point called a "hub" that may be a hub, switch or router. Devices typically connect to the hub with Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) Ethernet. Compared to the bus topology, a star network generally requires more cable, but a failure in any star network cable will only take down one computer's network access and not the entire LAN. (If the hub fails, however, the entire network also fails.)
Diagram:->
Advantages of a Star Topology
Easy to install and wire. No disruptions to the network then connecting or removing devices. Easy to detect faults and to remove parts.
Disadvantages of a Star Topology
Requires more cable length than a linear topology. If the hub or concentrator fails, nodes attached are disabled. More expensive than linear bus topologies because of the cost of the concentrators.
The protocols used with star configurations are usually Ethernet or Local Talk. Token Ring uses a similar topology, called the star-wired ring.
3|Page
Chapter 2: Types Of Network
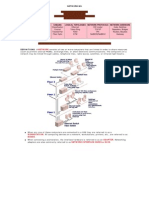
Ring Topology :
In a ring network, every device has exactly two neighbors for communication purposes. All messages travel through a ring in the same direction (either "clockwise" or "counterclockwise"). A failure in any cable or device breaks the loop and can take down the entire network. There is no central or predomi8nant computer in this network Data must travel around the ring to each station until it reaches at the desired station. A unidirectional ring moves data in one direction only; a bidirectional rings can have data in both directions, but in only one direction at a time, when one node malfunctions in a bidirectional ring a message from an adjacent node can usually be send in opposite direction, still allowing communication among all the active nodes in a network .In a unidirectional ring if one of the nodes stop working the complete network will get affected. To implement a ring network, one typically uses FDDI, SONET, or Token Ring technology. Ring topologies are found in some office buildings or school campuses.
Diagram:->
4|Page
Chapter 2: Types Of Network Bus Topology
Bus networks (not to be confused with the system bus of a computer) use a common backbone to connect all devices. A single cable, the backbone functions as a shared communication medium that devices attach or tap into with an interface connector. A device wanting to communicate with another device on the network sends a broadcast message onto the wire that all other devices see, but only the intended recipient actually accepts and processes the message. Ethernet bus topologies are relatively easy to install and don't require much cabling compared to the alternatives. 10Base-2 ("Thin Net") and 10Base-5 ("Thick Net") both were popular Ethernet cabling options many years ago for bus topologies. However, bus networks work best with a limited number of devices. If more than a few dozen computers are added to a network bus, performance problems will likely result. In addition, if the backbone cable fails, the entire network effectively becomes unusable.
Diagram:->
Advantages of a Linear Bus Topology
Easy to connect a computer or peripheral to a linear bus. Requires less cable length than a star topology.
Disadvantages of a Linear Bus Topology
Entire network shuts down if there is a break in the main cable. Terminators are required at both ends of the backbone cable. Difficult to identify the problem if the entire network shuts down. Not meant to be used as a stand-alone solution in a large building.
5|Page
Chapter 2: Types Of Network Tree Topology
Tree topologies integrate multiple star topologies together onto a bus. In its simplest form, only hub devices connect directly to the tree bus, and each hub functions as the "root" of a tree of devices. This bus/star hybrid approach supports future expandability of the network much better than a bus (limited in the number of devices due to the broadcast traffic it generates) or a star (limited by the number of hub connection points) alone.
Diagram:->
Advantages of a Tree Topology
Point-to-point wiring for individual segments. Supported by several hardware and software venders.
Disadvantages of a Tree Topology
Overall length of each segment is limited by the type of cabling used. If the backbone line breaks, the entire segment goes down. More difficult to configure and wire than other topologies.
6|Page
Chapter 2: Types Of Network Mesh Topology
Mesh topologies involve the concept of routes. Unlike each of the previous topologies, messages sent on a mesh network can take any of several possible paths from source to destination. (Recall that even in a ring, although two cable paths exist, messages can only travel in one direction.) Some WANs, most notably the Internet, employ mesh routing. A mesh network in which every device connects to every other is called a full mesh. As shown in the illustration below, partial mesh networks also exist in which some devices connect only indirectly to others.
Diagram:->
Hybrid Topology
A combination of any two or more network topologies. Note 1: Instances can occur where two basic network topologies, when connected together, can still retain the basic network character, and therefore not be a hybrid network. For example, a tree network connected to a tree network is still a tree network. Therefore, a hybrid network accrues only when two basic networks are connected and the resulting network topology fails to meet one of the basic topology definitions. For example, two star networks connected together exhibit hybrid network topologies. Note 2: A hybrid topology always accrues when two different basic network topologies are connected.
7|Page
Chapter 2: Types Of Network Ethernet:
Ethernet is a physical and data link layer technology for local area networks (LANs). Ethernet was invented by engineer Robert Metcalfe. When first widely deployed in the 1980s, Ethernet supported a maximum theoretical data rate of 10 megabits per second (Mbps). Later, so-called "Fast Ethernet" standards increased this maximum data rate to 100 Mbps. Today, Gigabit Ethernet technology further extends peak performance up to 1000 Mbps. However today the technology is also available that supports data transfer upto 5Gbps.
8|Page
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Bandwidth Modem: LAN - Local Area NetworkDokument5 SeitenBandwidth Modem: LAN - Local Area NetworkYvette IyadedeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Networking in DMRCDokument16 SeitenNetworking in DMRCaanchalbahl62100% (1)
- Computer NetworkDokument351 SeitenComputer NetworkRanjan Saini100% (1)
- Lab ManualDokument12 SeitenLab ManualRai HessyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4335 NetworkingemisDokument4 Seiten4335 NetworkingemisFavour JamesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Networks-4Dokument6 SeitenIntroduction To Networks-4deepheat_008Noch keine Bewertungen
- Network PDFDokument66 SeitenNetwork PDFq_riusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Star Topology Many Home Networks Use The Star Topology. A Star Network Features ADokument6 SeitenStar Topology Many Home Networks Use The Star Topology. A Star Network Features AsabahafzalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Definition - What Does Computer Networking Mean?Dokument3 SeitenDefinition - What Does Computer Networking Mean?Kenneth Jed SolomoNoch keine Bewertungen
- IIIT Network Design D.deepak IIIT HyderabadDokument9 SeitenIIIT Network Design D.deepak IIIT HyderabadHarshit PahujaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study About Basic of Network (Topologies) and Types of network-LAN, Man, WanDokument11 SeitenStudy About Basic of Network (Topologies) and Types of network-LAN, Man, WanAnonymous aQxekTRNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Computer Network Works: Local Area Networks (Lans) Wide Area Networks (Wans) InternetDokument9 SeitenHow Computer Network Works: Local Area Networks (Lans) Wide Area Networks (Wans) InternetASHFORD BORJANoch keine Bewertungen
- ICT Fundamentals ReportDokument49 SeitenICT Fundamentals ReportJigs OlbesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Networks Toplogys1Dokument9 SeitenComputer Networks Toplogys1ammapetNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Network TopologyDokument7 SeitenTypes of Network TopologyMarvin OrbigoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CS 111Dokument2 SeitenCS 111Oıɔɐuƃı ɹɐ ʎɐɾNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ccna R&SDokument122 SeitenCcna R&Sdhileep sNoch keine Bewertungen
- Networking BasicsDokument102 SeitenNetworking Basicssan1507Noch keine Bewertungen
- Netwrkd Types and TopologyDokument5 SeitenNetwrkd Types and TopologyHerbert Shirov Tendido SecurataNoch keine Bewertungen
- VYSHNAVI.M (18bcs) : Computer NetworksDokument6 SeitenVYSHNAVI.M (18bcs) : Computer Networks18BCS120 VyshnaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Networking: Different Types of Network TopologyDokument9 SeitenBasic Networking: Different Types of Network TopologySRGiramNoch keine Bewertungen
- IT Web TechnologyDokument79 SeitenIT Web TechnologyDale BaltazarNoch keine Bewertungen
- INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER NETWORK Cyber CrimeDokument6 SeitenINTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER NETWORK Cyber CrimeAkriti SaxenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 8 Second Term NoteDokument21 SeitenGrade 8 Second Term NoteThiseni De SilvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Setting Up Computer NetworksDokument7 SeitenSetting Up Computer NetworksNinja ni Zack PrimoNoch keine Bewertungen
- DC-Lec-03 & 04 (Physical Structure of Network)Dokument44 SeitenDC-Lec-03 & 04 (Physical Structure of Network)tabby919100% (4)
- Computer TopologyDokument14 SeitenComputer TopologytamnumakamseuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Communication & NetworkingDokument24 SeitenData Communication & NetworkingZulqarnain JamilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ccna 1Dokument64 SeitenCcna 1Nikhil ThavamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Administrate Network and Hardware PeripheralsDokument92 SeitenAdministrate Network and Hardware PeripheralsMintesnot AdeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Network Topologies 3Dokument12 SeitenNetwork Topologies 3家星Noch keine Bewertungen
- CDCDokument9 SeitenCDCMelvin P. FiguraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Application: Surbhi Goel 12455 Bcom Hons A Pgdav College DuDokument17 SeitenComputer Application: Surbhi Goel 12455 Bcom Hons A Pgdav College DuManish YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Network BasicsDokument57 SeitenNetwork BasicsPunitNoch keine Bewertungen
- NetworkingDokument9 SeitenNetworkingalmightyfavouriteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Core 2Dokument30 SeitenCore 2keanee simbajonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Communication: Unit Viii LanDokument30 SeitenComputer Communication: Unit Viii LanleensNoch keine Bewertungen
- Working2022 PDFDokument9 SeitenWorking2022 PDFKrrish KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- TopologiesDokument8 SeitenTopologiesvigneshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adama Poly Technique Colleg1Dokument32 SeitenAdama Poly Technique Colleg1Mahdi ZeynNoch keine Bewertungen
- Networking BasicsDokument23 SeitenNetworking Basicscool.tba100% (2)
- Unit 3 FOC Network TopologyDokument7 SeitenUnit 3 FOC Network TopologybalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topology in Network DesignDokument5 SeitenTopology in Network DesignakshayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Comp Networks - BarungiDokument27 SeitenIntroduction To Comp Networks - BarungiMasaba Denis MadenNoch keine Bewertungen
- COMPUTER NETWORK-BY Ankit PatnaikDokument18 SeitenCOMPUTER NETWORK-BY Ankit PatnaikTuhina MistryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of NetworkDokument16 SeitenTypes of NetworkPriyank RathoreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer NetworkDokument58 SeitenComputer Networkshivang.goyal02Noch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Computer NetworkingDokument44 SeitenIntroduction To Computer Networkingjohn100% (1)
- 12th IP Networking 3-UnitDokument40 Seiten12th IP Networking 3-UnitHridyanshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Communication and Etworks: Prepared by Senait KDokument11 SeitenData Communication and Etworks: Prepared by Senait KSenait Kiros100% (1)
- Final CN Lab ManualDokument49 SeitenFinal CN Lab Manualharishpillai1994Noch keine Bewertungen
- PC Hardware and NetworkingDokument93 SeitenPC Hardware and NetworkingPrince DeuelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer NetworkDokument164 SeitenComputer NetworkBipin PrajapatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Network Topology 1Dokument10 SeitenNetwork Topology 1anonymousNoch keine Bewertungen
- TopololololologyDokument7 SeitenTopololololologyapi-275907560Noch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Network FundamentalsDokument41 SeitenComputer Network FundamentalsShadowCrew CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Computer Networks?Dokument8 SeitenWhat Is Computer Networks?Katrina Mae VillalunaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Networking: An introductory guide for complete beginners: Computer Networking, #1Von EverandComputer Networking: An introductory guide for complete beginners: Computer Networking, #1Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (2)
- Introduction to Internet & Web Technology: Internet & Web TechnologyVon EverandIntroduction to Internet & Web Technology: Internet & Web TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exchange Rate DeterminationDokument13 SeitenExchange Rate DeterminationsweetashusNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Summer Internship Presentation ON "Banking Operations" inDokument16 SeitenA Summer Internship Presentation ON "Banking Operations" insweetashusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tools of Structured System Analysis and DesignDokument25 SeitenTools of Structured System Analysis and DesignsweetashusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Methods of CostingDokument21 SeitenMethods of CostingsweetashusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theories of Exchange RateDokument10 SeitenTheories of Exchange RatesweetashusNoch keine Bewertungen
- GSB Solar Product Catalog A4Dokument40 SeitenGSB Solar Product Catalog A4mohamed husseinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project SchedulingDokument61 SeitenProject SchedulingGummanur SreenathNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resistors: Take A Stance, The Resist StanceDokument35 SeitenResistors: Take A Stance, The Resist Stancepavan pujarNoch keine Bewertungen
- MB-910 enDokument74 SeitenMB-910 enadrianoglopesNoch keine Bewertungen
- ABEn 145 - Tribunalo - Lab 4Dokument14 SeitenABEn 145 - Tribunalo - Lab 4Jaylou OpondaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Create Report Net Content StoreDokument26 SeitenCreate Report Net Content StoreJi RedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deep Learning Based Classification On Fruit Diseases An Application For Precision AgricultureDokument14 SeitenDeep Learning Based Classification On Fruit Diseases An Application For Precision AgricultureJuan PalaciosNoch keine Bewertungen
- ES1688 AudioDrive (Summary)Dokument4 SeitenES1688 AudioDrive (Summary)GregNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prediction of Overshoot and Crosstalk of Low Voltage GaN HEMTDokument27 SeitenPrediction of Overshoot and Crosstalk of Low Voltage GaN HEMTfirststudentNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modula WMSDokument8 SeitenModula WMSIbai Zabala BengoaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amiga 500 IntroductionDokument294 SeitenAmiga 500 IntroductionMalcolmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thierry Bardini - BootstrappingDokument324 SeitenThierry Bardini - Bootstrappingh0ry0% (1)
- SRT/2020-21/11/29 To. M/S Deputy Director Research Lab: Punjab PWD (B&R) PatialaDokument4 SeitenSRT/2020-21/11/29 To. M/S Deputy Director Research Lab: Punjab PWD (B&R) PatialaAyush GoyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hyundai Part Catalogue D6ACDokument157 SeitenHyundai Part Catalogue D6ACHammim Hamzhahh100% (1)
- Schematics 3250Dokument9 SeitenSchematics 3250pronomixNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7 Tools MosaLingua Ebook - 3rd Edition - ENDokument20 Seiten7 Tools MosaLingua Ebook - 3rd Edition - ENBella AndryczkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- En Iso 9712 - 2013Dokument42 SeitenEn Iso 9712 - 2013alilka404Noch keine Bewertungen
- Open Transaction Manager Access Guide and Reference: IBM ConfidentialDokument183 SeitenOpen Transaction Manager Access Guide and Reference: IBM ConfidentialvgrynyukNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fire-Lite ACM-16ATF Data SheetDokument4 SeitenFire-Lite ACM-16ATF Data SheetJMAC SupplyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter2 Mobility ManagementDokument13 SeitenChapter2 Mobility ManagementSuraj Shah0% (2)
- Data SheetDokument24 SeitenData Sheetbashok20Noch keine Bewertungen
- Adam PMB53 Moisture Analyzer User ManualDokument84 SeitenAdam PMB53 Moisture Analyzer User Manualpwrage6561Noch keine Bewertungen
- Kpaw, LLC v. Apple, IncDokument19 SeitenKpaw, LLC v. Apple, IncLucas NolanNoch keine Bewertungen
- MS Word 2. ExcelDokument13 SeitenMS Word 2. ExcelKunjal PalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Movi PackDokument6 SeitenMovi PackManel MontesinosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Instrument Landing SystemDokument62 SeitenInstrument Landing Systemzeeshan_946461113100% (1)
- F FC FC JG DDokument9 SeitenF FC FC JG DRAJANoch keine Bewertungen
- 3-Roll of Engineers 2010 AlphaDokument46 Seiten3-Roll of Engineers 2010 AlphahansdubarryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deep Security Container Protection Customer PresentationDokument42 SeitenDeep Security Container Protection Customer PresentationsaurabhbectorNoch keine Bewertungen
- WikwikDokument2 SeitenWikwikDavid GusarishviliNoch keine Bewertungen