Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
QB Mol Bio
Hochgeladen von
rajusirivastavCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
QB Mol Bio
Hochgeladen von
rajusirivastavCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
1) A student inspired by Meselson and Stahl experiment want to
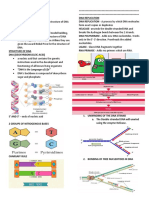
know what happens to histones during eukaryotic DNA replication. He designed protocol whose steps are below: Step 1 : grow cells for several generations in medium that contains amino acids labeled with a heavy isotope Step 2 : transfer the cells to a medium that contains amino acids with light isotope Step 3 : isolate histone octamers before and after replication and subject them to density gradientcentrifugation Observation : octamer prior to replication shown single band lower in test tube while after replication octamer shown broad band but upper in position in comparison to earlier band. The correct conclusion will be a. histone followed semi-conservative model of replication like DNA b. after DNA replication, the new octamers are a random mixture of old and new histone c. new octamer and old octamer are in 1 : 1 after DNA replication d. nothing happened to old histones, they remained intact.
2) At least 10 percent of human DNA exists as repeated multiples of relatively short sequences of nucleotides. Which of the following statements about this repetitive DNA is correct? a. much of the repetitive DNA is transcribed into messenger RNA b. repetitive DNA is largely responsible for the production of enzymes and other protein molecules c. most repeated sequences are associated with detectable phenotypes d. highly repeated sequences rapidly reassociate in DNA hybridization studies. 3) The conformation of a nucleotide in DNA is affected by rotation about how many bonds? a. 4 b. 6 c. 7 d. 3
4) What would stop DNA replication in bacteria? P. addition of a DNA polymerase inhibitor Q. addition of dideoxyribonucleotides (ddNTP) R. addition of lamin inhibitor S. addition of actin inhibitor a. P and Q b. Q and R c. R and S d. P and S 5) Okazaki fragments were prepared from an E.coli strain harboring pBR322 plasmid. These fragments were then hybridized to single stranded DNA molecules prepared by carefully separating the two strands of the E.coli chromosome and the plasmid. The Okazaki fragments would anneal to a. both the strands of the chromosome and the plasmid b. both the strands of the chromosome but only one strand of the plasmid c. one strand of the chromosome but both the strands of the plasmid d. one strand each of the chromosome and the plasmid 6) Which of the following covalent bond types are found in the structure of ATP? a. N-glycosidic, thioester, phosphodiester b. phosphoanhydride, phosphomonoester, N-glycosidic c. ester, ether, phosphoanhydride d. ether, thioester, phosphomonoester 7) A nucleic acid has following base composition: A: 30 percent G: 40 percent What can be inferred from this data? a. the nucleic acid is a RNA b. the nucleic acid is a DNA c. the nucleic acid is two-stranded d. the nucleic acid is single-stranded
8) Which statement about the DnaB helicase are true? P. DnaB helicase is a ring-shaped molecule and the dsDNA goes through the hole Q. DnaB helicase is loaded onto the lagging strand by the clamp loader R. DnaB is loaded onto ssDNA at oriC by DnaC S. interaction between the tau subunit of the replisome and DnaB causes the helicase to go slower T. DnaB moves in 5 to 3 direction a. P and R b. R and T c. Q and R d. S and T 9) Okazaki fragments are formed during DNA synthesis, because P. DNA synthesis extends from 5 to 3 direction Q. Their synthesis are opposite to the direction of replication fork R. DNA ahead of replication fork is positively supercoiled S. DNA synthesis is semi-conservative a. Q and R b. P and Q c. R and S d. S and P 10) Match the terms in group I with terms in group II Group I Group II P. RNase-P 1. lac operon Q. Leucine zipper 2. rRNA gene transcription R. RNA pol-I 3. tRNA gene transcription S. Attenuation 4. Transcription factors 5. Ribozymes 6. trp operon 7. mRNA splicing a. P-7, Q-5, R-3, S-1 b. P-4, Q-5, R-2, S-1 c. P-5, Q-4, R-2, S-6 d. P-4, Q-5, R-3, S-6
11) Which of the following statements about DNA polymerases are correct? (a) They add deoxyribonucleotide units to the 3-hydroxyl of a primer. (b) They use the template strand to help choose which deoxyribonucleotide unit to add to the growing DNA chain. (c) They contain a 35 nuclease that cleaves phosphodiester bonds of misincorporated deoxyribonucleotides. (d) They check the incoming deoxyribonucleotide triphosphate (dNTP) to help insure that the correct, complementary choice is made. (e) They bind one complementary dNTP and add a second complementary dNTP to initiate a new DNA chain. 1. a and b 2. a, b c and d 3. only c and d 4. a, b, c and e 12. Mg2+; serves which of the following functions in the reaction catalyzed by DNA polymerases? (a) stabilizes the pentacoordinate transition state of the phosphodiester bond formation (b) precipitates inorganic phosphate (Pi) arising from the reaction (c) interacts with the 3-hydroxyl of the incoming dNTP (d) forms a bridge between the 3-hyroxyl of the primer and a phosphate in the dNTP (e) stabilizes the negative charge on the departing pyrophosphate, which is derived from the incoming dNTP 1. a and c 2. a, c, d and e 3. only d 4. a, d and e 13. Which of the following statements about DNA molecules that are topoisomers are correct? (a) They are bound to topoisomerases. (b) They differ from one another topologically only in that they have different linking numbers. (c) They may be separated from one another by electrophoresis.
(d) They have identical molecular weights. (e) They are topological or spatial isomers. 1. c, d and e 2. b, c and d 3. b, c, d and e 4. a and b 14. Which of the following statements about topoisomerases are correct? (a) They alter the linking numbers of topoisomers. (b) They break and reseal phosphodiester bonds. (c) They require NAD; as a cofactor to supply the energy to drive the conversion of a supercoiled molecule to its relaxed form. (d) They form covalent intermediates with their DNA substrates. (e) They can, in the case of a particular type of topoisomerase, use ATP to form negatively supercoiled DNA from relaxed DNA in E. coli. 1. a, b, c and d 2. a, b and c 3. a and c 4. a, b, d and e 15. Which of the following statements about DNA replication in E. coli are correct? (a) It occurs at a replication fork. (b) It starts at a unique locus on the chromosome. (c) It proceeds with one replication fork per replicating molecule. (d) It is bidirectional. (e) It involves discontinuous synthesis on the leading strand. (f) It uses RNA transiently as a template. 1. a, b. and d 2. b, c and f 3. both d and c 4. a, b, c and f 16. Which of the following statements about DNA polymerase III holoenzyme from E. coli are correct? (a) It elongates a growing DNA chain hundreds of times faster than does DNA polymerase I. (b) It associates with the parental template, adds a few nucleotides to the growing chain, and then dissociates before initiating another synthesis cycle.
(c) It maintains a high fidelity of replication, in part by acting in conjunction with a subunit containing a 3D5 exonuclease activity. (d) When replicating DNA, it is a molecular assembly composed of at least 10 different kinds of subunits. 1. 2. 3. 4. a, b and d a, c and d only d a, b, c and e
17. Which of the following statements about DNA ligase are correct? (a) It forms a phosphodiester bond between a 5-hydroxyl and a 3phosphate in duplex DNA. (b) It requires a cofactor, either NAD; or ATP, depending on the source of the enzyme, to provide the energy to form the phosphodiester bond. (c) It catalyzes its reaction by a mechanism that involves the formation of a covalently linked enzyme adenylate. (d) It catalyzes its reaction by a mechanism that involves the activation of a DNA phosphate through the formation of a phosphoanhydride bond with AMP. (e) It is involved in DNA replication, repair, and recombination. 1. both d and e 2. only a 3. b, c, d and e 4. a, b and c 18. In semiconservative replication of DNA, a. the original double helix remains intact and a new double helix forms. b. the strands of the double helix separate and act as templates for new strands. c. polymerization is catalyzed by RNA polymerase. d. polymerization is catalyzed by a double helical enzyme. e. DNA is synthesized from amino acids. 19. Which of the following does not occur during DNA replication? a. Unwinding of the parent double helix b. Formation of short pieces that are connected by DNA ligase c. Complementary base pairing
d. Use of a primer e. Polymerization in the 3-to-5 direction
20. One strand of DNA has the sequence 5ATTCCG3. The complementary strand for this is a. 5TAAGGC3 b. 5ATTCCG3 c. 5ACCTTA3 d. 5CGGAAT3 e. 5GCCTTA3 21. The role of DNA ligase in DNA replication is to a. add more nucleotides to the growing strand one at a time. b. open up the two DNA strands to expose template strands. c. ligate base to sugar to phosphate in a nucleotide. d. bond Okazaki fragments to one another. e. remove incorrectly paired bases. 22.
23.
24. Which one of the following DNA polymerase is essential for both the replication and repair of DNA? (a) DNA polymerase I (b) DNA polymerase II (c) DNA polymerase III (d) DNA polymerase d
25. Which of the following processes does not take place in the 53 direction? 1. DNA replication 2. Transcription 3. Nick translation 4. RNA editing 27. A culture of E. coli growing in a medium containing 15NH4Cl is switched to a medium containing 14NH4Cl for three generations (an eightfold increase in population). What is the molar ratio of hybrid DNA (15N14N) to light DNA (14N14N) at this point? 1. 0.33 2. 0 .60 3. 0.80 4. 1.0
26. DNA repair, synthesis and recombination are intimately connected and inter dependent. An apparent commonality between processes of DNA replication and repair in the enzymatically catalyzed synthesis of DNA polynucleotide segments, which can be assembled with preexisting polynucleotides, leading to repair or replication. Synthesis of these polynucleotide segments is catalyzed by a group of enzymes DNAdependant DNA polymerases. In the case of E.coli, DNA polymerase has been isolated in three distinct forms whereas five main types of polymerase have been isolated from mammalian cells. All the polymerases synthesize polynucleotides only in the 5' 3' direction. If polynucleotide chains could be elongated in 3 5' direction, the hypothetical growing 5' terminus, rather than the incoming nucleotide, would carry a triposphate that is unsuitable for further elongation. The 3' 5 exonuclease activity is not associated with all the polymerases and only present in (A) All E. coli DNA polymerases but not all mammalian polymerases. (B) Pol I, Pol II, Pol III, Pol , Pol .
(C) Pol I, Pol II, Pol , Pol, Pol (D) Pol I, Pol II, Pol, Pol . The correct statements are 1. (A) and (B). 2. (A), (B) and (C). 3. (A) and (C). 4. (A), (C) and (D). 28. Deletion of the leader sequence of trp operon of E. coli would result in a. decreased transcription of trp operon b. increased transcription of trp operon c. no effect on transcription d. decreased transcription of trp operon in the presence of tryptophan 29. Expression in poor amount and inactive form of a eukaryotic protein from eukaryotic gene in Escherichia coli using its expression vector is due to P. the absence of capping mechanism of mRNA Q. codon bias R. absence of polyadenylation S. absence of proper glycosylation a. P, Q b. Q, R c. Q, S d. P, S 30. If E. coli bacteria are grown in the absence of both glucose and lactose, which of the following events will occur? P. the lac repressor will bind to the operator sequence Q. the CAP (catabolite gene activator protein) will activate transcription R. RNA polymerase holoenzyme will bind to the lac promoter and form open complex S. the lac operon will be transcriptionally active a. only P b. only Q c. P and R d. Q and S
31. Which of the statements are correct? Spliceosomes P. are composed of RNA and protein Q. recognize RNA sequences that signal for removal of introns R. can produce different mRNA molecules by splicing at alternate site S. mediates splicing of group I introns a. P and Q b. P, R and S c. P, Q and R d. P, Q, R and S 32. Which of the following are the mechanism of action of antibiotics? P. interfere with bacterial cell wall synthesis Q. inhibit bacterial transcription of DNA R. inhibit translation of bacterial mRNA S. change the permeability of plasma membrane a. P and Q b. R and S c. P, Q and R d. P, Q, R and S 33. A mutant of E.coli was found which did not synthesize -galactosidase in the presence as well as in the absence of the inducer, IPTG. The investigation revealed that the structural genes of the lac operon were unaltered in the mutant, but one of the controlling genes (I or O) was mutated. The different allelic forms of the regulator gene and the operator gene are as follows: I+-wild type regulator gene Ic-Constitutive regulator Is-Repressor form which is insensitive to inducer O+-Wild type operator gene Oc-Constitutive operator Which of the following mutation in the controlling genes was responsible for the above mentioned behaviour of the E.coli mutant? a. I+O+ b. Ic O+ c. Is O+ d. I+ Oc
34. Which combination of the following statements with regard to gene expression is true? P. Heteronuclear RNA represents contiguous segment of genomic DNA Q. UTRs are part of heteronuclear RNA but not of mRNA R. UTRs are part of exons S. Translation start codon must be in the first exon a. P - true, Q - false, R - false, S - false b. P - true, Q - false, R - true, S - false c. P - true, Q - true, R - false, S - true d. P - false, Q - true, R - true, S true 35. Match the subunit of the RNA polymerase of E. coli in the left column with its putative function during catalysis from the right column. (a) (1) binds the DNA template (b) (2) binds regulatory proteins and sequences (c) (3) binds NTPs and catalyzes bond formation (d) 70 (4) recognizes the promoter and initiates synthesis 1.a-2, b-3, c-1, d-4 2. a-2, b-3, c-4, d-1 3. a-4, b-3, c-1, d-5 4. a-2, b-4, c-3, d-1 36) Which of the following statements about E. coli promoters are correct? (a) They may exhibit different transcription efficiencies. (b) For most genes they include variants of consensus sequences. (c) They specify the start sites for transcription on the DNA template. (d) They have identical and defining sequences. (e) They are activated when C or G residues are substituted into their 10 regions by mutation. (f) Those that have sequences that correspond closely to the consensus sequences and are separated by 17 base pairs are very efficient. 1. a, b, d, and, f 2. a, b, c and f 3. only a and b 4. a, b, c, d
37. The sequence of a duplex DNA segment in a DNA molecule is 5-ATCGCTTGTTCGGA-3 3-TAGCGAACAAGCCT-5 When this segment serves as a template for E. coli RNA polymerase, it gives rise to a segment of RNA with the sequence 5-UCCGAACAAGCGAU-3 Which of the following statements about the DNA segment are correct? (a) The top strand is the coding strand. (b) The bottom strand is the sense strand. (c) The top strand is the template strand. (d) The bottom strand is the antisense strand. 1. only A 2. both b and c 3. a, b, c and d 4. only d 38. Which of the following statements about the subunit of RNA polymerase are not correct? (a) It enables the enzyme to transcribe asymmetrically. (b) It confers on the core enzyme the ability to initiate transcription at promoters. (c) It decreases the affinity of RNA polymerase for regions of DNA that lack promoter sequences. (d) It facilitates the termination of transcription by recognizing hairpins in the transcript. 1. a and b 2. a, b, and c 3 both c and d 4 only d 39. Which of the following statements about the protein of E. coli are correct? (a) It is an ATPase that is activated by binding to single-stranded DNA. (b) It recognizes specific sequences in single-stranded RNA. (c) It recognizes sequences in the DNA template strand. (d) It causes RNA polymerase to terminate transcription at template sites that are different from those that lead to r-independent termination. (e) It acts as a RNADNA helicase. 1. a, b and c 2. both d and e 3. c, d and e
4. both a and e 40. Which of the following statements about eukaryotic mRNAs are correct? (a) They are derived from larger RNA precursors. (b) They result from extensive processing of their primary transcripts before serving as translation components. (c) They usually have poly(A) tails at their 5 ends. (d) They have a cap at their 3 ends. (e) They are often encoded by noncontiguous segments of template DNA. 1.a, b, and e 2. only a 3. both d and e 4. both c and d 41. Which of the following statements about enhancers are correct? (a) They function as promoters. (b) They function when in either orientation in the DNA. (c) They function when on either side of the activated promoter. (d) They function even when located many base pairs away from the promoter. (e) They function only in specific types of cells. 1. only b 2. a, b. c, d and e 3. b, c d, and e 4. bith c and d 42. Which of the following are important sequence elements in the splicing reactions that produce eukaryotic mRNAs? (a) exon sequences located between 20 and 50 nucleotides from the 5 splice site (b) exon sequences located between 20 and 50 nucleotides from the 3 splice site (c) intron sequences located between 20 and 50 nucleotides from the 5 splice site (d) intron sequences located between 20 and 50 nucleotides from the 3 splice site (e) intron sequences at the 5 splice site (f) intron sequences at the 3 splice site 1. d. e and f 2. only b
3. a,d and e 4.both a and e 43. Eukaryotic mRNA splicing involves which of the following? (a) the formation of 2 5 phosphodiester bonds (b) a sequence-specific endoribonuclease that hydrolyzes the phosphodiester bond at the junctions of the intron with the exon (c) the spliceosome (d) the coupling of phosphodiester bond formation to ATP hydrolysis (e) the formation of lariat intermediates 1.both a and b 2. a, b and e 3. only c 4. a, c and e 44.
45.
46.
47.
48.
49.
50.
51.
52.
53.
54.
55.
56.
57.
58.
59. In zinc finger proteins, the amino acid residues that coordinate zinc are (A) Cys and His (B) Asp and Glu (C) Arg and Lys (D) Asp and Arg 60.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- CH 16 and 17 Worksheet-1Dokument3 SeitenCH 16 and 17 Worksheet-1Dani Jo OwensNoch keine Bewertungen
- RNA-Seq and Transcriptome Analysis: Jessica HolmesDokument98 SeitenRNA-Seq and Transcriptome Analysis: Jessica HolmesBiswaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DNA Manipulative EnzymesDokument17 SeitenDNA Manipulative EnzymesZain Ul AbedienNoch keine Bewertungen
- RiboswitchesDokument30 SeitenRiboswitchesYaseswini NeelamrajuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet On DNA and RNA AnswersDokument3 SeitenWorksheet On DNA and RNA AnswersSelena CoronelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity # 12 Gene Therapy AnswerDokument3 SeitenActivity # 12 Gene Therapy AnswerDeocel May VilloriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jun 23Dokument28 SeitenJun 23Sarah DevjiyaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- DNA Structure and Analysis: Chapter 14 (Translation and Protein)Dokument2 SeitenDNA Structure and Analysis: Chapter 14 (Translation and Protein)Cobe Christian LascunaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Recombinant DNA Technology and Its Applications: A Review: August 2018Dokument11 SeitenRecombinant DNA Technology and Its Applications: A Review: August 2018Asteria SeliNoch keine Bewertungen
- BiotechDokument5 SeitenBiotechkaiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DNA Replication Worksheet-2 1Dokument6 SeitenDNA Replication Worksheet-2 1La’Niyah WitherspoonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mus Musculus Transformation Related Protein 73 (Trp73), Transcript Variant 3, mRNADokument7 SeitenMus Musculus Transformation Related Protein 73 (Trp73), Transcript Variant 3, mRNAEeeeeeeeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Self-Learning Home Task (SLHT)Dokument11 SeitenSelf-Learning Home Task (SLHT)GraceEstoleCalo100% (1)
- CBSE Class 12 Biology Question Paper Solution 2010 Set 1Dokument8 SeitenCBSE Class 12 Biology Question Paper Solution 2010 Set 1Bhavya PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biotech Reviewer 2nd Qtr. GRADE 8Dokument4 SeitenBiotech Reviewer 2nd Qtr. GRADE 8Andrew P. Rico0% (1)
- Lecture 1 - Gene Transfer in BacteriaDokument52 SeitenLecture 1 - Gene Transfer in BacteriaAbraham Kang0% (1)
- Paul S. Freemont - Richard I. Kitney Synthetic Biology A Primer World Scientific Publishing - 2012Dokument263 SeitenPaul S. Freemont - Richard I. Kitney Synthetic Biology A Primer World Scientific Publishing - 2012kavir81092Noch keine Bewertungen
- Biotechnology Grade 8 2019-2020 Ms. April Estrella Vale: Subject Grade Level School Year Teacher Subject DescriptionDokument5 SeitenBiotechnology Grade 8 2019-2020 Ms. April Estrella Vale: Subject Grade Level School Year Teacher Subject DescriptionRhan AlcantaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 16 Nucleotide MetabolismDokument71 Seiten16 Nucleotide MetabolismkalkidanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Methods of Gene TransferDokument19 SeitenMethods of Gene TransferSudarshini BorugaddaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6 Mechanism of EvolutionDokument1 Seite6 Mechanism of EvolutionCj LinderoNoch keine Bewertungen
- X Men GeneticsDokument2 SeitenX Men GeneticsPoohbearrr :Noch keine Bewertungen
- L2 - DNA KNex LabDokument16 SeitenL2 - DNA KNex LabChristian MartinezNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2022 Nucleic Acid and Gene Expression Problem Set (Teacher)Dokument28 Seiten2022 Nucleic Acid and Gene Expression Problem Set (Teacher)Sundaravadivel Prabhav (Njc)Noch keine Bewertungen
- NeomycinDokument3 SeitenNeomycinDilek DabanlıNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transcription and Translation Power PointDokument21 SeitenTranscription and Translation Power Pointapi-176402481Noch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 3.2 Karyogram PracticeDokument2 SeitenTopic 3.2 Karyogram PracticeAleksandra LukanovskaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tesis doctoral de Bryan Keith Holland - “Discovery of mature microRNA sequences within the protein-coding regions of global HIV-1 genomes - Predictions of novel mechanisms for viral infection and pathogenicity”Dokument183 SeitenTesis doctoral de Bryan Keith Holland - “Discovery of mature microRNA sequences within the protein-coding regions of global HIV-1 genomes - Predictions of novel mechanisms for viral infection and pathogenicity”Omar Alejandro Herrera ArenasNoch keine Bewertungen
- A2 Edexcel Biology Session 4 7 TranscripDokument25 SeitenA2 Edexcel Biology Session 4 7 TranscripRick WuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch16 Test File-Regulation of Gene ExpressionDokument38 SeitenCh16 Test File-Regulation of Gene ExpressionRojan MirmohamadiNoch keine Bewertungen