Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Fluid Statics - (CO2) PDF
Hochgeladen von
adibazmi93Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Fluid Statics - (CO2) PDF
Hochgeladen von
adibazmi93Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
CHAPTER 02
PRESSURE
&
Fluid statics
1
PRESSURE
1. Defined as a normal force exerted by a fluid per
unit area
P = F/A
2. The pressure at any point in a fluid is the same
in all direction.
3. The only forces between adjacent surface are
pressure forces normal to the surfaces.
4. There are no shearing stresses present in a fluid at
rest
2
Cont. PRESSURE
A
C
B
Acos
Asin
P2
P3
P1
A
Consider a small triangular element ABC at a
point in a fluid, if area AC is A, then area
AB=Asin and area BC=Acos.
For horizontal equilibrium,
For vertical equilibrium,
Thus, the pressure at any point in a fluid is the
same in all direction.
2 1
2 1
sin sin
p p
A p A p
=
= u u
3 1
2 1
cos cos
p p
A p A p
=
= u u
3
Pressure increases with depth:
Relationship Between Pressure and Depth
Cont. PRESSURE
z g P A = A
and
0
1 1
P gz P + = 0
2 2
P gz P + =
So, we obtain:
4
Cont. PRESSURE
Pressure At a Point
5
Cont. PRESSURE
6
Cont. PRESSURE
7
1. The pressure at a point within a fluid mass will be
designated as either an absolute pressure or a gage
pressure.
2. Absolute pressure is measured relative to a
perfect vacuum (absolute zero pressure), where as
gage pressure is measured relative to the local
atmospheric pressure.
Cont. PRESSURE
8
Cont. PRESSURE
9
A barometer is a scientific instrument used to measure atmospheric pressure. It can
measure the pressure exerted by the atmosphere by using mercury. (using water might be
difficult)
BAROMETER
10
~ One of the apparatus we use to measure the pressure in a tank.
~ Mainly consist of glass or plastic U-Tube (different fluid : oil, mercury, water).
MANOMETER
C B
P P =
fluid
1,
fluid 1
A
B
C
h
1
h
2
D
2,
fluid 2
Air
1 1
gh P P
A B
+ =
2 2
gh P P
D C
+ =
Air
11
A pressure gage connected to a chamber reads
65kPa at a location where the atmospheric
pressure is 1.013 bar. Determine the absolute
pressure in the chamber. If the pressure give
reading -10 kPa. Also determine the absolute
pressure
EXAMPLE 01
12
Figure show a manometer with an angle
of 20
0
that used to measure air pressure in
a closed tank. The specific gravity of
manometric fluid that had been used in
this type of manometer is 0.75. If
atmospheric pressure is 200kPa, find the
absolute pressure in closed tank in unit of
kPa. [ g = 9.81 m/s
2
]
EXAMPLE 02
A
In gas, pressure is equal regardless of elevation except for
big difference (hundred meters) of elevation
13
BUOYANCY
The difference between two
forces, F
B
(upward) and F
T
(downward) is a net upward force
called Buoyant Force.
The buoyant force is caused by
the increase of pressure in a fluid
with depth.
( )
B Bottom Top f f f f
F F F g s h A ghA ghA gV = = + = =
14
STABILITY
A floating body is:
Stable if the center of gravity G is below the centroid B of the body or if
the metacenter M is above point G.
Unstable if the point M is below point G.
B
G
15
A crane is used to lower weights into the sea (density 1025 kg/m
3
) for an
underwater construction project. Determine the tension in the rope of
the crane due to a rectangular 0.4m x 0.4m x 3m concrete block (density
2300 kg/m
3
) when it is (a) suspended in the air and (b) completely
immersed in water.
EXAMPLE 03
(a) (b)
16
HYDROSTATIC
FORCES
SUBMERGED
PLANE SURFACES
SUBMERGED
CURVED SURFACES
Fluid static (hydrostatic forces) is used to determine the force acting
on submerged bodies.
It is necessary to calculate the magnitudes and locations of forces
that act on plane and curved surfaces.
17
SUBMERGED PLANE SURFACES
A gh F
c
=
u sin
c c
y h =
c
xx
c p
Ay
I
y y + =
18
SUBMERGED PLANE SURFACES
19
SUBMERGED PLANE SURFACES
Area and Moments of Inertia for Some Common Geometries
20
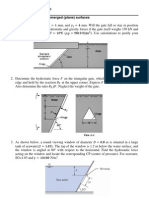
EXAMPLE 04
1.2m wide and 2m high rectangular gate shown below is laying underwater at
angle of 30 with the horizontal water surface. Determine the force F acting
on the gate and the vertical center of pressure, h
P
21
30
y
C
y
P
h
C
h
P
8.6 m
Gate
Water
2 m
EXAMPLE 05
2.0m wide rectangular gate shown in figure is hinged at B and making an
angle of 45 with the horizontal. Determine the minimum force F required to
open the water gate which act on the gate center.
2m
5m
22
SUBMERGED CURVED SURFACES
A h g Fh
=
gV Fv =
2
2
V H R
F F F + =
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
H
V
F
F
1
tan u
23
SUBMERGED CURVED SURFACES
24
EXAMPLE 06
Determine the forces acting on a curved surface.
i) The horizontal force, F
H
ii) The vertical force, F
V
and
iii) Resultant force, F
R
Width=2m
25
EXAMPLE 07
Determine the forces acting on a curved surface.
i) The horizontal force, F
H
ii) The vertical force, F
V
and
iii) Resultant force, F
R
Width=1m
4
2
x
y =
26
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Bobcat T250Dokument964 SeitenBobcat T250Облачно100% (2)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- PRINCIPLES OF HYDROSTATIC PRESSUREDokument55 SeitenPRINCIPLES OF HYDROSTATIC PRESSUREChristine LaurdenNoch keine Bewertungen
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- Kalkulasi Steam Drum - ThermaxDokument52 SeitenKalkulasi Steam Drum - Thermaxlutfi_ismailNoch keine Bewertungen
- API Calculations, Influx Gradient, Well Control CalculationsDokument10 SeitenAPI Calculations, Influx Gradient, Well Control CalculationsMohitTagotra100% (1)
- ASME VIII Div. 1 - 6 Pressure TestingDokument11 SeitenASME VIII Div. 1 - 6 Pressure TestingYoucef ChorfaNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Hydraulic Manual 02Dokument196 SeitenGeneral Hydraulic Manual 02Malek r.i.pNoch keine Bewertungen
- Section 6 - CalculationsDokument29 SeitenSection 6 - CalculationsLeslie Le Jet MatsiengouniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Petroleum Production Engineering: Reservoir and Tubing PerformanceDokument20 SeitenPetroleum Production Engineering: Reservoir and Tubing PerformanceAminah Abdullah100% (1)
- 2 Variable Valve TimingDokument30 Seiten2 Variable Valve Timingadibazmi93100% (1)
- 2000-Comparison of Design Methods For A Tank-Bottom Annular Plate and Concrete RingwallDokument7 Seiten2000-Comparison of Design Methods For A Tank-Bottom Annular Plate and Concrete RingwallbehzadNoch keine Bewertungen
- GRUNDFOS - Mechanical Shaft SealsDokument106 SeitenGRUNDFOS - Mechanical Shaft Sealsrdavid@hotmail.it100% (2)
- SKF - 3 Barrier SolutionDokument13 SeitenSKF - 3 Barrier Solutionadibazmi93Noch keine Bewertungen
- BMW Films Campaign AnalysisDokument14 SeitenBMW Films Campaign Analysisyudhie_7100% (2)
- Curs IPv6 PDFDokument120 SeitenCurs IPv6 PDFadibazmi93Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 09 - Gas Turbines I PDFDokument25 SeitenLesson 09 - Gas Turbines I PDFadibazmi93Noch keine Bewertungen
- Steam Turbine PDFDokument77 SeitenSteam Turbine PDFadibazmi93100% (1)
- Img 0003Dokument1 SeiteImg 0003adibazmi93Noch keine Bewertungen
- What Is A Mechanical Seal PDFDokument2 SeitenWhat Is A Mechanical Seal PDFIrma Tri Puspita SariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diploma in Mechanical Engineering Course Check ListDokument1 SeiteDiploma in Mechanical Engineering Course Check Listadibazmi93Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Statics Chapter SummaryDokument56 SeitenFluid Statics Chapter SummaryNur KamiliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Mechanics - Resource BookDokument167 SeitenFluid Mechanics - Resource BookAkshat ModiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01 Fluid Mechanics Synopsis - (01-20)Dokument20 Seiten01 Fluid Mechanics Synopsis - (01-20)Prabhu Krupa BiswalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fmcpra2 Lab Report PDFDokument20 SeitenFmcpra2 Lab Report PDFNzeza Carine100% (1)
- Incline HydroDokument13 SeitenIncline HydroRenneil De PabloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Center of Pressure On A Submerged Plane SurfaceDokument12 SeitenCenter of Pressure On A Submerged Plane SurfaceStephen Mirdo88% (42)
- Experiment # 04Dokument8 SeitenExperiment # 04shahryarahmad100% (1)
- Module and Activity 1 Fluid Mechanics ENSC 26A BSEE 201Dokument16 SeitenModule and Activity 1 Fluid Mechanics ENSC 26A BSEE 201niel lunaNoch keine Bewertungen
- FMHM GTU Study Material E-Notes Unit-2 04042021064559PMDokument13 SeitenFMHM GTU Study Material E-Notes Unit-2 04042021064559PMDarshana GajjarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multi Phase PR - DropDokument43 SeitenMulti Phase PR - Dropmts1234Noch keine Bewertungen
- Man TC 032 PDFDokument10 SeitenMan TC 032 PDFVendro MunajadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deepwater Cementing Challenges and SolutionsDokument42 SeitenDeepwater Cementing Challenges and SolutionsДмитрий ЩербаковNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluids Set 2Dokument3 SeitenFluids Set 2Jamie Amanda FaderonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arba Minch University Engineering Faculty Civil Engineering DepartmentDokument20 SeitenArba Minch University Engineering Faculty Civil Engineering Departmentastewayb_964354182100% (1)
- 15 08 14 15 46 55 2808 Ccet0280 PDFDokument103 Seiten15 08 14 15 46 55 2808 Ccet0280 PDFGaurav RajputNoch keine Bewertungen
- Model Curriculum Diploma Civil Engineering 310812Dokument66 SeitenModel Curriculum Diploma Civil Engineering 310812Aravind KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 3Dokument4 SeitenTutorial 3RagngeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanical Final Year Projetct - Hydraulic BicycleDokument96 SeitenMechanical Final Year Projetct - Hydraulic BicycleTarun GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- System Specification - PVC-U MetricDokument14 SeitenSystem Specification - PVC-U MetricjavaherNoch keine Bewertungen
- Syllabus DBATUDokument88 SeitenSyllabus DBATUShivanand ArwatNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2022NOV HPGE UnlockedDokument4 Seiten2022NOV HPGE UnlockedKristelle V. TorrealbaNoch keine Bewertungen