Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Procedures For HBsAg-Positive
Hochgeladen von
Miftah WiryaniOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Procedures For HBsAg-Positive
Hochgeladen von
Miftah WiryaniCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
SAMPLE: Enter Your Own Facility Information
Procedures for HBsAg-Positive and Unknown Mothers and Newborns Non-Patient Specific Standing Order for the Hepatitis B Birth Dose1
Date
POLICY STATEMENT: The Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP), American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP), and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommend identification of women who are HBsAg-positive through screening and prophylaxis of their newborns. Proper prophylaxis and completion of the hepatitis B vaccine series can reduce neonatal infection and the potential sequelae by 95%. New York State Public Health Law (NYSPHL) 2500-e mandates that all pregnant women be tested for hepatitis B infection and that all newborns born to infected mothers must be given hepatitis B immune globulin (HBIG) and hepatitis B vaccine within 12 hours of birth. NYSPHL 2500-e mandates that pregnant women who have not been tested or whose test results are unknown be tested immediately (STAT) after admission. Until the test result is known, the woman is assumed to be HBsAg-positive. EQUIPMENT/SUPPLIES: Hepatitis B Vaccine Information Statement Screening and consent form Hepatitis B Vaccine (RECOMBIVAX HB or Engerix-B) Intramuscular, Dose: 0.5 mL. Hepatitis B immune globulin (HBIG) Intramuscular, Dose: 0.5 mL Syringes with " (22-25 gauge) needles COMPETENCY REQUIRED: Current CPR certification1 PROCEDURES: Vaccination of newborns at birth If mother is HBsAg-positive: 1. Newborns born to mothers who are HBsAg-positive must receive hepatitis B immune globulin (HBIG) and hepatitis B vaccine within 12 hours of birth. 2. For newborns weighing less than 2,000 grams, the initial dose of vaccine does not count toward the three dose vaccine series. If mother has unknown HBsAg status: 3. Newborns born to mothers whose HBsAg status is unknown must receive hepatitis B vaccine within 12 hours of birth. 4. The mother must have blood drawn as soon as possible to determine her HBsAg status. 5. If the mother is found to be HBsAg-positive the newborn must receive HBIG as soon as possible, but no later than seven days after birth. 6. Because of the potentially decreased immunogenicity of vaccine in newborns weighing less than 2000g, these newborns must receive both hepatitis B vaccine and HBIG if the mothers HBsAg status cannot be determined 12 hours of birth.2 For HBsAg positive mother upon admission to labor and delivery 1. Examine a copy of the original laboratory report of the pregnant womans hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) test result to verify that the correct test was performed and to verify that the testing date was during this pregnancy and not a previous one.
SAMPLE: Enter Your Own Facility Information
Date
a. Place a copy of the original HBsAg laboratory report into the pregnant womans medical record and the newborns medical record. b. HBsAg test results, including date, must be in both mother and newborn medical records. 3 2. Provide the mother with a Vaccine Information Statement (VIS) upon admission to labor and deliverable or before vaccine administration and ensure the VIS date is accurate.4 3. Obtain written consent for vaccination from the mother upon admission to the hospital preferably before the mother enters the delivery room. 4. Obtain the name, address, and phone number of the newborns primary care provider. a. Notify the pediatric provider of the mothers test result b. Obtain an order for HBIG 5 c. There is little benefit in giving HBIG if more than 7 days have elapsed since birth 5. Provide counsel to the mother. Tell her the following: a. That she may breast-feed her newborn upon delivery, even before hepatitis B vaccine and HBIG are given b. That it is critical for her newborn to complete the full hepatitis B vaccine series on the recommended schedule c. That after completion of at least 3 doses of the hepatitis B vaccine series, blood will need to be drawn from the newborn at 9 months of age (usually done at a well-child visit) to determine if the newborn developed a protective immune response to vaccination or needs additional management d. About modes of hepatitis B virus (HBV) transmission and the need for testing and vaccination of susceptible household, sexual, and needle-sharing contacts e. That she needs to have a medical evaluation for chronic hepatitis B, including an assessment of whether she is eligible for antiviral treatment if not already done 6. In accordance with NYSPHL 2500-e, if the mother refuses vaccination of the newborn after counseling, then contact Child Protective Services (CPS) and the county health department where the mother resides as soon as possible. Post exposure prophylaxis is significantly reduced the longer vaccine administration is delayed. For newborn of HBsAg positive mother 1. Administer single-antigen hepatitis B vaccine (0.5 mL, IM) preferably in the delivery room and within 12 hours of birth. 2. Per medical order, administer HBIG (0.5mL, IM) at separate site from vaccine within 12 hours of birth preferably in the delivery room.5 3. Document the HBIG and hepatitis B vaccine doses in the newborns medical record and include date, time, site of administration, and manufacturer lot number. 4. Give the mother an immunization record card that includes the hepatitis B vaccination and HBIG dates.
SAMPLE: Enter Your Own Facility Information
Date
a. Explain the need for the complete hepatitis B vaccine series to protect her newborn. b. Remind her to bring the card with her each time her child sees a provider. 5. Notify the county health department where the mother resides within 24 hours of the newborns birth and provide the date and time of administration of HBIG and hepatitis B vaccine doses. 6. Indicate the mothers HBsAg status on the NYSDOH Newborn Screening Blood Collection Form as Pos. (positive). 7. Indicate the HBV vaccine administration on the Statewide Perinatal Data System (SPDS).6 8. In accordance with NYSPHL 2500-e, if the mother refuses vaccination of the newborn after counseling, then CPS and the county health department where the mother resides must be contacted within 24 hours. For mother with unknown HBsAg status upon admission to labor and delivery 1. NYSPHL 2500-e requires that when any woman who has not been tested for HBsAg during pregnancy or whose test result is not available upon time of admission a. STAT test must be performed, with the date and time of blood collection recorded in both the maternal and newborn medical records. b. Contact the laboratory to confirm receipt of blood sample and need for STAT results. 2. Provide the mother with a Vaccine Information Statement (VIS) upon admission to labor and deliverable or before vaccine administration and ensure the VIS date is accurate.4 3. Obtain written consent for vaccination from the mother upon admission to the hospital preferably before the mother enters the delivery room. 4. In accordance with NYSPHL 2500-e, if the mother refuses vaccination of the newborn after counseling and test results are not available within 24-48 hours, then CPS and the county health department where the mother resides must be contacted. Forty-eight (48) hours is the maximum time for vaccination of a newborn when the mothers test results are pending. Post exposure prophylaxis is significantly reduced the longer vaccine administration is delayed. For newborn of mother with unknown HBsAg status 1. If the mothers HBsAg test result is not available, administer single-antigen hepatitis B vaccine (0.5mL, IM) within 12 hours of birth. Do not wait for test results before giving vaccine. 2. Give the mother an immunization record card that includes the hepatitis B vaccination date. a. Explain the need for the complete hepatitis B vaccine series to protect her newborn. b. Remind her to bring the card with her each time her child sees a provider.
SAMPLE: Enter Your Own Facility Information
Date
3. If the mothers result remains unknown at the time of newborn discharge: a. Notify the parents, the newborns primary care provider and the county health department where the mother resides that the result is pending since there is little benefit in giving HBIG if more than 7 days have elapsed since birth b. The only exception is when the newborn weighs less than 2,000g. In this case, the newborn must be given both hepatitis B vaccine and HBIG within 12 hours of birth if the mothers HBsAg status cannot be determined c. Document contact information for the parents (e.g., addresses, telephone numbers, and emergency contacts) in case further treatment is needed 4. If the mothers test result comes back positive, obtain order and administer HBIG (0.5mL, IM) to the newborn immediately, but definitely within seven days of birth.5 (See #3a above.) 5. Indicate the mothers HBsAg status on the NYSDOH Newborn Screening Blood Collection Form as either Pos. (positive) or Neg. (negative). Indicate status as Unk. (unknown) only if mothers test results are not available on newborn discharge. 6. Indicate the hepatitis B vaccine administration and HBIG if given on the Statewide Perinatal Data System (SPDS).6 REFERENCES
1
NYS Nurse Practice Act (Education Law Article 139 6909) authorizes the administration of non-patient specific orders for certain immunizations, anti-anaphylactic agents, and HIV and tuberculosis tests across all service delivery systems. A registered professional nurse may execute a non-patient specific regimen prescribed or ordered by a licensed physician or certified nurse practitioner, pursuant to regulations promulgated by the Commissioner of Education. www.op.nysed.gov/prof/nurse/immunguide.htm
2
NYSPHL 2500-e states if an infant of HBsAg positive mother is medically unstable, the infants health care provider may defer vaccine and HBIG until the infant is medically stable.
3
NYSPHL 2500-e mandates that all newborns born to HBsAg-positive women are treated with hepatitis B vaccine and HBIG within 12 hours of birth and with the complete vaccine series. Title 10 Subpart 69-3.3 requires health care facilities to screen and report HBsAg status for all pregnant women, record tests results in newborn medical records, respond to inquiries from local health officers, and provide written documents to accompany newborns transferring between facilities.
4
Federal law requires that you give parents a Hepatitis B Vaccine Information Statement (VIS) before vaccine administration. To obtain a VIS, download it from the IAC website at www.immunize.org/vis or call your county health department.
5
The NYS Nurse Practice Act (Education Law Article 139 6909) does not authorize the administration of HBIG without a patient specific order.
6
This information is automatically transferred to the NYS Immunization Information System (NYSIIS) as required by NYSPHL 2168.
______________________________________________
Authorizing Physician or Nurse Practitioner
From___/___/___to___/___/___
Effective Dates
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Ukuran GigiDokument6 SeitenUkuran GigiMiftah WiryaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5795)
- Section 901 Coarse Aggregate 901-1 General. 901-1.1 Composition: Coarse Aggregate Shall Consist of Naturally Occurring MaterialsDokument6 SeitenSection 901 Coarse Aggregate 901-1 General. 901-1.1 Composition: Coarse Aggregate Shall Consist of Naturally Occurring MaterialsMiftah WiryaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- InTech-Epidemiology and Risk Factors of Periodontal DiseaseDokument19 SeitenInTech-Epidemiology and Risk Factors of Periodontal DiseaseJoji IsacNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- SialolithiasisDokument4 SeitenSialolithiasisMiftah WiryaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Interpretation of Hepatitis B Serologic Test ResultsDokument1 SeiteInterpretation of Hepatitis B Serologic Test ResultsMUHAMMAD JAWAD HASSANNoch keine Bewertungen
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- PD 3110 Major Glossectomy Surgery PDFDokument8 SeitenPD 3110 Major Glossectomy Surgery PDFMiftah WiryaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Glossectomy PDFDokument12 SeitenGlossectomy PDFMiftah WiryaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Antimicrobial ChitosanDokument7 SeitenAntimicrobial ChitosanMiftah WiryaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- ChemoMechanical Debridement - IrrigationDokument15 SeitenChemoMechanical Debridement - IrrigationMiftah WiryaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Dental CariesDokument8 SeitenDental CariesMiftah WiryaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vacuna Hepatitis BDokument2 SeitenVacuna Hepatitis Bluis alejandro rodriguez moraNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- CHN Combined WordDokument88 SeitenCHN Combined WordRayne BonifacioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hep B Vaccine Drug StudyDokument2 SeitenHep B Vaccine Drug StudyFrian MariñasNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- ImmunisasiDokument4 SeitenImmunisasiJessica LawrenceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Hepatitis B and C InfectionDokument7 SeitenHepatitis B and C InfectionDewie HutagaolNoch keine Bewertungen
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- CHN (Clinical Rotation) - LECTUREDokument27 SeitenCHN (Clinical Rotation) - LECTURERhona Marie AcuñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- HepB Provider Tipsheet 508Dokument2 SeitenHepB Provider Tipsheet 508Jamshaid AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- HexaximeDokument12 SeitenHexaximekanharitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- BCG Hepatitisb Hexa1 Hexa2 Penta: Baby Immunization Schedule - QatarDokument3 SeitenBCG Hepatitisb Hexa1 Hexa2 Penta: Baby Immunization Schedule - QatarKiran Kumar AkulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Seminar: Christian Trépo, Henry L Y Chan, Anna LokDokument11 SeitenSeminar: Christian Trépo, Henry L Y Chan, Anna LokGERALDINE JARAMILLO VARGASNoch keine Bewertungen
- p3085 PDFDokument1 Seitep3085 PDFEivon Eyaf Love TormonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intrauterine InfectionDokument64 SeitenIntrauterine Infectionthapan87100% (1)
- Hepatitis b-1Dokument7 SeitenHepatitis b-1api-550162163Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- LIST OF REGISTERED DRUGS As of December 2012Dokument19 SeitenLIST OF REGISTERED DRUGS As of December 2012Benjamin TantiansuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hepatitis B Vaccine and Immunoglobulin Key ConceptDokument7 SeitenHepatitis B Vaccine and Immunoglobulin Key ConceptMai Hoàng Dương QuangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Viral Hepatitis in Pregnancy PDFDokument15 SeitenViral Hepatitis in Pregnancy PDFBerri Rahmadhoni100% (2)
- WA Immunisation ScheduleDokument1 SeiteWA Immunisation ScheduleShin Thian FooNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Hepatits: Nitha K 2nd Year MSC NursingDokument88 SeitenHepatits: Nitha K 2nd Year MSC NursingNITHA KNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pelagio-Drug Study-NewbornDokument6 SeitenPelagio-Drug Study-NewbornShiena Mae PelagioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Expanded Program On Immunization (EPI) 7 Vaccine-Preventable Diseases VaccinesDokument7 SeitenExpanded Program On Immunization (EPI) 7 Vaccine-Preventable Diseases VaccinesLuiciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hepatitis Learning GuideDokument71 SeitenHepatitis Learning Guidequimico clinico 27100% (10)
- Newborn CareDokument15 SeitenNewborn Caresupritha50% (2)
- Epidemiology Exam Questions and AnswersDokument107 SeitenEpidemiology Exam Questions and Answersdimitrios82% (34)
- Quiz On ImmunizationDokument56 SeitenQuiz On ImmunizationFreniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hepatitis B OverviewDokument11 SeitenHepatitis B OverviewJose RonquilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hep B VaccineDokument2 SeitenHep B VaccineJeremy SuhardiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hepatitis B and You: What You Need To KnowDokument11 SeitenHepatitis B and You: What You Need To KnowMalar MuthiahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
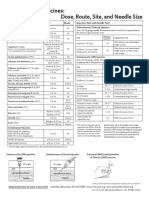
- Injection Site and Needle Size Vaccine Dose RouteDokument1 SeiteInjection Site and Needle Size Vaccine Dose RouteDr Ambana GowdaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adult Immunization Schedule by Vaccine and Age Group - CDCDokument17 SeitenAdult Immunization Schedule by Vaccine and Age Group - CDCCamacaro Arevalo JoseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Immunization Waiver FormDokument1 SeiteImmunization Waiver Formemmanuel espidaNoch keine Bewertungen