Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
401
Hochgeladen von
Justine Louise Bravo FerrerOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
401
Hochgeladen von
Justine Louise Bravo FerrerCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
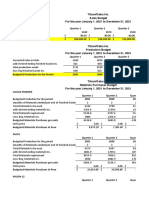
Problem A You are given the following information from the records of Jay Pea Inc.
Total direct labor hours 250,000 Direct costs 10,000,000 Total indirect labor hours 50,000 Total indirect labor related costs 5,000,000 Total indirect non labor related factory costs 7,000,000 41. from the foregoing budgeted data, calculate the budgeted indirect cost rate that would be used in a normal costing system. Problem B The following costs were incurred in January: Direct materials 33,000 Direct labor 28,000 Manufacturing overhead 69,000 Selling expense 16,000 Administrative expense 21,000 42. What is the total of the conversion costs during the month? 43. The prime costs totalled____________ Problem C During the month of January, direct labor costs totalled 1,700,000 and direct labor cost was 60% of prime cost. Total manufacturing costs during January were 8,200,000. The work in process inventory increased 200,000 and finished goods inventory also increased by 112,500. 44. What is the total of manufacturing overhead? 45. Compute for the cost of goods manufactured. 46. Compute for the cost of goods sold. Problem D Ham Burg is a small food cart business, during the next month; the company expects to sell 500 premium foot long sausage sandwiches. The company has the following revenue and cost structure: Selling price per unit 60 Cost per unit 15 Sellers commission 10% of sales Advertising expense 5000 per month Admin expense 3000 per month plus 20% of sales 47. The expected gross profit next month is? 48. The expected total administrative expense next month is? 49. The expected net operating income is?
Problem E Royal Co. produces three types of mens undershirts: t-shirts, v-neck and athletic shirts. In the folding and packaging department, cost is applied to each type of undershirt based on the standard time allowed to fold and package each type of undershirt. The standard time to fold and package each type of undershirt is as follows: T shirt 40 seconds per shirt v- Neck shirt 40 seconds per shirt Athletic shirt 20 seconds per shirt During the month of April, royal produces and sold 50,000 t shirts, 30,000 v-neck shirts and 20,000 athletic shirts. The folding and packaging department costs were 78,200 during April. 50. How much folding and packaging costs should be applied to each T-shirt? Problem F KP manufacturing which began operation on January 1 of the current year produces an industrial scraper that sells for 325 per unit, information related to the current years activities follows: Number of scrapers produced 20,000 Number of scrapers sold 17,000 Variable costs per unit: Direct material 25 Direct labor 35 Manufacturing overhead 60 Annual fixed costs: Manufacturing overhead 400,000 Selling and admin 140,000 KP carries its finished goods inventory at the average unit cost of production. There was no work in process at year end, 51. Compute the companys average unit cost of production. 52. Determine the cost of December 31 finished goods inventory. Problem G A company using the normal costing system and implements the voucher system, has the following data for its first year of operations: a. Direct materials purchases 10,000,000 b. Factory payroll (85% of which is direct labor) 6,000,000 c. Actual factory overhead 4,500,000 The cost of the ending inventories are as follows: Materials 135,000 Work-in-process 555,000 Finished goods 500,000
Page | 1
The company after consulting engineers and other experts initially decided to apply a factory overhead rate that is equivalent to 90% of direct labor cost. Any difference between the actual and applied factory overhead is eventually closed to the cost of goods sold. The total of the vouchers payable (Cr) column in the voucher register amounted to 25,000,000 while the total of the checks issued based on the check register is 23,450,000 53. under the normal costing system, what is the total manufacturing cost? 54. The entry to transfer the cost of goods sold manufactured to finished goods inventory involves a debit to _________ 55. What amount should be presented as vouchers payable in the statement of financial position? TRUE OF FALSE 1. Rent on a factory building used in the production process would be classify as a period cost and fixed cost. 2. Period costs are found only in manufacturing companies, not in merchandising companies. 3. Depreciation on equipment a company uses in selling and administrative activities would be classified as product cost. 4. If the finished goods inventory increases between the beginning and end of the period, then the cost of goods manufactured is smaller than the cost of cost of goods sold. 5. The cost of goods manufactured is calculated by adding the amount of work in process at the end of the year to the cost of raw materials used, direct labor worked, and manufacturing overhead incurred for the year and then subtracting work in process at the beginning of the year. 6. A variable cost is a cost that remains constant in total throughout wide ranges of activity. 7. If the activity level increases, then one would expect the variable cost per unit to increase as well. 8. Fixed costs expressed on a per unit basis vary inversely with changes in activity. 9. Calculation of fixed costs on a per unit basis is critical for internal reporting managers. 10. Managements strategy will determine to a large degree the classification of a fixed cost as discretionary or committed. 11. A cost is either direct or indirect. The classification will not change of the cost object changes. 12. The amount that a manufacturing company could earn by renting unused portion of its warehouse in an example of an opportunity cost.
true
true false true true
false
false false false false false true
13. Internal failure costs result from identification of defects during appraisal process. Such costs may include scrap, rejected products, rework and downtime. 14. Under the voucher system, all cash disbursements made by every check is in payment of numbered voucher. 15. The check register is the basic journal for classifying and summarizing expenditures. 16. Accumulating costs simply means that costs are recorded for use. 17. Inseparability means that differences in customers affect the service firm more than manufacturing firm. 18. In actual system, the firm applies actual costs of direct materials and direct labor while overhead is applied based on a predetermined estimate. 19. Each general ledger account, called controlling accounts, is supported by a number of special journals also known as subsidiary records. 20. In voucher system, the voucher register is a columnar journal that records purchases of all goods, services and equipment.
MULTIPLE CHOICE 21. As the level of activity increases, how will mixed cost in toal and per unit behave? *In total: increase,Per unit: decrease 22. Since Anytime Pizza is open 24 hours a day, its pizza oven is constantly on and is therefore always using natural gas. However, when there is no pizza in the oven, the oven automatically lowers its flame reduces its natural gas usage by 70%. The costs of natural gas would best be described as a: *Mixed Cost 23. When the activity level is expected to decline within the relevant range what effects would be anticipated with respect to each of the following? * Fixed costs per unit : Increase , Variable costs per unit: no change 24. Indirect labor is a part of: *conversion cost 25. Wages paid to a timekeeper in a factory are: *conversion cost 26. Property taxes on a companys factory building would be classified as a(in): *product cost 27. The nursing station on the fourth floor of north hospital is responsible for the care of patients who have undergone
false
false false true true true
false true
Page | 2
orthopaedic surgery. The costs of drugs administered by the nursing station to patients would be classified as: * Direct costs of the patients 28. The costs of staffing and operating and accounting department at central hospital would be considered by the department of surgery to be: * Indirect costs 29. Differential costs can: *be either fixed or variable 30. PING AIRLINES in the pacific corporation provided the following summary of iits quality report for the last two years: Summary of quality cost report (in thousands) This year last year Prevention cost 300 200 Appraisal cost 315 210 Internal failure cost 114 190 External failure costs 621 1200 On the basis of this report, which one of the following statements is most likely correct? *an increase in prevention and appraisal costs resulted in fewer defects, and therefore, resulted in a decrease in internal and external failure costs. 31. In a manufacturers statement of financial position, three inventories may be reported: *finished goods, direct labor and materials 32. A cost accounting system is vital to an entity, what cost accounts systems change, which costs is frequently ignored? * educating users 33. What kind of authority is exercised over subordinates? * Line 34. Which of the following is least likely to be an objective of a cost accounting system? * Sales and commission determination 35. reports which forecast the effect proposed anticipated programs on future operations and financial conditions, and issued regularly for use short or long range planning are referred to as *planning reports 36. The formula for cost of goods sold is * beg work in process plus the sum of direct materials, direct labor and overhead less ending work in process 37. Which is the best explanation of traditional cost accounting? *the general ledger, subsidiary accounts and related records used to accumulate the cost of goods and services provided by entity
38. A plant meters electricity usage at the department level. The department contains several product operations, including the manufacturing of tennis balls. For a can of tennis balls, which of the following is electricity considered? *a variable indirect cost 39. If a firm is more concerned with reliability of data than with the speed at which the data is available. Which of the following costing methods would be the best fit? * Actual costing 40. The motive for normalizing factory overhead costs to avoid the fluctuation in cost per unit resulting from changes in the volume of units * produced in the period
Page | 3
ANSWERS: 41. indirect labor related costs Add: indirect labor non related factory costs Total Divide by: direct labor hours/ costs Indirect cost rate 5,000,000 7,000,000 12,000,000 250,000
48. Regular administrative expense per month 5,000,000 Add: additional expense 7,000,000 (20%*30,000) 12,000,000 Total administrative expense 10,000,000 120% 49. Sellers commission (10%*30,000) Advertising expense Administrative expense Total operating expense Gross profit Less: operating expense Net operating income 3,000 6,000 9,000
42. Direct labor Add:Factory overhead Conversion cost 28,000 69,000 97,000
3,000 5,000 9,000 17,000 22,500 17,000 5,500
43. Direct materials Add: direct labor Prime Cost 33,000 28,000 61,000
50. Type of shirt t- shirt v- neck Athletic shirt Time (in seconds) 40 40 20 Number of shirts 50,000 30,000 20,000 Total time 2,000,000 1,200,000 400,000 3,600,000 Ratio 20/36 12/36 4/36 36/36
44. Total manufacturing cost Less: direct labor Direct materials[(1,700,000/60%)*40%] Factory overhead 8,200,000 1,700,000 1,133,333 5,366,667
45. Total manufacturing cost Less: increase in work in process Cost of goods manufactured 8,200,000 200,000 8,000,000
Folding and packaging department cost Multiply by: ratio of t shirts Total costs of folding and packaging for shirts Divide by: number of shirts Folding and packaging cost applied to each t shirt
78,200 20/36 43,444.44 50,000 .8689
46. Cost of goods manufactures Less: increase in finished goods Cost of goods sold 8,000,000 112,500 7,887,500 52. 47. Sales (P60*500) Cost of goods sold (P15*500) Gross profit 30,000 7,500 22,500 51.
Page | 4
53. Raw materials used (10,000,000-135,000) Direct labor (6,000,000*85%) Factory overhead (5,100,000*90%) Total manufacturing cost 9,865,000 5,100,000 4,590,000 19,555,000
54. Total manufacturing cost Work in process end Cost of goods manufactured Finished goods inventory 19,555,000 555,000 19,000,000 19,000,000
55. Vouchers payable Issued checks Vouchers payable in statement of financial position 25,000,000 23,450,000 1,550,000
Page | 5
1.
2.
3. 4.
5.
6. 7. 8. 9.
10. 11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17. 18.
The control system for materials should encourage cost reductions by eliminating waste and operational inefficiencies. Because raw materials usually represent a significant portion of a manufacturers current asset and often comprise more than 50% of a products manufacturing cost, a business must control its materials form the time they are ordered until the time they are shipped to customers in the form of finished goods. The purchasing department or office are responsible for buying the materials needed by a manufacturer. The form used to notify the purchasing agent that additional materials are needed is known as purchase requisition. The accounting department compares the receving report with the vendors invoice and the purchase order to determine that the materials received are those ordered and billed. Direct costs and controllable costs have the same meaning, Common cost incurred for the benefit of more than one cost objective. A difference in cost between one course of action and another is an opportunity cost. When an invoice or bill is received and payment is to be made immediately, undrr voucher system, only check is to be prepared. The voucher is filed in the unpaid vouchers file according to its numerical sequence. If a check is issued in partial payment of a suppliers invoice, the original voucher is cancelled and two new vouchers are prepared. Once costs have been accoumulated and measured, they are assigned to units of product manufactures or units of service delivered. Cost systems that measure overhead costs on a predetermined basis and use actual costs for direct materials and direct labor are called normal cost system. A cost accountant needs to develop source documents which keep track of costs that are incurred, The variance is considered over applied when applied factory overhead exceeds factory overhead incurred The chart of accounts under a manufacturing business differs from that under a service business with respect to the account titles that affect cost of goods manufactured and cost of goods sold. The system that accumulates cost of products by job is called job order costing. A job order cost sheet is used to accumulate the costs of materials, labor and factory overhead applicable to a process.
19. If a company uses predetermined overhead rates, actual manufacturing overhead costs of a period will be recorder in the manufacturing overhead account, but they will not be recorder on the job cost sheets for the period. 20. In a job order cost system, depreciation on factory equipment should be charged directly to the worki in process account. 21. Commissions paid to salespeople 22. Straight line depreciation on the factory bldg. 23. Salary of the plant supervisor. 24. Wages of the assembly line workers. 25. Machine lubricant used in production activities. 26. Purchase requi- prodn dept supervisor 27. Purchase order-purchasing officer 28. Receiving report- receiving clerk 29. Dr cr memo- accountant 30. Materials requi- prod dept supervisor 31. On the sched of cost of goods manufactured the final cost of goods manu figure represents: The amount of cost of goods completed during current year whether they were started before or during the current year. 32. Tall tales company uses direct labor costs as a basis for computing its predetermined overhead rate. In computing the predetermined overhead rate for last year, the company misclassified a portion of direct labor costs as indirect labor. The effect of this misclassification will be: Overstate the predetermined iverhead rate. 33. When manufacturing overhead is applied to production, it is added to: The work in process account 34. Under a job order costing system, the amount transferred from work in process to finished goods is the sum of the costs charged to all jobs : Completed during the period. 35. Which of the ff industries would be least likely to used a job order costing system?: Oil refinery 36. The job order costing method is used in accumulating product cost when: The product is manufactured on the basis of customers order received. 37. The ff characteristics apply to both the process costing method and the job order costing method except: identifiable batched of prod/ equi units of prod/ use of est costs 38. A method that accumulates costs products by job: Job order cost system 39. The predetermine overhead rate is usually applied to the product when: The job is already completed or it is the end of the reporting period. 40. The voucher system is applicable to: Both normal and actual cost system
Page | 6
True OR false ANSWERS:
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20.
T T T T T F T F F F T T T T T T T F T F
Page | 7
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Cost Accounting QuestionsDokument52 SeitenCost Accounting QuestionsEych Mendoza67% (9)
- Act Exam 1Dokument14 SeitenAct Exam 1aman_nsu100% (1)
- Sample Questions Part 2 - Feb08 (Web)Dokument15 SeitenSample Questions Part 2 - Feb08 (Web)AccountingLegal AccountingLegalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 Steps To Precision Maintenance Reliability SuccessDokument11 Seiten10 Steps To Precision Maintenance Reliability SuccessElvis DiazNoch keine Bewertungen
- E Health Business PlanDokument36 SeitenE Health Business PlanZaman Ali100% (1)
- Test I. True-False Direction: Write T If The Statement Is Correct and F If It Is Wrong BesideDokument8 SeitenTest I. True-False Direction: Write T If The Statement Is Correct and F If It Is Wrong BesideXingYang KiSada0% (1)
- KA SET A Cost PrelimsDokument16 SeitenKA SET A Cost PrelimsGeozelle BenitoNoch keine Bewertungen
- University of Caloocan City Cost Accounting & Control Midterm ExaminationDokument8 SeitenUniversity of Caloocan City Cost Accounting & Control Midterm ExaminationAlexandra Nicole IsaacNoch keine Bewertungen
- T2 Mock Exam (Dec'08 Exam)Dokument12 SeitenT2 Mock Exam (Dec'08 Exam)vasanthipuruNoch keine Bewertungen
- EXAMDokument41 SeitenEXAMJoebet Balbin BonifacioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment-1.1 2.2Dokument22 SeitenAssignment-1.1 2.2Sophia Marie Eredia Ferolino100% (2)
- SAG - Front Office Services NC IIDokument6 SeitenSAG - Front Office Services NC IImiles1280Noch keine Bewertungen
- CIMA Certificate Paper C4 Fundamentals of Business Economics Practice RevisionDokument241 SeitenCIMA Certificate Paper C4 Fundamentals of Business Economics Practice RevisionNony Um'yioraNoch keine Bewertungen
- MNM3702 Full Notes - Stuvia PDFDokument57 SeitenMNM3702 Full Notes - Stuvia PDFMichaelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strategic Cost Management FinalsDokument17 SeitenStrategic Cost Management FinalshsjhsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practical Guide To Production Planning & Control [Revised Edition]Von EverandPractical Guide To Production Planning & Control [Revised Edition]Bewertung: 1 von 5 Sternen1/5 (1)
- Cost Accounting RTP CAP-II June 2016Dokument31 SeitenCost Accounting RTP CAP-II June 2016Artha sarokarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 Acct 1abDokument16 Seiten10 Acct 1abJerric Cristobal100% (1)
- A Comparative Analysis On Fuel-Oil Distribution Companies of BangladeshDokument15 SeitenA Comparative Analysis On Fuel-Oil Distribution Companies of BangladeshTanzir HasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 97 - Test 1 MGT 605Dokument8 Seiten97 - Test 1 MGT 605Anonymous AGI7npNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 4 - Multiple Job Order Cost SystemDokument24 SeitenModule 4 - Multiple Job Order Cost SystemSonali Jagath100% (1)
- UGRD-MGT6147 Strategic Cost Management Prelim ExaminationDokument13 SeitenUGRD-MGT6147 Strategic Cost Management Prelim Examinationjonathan anatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reviewer in Cost Accounting (Midterm)Dokument11 SeitenReviewer in Cost Accounting (Midterm)Czarhiena SantiagoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prelim ExaminationDokument46 SeitenPrelim ExaminationJenny Rose M. YocteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cost Management: A Case for Business Process Re-engineeringVon EverandCost Management: A Case for Business Process Re-engineeringNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6 Applied Performance PracticesDokument3 SeitenChapter 6 Applied Performance PracticesJustine Louise Bravo Ferrer100% (1)
- 23 - GE Nine Cell MatrixDokument24 Seiten23 - GE Nine Cell Matrixlali62100% (1)
- Chapter 2 EditedDokument23 SeitenChapter 2 EditedttttNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management Accounting: Decision-Making by Numbers: Business Strategy & Competitive AdvantageVon EverandManagement Accounting: Decision-Making by Numbers: Business Strategy & Competitive AdvantageBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Lazaro Vs SSSDokument2 SeitenLazaro Vs SSSFatima Briones100% (1)
- Reviewer: Accounting For Manufacturing OperationsDokument16 SeitenReviewer: Accounting For Manufacturing Operationsgab mNoch keine Bewertungen
- Midterm Test BankDokument3 SeitenMidterm Test BankSITTIE SAILAH PATAKNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ac102 Rev01-03Dokument24 SeitenAc102 Rev01-03Aaron DownsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Survey of Accounting 6th Edition Warren Test BankDokument48 SeitenSurvey of Accounting 6th Edition Warren Test Bankdariusarnoldvin100% (26)
- General Instructions: Write All Your Answers in The Assignment Notebook Only. Answers Will Be Declared Later This Week. True or FalseDokument5 SeitenGeneral Instructions: Write All Your Answers in The Assignment Notebook Only. Answers Will Be Declared Later This Week. True or FalseIrishNoch keine Bewertungen
- True/False Questions: labor-intensive (cần nhiều nhân công)Dokument31 SeitenTrue/False Questions: labor-intensive (cần nhiều nhân công)Ngọc MinhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accounting and Finance-1Dokument36 SeitenAccounting and Finance-1Rao Zaheer100% (1)
- Paper - 4: Cost Accounting and Financial Management Section A: Cost Accounting QuestionsDokument22 SeitenPaper - 4: Cost Accounting and Financial Management Section A: Cost Accounting QuestionsSneha VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz 1 - Chapt 19-20-21Dokument7 SeitenQuiz 1 - Chapt 19-20-21Giovanna CastilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- CostDokument3 SeitenCostmaria cruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Examination Cost Accounting 2019 FinalDokument6 SeitenFinal Examination Cost Accounting 2019 FinalElias DeusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Exam Chapter 1-3Dokument5 SeitenPractice Exam Chapter 1-3Renz Paul MirandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Remedial 2Dokument6 SeitenRemedial 2Jelwin Enchong BautistaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap 018Dokument43 SeitenChap 018josephselo100% (1)
- Ac102 ch2Dokument21 SeitenAc102 ch2Fisseha GebruNoch keine Bewertungen
- UntitledDokument65 SeitenUntitledGleiza HoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Exam AkmenlanDokument12 SeitenFinal Exam AkmenlanThomas DelongeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prelim ExaminationDokument4 SeitenPrelim ExaminationEllen Gold PalmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- First Term Exam (Sba) : RequiredDokument23 SeitenFirst Term Exam (Sba) : RequiredblueberryNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACC213 ReviewerDokument6 SeitenACC213 ReviewerSHAZ NAY GULAYNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 10Dokument11 SeitenChapter 10clarice razonNoch keine Bewertungen
- PrelimsDokument5 SeitenPrelimsJamii Dalidig MacarambonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hi HiDokument27 SeitenHi HiQuế Hoàng Hoài Thương0% (1)
- Cga-Canada Management Accounting Fundamentals (Ma1) Examination March 2014 Marks Time: 3 HoursDokument18 SeitenCga-Canada Management Accounting Fundamentals (Ma1) Examination March 2014 Marks Time: 3 HoursasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Job Order CostingDokument45 SeitenJob Order CostingCleofe Alicnas100% (3)
- Additional FINAL ReviewDokument41 SeitenAdditional FINAL ReviewMandeep SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 MCQTFDokument6 SeitenChapter 2 MCQTFstudent.devyankgosainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 2 - RevisionDokument4 SeitenModule 2 - RevisionFara Yusuf sayedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Q.9. Differentiate Direct Cost and Direct Costing?Dokument10 SeitenQ.9. Differentiate Direct Cost and Direct Costing?Hami KhaNNoch keine Bewertungen
- MG WE FNSACC517 Provide Management Accounting InformationDokument9 SeitenMG WE FNSACC517 Provide Management Accounting InformationGurpreet KaurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mangament AccountingDokument17 SeitenMangament AccountingDue WellNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management AccountingDokument33 SeitenManagement AccountingjazzmahbubNoch keine Bewertungen
- Handout 3 Cost ManagementDokument10 SeitenHandout 3 Cost ManagementNikki San GabrielNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH.3 COMM 305 Managerial AccountingDokument19 SeitenCH.3 COMM 305 Managerial Accountingryry1616Noch keine Bewertungen
- BU330 Accounting For Managers Exam Part 1Dokument6 SeitenBU330 Accounting For Managers Exam Part 1G JhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management Accounting Strategy Study Resource for CIMA Students: CIMA Study ResourcesVon EverandManagement Accounting Strategy Study Resource for CIMA Students: CIMA Study ResourcesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Remodelers Cost of Doing Business Study, 2023 EditionVon EverandRemodelers Cost of Doing Business Study, 2023 EditionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Corporation Notes - Law3A JBTDokument34 SeitenCorporation Notes - Law3A JBTJustine Louise Bravo FerrerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Who Is SheDokument2 SeitenWho Is SheJustine Louise Bravo FerrerNoch keine Bewertungen
- I Must Be Like This Because IDokument3 SeitenI Must Be Like This Because IJustine Louise Bravo FerrerNoch keine Bewertungen
- AseanDokument1 SeiteAseanJustine Louise Bravo FerrerNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 12Dokument1 Seite2 12Justine Louise Bravo FerrerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Text DFDDokument5 SeitenText DFDJustine Louise Bravo FerrerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Text DFDDokument5 SeitenText DFDJustine Louise Bravo FerrerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Documentation Format Cover Page: It Systems Analysis and DesignDokument2 SeitenFinal Documentation Format Cover Page: It Systems Analysis and DesignJustine Louise Bravo FerrerNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is The Clean Water ActDokument3 SeitenWhat Is The Clean Water ActJustine Louise Bravo FerrerNoch keine Bewertungen
- AseanDokument1 SeiteAseanJustine Louise Bravo FerrerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Excel Text Functions ListDokument5 SeitenExcel Text Functions ListJustine Louise Bravo FerrerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Consumer Rights (Reaction)Dokument1 SeiteConsumer Rights (Reaction)Justine Louise Bravo FerrerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Environmental Impact AssessmentDokument13 SeitenEnvironmental Impact AssessmentJustine Louise Bravo FerrerNoch keine Bewertungen
- 21 Irrefundable Laws of LeadershipDokument2 Seiten21 Irrefundable Laws of LeadershipJustine Louise Bravo FerrerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assymmetric InfoDokument41 SeitenAssymmetric InfoJustine Louise Bravo FerrerNoch keine Bewertungen
- SLU NSTP Form 11 - NSTP Activity PaperDokument1 SeiteSLU NSTP Form 11 - NSTP Activity PaperRoxanne Joy MejiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 21 Irrefundable Laws of LeadershipDokument2 Seiten21 Irrefundable Laws of LeadershipJustine Louise Bravo FerrerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Graphical Representation of DataDokument6 SeitenGraphical Representation of DataJustine Louise Bravo FerrerNoch keine Bewertungen
- OrganizationDokument12 SeitenOrganizationJustine Louise Bravo FerrerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assymmetric InfoDokument41 SeitenAssymmetric InfoJustine Louise Bravo FerrerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Game Theory 1Dokument26 SeitenGame Theory 1kodiraRakshithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parents Orguardians Authorization Form For NSTP 1&2 Summer 2011Dokument1 SeiteParents Orguardians Authorization Form For NSTP 1&2 Summer 2011Marie Dhonne100% (1)
- AgencyDokument33 SeitenAgencyJustine Louise Bravo FerrerNoch keine Bewertungen
- AccountingDokument13 SeitenAccountingbeshahashenafe20Noch keine Bewertungen
- Acctg 202 Di Pa FinalDokument10 SeitenAcctg 202 Di Pa FinalJoshua CabinasNoch keine Bewertungen
- IDC IBM Honda Case Study May2017Dokument6 SeitenIDC IBM Honda Case Study May2017Wanya Kumar (Ms.)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Nestle CSRDokument309 SeitenNestle CSRMaha AbbasiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Construction Cost Handbook CNHK 2023Dokument63 SeitenConstruction Cost Handbook CNHK 2023wlv hugoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indo Gold Mines PVT LTDDokument30 SeitenIndo Gold Mines PVT LTDSiddharth Sourav PadheeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Commercial Invoice Vishvamata WOODWARD FINAL DRIVER BOXDokument1 SeiteCommercial Invoice Vishvamata WOODWARD FINAL DRIVER BOXSiva RamanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ABS Summary TextDokument12 SeitenABS Summary TextjesusmemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Examples Transfer PricingDokument15 SeitenExamples Transfer PricingRajat RathNoch keine Bewertungen
- End-Of-Course Test BDokument5 SeitenEnd-Of-Course Test BAngel Reynaldo Panduro MiyakeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Internal Sales Representative As of SAP ERP EhP5 (New)Dokument32 SeitenInternal Sales Representative As of SAP ERP EhP5 (New)Khalid SayeedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comparing FTTH Access Networks Based On P2P and PMP Fibre TopologiesDokument9 SeitenComparing FTTH Access Networks Based On P2P and PMP Fibre TopologiesWewe SlmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 5Dokument31 SeitenLesson 5Glenda DestrizaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Creating Customer Value, Satisfaction and LoyaltyDokument20 SeitenCreating Customer Value, Satisfaction and Loyaltymansi singhNoch keine Bewertungen
- CASESTUDYDokument21 SeitenCASESTUDYLouise Lopez AlbisNoch keine Bewertungen
- !!!EVA 019 AtevaOverviewGradesSheet TS EN 0416 PDFDokument2 Seiten!!!EVA 019 AtevaOverviewGradesSheet TS EN 0416 PDFSlava75Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2189XXXXXXXXX316721 09 2019Dokument3 Seiten2189XXXXXXXXX316721 09 2019Sumit ChakrabortyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shivani Singhal: Email: PH: 9718369255Dokument4 SeitenShivani Singhal: Email: PH: 9718369255ravigompaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Distance Learning 2016 Telecom AcademyDokument17 SeitenDistance Learning 2016 Telecom AcademyDyego FelixNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leadership Development at Hindustan Unilever Limited FinalDokument10 SeitenLeadership Development at Hindustan Unilever Limited FinaldurdenNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Commerce?: Comprehensive DefinitionDokument31 SeitenWhat Is Commerce?: Comprehensive Definitionmuhammad riazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Example of RFP For Credit ScoringDokument4 SeitenExample of RFP For Credit ScoringadaquilaNoch keine Bewertungen

















![Practical Guide To Production Planning & Control [Revised Edition]](https://imgv2-2-f.scribdassets.com/img/word_document/235162742/149x198/2a816df8c8/1709920378?v=1)