Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Minimal Intervention Dentistry
Hochgeladen von
Hanan MohCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Minimal Intervention Dentistry
Hochgeladen von
Hanan MohCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
(1)
Overseas Trained Dentists
Overseas Trained Dentists
February 2005
February 2005
MINIMUM INTERVENTION
MINIMUM INTERVENTION
DENTISTRY
DENTISTRY
OPERATIVE
OPERATIVE
PRINCIPLES
PRINCIPLES
Martin J Tyas
Martin J Tyas
Professor
Professor
School of Dental Science
School of Dental Science
University of Melbourne
University of Melbourne
(2)
Overseas Trained Dentists
Overseas Trained Dentists
February 2005
February 2005
SYNOPSIS
SYNOPSIS
to discuss some of the changes
to discuss some of the changes
which have taken place in the
which have taken place in the
restoration of carious teeth, with
restoration of carious teeth, with
particular emphasis on
particular emphasis on
minimum
minimum
intervention
intervention
(3)
Overseas Trained Dentists
Overseas Trained Dentists
February 2005
February 2005
Greene
Greene
Vardiman
Vardiman
BLACK
BLACK
(1835
(1835
-
-
1915)
1915)
(4)
Overseas Trained Dentists
Overseas Trained Dentists
February 2005
February 2005
GV BLACK
GV BLACK
extensive research on
extensive research on
amalgam (Dental Cosmos,
amalgam (Dental Cosmos,
1896)
1896)
A Work on Operative
A Work on Operative
Dentistry in Two Volumes
Dentistry in Two Volumes
(1908)
(1908)
(5)
Overseas Trained Dentists
Overseas Trained Dentists
February 2005
February 2005
BLACK
BLACK
S TEACHINGS
S TEACHINGS
highly
highly
formalised
formalised
cavity designs;
cavity designs;
precise size and geometry
precise size and geometry
weak, non
weak, non
-
-
adhesive
adhesive
materials
materials
extension for prevention
extension for prevention
(6)
Overseas Trained Dentists
Overseas Trained Dentists
February 2005
February 2005
(7)
Overseas Trained Dentists
Overseas Trained Dentists
February 2005
February 2005
SURGICAL MODEL
SURGICAL MODEL
(
(
1900
1900
-
-
1980s)
1980s)
caries can be
caries can be
cured
cured
by
by
excision of all decayed tooth
excision of all decayed tooth
structure, and replacement
structure, and replacement
with a filling material
with a filling material
(8)
Overseas Trained Dentists
Overseas Trained Dentists
February 2005
February 2005
STRUCTURALLY WEAKENED
STRUCTURALLY WEAKENED
TOOTH
TOOTH
NON
NON
-
-
ADHESIVE RESTORATIVE
ADHESIVE RESTORATIVE
MATERIAL
MATERIAL
+
+
HIGH INCIDENCE OF
HIGH INCIDENCE OF
SUBSEQUENT TOOTH FRACTURE
SUBSEQUENT TOOTH FRACTURE
(9)
Overseas Trained Dentists
Overseas Trained Dentists
February 2005
February 2005
(10)
Overseas Trained Dentists
Overseas Trained Dentists
February 2005
February 2005
WHAT
WHAT
S CHANGED?
S CHANGED?
enhanced understanding of the carious
enhanced understanding of the carious
process
process
an infectious disease
an infectious disease
demineralisation/remineralisation
demineralisation/remineralisation
cycle
cycle
recognition of the rle of fluoride
recognition of the rle of fluoride
development of adhesive materials
development of adhesive materials
glass
glass
-
-
ionomer cement
ionomer cement
resin
resin
resin
-
-
-
based materials
based materials
based materials
(11)
Overseas Trained Dentists
Overseas Trained Dentists
February 2005
February 2005
MEDICAL MODEL
MEDICAL MODEL
OF
OF
MINIMUM
MINIMUM
INTERVENTION
INTERVENTION
DENTISTRY
DENTISTRY
reduction in cariogenic bacteria
reduction in cariogenic bacteria
reduction in cariogenic bacteria
preventive measures
preventive measures
preventive measures
remineralisation of early lesions
remineralisation of early lesions
minimum surgical intervention of
minimum surgical intervention of
cavitated lesions
cavitated lesions
repair of defective restorations
repair of defective restorations
Tyas et al., Tyas et al., Int Int Dent J 2000;50:1 Dent J 2000;50:1- -12 12
(12)
Overseas Trained Dentists
Overseas Trained Dentists
February 2005
February 2005
REMINERALISATION OF EARLY
REMINERALISATION OF EARLY
ENAMEL LESIONS
ENAMEL LESIONS
casein phosphopeptide-amorphous
calcium phosphate (CPP-ACP)
releases Ca
++
, PO
4
--
sugar-free gum (Recaldent
);
toothpaste; mouthwash
casein phosphopeptide
casein phosphopeptide
-
-
amorphous
amorphous
calcium phosphate (CPP
calcium phosphate (CPP
-
-
ACP)
ACP)
releases Ca
releases Ca
++ ++
, PO
, PO
4 4
-- --
sugar
sugar
-
-
free gum (
free gum (
Recaldent
Recaldent
);
);
toothpaste; mouthwash
toothpaste; mouthwash
Reynolds (1998). J Spec Care Dent 18:8 Reynolds (1998). J Spec Care Dent 18:8- -16 16
fluoride + CPP
fluoride + CPP
-
-
ACP
ACP
(CPP
(CPP
-
-
ACFP)
ACFP)
additive effect of F
additive effect of F
- -
Prof L J Walsh, U of Q
Prof L J Walsh, U of Q
(13)
Overseas Trained Dentists
Overseas Trained Dentists
February 2005
February 2005
INDICATIONS FOR RESTORATION
INDICATIONS FOR RESTORATION
(
(
SURGICAL APPROACH
SURGICAL APPROACH
)
)
cavitation rendering
cavitation rendering
plaque control
plaque control
unachievable
unachievable
aesthetics
aesthetics
unsatisfactory
unsatisfactory
function
function
compromised
compromised
(14)
Overseas Trained Dentists
Overseas Trained Dentists
February 2005
February 2005
(15)
Overseas Trained Dentists
Overseas Trained Dentists
February 2005
February 2005
ADHESIVE
ADHESIVE
PREPARATIONS
PREPARATIONS
conservative cavity
conservative cavity
macromechanical retention not
macromechanical retention not
required
required
reduction in microleakage
reduction in microleakage
reduced incidence of secondary caries
reduced incidence of secondary caries
reduced marginal staining
reduced marginal staining
reduced pulp damage
reduced pulp damage
restoration of tooth strength
restoration of tooth strength
(16)
Overseas Trained Dentists
Overseas Trained Dentists
February 2005
February 2005
DENTINE CARIES
DENTINE CARIES
infected
infected
(outer carious) dentine (A)
(outer carious) dentine (A)
soft, moist, pale yellow/brown
soft, moist, pale yellow/brown
heavy bacterial load
heavy bacterial load
collagen degraded
collagen degraded
non
non
-
-
remineralisable
remineralisable
affected
affected
(inner carious) dentine (B)
(inner carious) dentine (B)
hard, dry, dark brown/black
hard, dry, dark brown/black
few or no bacteria
few or no bacteria
collagen cross
collagen cross
-
-
links intact
links intact
remineralisable
remineralisable
A A
B B
(17)
Overseas Trained Dentists
Overseas Trained Dentists
February 2005
February 2005
PRINCIPLES OF MINIMUM
PRINCIPLES OF MINIMUM
INTERVENTION RESTORATIONS
INTERVENTION RESTORATIONS
only degraded enamel and
only degraded enamel and
infected
infected
dentine should be removed;
dentine should be removed;
affected
affected
dentine can be left
dentine can be left
undermined enamel can be supported by
undermined enamel can be supported by
the adhesive restorative material
the adhesive restorative material
the cavity shape is dictated by the caries
the cavity shape is dictated by the caries
and is unique
and is unique
Black
Black
s
s
formal
formal
cavity designs are obsolete
cavity designs are obsolete
(18)
Overseas Trained Dentists
Overseas Trained Dentists
February 2005
February 2005
(19)
Overseas Trained Dentists
Overseas Trained Dentists
February 2005
February 2005
GLASS
GLASS
-
-
IONOMER CEMENTS
IONOMER CEMENTS
powder (basic)
powder (basic)
fluoroaluminosilicate glass
fluoroaluminosilicate glass
liquid (acidic)
liquid (acidic)
aqueous polyalkenoic acid
aqueous polyalkenoic acid
setting reaction
setting reaction
acid:base
acid:base
(resin polymerisation)
(resin polymerisation)
(20)
Overseas Trained Dentists
Overseas Trained Dentists
February 2005
February 2005
GLASS IONOMER CEMENTS
GLASS IONOMER CEMENTS
tooth
tooth
-
-
coloured
coloured
moisture
moisture
-
-
tolerant
tolerant
adhesive to tooth structure
adhesive to tooth structure
release fluoride
release fluoride
prevent secondary caries?
prevent secondary caries?
promotes remineralisation of
promotes remineralisation of
affected
affected
dentine?
dentine?
brittle
brittle
(21)
Overseas Trained Dentists
Overseas Trained Dentists
February 2005
February 2005
Ngo, Ngo, in in Mount 2002 Mount 2002
(22)
Overseas Trained Dentists
Overseas Trained Dentists
February 2005
February 2005
MINIMAL INTERVENTION APPROACHES
MINIMAL INTERVENTION APPROACHES
occlusal surfaces
occlusal surfaces
fissure sealant
fissure sealant
preventive resin restoration
preventive resin restoration
posterior approximal surfaces
posterior approximal surfaces
tunnel
tunnel
and
and
internal
internal
preparations
preparations
slot
slot
preparations
preparations
(23)
Overseas Trained Dentists
Overseas Trained Dentists
February 2005
February 2005
FISSURE SEALANT
FISSURE SEALANT
(24)
Overseas Trained Dentists
Overseas Trained Dentists
February 2005
February 2005
Dr Hien Ngo
Adelaide
PREVENTIVE RESIN RESTORATION
PREVENTIVE RESIN RESTORATION
(25)
Overseas Trained Dentists
Overseas Trained Dentists
February 2005
February 2005
(26)
Overseas Trained Dentists
Overseas Trained Dentists
February 2005
February 2005
GIC
GIC
(27)
Overseas Trained Dentists
Overseas Trained Dentists
February 2005
February 2005
(28)
Overseas Trained Dentists
Overseas Trained Dentists
February 2005
February 2005
THE APPROXIMAL CAVITY
THE APPROXIMAL CAVITY
(29)
Overseas Trained Dentists
Overseas Trained Dentists
February 2005
February 2005
EVOLUTION OF THE APPROXIMAL CAVITY
EVOLUTION OF THE APPROXIMAL CAVITY
Soderholm,
Soderholm,
Tyas & J okstad.
Tyas & J okstad.
Crit Rev Oral
Crit Rev Oral
Biol
Biol
Med
Med
1998;9:464
1998;9:464
-
-
79
79
(30)
Overseas Trained Dentists
Overseas Trained Dentists
February 2005
February 2005
Hunt, 1984 Hunt, 1984
Knight, 1984 Knight, 1984
TUNNEL PREPARATION
TUNNEL PREPARATION
GIC
GIC
(31)
Overseas Trained Dentists
Overseas Trained Dentists
February 2005
February 2005
(32)
Overseas Trained Dentists
Overseas Trained Dentists
February 2005
February 2005
Lasfargues et al. Lasfargues et al.
SLOT PREPARATION
SLOT PREPARATION
(33)
Overseas Trained Dentists
Overseas Trained Dentists
February 2005
February 2005
MANAGEMENT OF DEFECTIVE
MANAGEMENT OF DEFECTIVE
RESTORATIONS
RESTORATIONS
(34)
Overseas Trained Dentists
Overseas Trained Dentists
February 2005
February 2005
RESTORATION REPLACEMENT
RESTORATION REPLACEMENT
60
60
% of a general practitioner
% of a general practitioner
s time is
s time is
spent replacing restorations
spent replacing restorations
most frequent reason is secondary caries
most frequent reason is secondary caries
replacement results in
replacement results in
larger cavity
larger cavity
damage to adjacent teeth
damage to adjacent teeth
increased risk of more complex
increased risk of more complex
restorations
restorations
new defects introduced
new defects introduced
(35)
Overseas Trained Dentists
Overseas Trained Dentists
February 2005
February 2005
(36)
Overseas Trained Dentists
Overseas Trained Dentists
February 2005
February 2005
OPTIONS FOR MANAGEMENT
OPTIONS FOR MANAGEMENT
recontour
recontour
and/or polish
and/or polish
fissure seal margins
fissure seal margins
repair local defect
repair local defect
replace restoration
replace restoration
INCREASINGLY
INCREASINGLY
INVASIVE
INVASIVE
(37)
Overseas Trained Dentists
Overseas Trained Dentists
February 2005
February 2005
(38)
Overseas Trained Dentists
Overseas Trained Dentists
February 2005
February 2005
(39)
Overseas Trained Dentists
Overseas Trained Dentists
February 2005
February 2005
(40)
Overseas Trained Dentists
Overseas Trained Dentists
February 2005
February 2005
(41)
Overseas Trained Dentists
Overseas Trained Dentists
February 2005
February 2005
(42)
Overseas Trained Dentists
Overseas Trained Dentists
February 2005
February 2005
(43)
Overseas Trained Dentists
Overseas Trained Dentists
February 2005
February 2005
SOME INDICATIONS FOR
SOME INDICATIONS FOR
RESTORATION REPLACEMENT
RESTORATION REPLACEMENT
extensive secondary caries
extensive secondary caries
cannot be removed in a repair
cannot be removed in a repair
procedure
procedure
aesthetic need
aesthetic need
pulpal pathology
pulpal pathology
(44)
Overseas Trained Dentists
Overseas Trained Dentists
February 2005
February 2005
The professional man has no
The professional man has no
right to be other than a continuous
right to be other than a continuous
student
student
GV BLACK:
GV BLACK:
(45)
Overseas Trained Dentists
Overseas Trained Dentists
February 2005
February 2005
TWENTIETH CENTURY (GV BLACK)
TWENTIETH CENTURY (GV BLACK)
Extension for prevention
Extension for prevention
TWENTY
TWENTY
-
-
FIRST CENTURY
FIRST CENTURY
Prevention of extension
Prevention of extension
OPERATIVE DENTISTRY
OPERATIVE DENTISTRY
(46)
Overseas Trained Dentists
Overseas Trained Dentists
February 2005
February 2005
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Dental CodingDokument74 SeitenDental CodingSakshi Bishnoi100% (2)
- Dental ProductsDokument17 SeitenDental Productsade safitri100% (1)
- Dentistry For DummiesDokument98 SeitenDentistry For DummiesKristina Robles75% (4)
- Etiology of MalocclusionDokument28 SeitenEtiology of MalocclusionPriyaancaHaarsh100% (3)
- Dental CariesDokument25 SeitenDental CariesFemi100% (1)
- Restoring Endodontically Treated TeethDokument20 SeitenRestoring Endodontically Treated Teethlishenwong100% (1)
- Traumatic InjuriesDokument43 SeitenTraumatic Injuriessandsiramesh100% (1)
- Non Carious LesionsDokument38 SeitenNon Carious LesionsDrVarun Menon75% (4)
- Management of Discoloured Teeth: Presented By: Amisha Jain M.D.S II YearDokument44 SeitenManagement of Discoloured Teeth: Presented By: Amisha Jain M.D.S II YearANUBHANoch keine Bewertungen
- Crown LengtheningDokument89 SeitenCrown LengtheningMohamadAl-askar83% (6)
- Stain Removing and Whitening by Baking Soda Dentifrice PDFDokument7 SeitenStain Removing and Whitening by Baking Soda Dentifrice PDFDoruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diagnosing and Managing Orofacial Dental Pain EmergenciesDokument151 SeitenDiagnosing and Managing Orofacial Dental Pain EmergenciesHanan Moh91% (22)
- Diagnosing and Managing Orofacial Dental Pain EmergenciesDokument151 SeitenDiagnosing and Managing Orofacial Dental Pain EmergenciesHanan Moh91% (22)
- Developmental Anomalies of The ToothDokument14 SeitenDevelopmental Anomalies of The ToothAman Chowdhry100% (1)
- Cu Sil DenturesDokument6 SeitenCu Sil Denturessiddu76Noch keine Bewertungen
- Dental Caries: by DR: Hanan Eid GamalDokument107 SeitenDental Caries: by DR: Hanan Eid Gamalruchika100% (1)
- Are Occulsion and Comprehensive Dentistry Really That ImportantDokument20 SeitenAre Occulsion and Comprehensive Dentistry Really That ImportantAhmed HamzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Finishing & DetailingDokument28 SeitenFinishing & DetailingBikramjeet Singh100% (4)
- Improving Aesthetics in Patients With Complete DenturesDokument4 SeitenImproving Aesthetics in Patients With Complete DenturesMohsin HabibNoch keine Bewertungen
- CLEAR ALIGNERS PedagogyDokument23 SeitenCLEAR ALIGNERS PedagogyGudiyA Kaur100% (1)
- Oral Hygiene 10 PDFDokument22 SeitenOral Hygiene 10 PDFSree Latha100% (2)
- English For DentistsDokument5 SeitenEnglish For DentistsPalmira Aragonés RubioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Occupational Dental Erosion: Worksafebc Evidence Based Practice GroupDokument36 SeitenOccupational Dental Erosion: Worksafebc Evidence Based Practice GroupSilvia CidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dr. Vibha Hegde - 18Dokument5 SeitenDr. Vibha Hegde - 18Biswaroop ChandraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Behind The Scenes at The Toothpaste Aisle: The Chemistry of Dental MaterialsDokument2 SeitenBehind The Scenes at The Toothpaste Aisle: The Chemistry of Dental Materialskurnia ramadaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 SMDokument11 Seiten1 SMLuis SanchezNoch keine Bewertungen
- InTech-Molar Incisor Hypomineralization Morphological Aetiological Epidemiological and Clinical ConsiderationsDokument25 SeitenInTech-Molar Incisor Hypomineralization Morphological Aetiological Epidemiological and Clinical ConsiderationsNeagu EmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Part 4s Lecture List UpdatedDokument6 SeitenPart 4s Lecture List Updatedmusy9999Noch keine Bewertungen
- White Spot Lesions ReviewDokument2 SeitenWhite Spot Lesions ReviewsyedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dental Caries DevelopmentDokument8 SeitenDental Caries Developmentريام الموسويNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bast Dental EmergenciesDokument28 SeitenBast Dental Emergenciesjamie chewNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eb 79Dokument5 SeitenEb 79mohammad naufalNoch keine Bewertungen
- DMF and Def Index: Factors Affecting Caries PrevalenceDokument6 SeitenDMF and Def Index: Factors Affecting Caries Prevalencenimisha kakkadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dental Plaque and Caries by Agbafor Chidera Autosaved)Dokument14 SeitenDental Plaque and Caries by Agbafor Chidera Autosaved)Agbafor DeraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dental Caries Causes, Types & PreventionDokument4 SeitenDental Caries Causes, Types & PreventionChana 'eLecter' ChuLumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Esthetic Management of Anterior Teeth with GiomerDokument7 SeitenEsthetic Management of Anterior Teeth with GiomerFoysal Sirazee100% (1)
- pubmed-9395117Dokument3 Seitenpubmed-9395117Nabilaa PutriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dental TerminologyDokument86 SeitenDental TerminologyREFTA DEVINoch keine Bewertungen
- Mouth Preparation for Removable Partial DenturesDokument45 SeitenMouth Preparation for Removable Partial DenturesArbaz SajjadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Non Cervical Lesions Meena MamDokument120 SeitenNon Cervical Lesions Meena Mamanshida v pNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dentifrices - An Update: Robin Davies, Crispian Scully, Antony J. PrestonDokument7 SeitenDentifrices - An Update: Robin Davies, Crispian Scully, Antony J. Preston2oclockNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Prevalence of Neсariodental Diseases of the Tooth in the Valley (Foothills)Dokument6 SeitenThe Prevalence of Neсariodental Diseases of the Tooth in the Valley (Foothills)Central Asian StudiesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acondicionamiento, Adhesión y Cementado de Aparatología Ortodóncica en Dientes Con Alteraciones Del Esmalte. Revisión de LiteraturaDokument10 SeitenAcondicionamiento, Adhesión y Cementado de Aparatología Ortodóncica en Dientes Con Alteraciones Del Esmalte. Revisión de Literaturaruqoyah022Noch keine Bewertungen
- Peraturan Bpjs Poli GigiDokument11 SeitenPeraturan Bpjs Poli GigitarikusumaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Preven Lec 2Dokument7 SeitenPreven Lec 2ريام الموسويNoch keine Bewertungen
- Are Uoride Releasing Dental Materials Clinically Effective On Caries Control?Dokument11 SeitenAre Uoride Releasing Dental Materials Clinically Effective On Caries Control?Kary RojasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management of The Compromised First Permanent Molar CG-A010 - 04 UpdatedDokument8 SeitenManagement of The Compromised First Permanent Molar CG-A010 - 04 UpdatedmahmoudNoch keine Bewertungen
- Overlay DentureDokument5 SeitenOverlay DentureAmar BhochhibhoyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dis ColorDokument13 SeitenDis ColortarekrabiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan For Dental AnatomyDokument3 SeitenLesson Plan For Dental AnatomyAnderson Macena de AraujoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manage Discoloured Teeth Inside Outside BleachingDokument8 SeitenManage Discoloured Teeth Inside Outside BleachingJesus Manuel Lopez VidalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dental caries classification and nomenclatureDokument26 SeitenDental caries classification and nomenclatureVinceEjorangoCabigaoNoch keine Bewertungen
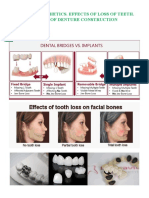
- Unit Iv. Prosthetics. Effects of Loss of Teeth. Stages of Denture ConstructionDokument7 SeitenUnit Iv. Prosthetics. Effects of Loss of Teeth. Stages of Denture ConstructionTolea SirghiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oral HygieneDokument4 SeitenOral HygieneНаталя ГодованецьNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mynenivenkatasatya (2020), Effectiveness of A Novel Dentifrice Containing Stabilized Chlorine Dioxide, Sarkosyl, and Sodium FluorideDokument11 SeitenMynenivenkatasatya (2020), Effectiveness of A Novel Dentifrice Containing Stabilized Chlorine Dioxide, Sarkosyl, and Sodium FluoridePhuong ThaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medical Students PptDokument85 SeitenMedical Students PptYonas YemidiralemNoch keine Bewertungen
- IKGM - ASSIGNMENT - 121221069 - Samuel King KurniawanDokument8 SeitenIKGM - ASSIGNMENT - 121221069 - Samuel King Kurniawansamuelkingkurniawan74Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1why To Restore Teeth2011-5Dokument367 Seiten1why To Restore Teeth2011-5dr_ahmad_zuhdiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit Iv. Prosthetics. Effects of Loss of Teeth. Stages of Denture ConstructionDokument8 SeitenUnit Iv. Prosthetics. Effects of Loss of Teeth. Stages of Denture ConstructionStanislavNemtanuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Role of Floride in Dentistry - Global PerspectiveDokument10 SeitenRole of Floride in Dentistry - Global PerspectiveZainabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ultradent Catalogue ANZ 2013Dokument134 SeitenUltradent Catalogue ANZ 2013Dorin PupezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Role of Calculus in Periodontal DiseaseDokument4 SeitenRole of Calculus in Periodontal DiseaseBethany PinnockNoch keine Bewertungen
- Artigo 7Dokument25 SeitenArtigo 7Júlia OliveiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8 Tooth Ankylosis Andits Orthodontic ImplicationDokument6 Seiten8 Tooth Ankylosis Andits Orthodontic ImplicationPretty HiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DentistryDokument20 SeitenDentistrySameer HussainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oral CancerDokument10 SeitenOral CancerHanan MohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class II Amalgam PreparationDokument41 SeitenClass II Amalgam PreparationHanan MohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mandibular NerveDokument1 SeiteMandibular NerveHanan MohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tooth PreparationDokument1 SeiteTooth PreparationHanan MohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bur For CrownDokument1 SeiteBur For CrownHanan MohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Needle StickDokument38 SeitenNeedle StickHanan MohNoch keine Bewertungen
- ExamDokument2 SeitenExamHanan MohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enamel 2Dokument1 SeiteEnamel 2Hanan MohNoch keine Bewertungen
- R HatsDokument36 SeitenR HatsHanan MohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Needle StikDokument8 SeitenNeedle StikHanan MohNoch keine Bewertungen
- R TraumaDokument6 SeitenR TraumaHanan MohNoch keine Bewertungen
- 60 SAQsDokument5 Seiten60 SAQsAlthaf RajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- K9 Ve Balista Spring Başarı OranlarıDokument8 SeitenK9 Ve Balista Spring Başarı OranlarıRümeysa AydınNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formative CellsDokument33 SeitenFormative CellsSrishti SrivastavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tooth AcheDokument8 SeitenTooth AcheWerly Eka LiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coachman Reconstruction of Pink and White EstheticsDokument4 SeitenCoachman Reconstruction of Pink and White EstheticsLynda M. NaranjoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dentin Post: An Innovative Method For Restoring Endodontically Treated TeethDokument4 SeitenDentin Post: An Innovative Method For Restoring Endodontically Treated TeethInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Facially Driven Complete-Mouth Rehabilitation With Ultrathin CAD CAM Composite Resin Veneers For A Patient With Severe Tooth Wear A Minimally Invasive ApproachDokument11 SeitenA Facially Driven Complete-Mouth Rehabilitation With Ultrathin CAD CAM Composite Resin Veneers For A Patient With Severe Tooth Wear A Minimally Invasive ApproachAlex Gutierrez AcostaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prosthodontic Rehabilitation With Onlay Removable Partial Denture: A CaseDokument7 SeitenProsthodontic Rehabilitation With Onlay Removable Partial Denture: A CasePhanQuangHuyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jurnal Porio 1Dokument3 SeitenJurnal Porio 1Neo YustindraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Immediate Implant LoadingDokument6 SeitenAdvantages and Disadvantages of Immediate Implant LoadingsheetalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prosthodontic Management of Severely ResorbedDokument2 SeitenProsthodontic Management of Severely ResorbedAamir BugtiNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Comparative Evaluvation of Herbst Appliance and The Advan Sync 2 in The Treatment of Class Ii MalocclusionDokument24 SeitenA Comparative Evaluvation of Herbst Appliance and The Advan Sync 2 in The Treatment of Class Ii MalocclusionIJAR JOURNALNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gutiera BruxismDokument3 SeitenGutiera BruxismGeorgeIliescuNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Case Report On Combination of Vista With Connective Tissue Graft As A Predictable Surgical Approach in Management of Multiple Gingival RecessionDokument5 SeitenA Case Report On Combination of Vista With Connective Tissue Graft As A Predictable Surgical Approach in Management of Multiple Gingival RecessionInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Historia Diente Ro 01-Cecilia-BacaliDokument5 SeitenHistoria Diente Ro 01-Cecilia-BacaliAARON DIAZ RONQUILLONoch keine Bewertungen
- Principles of Endodontic Diagnosis - 2020Dokument9 SeitenPrinciples of Endodontic Diagnosis - 2020Ina BogdanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Miniscrew Applications in OrthodonticsDokument28 SeitenMiniscrew Applications in OrthodonticsNgo Viet ThanhNoch keine Bewertungen
- 431 PDS-Adams ClaspDokument5 Seiten431 PDS-Adams ClaspKirthika KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arch Expansion DR SaadDokument41 SeitenArch Expansion DR Saadahmed saad100% (1)
- Treating Multiple Dental Injuries in a Teen Girl After a Car AccidentDokument7 SeitenTreating Multiple Dental Injuries in a Teen Girl After a Car AccidentDiego Andres Hincapie HerreraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinicians Report February 2022, V15,2Dokument10 SeitenClinicians Report February 2022, V15,2YA MaytelesNoch keine Bewertungen
- GoldenDokument308 SeitenGoldenammarkochiNoch keine Bewertungen
- J, C Early Vs LateDokument225 SeitenJ, C Early Vs LateVenkat ChintadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 02 D017 9074Dokument10 Seiten02 D017 9074Rahma Aulia LestariNoch keine Bewertungen