Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Ee115hw+sol03 06 N PDF
Hochgeladen von
thinkberry22Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Ee115hw+sol03 06 N PDF
Hochgeladen von
thinkberry22Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
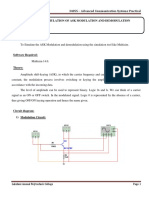
EE115. Solutions For Home Assignment #3.
4.2-1 (10 points) For each of the following baseband signals:
() :(t) = cos 1000t
() :(t) = 2 cos 1000t + cos 2000t
() :(t) = cos 1000t cos 3000t
(a) Sketch the spectrum of :(t).
(b) sketch the spectrum of DSB-SC signal :(t) cos 10. 000t.
(c) Identify the upper sideband (USB) and lower sideband (LSB) spectra.
Solution 4.2-1
i)
:(t) = cos 1000t
c
DSB
= :(t) cos 1000t = cos 1000t cos 10000t
=
1
2
[cos 9000t + cos 11000t]
1o1 : cos 9000t. lo1 : cos 11000t
ii)
:(t) = 2 cos 1000t + cos 2000t
c
DSB
(t) = :(t) cos 10000t
= cos 9000t + cos 11000t +
1
2
[cos 8000t + cos 12000t]
= cos 9000t +
1
2
cos 8000t + cos 11000t +
1
2
cos 12000t
1o1 : cos 9000t +
1
2
cos 8000t. lo1 : cos 11000t +
1
2
cos 12000t
iii)
:(t) = cos 1000t cos 3000t =
1
2
[cos 2000t + cos 4000t]
c
DSB
= :(t) cos 10000t =
1
2
[cos 2000t + cos 4000t] cos 10000t
=
1
2
[cos 8000t + cos 12000t + cos 6000t + cos 14000t]
1o1 :
1
2
[cos 8000t + cos 6000t]. lo1 :
1
2
[cos 12000t + 14000t]
Case Baseband Frequency DSB Frequency LSB Frequency USB Frequency
i) 1000 9000 & 11000 9000 11000
ii) 1000 9000 & 11000 9000 11000
2000 8000 & 12000 8000 12000
iii) 2000 8000 & 12000 8000 12000
4000 6000 & 14000 6000 14000
baseband DSB
9000 11000
0
0 -1000 1000
-11000 -9000
Case i)
Case ii)
-2000 -1000 0 1000 2000 -12000 -10
4
-8000 9000 11000
12000
10
4
0
Case iii)
0 -4000 -2000 2000 4000 0 8000 12000
4.2-2 (10 points) Repeat parts (a), (b) and (c) of Prob. 4.2-1 if
() :(t) = (t) ((t) denotes rectangular pulse)
() :(t) = c
jtj
Solution 4.2-2
i)
:(t) = (t) $sinc(
.
2:
)
c
DSB
(t) = (t) cos 10000t $
1
2
[sinc
. 10000
2:
+ sinc
. + 10000
2:
1o1 :
1
2
sinc
. 10000
2:
. lo1 :
1
2
sinc
. + 10000
2:
ii)
:(t) = c
jtj
$
2
.
2
+ 1
c
DSB
(t) = c
jtj
cos 10000t $
1
(. 10000)
2
+ 1
+
1
(. + 10000)
2
+ 1
1o1 :
1
(. 10000)
2
+ 1
. lo1 :
1
(. + 10000)
2
+ 1
Baseband DSB
USB
LSB
LSB USB
10
4
2 4
USB USB LSB
10
4
i)
ii)
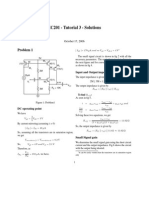
*4.2-4 (10 points)
Figure P4.2-4a shows a DSB-SC modulators. The carrier available at the multiplier is
a distorted sinusoid given by c
1
cos .
c
t + c
2
cos
2
.
c
t. The spectrum of :(t) is shown in Fig.
P4.2-4b
(a) Determine the signals and sketch their spectra at points / and c.
(b) What kind of lters is required in Fig. P4.2-4a?
(c) what is the minimum value of .
c
required for this scheme to work?
0 2B -2B
A
M()
km(t)cos
c
t m(t)
Filter
Distorted
carrier
a b c
(a)
(b)
Figure 1: Fig. P4.2-4
Solution 4.2-4
`(.) =
1
j.j
2:1
. . 2:1
From pair 19 in Table 3.1 (Lathi, 3
d
edition) or pair 15 in Table 2.1 (Lathi, 2
nd
edition),
:(t) = 1sinc
2
1t
Let us now consider the signal at point b,
c
b
(t) = :(t)[c
1
cos .
c
t + c
2
cos
2
.
c
t]
= :(t)[c
1
cos .
c
t +
c
2
2
+
c
2
2
cos 2.
c
t]
= c
1
:(t) cos .
c
t +
c
2
2
:(t) +
c
2
2
:(t) cos 2.
c
t
Therefore
1
b
(.) =
c
1
2
[`(. + .
c
) + `(. .
c
)] +
c
1
2
`(.) +
c
1
4
[`(. + 2.
c
) + `(. 2.
c
)]
The spectrum is shown in the gure below:
0 2B
c
2
c
a
2
A/2
a
2
A/4
a
1
A/2
(b) By inspection of Figure above, we see that the desired modulated signal can be
obtained by using a bandpass lter with center frequency .
c
. The output of this lter is
c
c
(t) = c
1
:(t) cos .
c
t
(c) By inspection of 1
b
(.), it is clear that to be able to lter our the modulated signal,
.
c
4:1 so that the spectra do not overlap.
*4.2-5 (10 points)
Show that the scheme shown in Fig. P4.2-5 can be used to generate DSB-SC signal.
Assuming that :(t) is a signal bandlimited to 1 Hz, nd the signals and sketch their
spectra at points c. /. c and d. Explain the nature of the lter in this gure. Is there any
restriction on the bandwidth of :(t) for this scheme to work?
Acos
c
t
c
x
2
d
Filter
km(t)cos
c
t m(t)
a
x
b
Squarer
Figure 2: Fig. P4.2-5
In sketching spectra, relative amplitudes of various spectral components are not impor-
tant. However, pay attention to locations of spectra along the . (horizontal) axis.
Solution 4.2-5
at a:
,
a
(t) = :(t)
at b:
,
b
(t) = :(t) + cos .
c
t
at c:
,
c
(t) = [:(t) + cos .
c
t]
2
= :
2
(t) +
2
cos
2
.
c
t + 2:(t) cos .
c
t
= :
2
(t) +
2
2
+
2
2
cos 2.
c
t + 2:(t) cos .
c
t
at d:
,
d
(t) = 2:(t) cos .
c
t
The lter should be a bandpass lter centered at . = .
c
and having a bandwidth 21 Hz.
From gure c, we observe that . 6:1 in order to obtain modulated signal without
distortion.
0 2B
(a)
0 2B
c
(b)
4B
4B
c
2
c
(c)
c
(d)
Output
) cos( + t A
c
t t m
c
cos ) (
Lowpass
filter
Figure 3: Fig.P4.2-6
4.2-6 (10 points)
A DSB-SC signal :(t) cos .
c
t is demodulated using a locally generated carrier cos(.
c
t+
o) as shown in Fig. P4.2-6. Show that this scheme can demodulate the signal as long as o
is a constant (not time-varying) and is not :,2. What is the output if o = :,4 and :,2?
Solution 4.2-6
The demodulator output is:
G
0
(t) = :(t) cos .
c
t cos(.
c
t + o)
=
1
2
:(t) cos o +
1
2
:(t) cos(2.
c
t + o)
After the lowpass lter, the output is:
1
2
:(t) cos o
If o is a constant 6=
2
, then the output is proportional to :(t)
If o =
4
. output =:(t),(2
p
2)
If o =
2
. output = 0.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- 49 WiresharkDokument8 Seiten49 Wiresharkalguacil2013Noch keine Bewertungen
- MIT 6.341 Lecture 20 - The Goertzel Algorithm and Chirp TransformDokument4 SeitenMIT 6.341 Lecture 20 - The Goertzel Algorithm and Chirp Transformc_mc2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Overstress (EOS): Devices, Circuits and SystemsVon EverandElectrical Overstress (EOS): Devices, Circuits and SystemsNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9086 CMOS Analog Design Chapter 6Dokument24 Seiten9086 CMOS Analog Design Chapter 6Yogindr SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arinc 429Dokument21 SeitenArinc 429F Sa AbbasiNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE 179 Digital and Analog Communication Systems Homework SolutionsDokument6 SeitenEE 179 Digital and Analog Communication Systems Homework SolutionsAnthony KwoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Proficy HMI - SCADA Cerver RedundancyDokument36 SeitenProficy HMI - SCADA Cerver RedundancyAhmed RamadanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hw3 Chap4 SolutionDokument13 SeitenHw3 Chap4 Solutioncoasterfan13100% (1)
- Introduction To Microelectronic FabricationDokument87 SeitenIntroduction To Microelectronic FabricationBhushan Yadav81% (27)
- Optimum Array Processing: Part IV of Detection, Estimation, and Modulation TheoryVon EverandOptimum Array Processing: Part IV of Detection, Estimation, and Modulation TheoryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Catalogo Huawei Antenas y Linea de ProductosDokument410 SeitenCatalogo Huawei Antenas y Linea de Productosrichard chavezNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE 330 Lab - 7 Spring 2013Dokument6 SeitenEE 330 Lab - 7 Spring 2013Tuan VoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ADSP7Dokument3 SeitenADSP7Raj KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 6Dokument12 SeitenLab 6Sujan HeujuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap003 ch3 Solution of Power Electronics by Daniel WDokument33 SeitenChap003 ch3 Solution of Power Electronics by Daniel WMiiguel Angel LópezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design, Simulate and Approximate Parallel Coupled Microstrip Bandpass Filter at 2.4 GHZDokument5 SeitenDesign, Simulate and Approximate Parallel Coupled Microstrip Bandpass Filter at 2.4 GHZNabil DakhliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Engineering Lab ReportDokument7 SeitenElectrical Engineering Lab ReportFrancis Paul SantiagoNoch keine Bewertungen
- DCOM Lab ManualDokument38 SeitenDCOM Lab ManualGaurav Kalra0% (1)
- Device Modelling and Simulation of Logic Gates using NGSPICEDokument11 SeitenDevice Modelling and Simulation of Logic Gates using NGSPICEBT19ECE067 MiteshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Model QP - MPMC Lab - Wo Split UpDokument3 SeitenModel QP - MPMC Lab - Wo Split Upsujaganesan20090% (1)
- Dsplabmanual-By 22Dokument64 SeitenDsplabmanual-By 22debasnan singh100% (1)
- DSPDokument5 SeitenDSPKarishma SavNoch keine Bewertungen
- DSP Practical FileDokument18 SeitenDSP Practical FileDivyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MM Lab Manual 8085 Part1Dokument38 SeitenMM Lab Manual 8085 Part1shylaja9Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ec 6511 Digital Signal Processing Lab Manual PDFDokument88 SeitenEc 6511 Digital Signal Processing Lab Manual PDFBala913Noch keine Bewertungen
- Antenna FormulasDokument5 SeitenAntenna FormulasCioby CatalinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intensity ModulationDokument3 SeitenIntensity Modulationanon-323096100% (1)
- Experiment No. 01 Experiment Name-ASK ModulationDokument47 SeitenExperiment No. 01 Experiment Name-ASK ModulationmuskanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2: Mathematical Modelling of Translational Mechanical SystemDokument8 SeitenChapter 2: Mathematical Modelling of Translational Mechanical SystemNoor Nadiah Mohd Azali100% (1)
- Ec 1401 Vlsi DesignDokument2 SeitenEc 1401 Vlsi DesignsubhazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronic Jewellery Security Alarm System Using 8085 MicroprocessorDokument8 SeitenElectronic Jewellery Security Alarm System Using 8085 MicroprocessorAnand PrajapatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment No-8: Write A MATLAB Program To Plot The Following FunctionDokument2 SeitenExperiment No-8: Write A MATLAB Program To Plot The Following FunctionUnknown424Noch keine Bewertungen
- Finite Word Length EffectsDokument9 SeitenFinite Word Length Effectsohmshankar100% (2)
- Sat Comm Sys EngineeringDokument34 SeitenSat Comm Sys EngineeringHamis RamadhaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Signals & Systems Gate Complete Question SetDokument11 SeitenSignals & Systems Gate Complete Question SetAnonymous JnvCyu850% (1)
- ASK FSK PSK Simulation Using MultisimDokument6 SeitenASK FSK PSK Simulation Using MultisimSabari Muthu RamanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antenna and Wave Propagation NotesDokument150 SeitenAntenna and Wave Propagation NotesDamini0% (1)
- Anna University Digital Image Processing NotesDokument2 SeitenAnna University Digital Image Processing NotesgpalanimcaNoch keine Bewertungen
- dc01 Show - PpsDokument49 Seitendc01 Show - Ppsscribdacct123Noch keine Bewertungen
- 630 hw3 SolnDokument6 Seiten630 hw3 Solnboggled429Noch keine Bewertungen
- LIC Unit 3Dokument25 SeitenLIC Unit 3mekalajesiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laplace Transform ExamplesDokument19 SeitenLaplace Transform Exampleshamza abdo mohamoudNoch keine Bewertungen
- Signals and SystemsDokument30 SeitenSignals and SystemsMohammad Gulam Ahamad100% (3)
- Chapter IDokument84 SeitenChapter ISurbhi Pareek100% (1)
- 01 Experiment 1 - Familiarization of Components and InstrumentsDokument5 Seiten01 Experiment 1 - Familiarization of Components and InstrumentsNikita Mayee sahooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Signal ProcessingDokument7 SeitenDigital Signal Processingind sh1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Practical Signal ProcessingDokument30 SeitenPractical Signal ProcessingLokender TiwariNoch keine Bewertungen
- MATLAB-ZF-LMSDokument4 SeitenMATLAB-ZF-LMSImmanuel VinothNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Loop AntennasDokument5 Seiten1 Loop AntennasSilicon SolNoch keine Bewertungen
- 322 - EC8395 Communication Engineering - Notes PDFDokument124 Seiten322 - EC8395 Communication Engineering - Notes PDFAjitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ec 1015 Satellite Communication Anna University Question Paper MayDokument2 SeitenEc 1015 Satellite Communication Anna University Question Paper Maysanth_213Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 3 - Week 0: Assignment 0Dokument4 SeitenUnit 3 - Week 0: Assignment 0Akshay KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- On The Fundamental Aspects of DemodulationDokument11 SeitenOn The Fundamental Aspects of DemodulationAI Coordinator - CSC JournalsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 5 SolutionsDokument11 SeitenTutorial 5 SolutionsbarneyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pe Tutorial 6 PDFDokument12 SeitenPe Tutorial 6 PDFkibrom atsbhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fourier Series Representation of Periodic Signals ExplainedDokument78 SeitenFourier Series Representation of Periodic Signals Explainedmsh-666Noch keine Bewertungen
- DSP - Class NotesDokument52 SeitenDSP - Class NotesNikhil Pathak100% (3)
- EC524 2013 4 1 1 SheetsDokument13 SeitenEC524 2013 4 1 1 Sheets123vidyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BCH Codes ExplainedDokument43 SeitenBCH Codes Explainedchittic3Noch keine Bewertungen
- Modulation FM Sur Labview by Ameur1990Dokument13 SeitenModulation FM Sur Labview by Ameur1990Ameur HEDHLINoch keine Bewertungen
- DCDR ImpDokument3 SeitenDCDR Imppatel rahulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vacation Training ELEC 1200 Working with NI Instruments MultisimDokument5 SeitenVacation Training ELEC 1200 Working with NI Instruments Multisimjaya1816Noch keine Bewertungen
- To Design An Adaptive Channel Equalizer Using MATLABDokument43 SeitenTo Design An Adaptive Channel Equalizer Using MATLABAngel Pushpa100% (1)
- Writing Guidelines LectureDokument15 SeitenWriting Guidelines Lecturethinkberry22Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ieeet Ed03Dokument8 SeitenIeeet Ed03thinkberry22Noch keine Bewertungen
- KFUPM EE370 Final Exam Signals and SystemsDokument6 SeitenKFUPM EE370 Final Exam Signals and Systemsthinkberry22Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture Notes: Jay A. Farrell, Professor College of Engineering University of California, Riverside February 10, 2014Dokument153 SeitenLecture Notes: Jay A. Farrell, Professor College of Engineering University of California, Riverside February 10, 2014thinkberry22Noch keine Bewertungen
- EE 141 Homework 8: (X (N) ) With K 0, 1,, N 1, Determine The Following ExpressionsDokument1 SeiteEE 141 Homework 8: (X (N) ) With K 0, 1,, N 1, Determine The Following Expressionsthinkberry22Noch keine Bewertungen
- Writing Guidelines LectureDokument15 SeitenWriting Guidelines Lecturethinkberry22Noch keine Bewertungen
- EE132 Lab1 OL Vs CLDokument3 SeitenEE132 Lab1 OL Vs CLthinkberry22Noch keine Bewertungen
- Trigonometry SecretsDokument1 SeiteTrigonometry SecretsOggy22Noch keine Bewertungen
- EE 105: MATLAB As An Engineer's Problem Solving ToolDokument3 SeitenEE 105: MATLAB As An Engineer's Problem Solving Toolthinkberry22Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ee150hw06 2006Dokument1 SeiteEe150hw06 2006thinkberry22Noch keine Bewertungen
- EE105 Lecture NotesDokument153 SeitenEE105 Lecture Notesthinkberry22Noch keine Bewertungen
- Menu CoronaDokument1 SeiteMenu Coronathinkberry22Noch keine Bewertungen
- Keypad DatasheetDokument4 SeitenKeypad Datasheetthinkberry22Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture Notes: Jay A. Farrell, Professor College of Engineering University of California, Riverside February 10, 2014Dokument153 SeitenLecture Notes: Jay A. Farrell, Professor College of Engineering University of California, Riverside February 10, 2014thinkberry22Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ee150hw02 2012Dokument1 SeiteEe150hw02 2012thinkberry22Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ee 150 HW 05Dokument1 SeiteEe 150 HW 05thinkberry22Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ee150hw03 2012Dokument1 SeiteEe150hw03 2012thinkberry22Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ee150hw04 2012Dokument2 SeitenEe150hw04 2012thinkberry22Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1 2013Dokument11 Seiten1 2013thinkberry22Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ee150hw01 2010Dokument2 SeitenEe150hw01 2010thinkberry22100% (1)
- Trigonometry SecretsDokument1 SeiteTrigonometry SecretsOggy22Noch keine Bewertungen
- UCR EE 115 Introduction to Communication SystemsDokument1 SeiteUCR EE 115 Introduction to Communication Systemsthinkberry22Noch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Principles of Signal Reproduction: Skirts Are The Sides of A Tuned Circuit Response Curve (See Figure 4.0)Dokument4 SeitenBasic Principles of Signal Reproduction: Skirts Are The Sides of A Tuned Circuit Response Curve (See Figure 4.0)DARANoch keine Bewertungen
- Propagation Unit 2Dokument21 SeitenPropagation Unit 2KURRA UPENDRA CHOWDARYNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adsp PDFDokument1 SeiteAdsp PDFVishwajeet S BNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adv7340 7341 PDFDokument108 SeitenAdv7340 7341 PDFTheotech EletronNoch keine Bewertungen
- Site Solution Ericsson-Huawei-Nokia-Antenna 20160824 1730Dokument42 SeitenSite Solution Ericsson-Huawei-Nokia-Antenna 20160824 1730amirmfroozanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cisco Test-King 300-410 v2021-04-06 by Isabelle 85qDokument121 SeitenCisco Test-King 300-410 v2021-04-06 by Isabelle 85qMelroyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Al 7203Dokument2 SeitenAl 7203Leandro Aldrighi de AzevedoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alfoplus80 - e 004 13Dokument2 SeitenAlfoplus80 - e 004 13Ivan AcostaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CN 4 2022Dokument122 SeitenCN 4 2022Surendranath Reddy NarlaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Z9100-ON (Leaf 1) v2Dokument23 SeitenZ9100-ON (Leaf 1) v2José Carlos Miguel BarriosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flow-Gateway-Ve-10-20-Install GuideDokument21 SeitenFlow-Gateway-Ve-10-20-Install GuideToan NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- DNP3 Slave ProtocolDokument58 SeitenDNP3 Slave ProtocolBehzad Yahosseini0% (1)
- M.E. Comm. SystemsDokument105 SeitenM.E. Comm. SystemsShobana SNoch keine Bewertungen
- UBITX V6 MainDokument15 SeitenUBITX V6 MainEngaf ProcurementNoch keine Bewertungen
- EKI-7700 Series: User ManualDokument52 SeitenEKI-7700 Series: User ManualJoel Ventura EsquivelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Java Exam QuestionsDokument5 SeitenJava Exam QuestionsselvisasikalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Moxa Tech Note - What Is Turbo RingDokument4 SeitenMoxa Tech Note - What Is Turbo RingDennis ZoisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oracle Manager Self-Service Manual: Revised 2/12/14Dokument14 SeitenOracle Manager Self-Service Manual: Revised 2/12/14Marcela CostaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clase 22-Mod2Dokument39 SeitenClase 22-Mod2Alex Osores RiveraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cisco Systems, Inc. ASA 5510, ASA 5520, and ASA 5540: Level 2 ValidationDokument17 SeitenCisco Systems, Inc. ASA 5510, ASA 5520, and ASA 5540: Level 2 ValidationRichi VuvalineeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Boron DatasheetDokument27 SeitenBoron DatasheetjibaowlNoch keine Bewertungen
- MVP 2120 GlenayreDokument160 SeitenMVP 2120 GlenayreJason2017Noch keine Bewertungen
- Configuring SSHDokument4 SeitenConfiguring SSHMario BilićNoch keine Bewertungen
- KNTECH Product CatalogDokument13 SeitenKNTECH Product CatalogArioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Service Manual: LCD TVDokument96 SeitenService Manual: LCD TVpal-vireNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aastra 6755i Data SheetDokument2 SeitenAastra 6755i Data SheetCristhian HaroNoch keine Bewertungen