Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
28B
Hochgeladen von
Jamie SchultzOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
28B
Hochgeladen von
Jamie SchultzCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Sub: Structural Analysis
Topic : Force methods
MODULE- 28B
Analysis of statically indeterminate structures by force methods. . ___________________________________________________________________________
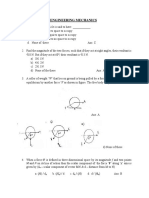
1. Identify the FALSE statement from the following, pertaining to the effects due to a temperature rise T in the bar BD alone in the plane truss shown below: (B) (C) (D)
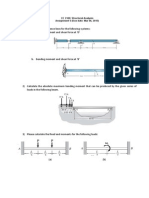
3. In the propped cantilever beam carrying a uniformly distributed load of w N/m, shown in the following figure, the reaction at the support B is
(A) No reactions develop at supports A and D (B) The bar BD will be subject to a tensile force (C) The bar AC will be subject to a compressive force (D) The bar BC will be subject to a tensile force 4. 2. The degree of static indeterminacy, , and the degree of kinematic indeterminacy, , for the plane frame shown below, assuming axial deformations to be negligible, given by
(A) (C)
(B) (D)
For the linear elastic beam shown in the figure, the flexural rigidity. EI, is 781250 kN-m2. When w = 10 kN/m, the vertical reaction RA at A is 50 kN. The value of RA for w = 100 kN/m is
(a) 500 kN (c) 250 kN 5.
(b) 425 kN (d) 75 kN
(A)
For the plane frame with an overhang as shown below, assuming negligible axial deformation, the degree of static indeterminacy, d, and the degree of kinematic indeterminacy, k, are
JH ACADEMY
Page 1
Sub: Structural Analysis
Topic : Force methods
(a) d = 3 and k = 10 (b) d = 3 and k = 13 (c) d = 9 and k = 10 (d) d= 9 and k = 13 6. The unit load method used in structural analysis is (a) applicable only to statistically indeterminate structures (b) another name for stiffness method (c) an extension of Maxwell's reciprocal theorem (d) derived from Castigliano's theorem A three-span continuous beam has a internal hinge at B Section B is at the mind-span of AC. Section R is at the midspan of CG. The 20 kN load is applied at section B whereas 10 kN loads are applied at sections D and F as shown in the figure. Span GH is subjected to uniformly distributed load of magnitude 5 kN/m. For the loading shown, shear force immediate to the right of section E is 9.84 kN upwards and the sagging moment at section E is 10.31 kN-m. 9.
(a) 9 (b) 8 (c)
(d)
Vertical reaction developed at B in the frame be-low due to the applied load of 100 kN (with 150, 000mm2 cross-sectional area and 3.125 x 109 mm4 moment of inertia for both members) is
7.
(a) 5.9 kN (c) 66.3 kN
(b)302 kN (d) 94.1 kN
10. Consider a propped cantilever beam ABC under two loads of magnitude P each as shown in the figure below. Flexural rigidity of the beam is EI.
A) The magnitude of the shear force immediate to the left and immediate to the right of section B are, respectively (a) 0 and 20 kN (b) 10 kN and 10 kN (c) 20 kN and 0 (d) 9.84 kN and 10.16 kN B) The vertical reaction at support H is (a) 15kN upward (b)9.84 kN upward (c) 15 kN downward (d) 9.84 kN downward 8. Considering beam as axially rigid, the degree of freedom of a plane frame shown below is
A) The reaction at C is (a) (upwards) (b) (c) (d) (downwards) (upwards) (downwards)
B) The rotation at B is (a) (clockwise) (b) (c) (anticlockwise) (clockwise)
JH ACADEMY
Page 2
Sub: Structural Analysis
Topic : Force methods
(d)
(anticlockwise)
11. The right triangular truss is made of members having equal cross sectional area of 1550 mm2 and Youngs modulus of 2 105 MPa. The horizontal deflection of the joint Q is
(A) (B) (C) (D)
0.255 0.589 0.764 1.026
15. Beam GHI is supported by three pontoons as shown in the figure below. The horizontal cross-sectional area of each pontoon is 8 m2, the flexural rigidity of the beam is 10000 kN-m2 and the unit weight of water is 10 kN/m3
(a) 2.47 mm (b) 10.25 mm (c) 14.31 mm (d) 15.68 mm 12. A two span continuous beam having equal spans each of length L is subjected to a uniformly distributed load w per unit length. The beam has constant flexural rigidly. a) The reaction at the middle support is (A) (B) (C) (D) b) The bending moment at the middle support is (a) (b) (c) (d)
a) When the middle pontoon is removed, the deflection at H will be (A) 0.2m (B) 0.4m(C) 0.6m (D) 0.8m b) When the middle pontoon is brought back to its position as shown in the figure above, the reaction at H will be (A) 8.6kN(B)15.7kN(C) 19.2kN (D)4.2kN 16. The degree of static indeterminacy of a rigidly jointed frame in a horizontal plane and subjected to vertical loads only, as shown in figure below is
13. The degree of static indeterminacy of the
rigid frame having two internal hinges as shown in the figure below, is
(A) 8 (B) 7 (C) 6 (D) 5 14. The members EJ and IJ of a steel truss shown in the figure below are subjected to a temperature rise of 30 C. The coefficient of thermal expansion of steel is 0.000012 per C per unit length. The displacement (mm) of joint E relative to joint H along the direction HE of truss, is
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D) 1
17. In the cantilever beam PQR shown in figure below, the segment PQ has flexural rigidity EI and the segment QR has infinite flexural rigidity.
a) The deflection and slope of the beam at 'Q' are respectively (A) (B)
JH ACADEMY
Page 3
Sub: Structural Analysis
Topic : Force methods
(C)
(D)
b) The deflection of the beam at 'R' is (A) (B) (C) (D)
18. A simply supported beam is subjected to a uniformly distributed load of intensity w per unit length, on half of the span from one end. The length of the span and the flexural stiffness are denoted as l and EI, respectively. The deflection at mid-span of the beam is (A) (C) (B) (D)
JH ACADEMY
Page 4
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Module 28CDokument24 SeitenModule 28CAfia S HameedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bar TrussDokument18 SeitenBar TrussJithinGeorgeNoch keine Bewertungen
- GATE Structure Qwestion PDFDokument117 SeitenGATE Structure Qwestion PDFmd alkarim100% (2)
- Ce 336Dokument7 SeitenCe 336reynanbelendhran23Noch keine Bewertungen
- 16BDokument13 Seiten16BBrynn AlexanderNoch keine Bewertungen
- CENG 198 Problem Set 1 Part1 QuestionsDokument1 SeiteCENG 198 Problem Set 1 Part1 QuestionsBryan Christian MendozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CENG198 CE Competency Appraisal IllDokument4 SeitenCENG198 CE Competency Appraisal IllJeric DinglasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 30 PDFDokument15 SeitenLec 30 PDFCipriano Irasmo Da SilvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 5: Force Method - Introduction and Applications Lecture 2: The Force MethodDokument15 SeitenModule 5: Force Method - Introduction and Applications Lecture 2: The Force Methodstephannie montoyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BTCE - 501 Roll No. - B.Tech. (Civil) End Semesterexamination-V Sem DEC-JAN2015 Structure Analysis IiDokument4 SeitenBTCE - 501 Roll No. - B.Tech. (Civil) End Semesterexamination-V Sem DEC-JAN2015 Structure Analysis IisdfghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strain Energy Method-2Dokument31 SeitenStrain Energy Method-2pengniumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strengh of Mateial Topic Wise Questions Sr. NoDokument28 SeitenStrengh of Mateial Topic Wise Questions Sr. NoAd PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Ball of Mass M Kept at The Corner As Shown in The Figure, Is Acted by A Horizontal Force F. The Correct Free Body Diagram of Ball IsDokument27 SeitenA Ball of Mass M Kept at The Corner As Shown in The Figure, Is Acted by A Horizontal Force F. The Correct Free Body Diagram of Ball IsًPreetham PNoch keine Bewertungen
- Civil Engineering Previous Papers2Dokument13 SeitenCivil Engineering Previous Papers2Haresh SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structural Mechanics Paper 2 Examples Paper 2Dokument6 SeitenStructural Mechanics Paper 2 Examples Paper 2Michael BlairNoch keine Bewertungen
- CE 2100: Structural Analysis Assignment 5 (Due Date: Mar 06, 2015)Dokument2 SeitenCE 2100: Structural Analysis Assignment 5 (Due Date: Mar 06, 2015)SaiRamNoch keine Bewertungen
- CIVE 6350: Adv Mechanics of Material February 12, 2015 Homework No. 4Dokument2 SeitenCIVE 6350: Adv Mechanics of Material February 12, 2015 Homework No. 4Amit JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- StructureDokument24 SeitenStructureFrank StephensNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering MechanicsDokument57 SeitenEngineering Mechanicsleah joylinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eng'G Mechanics & Strength of Matl'S: Chemical Engineering Reviewer Compiled By: Engr. Albert D.C. EvangelistaDokument15 SeitenEng'G Mechanics & Strength of Matl'S: Chemical Engineering Reviewer Compiled By: Engr. Albert D.C. EvangelistaAlyssa ApolinarioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strength of MaterialsDokument48 SeitenStrength of Materialspankajkumarhans100% (1)
- Tutorial 2 BFC20903 Sem1 20182019Dokument2 SeitenTutorial 2 BFC20903 Sem1 20182019ShueibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elecments of Civil Engineering June 2012Dokument4 SeitenElecments of Civil Engineering June 2012Prasad C MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ac 1 (1) (1) .2Dokument20 SeitenAc 1 (1) (1) .2Shyam K RautNoch keine Bewertungen
- CE2351 SA II - by EasyEngineering - Net 1234Dokument11 SeitenCE2351 SA II - by EasyEngineering - Net 1234SangeethaNoch keine Bewertungen
- m3l16 Lesson 16 The Slope-Deflection Method: Frames Without SideswayDokument24 Seitenm3l16 Lesson 16 The Slope-Deflection Method: Frames Without SideswayVitor ValeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Last Year Papaer 20112012Dokument14 SeitenLast Year Papaer 20112012Farah Hani TENoch keine Bewertungen
- GATE 2014 - Mechanical Engineering Important Questions-Strength of Materials (SOM)Dokument7 SeitenGATE 2014 - Mechanical Engineering Important Questions-Strength of Materials (SOM)Rahul BurmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 55685698obj CivilEngineering 2005paper IDokument16 Seiten55685698obj CivilEngineering 2005paper IAMIT KUMARNoch keine Bewertungen
- IES OBJ Civil Engineering 2006 Paper IDokument18 SeitenIES OBJ Civil Engineering 2006 Paper IvishnupsudhakaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question #1: CD and GH. Clearly State If TheDokument2 SeitenQuestion #1: CD and GH. Clearly State If ThePeter LiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structural Analysis 2 Solved MCQs (Set-1)Dokument6 SeitenStructural Analysis 2 Solved MCQs (Set-1)Hoo BilNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1111-110010-Mech - of SolidsDokument4 Seiten1111-110010-Mech - of SolidsjaydeepNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eng Mechancis Ias WorkbookDokument68 SeitenEng Mechancis Ias WorkbookJayditya KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Civil Engineering Pre 2013Dokument19 SeitenCivil Engineering Pre 2013chanderp_15Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1st Chapter Beam DeflectionDokument43 Seiten1st Chapter Beam Deflectionpratiksha nagargojeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 3Dokument5 SeitenTutorial 3TinkuDhullNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gujarat Technological University: InstructionsDokument3 SeitenGujarat Technological University: InstructionsBhavesh PipaliyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sub: Structural Analysis Module-24CDokument8 SeitenSub: Structural Analysis Module-24CAjay MalikNoch keine Bewertungen
- ENGR 220 Scoop Final Name: - : BC and The Reactions at ADokument9 SeitenENGR 220 Scoop Final Name: - : BC and The Reactions at AOndra LabíkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shear Force and Bendind MomentDokument8 SeitenShear Force and Bendind MomentAshish AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types Beam MCQDokument5 SeitenTypes Beam MCQMAULIN0% (1)
- Mech108 Test 1 2013-2014Dokument2 SeitenMech108 Test 1 2013-2014Annabella ConmeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structural 3 Q PDokument14 SeitenStructural 3 Q PKusum KalitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Mechanics Quiz PPT 21 1 .11.09Dokument68 SeitenFinal Mechanics Quiz PPT 21 1 .11.09Abhilash DayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 31CDokument14 Seiten31CAfia S HameedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment Sem 1 1516Dokument5 SeitenAssignment Sem 1 1516Jing HengNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 4 Frame Analysis Shear Walls HKUSTDokument9 SeitenLecture 4 Frame Analysis Shear Walls HKUSTApril Ingram100% (1)
- Theory of Structures-SFD & BMD 23.06.15 NotesDokument4 SeitenTheory of Structures-SFD & BMD 23.06.15 NotesashishpanigrahiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 3 Group Discussion QADokument10 SeitenWeek 3 Group Discussion QAyvjigvyggojhvNoch keine Bewertungen
- Slope-Deflection Method: Clifford Jay C. Ansino Theory of Structure Ii 5-BSCE-BDokument8 SeitenSlope-Deflection Method: Clifford Jay C. Ansino Theory of Structure Ii 5-BSCE-BKhen CatayasNoch keine Bewertungen
- GATE Mechanical Engineering 2010 PDFDokument13 SeitenGATE Mechanical Engineering 2010 PDFamitv4145Noch keine Bewertungen
- Me601 HW1Dokument6 SeitenMe601 HW1chinmayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gate 1533Dokument7 SeitenGate 1533Darshit D RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reviews in Computational ChemistryVon EverandReviews in Computational ChemistryAbby L. ParrillNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stress in ASME Pressure Vessels, Boilers, and Nuclear ComponentsVon EverandStress in ASME Pressure Vessels, Boilers, and Nuclear ComponentsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module-98B: Plane Table SurveyingDokument1 SeiteModule-98B: Plane Table SurveyingJamie SchultzNoch keine Bewertungen
- 96BDokument3 Seiten96BJamie SchultzNoch keine Bewertungen
- 89BDokument2 Seiten89BJamie SchultzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module-99B: Errors and AdjustmentsDokument1 SeiteModule-99B: Errors and AdjustmentsJamie SchultzNoch keine Bewertungen
- 95BDokument2 Seiten95BJamie SchultzNoch keine Bewertungen
- 87BDokument5 Seiten87BJamie Schultz100% (1)
- Module 83BDokument1 SeiteModule 83BJamie SchultzNoch keine Bewertungen
- 78BDokument3 Seiten78BJamie SchultzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module-79B: Sub: Environmental Engineering TopicDokument1 SeiteModule-79B: Sub: Environmental Engineering TopicJamie SchultzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module-82B: Sub: Environmental Engineering TopicDokument1 SeiteModule-82B: Sub: Environmental Engineering TopicJamie SchultzNoch keine Bewertungen
- 62BDokument2 Seiten62BJamie SchultzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 85BDokument1 SeiteModule 85BJamie SchultzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module-77B: Basic Unit Operations and Unit Processes For Surface Water Treatment, Distribution of WaterDokument1 SeiteModule-77B: Basic Unit Operations and Unit Processes For Surface Water Treatment, Distribution of WaterJamie SchultzNoch keine Bewertungen
- 71BDokument2 Seiten71BJamie SchultzNoch keine Bewertungen
- 76BDokument4 Seiten76BJamie SchultzNoch keine Bewertungen
- 67BDokument5 Seiten67BJamie SchultzNoch keine Bewertungen
- 68BDokument5 Seiten68BJamie Schultz100% (1)
- Module-74B: Types of Irrigation System, Irrigation Methods. Water Logging and Drainage, Sodic SoilsDokument1 SeiteModule-74B: Types of Irrigation System, Irrigation Methods. Water Logging and Drainage, Sodic SoilsJamie SchultzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module-69B: Flood Estimation, Reservoir Capacity, Reservoir and Channel RoutingDokument1 SeiteModule-69B: Flood Estimation, Reservoir Capacity, Reservoir and Channel RoutingJamie SchultzNoch keine Bewertungen
- 59BDokument2 Seiten59BJamie SchultzNoch keine Bewertungen
- 59BDokument2 Seiten59BJamie SchultzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module-60B: Sub: Fluid Mechanics TopicDokument1 SeiteModule-60B: Sub: Fluid Mechanics TopicJamie SchultzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module-57B: Potential Flow, Applications of Momentum and Bernoulli's EquationDokument1 SeiteModule-57B: Potential Flow, Applications of Momentum and Bernoulli's EquationJamie SchultzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engr. Yoshiaki C. Mikami, Bsce Msce-Ste RMP: Prepared byDokument27 SeitenEngr. Yoshiaki C. Mikami, Bsce Msce-Ste RMP: Prepared byDenzel NgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chassis Design ImportantDokument27 SeitenChassis Design ImportantNandan PoojaryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dim, Mam, Conjugate ReviewerDokument6 SeitenDim, Mam, Conjugate ReviewercabbieNoch keine Bewertungen
- STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS - II-CIVIL-5th - 2021-22Dokument2 SeitenSTRUCTURAL ANALYSIS - II-CIVIL-5th - 2021-22Amiya Ranjan MohantaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem Description: Problem 1: Deflection of A BeamDokument22 SeitenProblem Description: Problem 1: Deflection of A BeamCerita dan BeritaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9 Beam Deflection Kirislerin Yerdegistirmesi 03052021Dokument37 Seiten9 Beam Deflection Kirislerin Yerdegistirmesi 03052021Muhammet AkifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ansi Sdi C 2017 StandardDokument44 SeitenAnsi Sdi C 2017 Standarderky arkvathonejh100% (1)
- Assessment of Rotational Capacity Test Procedure FINALDokument21 SeitenAssessment of Rotational Capacity Test Procedure FINALzaheerahmed77Noch keine Bewertungen
- CE 470-Lect-10-R1 (Minimum Thickness Requirements of Two Way Slabs) (Read-Only)Dokument33 SeitenCE 470-Lect-10-R1 (Minimum Thickness Requirements of Two Way Slabs) (Read-Only)Jamal RkhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 7 Analysis and Design IIIDokument13 SeitenChapter 7 Analysis and Design IIImike smithNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0.0 (2023.10.13)Dokument135 Seiten0.0 (2023.10.13)Anh KyNoch keine Bewertungen
- SBE SS4-secure PDFDokument135 SeitenSBE SS4-secure PDFMyron OikonomakisNoch keine Bewertungen
- ..Dokument22 Seiten..Ghiffa Syauqiyya Harahap 1707113714Noch keine Bewertungen
- Theory of StructuresDokument67 SeitenTheory of Structuresjoyce_mabitasan67% (3)
- CLT Design: Using CWC'S 2017 Wood Design Manual and Woodworks® Sizer SoftwareDokument36 SeitenCLT Design: Using CWC'S 2017 Wood Design Manual and Woodworks® Sizer SoftwarepezhmankhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effective Moment of Inertia ModelsDokument117 SeitenEffective Moment of Inertia Modelsbhairavthakkar1975Noch keine Bewertungen
- Strength of Materials Thin Curved BarsDokument18 SeitenStrength of Materials Thin Curved Barshamza100% (1)
- Steel and Timber Project - Hernandez GroupDokument48 SeitenSteel and Timber Project - Hernandez GroupDean HernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4Dokument59 Seiten4Aqey QeyyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project: Date: Subject: Done By: Alex: 4/5/2017 4.2m Long Precast Plank RSKU KundangDokument2 SeitenProject: Date: Subject: Done By: Alex: 4/5/2017 4.2m Long Precast Plank RSKU KundangalexanderNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12.deformation in Ring and SquareDokument7 Seiten12.deformation in Ring and Squaresanan ali50% (2)
- Beam ReportDokument26 SeitenBeam ReportT0mahawk 45Noch keine Bewertungen
- Astm C 393Dokument4 SeitenAstm C 393Arash Aghagol0% (1)
- Composite Floor Deck DesignDokument4 SeitenComposite Floor Deck DesignsaipodinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Method T160 PDFDokument6 SeitenTest Method T160 PDFPalacios CervantesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Louden Catalog Dec 10Dokument1 SeiteLouden Catalog Dec 10Brad BorgesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steel DesignDokument25 SeitenSteel DesignjohnyNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASTM C497-20 Concrete Pipe, Box Sections and ManholesDokument17 SeitenASTM C497-20 Concrete Pipe, Box Sections and Manholesjoe jack100% (1)
- Finite Element Analysis Theory and Programming by C S KrishnamoorthyDokument137 SeitenFinite Element Analysis Theory and Programming by C S KrishnamoorthyMuthukumaran Sivalingam100% (1)
- European Codes - Steel Design To Eurocode 3 (EN 1993-1-1:2005)Dokument7 SeitenEuropean Codes - Steel Design To Eurocode 3 (EN 1993-1-1:2005)Chong Ting Sheng100% (1)