Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Ebenstein and Ebenstein CHAPTER 6
Hochgeladen von
David Bryan Tan OngOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Ebenstein and Ebenstein CHAPTER 6
Hochgeladen von
David Bryan Tan OngCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
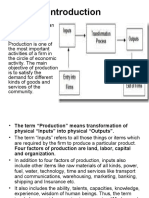
CHAPTER 6 * Productive Capacity is determined by the size and quality of the labor force, by the quantity and quality
of capital stock, by the nations technical knowledge along with the ability to use that knowledge, and by the nature of public and private institutions. BASIC CONCEPTS The production function specifies the maximum output that can be produced with a given quantity of inputs. It is defined for a given state of engineering and technical knowledge. Relationship between the amount of input required and the ampint of output that can be obtained. Useful way of describing the productive capabilities of a firm.
Total product Designates the total amount of output produced
Marginal Product Extra output produced by additional unit of that input while other inputs are held constant.
Average Product Equals total output divided by total units of input.
The a! of "i#ini$hing Return$ !olds that we will get less and less extra output when we add additional doses of an input while holding other inputs fixed. o "he marginal product of each unit of input will decline as the amount of that input increases# holding all other inputs constant. o $s more of an input such as labor is added to a fixed amount of land# machinery# and other inputs the labor has less and less of the other factors to work with. o %arginal product curve declines as labor inputs increase Return$ to Scale
Effects of scale increases of inputs on the quantity produced. &'hat is the effect when all inputs are increased( o )onstant returns to scale* case where change in all inputs leads to a proportional change in output. o Increasing returns to scale &economies of scale(* arise when an increase in all inputs leads to a more*than*proportional increase in the level of output. o Decreasing returns to scale* occur when a balanced increase of all inputs leads to a less*than*proportional increase in total output. o +caling up may eventually reach a point beyond which inefficiencies set in.
SHORT R%N and ON& R%N Short run ,eriod in which firms can ad-ust production by changing variable factors such as materials and labor but cannot change fixed factors such as capital. .nly variable factors can be ad-usted# fixed factors&i.e. plant and equipment( cannot be fully modified or ad-usted.
ong run ,eriod sufficiently long that all factors including capital can be ad-usted. ,eriod of time over which all inputs# fixed and variable# can be ad-usted.
'aria(le factor$* factors which are increased in the short run )i*ed factor$* those that cannot be changed in the short run because of physical condition or legal contracts. Technological change Improves productivity and raises living standards. o $ process of innovation is equivalent to a shift in the production function * hen there are market failures, technological regress might occur even in a market economy.
Productivit+ )oncept measuring the ratio of total output to a weighted average input o a(or productivit+* calculates the amount of output per unit labor
o Total factor productivit+* measures output per unit of total inputs &typically of capital and labor(. economies of scale and mass production have been important elements of productivity growth over the last century if increasing returns prevailed, the larger scale of inputs and production would lead to greater productivity Aggregate Production )unction
total output to the quantity of inputs &like labor# capital and
land( and to toal productivity. Bu$ine$$ fir#$
$re speciali/ed organi/ations devoted to managing the
process of production.
"hey exploit economies of mass production# raise funds and
organi/e factors of production.
Production is organized in firms because efficiency generally
requires large-scale production, the raising of significant financial resources and careful management and monitoring of ongoing activities.
, read $u##ar+
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Christian School Board Seat DisputeDokument2 SeitenChristian School Board Seat DisputeDavid Bryan Tan OngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Christian School Board Seat DisputeDokument2 SeitenChristian School Board Seat DisputeDavid Bryan Tan OngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Christian School Board Seat DisputeDokument2 SeitenChristian School Board Seat DisputeDavid Bryan Tan OngNoch keine Bewertungen
- PTE Mikro - 6 - Production and Business OrgDokument23 SeitenPTE Mikro - 6 - Production and Business OrgDwi Bagus Priambodo100% (1)
- What Is ProductivityDokument12 SeitenWhat Is ProductivityAsghar AbbasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Production and Cost TheoryDokument79 SeitenProduction and Cost TheoryMaria DatingalingNoch keine Bewertungen
- ProductionDokument33 SeitenProductionNaveen Krishna Sunkara0% (1)
- Industrial EconomicsDokument26 SeitenIndustrial Economicskissaraj0% (1)
- Sangwoo CaseDokument2 SeitenSangwoo CaseDavid Bryan Tan Ong100% (1)
- Chapter 5 The Production Process and CostsDokument6 SeitenChapter 5 The Production Process and CostsChristlyn Joy BaralNoch keine Bewertungen
- 26 Hansel Maratnan V DioknoDokument2 Seiten26 Hansel Maratnan V DioknoDavid Bryan Tan OngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Production and Business Organization PDFDokument12 SeitenProduction and Business Organization PDFUmerSaeedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Material No. 8 - Production AnalysisDokument9 SeitenMaterial No. 8 - Production AnalysisrhbqztqbzyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6.production and Business OrganizationDokument2 SeitenChapter 6.production and Business Organizationfrances leana capellan100% (1)
- Lecture Notes For Business Economics (BUS-704) - 4: - Dr. Mirza Azizul IslamDokument10 SeitenLecture Notes For Business Economics (BUS-704) - 4: - Dr. Mirza Azizul Islamtarek aminNoch keine Bewertungen
- Economics Chapter 6 SummaryDokument7 SeitenEconomics Chapter 6 SummaryAlex HdzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 3 QBDokument11 SeitenModule 3 QBKevin V bijuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 11Dokument13 SeitenLecture 11Rabie HarounNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Production FunctionDokument9 SeitenThe Production FunctionPankaj TirkeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microeconomics Chapter 06Dokument5 SeitenMicroeconomics Chapter 06Hasimuddin TafadarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Production and Business Organization: Chapter SixDokument14 SeitenProduction and Business Organization: Chapter Sixdipon sakibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theory of Production and Cost Analysis: Unit - IiDokument27 SeitenTheory of Production and Cost Analysis: Unit - IiRaj KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Production Theory Cost FunctionsDokument3 SeitenProduction Theory Cost FunctionsMarc Luis CartonerosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity 6 - Theory of Production and CostDokument5 SeitenActivity 6 - Theory of Production and CostJelo DavidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Micro Economics UNIT 2 BBADokument6 SeitenMicro Economics UNIT 2 BBAkunjapNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 7 EcoDokument4 SeitenCH 7 Ecosanchita kapoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Production FunctionDokument22 SeitenProduction FunctionAbhishek BoseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4 - Laws of ProductionDokument33 SeitenChapter 4 - Laws of ProductionGarima ThakurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity 8 - Theory of ProductionDokument3 SeitenActivity 8 - Theory of ProductionMarc Luis CartonerosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding Production Functions and EfficiencyDokument22 SeitenUnderstanding Production Functions and EfficiencySandhya ChimmiliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organisation of ProductionDokument11 SeitenOrganisation of ProductionCeliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theory of ProductionDokument35 SeitenTheory of ProductionShivanshKatochNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theory of Production: Dr. Bijit DebbarmaDokument16 SeitenTheory of Production: Dr. Bijit DebbarmaRaja SahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Smu Assanment (42 q3)Dokument2 SeitenSmu Assanment (42 q3)shaileshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 3: Managerial EconomicsDokument29 SeitenUnit 3: Managerial Economicsarjun singh100% (1)
- Industrial EconomicsDokument26 SeitenIndustrial Economicsnishanthreddy89Noch keine Bewertungen
- 3.1 Production Analysis and Concept of MarginalityDokument4 Seiten3.1 Production Analysis and Concept of MarginalityFoisal Mahmud RownakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Production Analysis - Managerial EconomicsDokument5 SeitenProduction Analysis - Managerial EconomicsPrincess Ela Mae CatibogNoch keine Bewertungen
- WEEK3 LESSON 4 Production FunctionDokument4 SeitenWEEK3 LESSON 4 Production FunctionSixd WaznineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 7 Production Function: ObjectivesDokument22 SeitenUnit 7 Production Function: ObjectivesHelen AkowNoch keine Bewertungen
- Returns To ScaleDokument43 SeitenReturns To ScaleVIDYA ANILNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4.production FunctionsDokument29 Seiten4.production FunctionsKanika BakshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- COST ESTIMATION FOR FOOD ENGINEERING PROJECTSDokument53 SeitenCOST ESTIMATION FOR FOOD ENGINEERING PROJECTSMohammad Reza AnghaeiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Production Unit - 4Dokument24 SeitenProduction Unit - 4Goutham AppuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 06 - Firms and ProductionDokument2 Seiten06 - Firms and ProductionMiiwKotiramNoch keine Bewertungen
- MANAGERIAL ECONOMICS: LAW OF VARIABLE PROPORTIONSDokument25 SeitenMANAGERIAL ECONOMICS: LAW OF VARIABLE PROPORTIONSRaunak KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4 - Theory of Production and CostsDokument27 SeitenChapter 4 - Theory of Production and Costsjosephyoseph97Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter Three (3) Theory of The Firm: Managerial EconomicDokument66 SeitenChapter Three (3) Theory of The Firm: Managerial EconomicTeshomeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final EconomicsDokument2 SeitenFinal EconomicsFaizan FiziNoch keine Bewertungen
- Production FunctionDokument49 SeitenProduction FunctionAnuj SaxenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Economics Project Production FunctionDokument13 SeitenEconomics Project Production FunctionApurva Gupta100% (2)
- Introduction to Production FunctionDokument85 SeitenIntroduction to Production Functionayushshrimal000_2201Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2 CC 4Dokument28 SeitenUnit 2 CC 4Kamlesh AgrawalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cost and Production Analysis: Presented byDokument54 SeitenCost and Production Analysis: Presented byPunith SubbuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amara Bandukada Umme Baba Ayush Parekh Suchit Chauhan Arul CollinsDokument36 SeitenAmara Bandukada Umme Baba Ayush Parekh Suchit Chauhan Arul CollinsBijoy BanerjeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Q. What Do You Mean by Productivity? What Are The Various Factors Affecting It?Dokument27 SeitenQ. What Do You Mean by Productivity? What Are The Various Factors Affecting It?Prabhat MalikNoch keine Bewertungen
- REVIEWER ME (Midterm)Dokument13 SeitenREVIEWER ME (Midterm)cynthia karylle natividadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Production Function NotesDokument10 SeitenProduction Function NotesSzaeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 5 - Production TheoryDokument29 SeitenTopic 5 - Production TheoryPatricia Ann TamposNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASOIUDokument20 SeitenASOIUElnur ƏhmədzadəNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6 Production and Business OrganizationDokument4 Seiten6 Production and Business OrganizationHalimaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manegrial EconomicsDokument16 SeitenManegrial EconomicsHiraBashirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theory of Production and Cost BA-IDokument21 SeitenTheory of Production and Cost BA-IHitesh BalhaliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Increasing Returns To Scale in ProductionDokument8 SeitenIncreasing Returns To Scale in ProductionjulieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes On Data PrivacyDokument2 SeitenNotes On Data PrivacyDavid Bryan Tan OngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Waiver 123Dokument1 SeiteWaiver 123David Bryan Tan OngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes On Data PrivacyDokument2 SeitenNotes On Data PrivacyDavid Bryan Tan OngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anabe v. Asian Construction G.R. No. 183233, December 23, 2009Dokument1 SeiteAnabe v. Asian Construction G.R. No. 183233, December 23, 2009David Bryan Tan OngNoch keine Bewertungen
- HLURB ResearchDokument1 SeiteHLURB ResearchDavid Bryan Tan OngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Waiver 123Dokument1 SeiteWaiver 123David Bryan Tan OngNoch keine Bewertungen
- ChecklistDokument1 SeiteChecklistDavid Bryan Tan OngNoch keine Bewertungen
- IRR of Domestic Workers ActDokument24 SeitenIRR of Domestic Workers ActRamil Sotelo SasiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Is Owned and Held: 1 Republic Act 7042Dokument2 SeitenIs Owned and Held: 1 Republic Act 7042David Bryan Tan OngNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4th Set Compiled Digest Labstand PDFDokument46 Seiten4th Set Compiled Digest Labstand PDFDavid Bryan Tan OngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Battered Woman LeaveDokument1 SeiteBattered Woman LeaveDavid Bryan Tan OngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Persons and Family Relations: Vice Dean Marciano G. Delson Atty. Francesca Lourdes M. SeñgaDokument16 SeitenPersons and Family Relations: Vice Dean Marciano G. Delson Atty. Francesca Lourdes M. SeñgaDavid Bryan Tan OngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Norkis V Buena VistaDokument28 SeitenNorkis V Buena VistaDavid Bryan Tan OngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ebenstein and Ebenstein CHAPTER 7Dokument4 SeitenEbenstein and Ebenstein CHAPTER 7David Bryan Tan OngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fortunato M. Lira For Petitioners (P) Rodolfo D. Mapile For Private Respondent (R)Dokument2 SeitenFortunato M. Lira For Petitioners (P) Rodolfo D. Mapile For Private Respondent (R)David Bryan Tan OngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Congress of The PhilippinesDokument10 SeitenCongress of The PhilippinesDbee DveeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Division of Labor SumaDokument13 SeitenDivision of Labor SumaDavid Bryan Tan OngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ebenstein and Ebenstein Chapter 9Dokument4 SeitenEbenstein and Ebenstein Chapter 9David Bryan Tan OngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Congress of The PhilippinesDokument10 SeitenCongress of The PhilippinesDbee DveeNoch keine Bewertungen
- American TobaccoDokument2 SeitenAmerican TobaccoDavid Bryan Tan OngNoch keine Bewertungen
- RA 10142 - Financial Rehabilitation and Insolvency Act (FRIA) of 2010Dokument75 SeitenRA 10142 - Financial Rehabilitation and Insolvency Act (FRIA) of 2010She Oh100% (1)
- Ebenstein and Ebenstein Chapter 8Dokument4 SeitenEbenstein and Ebenstein Chapter 8David Bryan Tan OngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Division of Labor 4Dokument4 SeitenDivision of Labor 4David Bryan Tan OngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Productive Capacity Factors and ConceptsDokument3 SeitenProductive Capacity Factors and ConceptsDavid Bryan Tan OngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quotations From Political ThinkersDokument35 SeitenQuotations From Political ThinkersDavid Bryan Tan OngNoch keine Bewertungen