Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
CryptographySyll 2
Hochgeladen von
avi_weberOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
CryptographySyll 2
Hochgeladen von
avi_weberCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Cryptography Course 780 (Graduate), 381.3 (Undergraduate) Fall 2004 Queens College r. !ent .
"o#lan $onday %&30 ' (&20 )e* +,-en,e "u-ld-ng, .oo/ 133 For as long as mankind has had the ability to communicate, there has been a need, a desire for privacy. This is a necessity of our species; to be able to conduct our business and conversations professional and intimate in such a way as they are not public for all to see. Cryptography, the art and science of keeping messages secure, has been practiced for nearly as long as there has been communication. The various forms and techniques of encryption, the heart of cryptography, have their origin in many diverse fields such as in linguistics, the arts and in the (disparate sciences. This course serves as an introduction to cryptographic practices. !e will learn about classical protocols and attacks (and some will be implemented and we will learn the mathematics needed to gain a firm foothold of how communication and information security is accomplished today. "nd then we will address, in the immortal words of #uffy, $!here do we go from here%& 'equired te(t) Introduction to Cryptography with Coding Theory by Trappe and !ashington, *rentice +all, ,--. /ptional te(t) Applied Cryptography by 0chneier, !iley, 1223 Course grades will be determined by five factors) performance on three problem sets (1-4 each , score on a midterm e(amination (,-4 , score on a final e(amination (,54 , work on a pro6ect where you will have to break a cipher (154 and attendance and participation (54 . 7ate problem sets will not be accepted. "ttendance in class is e(pected and lateness will count as half an absence. 8f, due to illness or emergency, you cannot attend a lecture, notify me in advance, if possible (boklan9cs.qc.edu or call (.:22 . +aving more than two une(cused absences may seriously 6eopardi;e your course grade. This course includes quite a bit of <athematics so a strong background is recommended. =ou will also need to program (well . The syllabus for the course will probably include the following topics (in addition to others ) elementary number theory for cryptography, basic field theory for cryptography, permutations and substitutions, discrete logarithms and the >iffie?+elman protocol, the >@0, .>@0, 'i6ndael and other block ciphers, Aeistel networks, block chaining modes, signatures, certificates, the >0" and the '0" scheme, @l Bamal, 'C: and other stream ciphers, hash functions, linear feedback shift registers, (primitive Balois polynomials, linear congruential generators, one?way trapdoor functions, Cnapsack, @nigma, DigenEre, key and random number generation, data integrity, one?time pads, language recognition (causality and quantum cryptography.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Lecture 5Dokument5 SeitenLecture 5avi_weberNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modulation and Delay Line Based Digital Audio EffectsDokument4 SeitenModulation and Delay Line Based Digital Audio Effectsavi_weberNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wave Equation Simulation in MatlabDokument7 SeitenWave Equation Simulation in MatlabJose FernandoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Journal of Statistic PDFDokument29 SeitenJournal of Statistic PDFsumantasorenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical Modeling Using Digital Waveguides Julius O. Smith IIIDokument28 SeitenPhysical Modeling Using Digital Waveguides Julius O. Smith IIIavi_weberNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leroux 2015 Sparse N MF 03Dokument21 SeitenLeroux 2015 Sparse N MF 03avi_weberNoch keine Bewertungen
- Move Manual RevA EN1Dokument14 SeitenMove Manual RevA EN1barrybearerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brian Freedman: Employment History: Security Supervisor 11/08 - PresentDokument2 SeitenBrian Freedman: Employment History: Security Supervisor 11/08 - Presentavi_weberNoch keine Bewertungen
- Audio Signal DFT SinusoidsDokument5 SeitenAudio Signal DFT Sinusoidsavi_weberNoch keine Bewertungen
- Graph Regularized Non-Negative Matrix Factorization For Data RepresentationDokument14 SeitenGraph Regularized Non-Negative Matrix Factorization For Data Representationavi_weberNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample 748086Dokument77 SeitenSample 748086avi_weber100% (1)
- The Multivariate Gaussian Distribution: 1 Relationship To Univariate GaussiansDokument10 SeitenThe Multivariate Gaussian Distribution: 1 Relationship To Univariate Gaussiansandrewjbrereton31Noch keine Bewertungen
- Solns 2Dokument5 SeitenSolns 2avi_weberNoch keine Bewertungen
- Graph Regularized Non-Negative Matrix Factorization For Data RepresentationDokument14 SeitenGraph Regularized Non-Negative Matrix Factorization For Data Representationavi_weberNoch keine Bewertungen
- Graph Regularized Non-Negative Matrix Factorization For Data RepresentationDokument14 SeitenGraph Regularized Non-Negative Matrix Factorization For Data Representationavi_weberNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solns 2Dokument5 SeitenSolns 2avi_weberNoch keine Bewertungen
- Probability ReviewDokument12 SeitenProbability Reviewavi_weberNoch keine Bewertungen
- Two Proofs of The Central Limit TheoremDokument13 SeitenTwo Proofs of The Central Limit Theoremavi_weberNoch keine Bewertungen
- A New Approach To Email Classification Using Concept Vector Space ModelDokument5 SeitenA New Approach To Email Classification Using Concept Vector Space Modelavi_weberNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solns 2Dokument5 SeitenSolns 2avi_weberNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Journal of Immunology 2012 Barua-1Dokument708 SeitenThe Journal of Immunology 2012 Barua-1avi_weberNoch keine Bewertungen
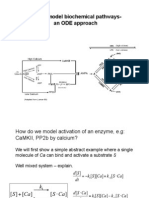
- How To Model Biochemical Pathways-An ODE ApproachDokument18 SeitenHow To Model Biochemical Pathways-An ODE Approachavi_weberNoch keine Bewertungen
- 232 HWAug 27Dokument1 Seite232 HWAug 27avi_weberNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math 232 Homework #4: 1 M 1 1 M M 1 0 2 MDokument1 SeiteMath 232 Homework #4: 1 M 1 1 M M 1 0 2 Mavi_weberNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5782)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (72)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- TorpeDokument49 SeitenTorpekrishnanandNoch keine Bewertungen
- June 2009 QP - Unit 1 Edexcel Physics A-LevelDokument21 SeitenJune 2009 QP - Unit 1 Edexcel Physics A-LevelAlinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Loughborough PhD thesis explores induction coil designDokument336 SeitenLoughborough PhD thesis explores induction coil designReki Swandana100% (1)
- ExclDokument14 SeitenExclAdahylNoch keine Bewertungen
- Universal Playfair Cipher Using MXN MatrixDokument5 SeitenUniversal Playfair Cipher Using MXN MatrixIJEC_EditorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Example 2Dokument7 SeitenExample 2Thái TranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solutions To Exercises On Mathematical IDokument15 SeitenSolutions To Exercises On Mathematical Izoni ianaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Algebra 1 Honors | Inequalities and Intervals: Finding Solutions to Inequalities and Interval NotationDokument3 SeitenAlgebra 1 Honors | Inequalities and Intervals: Finding Solutions to Inequalities and Interval NotationJoh TayagNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1 With VideoDokument17 SeitenModule 1 With VideoMia-Rayner Lang-ay SanchezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment (6) Boyles Law The Aim:: To Measure The Pressure of The AtmosphereDokument3 SeitenExperiment (6) Boyles Law The Aim:: To Measure The Pressure of The Atmosphereعمر احمد شاكرNoch keine Bewertungen
- Linear System Theory and Design 4Th Edition Full ChapterDokument41 SeitenLinear System Theory and Design 4Th Edition Full Chapterjamie.gardner403100% (26)
- Grades 1-12 Daily Lesson LogDokument5 SeitenGrades 1-12 Daily Lesson LogMarlaFirmalino100% (2)
- Theoretical Geomechanics-Marian Ivan Samizdat PressDokument81 SeitenTheoretical Geomechanics-Marian Ivan Samizdat PressaaminfarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Signal Generation and Spectral Analysis LabDokument4 SeitenDigital Signal Generation and Spectral Analysis LabPette MingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ingenieria de La Soldadura PDFDokument11 SeitenIngenieria de La Soldadura PDFedscesc10100% (1)
- Book of Abstracts of International Conference On Thermofluids IX 2017 PDFDokument106 SeitenBook of Abstracts of International Conference On Thermofluids IX 2017 PDFMirsalurriza MukhajjalinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Added Mass DerivationDokument2 SeitenAdded Mass DerivationIhab OmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Icse 10 Computer Chinni TR NoteDokument8 SeitenIcse 10 Computer Chinni TR NoteAD SOLUTIONSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Space State Average Method Full Bridge DC DC Converter PDFDokument4 SeitenSpace State Average Method Full Bridge DC DC Converter PDFvuongkaka91Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sense and ReferenceDokument10 SeitenSense and ReferenceRonald ChuiNoch keine Bewertungen
- FybaDokument234 SeitenFybaonlyvictoryNoch keine Bewertungen
- History of Complex NumbersDokument2 SeitenHistory of Complex NumbersMichelle 晶津Noch keine Bewertungen
- Wednesday 15 January 2020: Mathematics ADokument28 SeitenWednesday 15 January 2020: Mathematics ARoy TwinsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Linked List TechniquesDokument14 SeitenLinked List TechniquesKhải NguyễnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics Major LET Refresher CourseDokument9 SeitenMathematics Major LET Refresher Coursenovey_casio50% (2)
- Chain Rule To Extreme Value and Saddle PointsDokument83 SeitenChain Rule To Extreme Value and Saddle PointsVishwas SainiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 09 PFDokument57 SeitenCH 09 PFxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Civil Engineering - Surveying Multiple Choice Questions and Answers - Preparation For EngineeringDokument15 SeitenCivil Engineering - Surveying Multiple Choice Questions and Answers - Preparation For EngineeringMukesh Kumar64% (11)
- Tutorial On Compressed Sensing Exercises: 1. ExerciseDokument12 SeitenTutorial On Compressed Sensing Exercises: 1. ExercisepeterNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Book of SPCDokument208 SeitenThe Book of SPCmititicu100% (7)