Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Case Study 22 QA Business Quantitative Analysis
Hochgeladen von
jdrukis01Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Case Study 22 QA Business Quantitative Analysis
Hochgeladen von
jdrukis01Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Case Study 22 QA.
doc
Case Study 22 QA
Use Excels graphing tool to generate a converting Fahrenheit Degree to Celsius Degree.
Scenario:
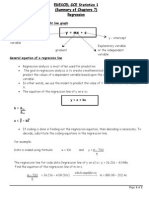
Objective: Learn how to compute and use regression equations to a set of data. Keywords and Concepts 1. Best fit straight line to a set of data 2. Bivariate scatter plot 3. Regression equation 4. Y = mX + C [C here is y-intercept of the equation, and not degree C] 5. Independent variable 6. Dependent variable 7. Slope (rate of change) of the best-fit line 8. Y-intercept 9. Correlation coefficient (r) The following graph shows a linear relationship of a scatter plot of Fahrenheit versus Celsius temperature programmed which is prepared in Excel spread-sheet. Given a collection of paired sample data, the following formula (regression equation) describes the relationship between X (independent or predictor variable) and Y (dependent or response variable): Y = mX + C (eq. 1)
where, m expresses the slope (rate of change) of the best-fit line, X is any particular X value within the range of the data set, and C represents the Y-intercept or the value of Y when X equals zero.
Case Study 22 QA.doc
Step 1:
a. Find the parameters of equation 1 mathematically through interpreting the required data from the graph [also assume that 70 degree F ~ 21 degree C]. b. After you find the regression equation, show your steps in finding your corresponding Fahrenheit temperatures for 23, 100, 0.0, & -40 degree Celsius. What can you tell from these results? c. Utilize Excel spread-sheet to program for y = m x + b for a range of Celsius temperature of 0 ~ 40. You need to generate a series of X, Y data within this range, using the equation of line that was found in part (a), and graph your data. Make sure to include in your graph the Excel equation to fitted line and the RMS, Root Mean Square value for further discussion and drawing conclusions [R^2]. d. Do you think the straight line is a good model for this conversion [F to C]? Why? Please discuss your answer.
Step 2:
Please utilize Excel to perform statistical method [different from graphing mathematical method] to find r, m, and b [correlation coefficient, slope, & Y-intercept] utilizing the following given data:
Y Fahrenheit Temperature X Celsius Temperature
32 0
40 4.44
60 15.5
80 26.6
100 37.7
Case Study 22 QA.doc
( Y)( X 2 ) ( X )( XY) C Y int ercept, C X2 X ( ) ( )2 N N
Case Study 22 QA.doc
Solutions:
Regression Equation We can use the 2 points to find the mathematical equation in Figure 1: P1 (0, 32) and P2 (21, 70 is given to us): Therefore m= 1.8, while Y-intercept is = 32 degree F at X = 0.0 degree C.
Following is the program for this question in Excel
Please notice another way of finding these parameters (m & b in Eq. 1) would be statistical method shown in the following (not required for this problem). Use equation 2 to compute m as follows:
mr SDY SD X
(eq. 2)
Case Study 22 QA.doc
The symbol r equals the correlation coefficient between X and Y; SDY and SDX are their respective X and Y variable standard deviations. The Y-intercept C computes in equation 3 as
C Y mX
(eq. 3)
Where, Y equals the mean of the Y scores, m equals the slope, and X equals the mean of the X scores. Equation 3 can be rewritten as follows:
C Y r( SDY )X SDX
(eq. 4)
Combining equations 2 and 3 expresses the equation for the best-fit regression line to predict Y (Y) from any X value in equation 5:
Y r( SDY ) X Y mX SDX
(eq. 5)
Alternatively, combining equations 2 and 4 expresses the equation for a straight line as:
Y r( SDY SD ) X Y (r Y ) X SDX SDX
(eq. 6)
The slope and Y-intercept of the best-fit regression line also can be computed from raw scores with the following formula (equation 7):
XY X Y ( ) ( )( ) N N N Slope, m 2 X X ( ) ( )2 N N
(eq. 7)
where, the equations numerator equals the numerator for the correlation coefficient ( r) and the denominator equals SDX. The raw score equation (eq. 8) computes the Y-intercept (C) as:
Case Study 22 QA.doc
( Y)( X 2 ) ( X )( XY) Y int ercept, C X 2 ) ( X )2 ( N N
(eq. 8)
The denominator in equation 8 equals the square of SDX. Example Given the following 5 data points for temperature in degrees Fahrenheit ( Yvariable) and temperature in degrees Celsius (X-variable), compute the equation for the best-fitting straight line.
Y Fahrenheit Temperature X Celsius Temperature
32 0
40 4.44
60 15.5
80 26.6
100 37.7
Step 1. Compute r, SDx, and SDy. Y=312; Y2=22624; X=84.36; X2=2395.65; XY=7015.6; N=5 r = 0.999
Y = 62.4; SDY = 25.12
X = 16.87; SDX = 13.95
Step 2. Compute the slope (m) and Y-intercept (C) using equations 2 and 4, respectively.
mr SDY SD X
(eq. 2)
m = 0.9999 (25.12 13.95) m = 1.80
C Y r( SDY )X SDX
6
(eq. 4)
Case Study 22 QA.doc
25.2 C 62.4(0.999 )16.87 13.95 C 32.0
Step 3. The equation for the regression of degrees Celsius on degrees Fahrenheit becomes: Y = mX + C Y = 1.8 X + 32.0 Step 4. Determine the best-fit straight line of the regression, and plot the individual data points as a scatter diagram. (See figure 1) Arbitrarily select a value of X near the maximum observed values of X, and substitute the score in the equation to solve for Y (predicted Y). Plot this point (X, Y) on the scatter gram. Repeat the procedure for another value of X near the minimum observed value of X. The straight line joining the two points represents the best-fitting straight line generated from the regression equation.
32 40 60 80 0 4.44 15.55 26.6
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsVon EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (8)
- Encryption Cheat SheetDokument3 SeitenEncryption Cheat SheetbabuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Regression and CorrelationDokument4 SeitenRegression and CorrelationClark ConstantinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 5 (CORRELATION AND REGRESSION)Dokument23 SeitenUnit 5 (CORRELATION AND REGRESSION)Zara NabilahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Structures Using C - Jagtap, Mali, 2022Dokument363 SeitenData Structures Using C - Jagtap, Mali, 2022chef54Noch keine Bewertungen
- Correlation and Regression Skill SetDokument8 SeitenCorrelation and Regression Skill SetKahloon ThamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 20 Correlation and RegressionDokument14 SeitenTutorial 20 Correlation and RegressionErvin SusantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 5: Correlation and RegressionDokument23 SeitenUnit 5: Correlation and RegressionLidiah ImzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Linear LawDokument29 SeitenLinear LawsusansoonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modeling and Simulating of Gas Turbine Cooled Blades: А. Pashayev, D. Askerov, R. Sadiqov, A. Samedov, and C. ArdilDokument6 SeitenModeling and Simulating of Gas Turbine Cooled Blades: А. Pashayev, D. Askerov, R. Sadiqov, A. Samedov, and C. ArdilganimechNoch keine Bewertungen
- Forecasting Techniques: Quantitative Techniques in ManagementDokument25 SeitenForecasting Techniques: Quantitative Techniques in ManagementvishalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solutions To Final1Dokument12 SeitenSolutions To Final1Joe BloeNoch keine Bewertungen
- POQ:quizDokument10 SeitenPOQ:quizHarsh ShrinetNoch keine Bewertungen
- Other OperationsDokument6 SeitenOther OperationsbertinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes On TensorsDokument11 SeitenNotes On TensorsSambit DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Regression and CorrelationDokument15 SeitenRegression and CorrelationsdffsjdfhgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answer Key: A. 0 B. 0.124 C. 0.814 D. 0.652 E. 1.318Dokument2 SeitenAnswer Key: A. 0 B. 0.124 C. 0.814 D. 0.652 E. 1.318Tejen SubediNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Method For Numerical Integration: by C. B. HaselgroveDokument15 SeitenA Method For Numerical Integration: by C. B. HaselgroveAbid MullaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 06 05 Adequacy of Regression ModelsDokument11 Seiten06 05 Adequacy of Regression ModelsJohn Bofarull GuixNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ptest 2 v1mrs ch9Dokument7 SeitenPtest 2 v1mrs ch9Solanchs SotoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Tutorial 9: Regression Modelling: 9.1 Fitting Linear Models: Linear RegressionDokument4 SeitenLab Tutorial 9: Regression Modelling: 9.1 Fitting Linear Models: Linear RegressionPragyan NandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment Responsion 08 Linear Regression Line: By: Panji Indra Wadharta 03411640000037Dokument11 SeitenAssignment Responsion 08 Linear Regression Line: By: Panji Indra Wadharta 03411640000037Vivie PratiwiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment Responsion 08 Linear Regression Line: By: Panji Indra Wadharta 03411640000037Dokument11 SeitenAssignment Responsion 08 Linear Regression Line: By: Panji Indra Wadharta 03411640000037Vivie PratiwiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment:: Graphing and Curve FittingDokument4 SeitenExperiment:: Graphing and Curve FittingMagnolia NorteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Function Generation Using Freudenstein's EquationDokument15 SeitenFunction Generation Using Freudenstein's Equationvenkatanaveen306Noch keine Bewertungen
- Finite Difference ProofDokument7 SeitenFinite Difference Proofsatish315kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- A D LN (2.000, 0.002) 2.000 0.002: EXAMPLE 20-7Dokument12 SeitenA D LN (2.000, 0.002) 2.000 0.002: EXAMPLE 20-7ABINAS NAYAKNoch keine Bewertungen
- Regression (Autosaved) (Autosaved)Dokument80 SeitenRegression (Autosaved) (Autosaved)DishaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 Simple Linear RegressionDokument62 SeitenChapter 1 Simple Linear RegressionDe El Eurey ShineNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Ybx: Scatter Diagram Correlation CoefficientDokument7 SeitenA Ybx: Scatter Diagram Correlation CoefficientNaheed Nazneen TuLiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBNST QUESTION BANK (2012-2013 Session) CSE-2nd YearDokument3 SeitenCBNST QUESTION BANK (2012-2013 Session) CSE-2nd YearRahul SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Section 10-5 Parametric EquationsDokument11 SeitenSection 10-5 Parametric EquationsBhupesh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Expt. 2 Graphing and Curve-FittingDokument5 SeitenExpt. 2 Graphing and Curve-Fittinguri choiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 5Dokument26 SeitenModule 5Kim Daniel EstoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- School of Mathematical SciencesDokument3 SeitenSchool of Mathematical Scienceslassti hmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Linear RegressionDokument8 SeitenLinear RegressionSailla Raghu rajNoch keine Bewertungen
- FreudDokument15 SeitenFreudKrishnanath ReghunadhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Properties of Graphs of Quadratic Functions: Math 2201 DateDokument10 SeitenProperties of Graphs of Quadratic Functions: Math 2201 DateCatalin BlesnocNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics For Management Chapter OneDokument15 SeitenMathematics For Management Chapter OneKubaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Numerical Solution of Ordinary Differential Equations Part 5 - Least Square RegressionDokument23 SeitenNumerical Solution of Ordinary Differential Equations Part 5 - Least Square RegressionMelih TecerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1.2Dokument26 SeitenChapter 1.2jeff00128Noch keine Bewertungen
- Curve FittingDokument7 SeitenCurve Fittingctg online63Noch keine Bewertungen
- Method of Least SquaresDokument4 SeitenMethod of Least Squareskhaled HyasatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematical Modelling: 6.1 Development of A Mathematical ModelDokument9 SeitenMathematical Modelling: 6.1 Development of A Mathematical ModelMahesh PatilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Functions and ApplicationsDokument30 SeitenFunctions and Applicationslala landNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 6B RegressionDokument13 SeitenTopic 6B RegressionMATHAVAN A L KRISHNANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Questions For CETDokument11 SeitenQuestions For CETSachin BharadwajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calreform3 PDFDokument166 SeitenCalreform3 PDFEgidius PutrandoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Combining Error Ellipses: John E. DavisDokument17 SeitenCombining Error Ellipses: John E. DavisAzem GanuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 7 - RegressionDokument2 SeitenChapter 7 - RegressionKasunDilshanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.4 Direction Fields: What's A Direction Field?Dokument11 Seiten1.4 Direction Fields: What's A Direction Field?crux_123Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1802SupplementaryNotes FullDokument235 Seiten1802SupplementaryNotes FullCourtney WilliamsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coordinate GeometryDokument6 SeitenCoordinate GeometryJosane WilliamsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Distance Regression by Gauss-Newton-type Methods and Iteratively Re-Weighted Least-SquaresDokument15 SeitenDistance Regression by Gauss-Newton-type Methods and Iteratively Re-Weighted Least-SquaresMárcioBarbozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Regression Using ExcelDokument2 SeitenRegression Using ExcelflgrhnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Use of Fast Fourier Transforms For Solving Partial Differential Equations in PhysicsDokument26 SeitenUse of Fast Fourier Transforms For Solving Partial Differential Equations in PhysicsEduardo SandovalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Homework 1Dokument8 SeitenHomework 1Andrés García Arce0% (1)
- RegressionDokument6 SeitenRegressionmirelaasmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Additional Mathematics Linear LawDokument30 SeitenAdditional Mathematics Linear LawDon Amaru Sarma50% (4)
- Digital Signal Processing (DSP) with Python ProgrammingVon EverandDigital Signal Processing (DSP) with Python ProgrammingNoch keine Bewertungen
- 16.323 Principles of Optimal Control: Mit OpencoursewareDokument4 Seiten16.323 Principles of Optimal Control: Mit OpencoursewareSantosh KiranNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2017 Book LightweightCryptographyForSecuDokument155 Seiten2017 Book LightweightCryptographyForSecu123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pla Implicitcerts 2008Dokument6 SeitenPla Implicitcerts 2008Nir InfosysNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reviews: Physics-Informed Machine LearningDokument19 SeitenReviews: Physics-Informed Machine LearningSebastián Nicolás Jara CifuentesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prediction of Water Quality Index (Wqi) Based On Artificial Neural Network (Ann)Dokument5 SeitenPrediction of Water Quality Index (Wqi) Based On Artificial Neural Network (Ann)adibmashuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Line Coding TechniquesDokument14 SeitenLine Coding TechniquesAkshita GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4-To-1 MUXDokument2 Seiten4-To-1 MUXMahijaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Artificial Intelligence - BasicsDokument5 SeitenArtificial Intelligence - Basicsarunspai1478Noch keine Bewertungen
- PVTOLDokument14 SeitenPVTOLJ Chesare Ortega MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Penelitian Skripsi NurfirmansyahDokument10 SeitenData Penelitian Skripsi NurfirmansyahStevan WardiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Linear Programming: Algorithmic and Geometric Foundations of OptimizationDokument28 SeitenIntroduction To Linear Programming: Algorithmic and Geometric Foundations of OptimizationinduputraputraNoch keine Bewertungen
- LAB 10 - Implementation of Discrete-Time FiltersDokument13 SeitenLAB 10 - Implementation of Discrete-Time FiltersM Hassan BashirNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Few Notes On Finite Element MethodDokument3 SeitenA Few Notes On Finite Element MethodSnehasish BhattacharjeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Collection FrameworkDokument4 SeitenCollection FrameworkSaurabh KothariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Frequency-Response Masking FIR Filters: Georg Holzmann June 14, 2007Dokument11 SeitenFrequency-Response Masking FIR Filters: Georg Holzmann June 14, 2007ammayi9845_930467904Noch keine Bewertungen
- Graph Theory NotesDokument2 SeitenGraph Theory NotesLeo SchizoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Algorithm Design: GCDDokument21 SeitenAlgorithm Design: GCDUdtaParindaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tio Ieoper2 Hw1Dokument1 SeiteTio Ieoper2 Hw1Hannah TioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Graph Coloring - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDokument17 SeitenGraph Coloring - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaVijaya Prakash RajanalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Econ 329 - Statistical Properties of The Ols Estimator: Sanjaya DesilvaDokument12 SeitenEcon 329 - Statistical Properties of The Ols Estimator: Sanjaya DesilvaArchivo RCNoch keine Bewertungen
- Subject Name: Digital Signal Processing Subject Code: 10EC52 Prepared By: S.Kareemulla & Prasanth S G & Archana (TE) Department: ECE Date: 10/11/2014Dokument12 SeitenSubject Name: Digital Signal Processing Subject Code: 10EC52 Prepared By: S.Kareemulla & Prasanth S G & Archana (TE) Department: ECE Date: 10/11/2014mohitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lect 1 - Intro To Automatic Control PDFDokument15 SeitenLect 1 - Intro To Automatic Control PDFYota KimireNoch keine Bewertungen
- Date Subject Unit Topic Name: Overview of SQL InjectionDokument4 SeitenDate Subject Unit Topic Name: Overview of SQL InjectionKshitija KulkarniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hightec Inc.Dokument10 SeitenHightec Inc.anurag4u10Noch keine Bewertungen
- MKTG 470 Regression AssignmentDokument2 SeitenMKTG 470 Regression Assignmentsudhir.kochhar3530Noch keine Bewertungen
- Association Analysis (DMDW)Dokument16 SeitenAssociation Analysis (DMDW)bhargaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- MA8452 QP Model Exam 2 - SNM Set ADokument2 SeitenMA8452 QP Model Exam 2 - SNM Set ATamilselviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Linear Regression With Multiple VariablesDokument56 SeitenLinear Regression With Multiple VariablesAsif Bin LatifNoch keine Bewertungen