Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Electrical Engineering
Hochgeladen von
rjrahul25Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Electrical Engineering
Hochgeladen von
rjrahul25Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING
CODE-09
PAPER-I
Net work : Steady state analysis of d.c. and a.c. network theorems Matrix Algebra, network functions, transient response frequency response, Lapalace transform, Fourier series and Fourier transform frequency spectral polezero concept, elementary, network synethsis. Statistics and Magnetics : Analysis of electrostatic and magnefespatic fields. Lapalace and poission equation, Solution of boundaries value problems Maxwell's equations, electromagnetic wave, Propagation ground and space waves propagation between earth station and satelites. Basic methods of measurements standards error analysis indicating instruments, cathod ray oscilloscope measurement of voltage current power resistance inductance capacitance, time frequency and flux electronic metres. Electronics : Vaccum and semi- conductor devices equivalent circuits transistor parameters determination of current and voltage gain and input and output impondences blasing techniques single and multi state audio and radio small signal and large signal amplifiers and their analysis, feed back amplifiers and oscillators, wave shaping circuits and time base generators analysis of different types of multivibrater and their uses, digital circuits. Electrical machines : Generation of a.m.f.e.m.r. and to rque in rotating machines, motor and generator characteristics of d.c. syahronous and induction machines equivalent circuits commutation, parallel operation, phasor diagrams and equivalent circuits of power transformer, determination of performance and efficiency, autotransformers, 3-phase transformers.
PAPER-II
SECTION-A Control system : Mathematical modelling of dynamic linear control system block diagrams and signal flow graphs, transient response, steady state error, stability frequency response techniques, root-locus techniques series compensation. Industrial Electronics : Principles and design of single phase and polyphase rectifiers, controlled rectification, smoothing filers, regulated power supplies, speed control circuits for drives invertors, d.c.to a.c. conversion choppers, timbers and welding circuits. SECTION-B (HEAVY CURRENTS) Electrical Machines : Induction Machines - Rotating magnetic field, polyphase mortar, principle of operation, phaser diagram or que slip characteristic equivalent circuit and determination of its parameters, circle diagram,
starter, speed control double cage motor,induction generator theory, phaser diagram characteristics and application of single phase motors. Application of two-phase induction motor. Sychronous Machines.- e.m.f. equation phaser and circle diagrams, operation on infinite bus, synchronizing power operating characteristics and performance by different methods sudden short circuit and analysis of oscillogram to determine machine reactances and time constant motor characteristics and performance, method of starting applications. Special Machines- Amplidyne and metadyne, operating characteristics and their application. Power systems and protection. - General layout and economics and different types of power stations, base load, peak-load and pumped-storage plants, economics of different systems of d.c.and a.c. power distribution transmission line parameter calculation concept of G.M.D. short medium and long transmission line, insulators, voltage distribution in a string of insulators and grading. Environmental effect on insulators, Fault calculation by symmetrical components, load flow analysis and economic operation, steady state and transient stability, switch gear. Methods of arch-extinction re-stricking and recovery voltage, testing of circuit breaker, protective relays, protective schemes for power system equipment C.T. and P.T.surges in transmission lines, travelling waves and protection. Utilisation :- Industrial drive electric motors for various drives, and estimates of their raping, behaviour of motors daring starting, acceleration, breaking and reversing operations, schemes of speed control for d.c.and induction, motors. Economics and other aspects of different systems of rail traction, mechanic of train movement and estimation of power and energy requirements and motor ratings, characteristics of traction motors, dielectric and induction heating.
or
SECTION-C (LIGHT CURRENT) Communication systems-Generation and detection of amplitude -frequency- phase and pulsemodulate signals using oscillators, modulators and demodulators. Comparison of modulated systems, noise problems, channel efficiency sampling theorem, sound and vision broadcast transmitting and receiving systems, antenna feeders and receiving circuits, transmission line at audio and ultra high frequencies. Micro-waves :- Electro magnetic waves in guided media, wave guide components, cavity resonator micro waves tubes and solid -state devices, micro- wave generators and amplifiers filters, micro-wave measuring technique micro-wave radiation pattern, communication and antenna systems. Radio aids to navigation. D.C. Amplier :- Direct coupled amplifiers, difference amplifiers choppers and analog computation.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Vapor Absorption Vs CompressionDokument3 SeitenVapor Absorption Vs Compression78kbalajiNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Understanding the Stirling Cycle Gas Power ProcessDokument3 SeitenUnderstanding the Stirling Cycle Gas Power ProcessRon QuerubinNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Applied Termo 122424Dokument3 SeitenApplied Termo 122424rjrahul25Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (894)
- Mechanical Refrigeration Cycles ExplainedDokument2 SeitenMechanical Refrigeration Cycles ExplainedAnkur Yash100% (1)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Applied Termo 122424Dokument4 SeitenApplied Termo 122424rjrahul25Noch keine Bewertungen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Introduction To Gas Power CyclesDokument3 SeitenIntroduction To Gas Power CyclesJoseph SajanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- 7 Open Feed Water HeaterDokument2 Seiten7 Open Feed Water HeatercaptainhassNoch keine Bewertungen
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Steam Jet RefrigerationDokument3 SeitenSteam Jet RefrigerationmontymilkyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- 12 Required Properties of Idea RefrigerantsDokument1 Seite12 Required Properties of Idea RefrigerantsDhanabal Palanisamy PNoch keine Bewertungen
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
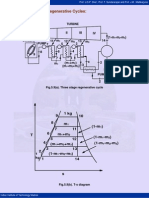
- 11 Multi Stage RSDokument3 Seiten11 Multi Stage RSAkhil DayaluNoch keine Bewertungen
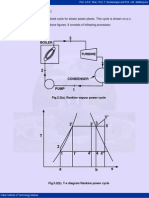
- 5 Modified Rankine CycleDokument3 Seiten5 Modified Rankine CycleMohammad Mussavvir100% (1)
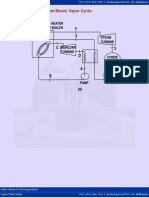
- IIT Madras Professors Explain Mercury-Steam Binary Vapor Power CycleDokument3 SeitenIIT Madras Professors Explain Mercury-Steam Binary Vapor Power CycleSekhar Babu PendyalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- 1 Introduction RefDokument1 Seite1 Introduction RefcaptainhassNoch keine Bewertungen
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- 10 Lenoir CycleDokument2 Seiten10 Lenoir Cyclecaptainhass100% (1)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- 4 Capacity of Steam Power PlantDokument4 Seiten4 Capacity of Steam Power PlantcaptainhassNoch keine Bewertungen
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- 1 Carnot VPC Iit LectureDokument2 Seiten1 Carnot VPC Iit LectureKapil GoyalNoch keine Bewertungen
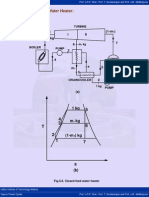
- 8 Closed Feed Water HeaterDokument2 Seiten8 Closed Feed Water HeaterallovidNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 Ericsson CycleDokument2 Seiten4 Ericsson CyclecaptainhassNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 Vortex Tube Non ConventionalDokument3 Seiten10 Vortex Tube Non ConventionalrajdrklNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vapor Absorption Vs CompressionDokument3 SeitenVapor Absorption Vs Compression78kbalajiNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- 7 Analysis of Simple Vapor Compression RCDokument2 Seiten7 Analysis of Simple Vapor Compression RCmahesh5277Noch keine Bewertungen
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- Understanding the Stirling Cycle Gas Power ProcessDokument3 SeitenUnderstanding the Stirling Cycle Gas Power ProcessRon QuerubinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class Test - 2 Course code-MEC-208 Material Science Roll No - Name - Section - C - 4912 (Odd Roll No.s) Time - 40 Min Max Marks-18Dokument1 SeiteClass Test - 2 Course code-MEC-208 Material Science Roll No - Name - Section - C - 4912 (Odd Roll No.s) Time - 40 Min Max Marks-18rjrahul25Noch keine Bewertungen
- Steam Jet RefrigerationDokument3 SeitenSteam Jet RefrigerationmontymilkyNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Lpuinstruction PlanDokument7 SeitenLpuinstruction Planrjrahul25Noch keine Bewertungen
- SDFJHJSDKFHKDokument1 SeiteSDFJHJSDKFHKrjrahul25Noch keine Bewertungen
- 12 Required Properties of Idea RefrigerantsDokument1 Seite12 Required Properties of Idea RefrigerantsDhanabal Palanisamy PNoch keine Bewertungen
- Material TestDokument1 SeiteMaterial Testrjrahul25Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Test-3 C-4912-OddDokument1 SeiteTest-3 C-4912-Oddrjrahul25Noch keine Bewertungen
- SFGFDDokument1 SeiteSFGFDrjrahul25Noch keine Bewertungen
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)