Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
EE1303 Lab Manual: Power Electronics Experiments
Hochgeladen von
Chaitanya SingumahantiOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
EE1303 Lab Manual: Power Electronics Experiments
Hochgeladen von
Chaitanya SingumahantiCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
EE1303-Power Electronics Lab Manual
Muthayammal Engineering college, Rasipuram.
1
MUTHAYAMMAL ENGINEERING COLLEGE, RASIPURAM
Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering
I Semester ME (PED)
Modeling and Simulation Laboratory
Manual
Prepared by Approved by
Prof.M.Muruganandam, M.E.(Ph.D), Dr P.Murugesan,B.E.,Ph.D.,
AP / EEE Proff. & HOD/EEE
Revision No.:0 Date:15.09.2008
EE1303-Power Electronics Lab Manual
Muthayammal Engineering college, Rasipuram.
2
EE1303-Power Electronics Lab Manual
Muthayammal Engineering college, Rasipuram.
3
INSTRUCTIONS TO THE CANDIDATE
SAFETY:
You are doing experiments in Power Electronics lab with high voltage and
high current electric power. It may cause even a fatal or loss of energy of your
body system. To avoid this please keep in mind the followings
In case of any wrong observations, you have to SWITCH OFF the power
supply related with it.
You have to tuck in your shirts or wear an overcoat.
You have to wear shoes compulsorily and stand on mats made by
insulating materials to electrically isolate your body from the earth.
ATTENDANCE:
If you absent for a lab class then you have lost several things to learn.
Laboratory should be treated as temple, which will decide your life. So dont fail
to make your presence with your record notebook having completed
experiments, observation with completed experiments, days experiment
particulars with required knowledge about it and stationeries.
RECORD:
Shows the performance of equipment and yourself. It will be very useful
for future reference. So keep it as follows.
Write neatly; as they have to be preserved enter the readings in the record
notebook those have been written in your observation.
Units should be written for all quantities.
Draw necessary graphs and complete the record before coming to the
next lab class.
Dont forget to write the theory with precaution and inference of each
experiment.
MAY I HELP YOU
1. Device ratings should be noted.
2. Moving coil meters should be used for DC measurements.
3. Moving iron meters should be used for AC measurements.
4. Use isolated supply for the CRO.
5. Use attenuation probe for high voltage measurements in CRO.
EE1303-Power Electronics Lab Manual
Muthayammal Engineering college, Rasipuram.
4
EE1303-Power Electronics Lab Manual
Muthayammal Engineering college, Rasipuram.
5
CONTENTS
Sl.No. Name of the experiment Page No.
1.
VI CHARACTERISTICS OF SCR
2
2.
VI CHARACTERISTICS OF TRIAC
8
3. VI CHARACTERISTICS OF MOSFET
14
4. VI CHARACTERISTICS OF IGBT
20
5. TRANSIENT CHARACTERISTICS OF MOSFET AND SCR
24
6. SINGLE PHASE AC TO DC FULLY CONTROLLED CONVERTER
30
7. SINGLE PHASE AC TO DC HALF CONTROLLED CONVERTER
36
8. STEP DOWN MOSFET BASED CHOPPER
42
9. STEP UP MOSFET BASED CHOPPER
46
10.
IGBT BASED SINGLE PHASE PWM INVERTER
50
11.
SERIES RESONANT DC-DC CONVERTER
(ZERO CURRENT SWITCHING)
56
12.
PARALLEL RESONANT DC-DC CONVERTER
(ZERO VOLTAGE SWITCHING)
60
EE1303-Power Electronics Lab Manual
Muthayammal Engineering college, Rasipuram.
6
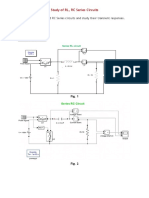
TRANSIENT CHARACTERISTICS OF MOSFET AND SCR
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM:
FOR MOSFET
MATLAB CIRCUIT FOR MOSFET
EE1303-Power Electronics Lab Manual
Muthayammal Engineering college, Rasipuram.
7
TRANSIENT CHARACTERISTICS OF MOSFET AND SCR
AIM:
(i) Obtain and explain both turning ON and turn OFF characteristics of
given SCR
(ii) Obtain and explain both turning ON and turn OFF characteristics of
given MOSFET.
APPARATUS REQUIRED:
S.No. Blocks Type Items Quantity
1 Simulink
i. Sink Scope 1
ii. Source Pulse Generator 1
2 Sim power system
i. Measurements
MC Ammeter 1
MC Voltmeter 1
ii. Elements - RLC series branch 1
iii. Power electronics
- MOSFET 1
- SCR 1
iV. Electrical source - DC source 1
PROCEDURE:
FOR MOSFET
1. Open MATLAB and open Simulink then create a new file (new module)
2. Connections are made as per the circuit diagram by taking the required items
from the corresponding blocks.
3. According to the MOSFET, we should give the block parameter for MOSFET,
RLC series branch, pulse generator and the scope.
4. Now simulate the circuit. The graph of Gate pulse, Drain current and drain to
source voltage can be shown.
5. Finally the print out of the MATLAB circuit and the output is taken.
EE1303-Power Electronics Lab Manual
Muthayammal Engineering college, Rasipuram.
8
FOR SCR
MATLAB CIRCUIT FOR SCR
EE1303-Power Electronics Lab Manual
Muthayammal Engineering college, Rasipuram.
9
FOR SCR
1. Open MATLAB and open Simulink then create a new file (new module)
2. Connections are made as per the circuit diagram by taking the required items
from the corresponding blocks.
3. According to the SCR, we should give the block parameter for SCR, RLC series
branch, pulse generator and the scope.
4. Now simulate the circuit. The graph of Gate pulse, Anode current and anode to
cathode voltage can be shown.
5. Finally the print out of the MATLAB circuit and the output is taken.
EE1303-Power Electronics Lab Manual
Muthayammal Engineering college, Rasipuram.
10
MODEL GRAPH:
FOR MOSFET
FOR SCR
EE1303-Power Electronics Lab Manual
Muthayammal Engineering college, Rasipuram.
11
INFERENCE:
DISCUSSION QUESTIONS:
1. What is MATLAB?
2. What is a transient characteristic?
3. What is commutation?
4. Where the natural commutation is not possible in SCR?
5. What is the function of scope in MATLAB?
RESULT:
EE1303-Power Electronics Lab Manual
Muthayammal Engineering college, Rasipuram.
12
SINGLE PHASE AC TO DC FULLY CONTROLLED CONVERTER
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM FOR R LOAD
Model graph for R Load
( = 30 , R=100 )
EE1303-Power Electronics Lab Manual
Muthayammal Engineering college, Rasipuram.
13
SINGLE PHASE AC TO DC FULLY CONTROLLED CONVERTER
AIM:
(i) To study the operation of single phase fully controlled bridge converter with R
and R-L loads for continuous and discontinuous conduction modes.
(ii) Also find the performance parameters (Rectification efficiency, form factor,
peak inverse voltage and ripple factor)
APPARATUS REQUIRED:
S.No. Name of the item Type Range Quantity
1 1 SCR bridge module TYN612 600V,12A 1
2 SCR Triggering Kit - - 1
3 Ammeter MC (0-500) mA 1
4 Voltmeter MC (0-30) V 1
5 CRO - - 1
6 CRO Brobe - - 1
7 Patch Cards - - 10
FORMULA USED:
For R load
1. Average dc output voltage V
dc
is ) cos 1 ( o
t
+ =
m
dc
V
V
2. RMS output voltage is V
rms
2
1
2
2 sin
2
1
(
|
.
|
\
|
+ =
o
o t
t
m rms
V V
For R-L load continuous conduction:
1. Average dc output voltage V
dc
is o
t
cos
2
m
dc
V
V =
2. RMS output voltage V
rms
is
s
m
rms
V
V
V = =
2
For RL load discontinuous conduction:
3. Average dc output voltage V
dc
is ) cos (cos | o
t
=
m
dc
V
V
4. RMS output voltage V
rms
is
2
1
2
2
2 sin
2
2 sin
2
(
|
.
|
\
|
+ =
o |
o |
t
m
rms
V
V
EE1303-Power Electronics Lab Manual
Muthayammal Engineering college, Rasipuram.
14
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM FOR R-L LOAD
Model graph for R-L Load with continuous conduction
( = 30 , R=100 , L=200mH)
Model graph for R-L Load with discontinuous conduction
( = 90 , R=100 , L=200mH)
EE1303-Power Electronics Lab Manual
Muthayammal Engineering college, Rasipuram.
15
General Formula:
5. Rectification efficiency
2
2
%
rms
dc
V
V
=
6. Form factor
dc
rms
V
V
FF =
7. Peak inverse voltage
m
V PIV =
8. Ripple factor 1
2
= FF RF
Where
m
V = maximum or peak voltage in volts =
s
V 2
s
V = Supply voltage in volts
= Firing angle
= Extinction angle
= Conduction angle = -
Procedure:
1. Connections are made as per the circuit diagram for R load
2. Switch on the triggering kit
3. Switch on the 230 V AC supply
4. Switch on the debounce logic
5. By varying potentiometer vary the firing angle of the converter in order to vary the
output voltage step by step.
6. For each step note down the firing angle, output voltage and load current.
7. The output voltage is theoretically calculated for each step and the readings are
tabulated.
8. Repeat the same procedure for RL load.
EE1303-Power Electronics Lab Manual
Muthayammal Engineering college, Rasipuram.
16
Tabulation for R load:
V
s
= R=
S.No. Firing Angle
in degree
I
dc
Measured
in milliamps
V
dc
Measured
in volts
V
dc
Calculated
in volts
V
rms
Calculated
in volts
Tabulation for RL load:
V
s
= R= L= =
S.No. Firing Angle
in degree
I
dc
Measured
in milliamps
V
dc
Measured
in volts
V
dc
Calculated
in volts
V
rms
Calculated
in volts
Continuous conduction
Discontinuous conduction
EE1303-Power Electronics Lab Manual
Muthayammal Engineering college, Rasipuram.
17
INFERENCE:
DISCUSSION QUESTIONS:
1. What is inversion mode of operation?
2. When we connect a freewheeling diode in full converter, what will be the output?
3. Why the inversion mode is not possible in semi converter?
4. Why the power factor of full converter is lower than semi converter?
5. What is,, and ?
RESULT:
EE1303-Power Electronics Lab Manual
Muthayammal Engineering college, Rasipuram.
18
SINGLE PHASE AC TO DC HALF CONTROLLED CONVERTER
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM FOR R LOAD
Model graph for R Load
( = 30 , R=100 )
EE1303-Power Electronics Lab Manual
Muthayammal Engineering college, Rasipuram.
19
SINGLE PHASE AC TO DC HALF CONTROLLED CONVERTER
AIM:
(i) To study the operation of single phase semi converter with R and R-L loads for
continuous and discontinuous conduction modes.
(ii) Also find the performance parameters (Rectification efficiency, form factor,
peak inverse voltage and ripple factor)
APPARATUS REQUIRED:
S.No. Name of the item Type Range Quantity
1 SCR module with protection TYN612 600V,12A 2
2 Diode module with protection BY126 - 3
3 SCR Triggering Kit - - 1
4 Battery - 12V 1
5 Ammeter MC (0-500) mA 1
6 Voltmeter MC (0-30) V 1
7 CRO - - 1
8 CRO Brobe - - 1
9 Patch Cards - - 10
FORMULA USED:
For R and RL load continuous & discontinuous conduction:
1. Average dc output voltage V
dc
is ) cos 1 ( o
t
+ =
m
dc
V
V
2. RMS output voltage is V
rms
2
1
2
2 sin
2
1
(
|
.
|
\
|
+ =
o
o t
t
m rms
V V
General Formula:
3. Rectification efficiency
2
2
%
rms
dc
V
V
= q
4. Form factor
dc
rms
V
V
FF =
5. Peak inverse voltage
m
V PIV =
6. Ripple factor 1
2
= FF RF
Where
m
V = maximum or peak voltage in volts =
s
V 2
s
V = Supply voltage in volts
o = Firing angle
| = Extinction angle
EE1303-Power Electronics Lab Manual
Muthayammal Engineering college, Rasipuram.
20
= Conduction angle = -
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM FOR R-L LOAD
Model graph for R-L Load with continuous conduction
( = 30 , R=100 , L=100mH)
Model graph for R-L Load with discontinuous conduction
( = 90 , R=100 , L=100mH)
EE1303-Power Electronics Lab Manual
Muthayammal Engineering college, Rasipuram.
21
Procedure:
1. Connections are made as per the circuit diagram for RL load
2. Switch on the triggering kit
3. Switch on the 230V AC supply
4. Switch on the debounce logic
5. By varying potentiometer vary the firing angle of the converter in order to vary the
output voltage step by step.
6. For each step note down the firing angle, output voltage and load current.
7. The output voltage is theoretically calculated for each step and the readings are
tabulated.
8. Repeat the same procedure for RL load.
EE1303-Power Electronics Lab Manual
Muthayammal Engineering college, Rasipuram.
22
Tabulation for R load:
V
s
= R=
S.No. Firing Angle
in degree
I
dc
Measured
in milliamps
V
dc
Measured
in volts
V
dc
Calculated
in volts
V
rms
Calculated
in volts
Tabulation for RL load:
S.No. Firing Angle
in degree
I
dc
Measured
in milliamps
V
dc
Measured
in volts
V
dc
Calculated
in volts
V
rms
Calculated
in volts
Continuous conduction
Discontinuous conduction
EE1303-Power Electronics Lab Manual
Muthayammal Engineering college, Rasipuram.
23
INFERENCE:
DISCUSSION QUESTIONS:
1. What is power electronics?
2. What are the types of converter in power electronics?
3. What is firing angle?
4. What is active load?
5. Why the negative voltage is not possible in semi converter?
6. What is freewheeling diode?
7. Is a separate freewheeling diode necessary for semi converter? Justify your answer.
RESULT:
EE1303-Power Electronics Lab Manual
Muthayammal Engineering college, Rasipuram.
24
STEP DOWN MOSFET BASED CHOPPER
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM
MODEL GRAPH
EE1303-Power Electronics Lab Manual
Muthayammal Engineering college, Rasipuram.
25
STEP DOWN MOSFET BASED CHOPPER
AIM:
To study the waveform for MOSFET based step down chopper for different load
for continuous and discontinuous conduction modes.
APPARATUS REQUIRED:
S.No. Name of the item Type Range Quantity
1 MOSFET Module IRF 840 - 1
2 Ammeter MC (0-500mA) 1
3 Voltmeter MC (0-30V) 1
4 Rheostat - - 1
5 RPS - (0-30V) 1
6 CRO - - 1
7 CRO Probe - - 1
8 Patch cards - - -
FORMULA USED:
1. Average dc output voltage V
dc
is
s dc
V V =
2. RMS output voltage V
rms
is
s rms
V V =
Where:
= Duty cycle of the chopper
T
T
ON
=
T
ON
= on time
T = Total time
Procedure:
1. Connections are made as per the circuit diagram.
2. Switch on the RPS and turn on triggering kit
3. Switch on the debounce logic
4. By changing the width of the pulse, obtain the different set of reading.
5. For each step note down the duty cycle, output voltage and load current and
tabulate it.
6. The output voltage is theoretically calculated.
7. Draw the graph as per the reading in the table.
EE1303-Power Electronics Lab Manual
Muthayammal Engineering college, Rasipuram.
26
TABULATION:
V
s
= T=
S.No. T
ON
in
ms
=
T
T
ON
I
dc
(Avg)
Measured
in mA
V
dc
(Avg)
Measured
in volts
V
dc
(Avg)
Calculated
in volts
s dc
V V =
1
2
3
4
5
EE1303-Power Electronics Lab Manual
Muthayammal Engineering college, Rasipuram.
27
INFERENCE:
DISCUSSION QUESTIONS:
1. What is chopper and what are the devices generally used for chopper?
2. What are the types of chopper?
3. What is step down chopper?
4. What are the control strategies used for choppers?
5. Why frequency modulation is not preferred mostly?
6. Why thyristor is not preferred in chopper circuit mostly?
RESULT:
EE1303-Power Electronics Lab Manual
Muthayammal Engineering college, Rasipuram.
28
STEP UP MOSFET BASED CHOPPER
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM:
Model graph for step up operation
EE1303-Power Electronics Lab Manual
Muthayammal Engineering college, Rasipuram.
29
STEP UP MOSFET BASED CHOPPER
AIM:
To study the waveform for MOSFET based step up chopper for different load for
continuous and discontinuous conduction modes.
APPARATUS REQUIRED:
S.No. Name of the item Type Range Quantity
1 MOSFET Module IRF 840 - 1
2 Ammeter MC (0-500mA) 1
3 Voltmeter MC (0-30V) 1
4 Rheostat - - 1
5 RPS - (0-30V) 1
6 Diode Py 127 - 1
7 Inductor Ferrite core 100mH 1
8 CRO - - 1
9 CRO Probe - - 1
10 Patch cards - - -
FORMULA USED:
Average dc output voltage V
dc
is
( )
=
1
s
dc
V
V
Where:
= Duty cycle of the chopper
T
T
ON
=
T
ON
= on time
T = Total time
PROCEDURE:
1. Connections are made as per the circuit diagram
2. Switch on the RPS and turn on triggering kit
3. Switch on the debounce logic
4. By changing the width of the pulse, obtain the different set of reading.
5. For each step note down the duty cycle, output voltage and load current and
tabulate it.
6. The output voltage is theoretically calculated for each step.
7. Draw the graph as per the reading in the table.
EE1303-Power Electronics Lab Manual
Muthayammal Engineering college, Rasipuram.
30
TABULATION:
V
s
= T=
S.No. T
ON
in
ms
=
T
T
ON
I
dc
(Avg)
Measured
in mA
V
dc
(Avg)
Measured
in volts
V
dc
(Avg)
Calculated
in volts
( )
=
1
s
dc
V
V
1
2
3
4
5
EE1303-Power Electronics Lab Manual
Muthayammal Engineering college, Rasipuram.
31
INFERENCE:
DISCUSSION QUESTIONS:
1. What is chopper and what are the devices generally used for chopper?
2. What are the types of chopper?
3. What is step up chopper?
4. What are the control strategies used for choppers?
5. Why frequency modulation is not preferred mostly?
6. Why thyristor is not preferred in chopper circuit mostly?
RESULT:
EE1303-Power Electronics Lab Manual
Muthayammal Engineering college, Rasipuram.
32
IGBT BASED SINGLE PHASE PWM INVERTER
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM
EE1303-Power Electronics Lab Manual
Muthayammal Engineering college, Rasipuram.
33
IGBT BASED SINGLE PHASE PWM INVERTER
AIM:
To study the operation of single-phase bridge inverter with sinusoidal pulse width
modulation with R load.
APPARATUS REQUIRED:
S.No. Name of the item Type Range Quantity
1 IGBT Module - - 1
2 Inverter control module - - 1
3 CRO - - 1
4 Ammeter MI (0-5A) 1
5 Voltmeter MI (0-300V) 1
6 Patch cards - - -
FORMULA USED:
1. Modulation index (m)
is m = A
r
/ Ac
2. Output voltage V
0
= m Vs
Where
A
r
= Amplitude of reference signal
A
c
= Amplitude of carrier signal
V
s
= Source voltage
EE1303-Power Electronics Lab Manual
Muthayammal Engineering college, Rasipuram.
34
Model graph
Sinusoidal Pulse width modulation
Voltage and current waveforms
EE1303-Power Electronics Lab Manual
Muthayammal Engineering college, Rasipuram.
35
Precaution:
1. Check whether AC main switch is off condition in both the trainer.
2. Check whether control module mode selector switch is in first position (Sine
wave).
3. Check whether control module pulse release switch SW4 in control module is off
position.
4. Check whether 24V AC switch is in off position.
Procedure:
1. Make the connection as per the circuit diagram.
2. Switch on the AC main in both the trainer.
3. Measure the amplitude and frequency of sine wave and carrier triangular wave
and tabulate it. Also adjust sine wave frequency to 50Hz.
4. Connect CRO probe to observe the load voltage and load current waveform.
5. Release the switch SW4 in the inverter control module and switch SW1 in the
IGBT power module.
6. Measure the output voltage.
7. Using the amplitude POT to vary step by step, for each step note down the
amplitude and frequency of sine wave and triangular waveform and also
measure the output voltage and tabulate it.
8. Then find the theoretical output voltage by using the formula.
EE1303-Power Electronics Lab Manual
Muthayammal Engineering college, Rasipuram.
36
Tabulation:
V
s
=
S.No. Amplitude
of carrier
triangular
wave
(A
c
) in
volts
Amplitude
of
reference
sine wave
(A
r
) in
volts
Modulation
index
m= A
r
/A
c
I
0
Measured
in Amps
V
0
Measured
in Volts
V
0
Calculated
in Volts
V
0
= m X V
s
1
2
3
4
5
6
EE1303-Power Electronics Lab Manual
Muthayammal Engineering college, Rasipuram.
37
INFERENCE:
DISCUSSION QUESTIONS:
1. What is inverter?
2. Why we go for PWM?
3. What are the different types of PWM?
4. What is modulation index and what are the types?
5. What are the advantages of IGBT?
RESULT:
EE1303-Power Electronics Lab Manual
Muthayammal Engineering college, Rasipuram.
38
SERIES RESONANT DC-DC CONVERTER
(ZERO CURRENT SWITCHING)
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM:
MODEL GRAPH:
EE1303-Power Electronics Lab Manual
Muthayammal Engineering college, Rasipuram.
39
SERIES RESONANT DC-DC CONVERTER
(ZERO CURRENT SWITCHING)
AIM:
To determine the voltage and current wave form of series resonant dc-dc
converter (Zero current switching).
APPARATUS REQUIRED:
S.No. Name of the item Type Range Quantity
1 Resonant converter module VPET-315 - 1
2 Ammeter MC (0-2) A 1
3 Voltmeter MC (0-30) V 1
4 CRO - - 1
5 CRO Brobe - - 1
6 Patch Cards - - 10
FORMULA USED:
Frequency
T
f
1
= Hz
Where:
T= Time
f = Frequency
PRECAUTIONS:
Initially keep the frequency adjustment POT in minimum position
PROCEDURE:
1. Connections are made as per the circuit diagram.
2. Initially keep frequency adjustment POT in minimum position.
3. Switch on the main supply
4. Connect the P Pin connector from PWM output and PWM input\
5. Connect the banana connector P
10
to P
4
, P
8
to P
11
6. Connect the current sensing resistor (1 / 20 W) across the banana connector P
2
to P
3
.
7. The voltmeter is connected across P
5
and P
12
EE1303-Power Electronics Lab Manual
Muthayammal Engineering college, Rasipuram.
40
TABULATION:
S.No. Time (ms)
Switching
Frequency
(KHz)
Output
Voltage (V)
Output
Current (A)
1
2
3
4
5
EE1303-Power Electronics Lab Manual
Muthayammal Engineering college, Rasipuram.
41
8. Connected the R load across P
5
and P
12
through ammeter.
9. Adjust the frequency POT and set switching frequency 40KHz.
10. Connect the CRO across the connector T1 (+) and ground. Another channel is
connected to P
2
(+), P
3
(-)
11. Now observe the switch voltage and current wave.
12. Similarly observe the switch voltage and current waveform for various switching
frequency.
INFERENCE:
DISCUSSION QUESTIONS:
1. What is resonance?
2. What is the condition for resonance?
3. What are the advantages of resonant converter?
4. What is soft switching?
5. What types of resonant converter?
6. What is zero current switching?
7. What is zero voltage switching?
RESULT:
EE1303-Power Electronics Lab Manual
Muthayammal Engineering college, Rasipuram.
42
PARALLEL RESONANT DC-DC CONVERTER
(ZERO VOLTAGE SWITCHING)
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM:
MODEL GRAPH:
EE1303-Power Electronics Lab Manual
Muthayammal Engineering college, Rasipuram.
43
PARALLEL RESONANT DC-DC CONVERTER
(ZERO VOLTAGE SWITCHING)
AIM:
To determine the voltage and current wave form of parallel resonant dc-dc
converter (Zero voltage switching).
APPARATUS REQUIRED:
S.No. Name of the item Type Range Quantity
1 Resonant converter module VPET-315 - 1
2 Ammeter MC (0-2) A 1
3 Voltmeter MC (0-30) V 1
4 CRO - - 1
5 CRO Brobe - - 1
6 Patch Cards - - 10
FORMULA USED:
Frequency
T
f
1
= Hz
Where:
T= Time
f = Frequency
PRECAUTIONS:
Initially keep the frequency adjustment POT in minimum position
PROCEDURE:
1. Connections are made as per the circuit diagram.
2. Initially keep frequency adjustment POT in minimum position.
3. Switch on the main supply
4. Connect the 9 Pin connector from PWM output and PWM input\
5. Connect the banana connector P
10
to P
4
, P
8
to P
11
6. Connect the current sensing resistor (1 / 20 W) across the banana connector P
2
to P
3
.
7. The voltmeter is connected across P
5
and P
12
EE1303-Power Electronics Lab Manual
Muthayammal Engineering college, Rasipuram.
44
TABULATION:
S.No. Time (ms)
Switching
Frequency
(KHz)
Output
Voltage (V)
Output
Current (A)
1
2
3
4
5
EE1303-Power Electronics Lab Manual
Muthayammal Engineering college, Rasipuram.
45
8. Connected the R load across P
5
and P
12
through ammeter.
9. Adjust the frequency POT and set switching frequency 40KHz.
10. Connect the CRO across the connector T1 (+) and ground. Another channel is
connected to P
2
(+), P
3
(-)
11. Now observe the switch voltage and current wave.
12. Similarly observe the switch voltage and current waveform for various switching
frequency.
INFERENCE:
DISCUSSION QUESTIONS:
1. What is resonance?
2. What is the condition for resonance?
3. What are the advantages of resonant converter?
4. What is soft switching?
5. What types of resonant converter?
6. What is zero current switching?
7. What is zero voltage switching?
RESULT:
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Pe Lab ManualDokument41 SeitenPe Lab ManualGopalakrishna Murthy C RNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Electronics Lab ManualDokument66 SeitenPower Electronics Lab Manualm_javaidkhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Electronics and Drives Laboratory ManualDokument71 SeitenPower Electronics and Drives Laboratory ManualSureshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Electronics Lab Manual (2012-2013)Dokument84 SeitenPower Electronics Lab Manual (2012-2013)srichanderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pelab NewDokument60 SeitenPelab NewRaghu PathyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ee2304 Lab ManualDokument49 SeitenEe2304 Lab ManualSohail KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Electronics Lab ManualDokument49 SeitenPower Electronics Lab ManualNeelakanth BenakalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Machine Lab ManualDokument61 SeitenElectrical Machine Lab ManualPrem SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Electronics Laboratory Using PspiceDokument4 SeitenPower Electronics Laboratory Using Pspicesivar22Noch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Electrical Lab ExperimentsDokument25 SeitenBasic Electrical Lab ExperimentschaitanyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE8261-Electric Circuits Lab Manual PDFDokument91 SeitenEE8261-Electric Circuits Lab Manual PDFPraveen Kumar50% (2)
- Resistors Series and Parallel Circuits AnalysisDokument7 SeitenResistors Series and Parallel Circuits AnalysisElvin FernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- PE Lab ManualDokument103 SeitenPE Lab ManualrajappalambodharaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical-Circuit - Simulation-Lab PDFDokument41 SeitenElectrical-Circuit - Simulation-Lab PDFBhabani sankar Kishan100% (1)
- Electrical-Circuit - Simulation-Lab PDFDokument41 SeitenElectrical-Circuit - Simulation-Lab PDFbh999Noch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Circuits and SimulationDokument64 SeitenElectrical Circuits and SimulationNaveen Yallapu0% (1)
- AC Electric Machines Lab ManulDokument98 SeitenAC Electric Machines Lab Manulmuhammad_sarwar_27Noch keine Bewertungen
- AC Electrical Circuits Lab Manual 123Dokument98 SeitenAC Electrical Circuits Lab Manual 123xyzzyzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Python Programming 2nd EditionDokument106 SeitenPython Programming 2nd Editionshivanand_shettennav100% (1)
- MES Lab ManualDokument58 SeitenMES Lab ManualNokhwrang BrahmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DC Machines and Transformers Lab ManualDokument50 SeitenDC Machines and Transformers Lab ManualSuseel MenonNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE6211-Electric Circuits Laboratory MANUALDokument78 SeitenEE6211-Electric Circuits Laboratory MANUALsakilakumaresanNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE8661-Power Electronics and Drives-Lab ManualDokument117 SeitenEE8661-Power Electronics and Drives-Lab ManualSam Jasper80% (5)
- Eee ELECTRICAL MACHINES-I DC LAB MANUAL 10122019 PDFDokument68 SeitenEee ELECTRICAL MACHINES-I DC LAB MANUAL 10122019 PDFSwaraj KaushkikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Preamble: Laboratory Manual Power Electronics and SimulationDokument80 SeitenPreamble: Laboratory Manual Power Electronics and SimulationDamodar Reddy MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control Systems and Simulation LabDokument91 SeitenControl Systems and Simulation Labkiran_y2Noch keine Bewertungen
- First Set PDF 2018-19 PDFDokument22 SeitenFirst Set PDF 2018-19 PDFLavankumar MudirajNoch keine Bewertungen
- List of ExperimentsDokument24 SeitenList of ExperimentsPrasann KatiyarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laboratory Experiment 1Dokument6 SeitenLaboratory Experiment 1Mark Jomel MangampoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acc ManualDokument44 SeitenAcc ManualDevendra VelhalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Machine-II Laboratory Manual B.Tech, 3 Yr, 5 Semester, Electrical Engg. DeptDokument28 SeitenElectrical Machine-II Laboratory Manual B.Tech, 3 Yr, 5 Semester, Electrical Engg. DeptMoumi PanditNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laboratory Manual For Ac Electrical CircuitsDokument90 SeitenLaboratory Manual For Ac Electrical CircuitsLharie Mae BecinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE8261 Electric Circuits Lab Manual EEE 1Dokument87 SeitenEE8261 Electric Circuits Lab Manual EEE 1Bala Anderson0% (1)
- ECI - UNIT 1 MarkDokument5 SeitenECI - UNIT 1 MarkSukesh RNoch keine Bewertungen
- 17eel37 Eml Lab ManualDokument64 Seiten17eel37 Eml Lab ManualpriyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Be-104 (Beee)Dokument69 SeitenBe-104 (Beee)Sunil NamdevNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Electronics Lab ManualDokument86 SeitenPower Electronics Lab ManualmadhueeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Circuit Simulation LabDokument41 SeitenElectrical Circuit Simulation LabNaveen Yallapu100% (1)
- Electrical MeasurementsDokument47 SeitenElectrical MeasurementsManikantaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BONDOC LAB EXP 1 ElexDokument10 SeitenBONDOC LAB EXP 1 Elexdiannesanjuan29Noch keine Bewertungen
- Power Electronics Lab ManualDokument37 SeitenPower Electronics Lab ManualDawod Shaaban Al-SulifanieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laboratory Manual For Ac Electrical CircuitsDokument78 SeitenLaboratory Manual For Ac Electrical CircuitsTammanurRaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resistors Series and Parallel Circuits LabDokument7 SeitenResistors Series and Parallel Circuits LabElvin FernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6a - RL and RC Series Circuit - MatlabDokument2 Seiten6a - RL and RC Series Circuit - MatlabRahul KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Machines-II Lab ManualDokument61 SeitenElectrical Machines-II Lab ManualNaga Raju100% (1)
- Dev Bhoomi Institute Chakrata Road, Navgaoun Manduwala, UttarakhandDokument32 SeitenDev Bhoomi Institute Chakrata Road, Navgaoun Manduwala, UttarakhandRockstar RichNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laboratory Manual For Ac Electrical CircuitsDokument80 SeitenLaboratory Manual For Ac Electrical CircuitsAngelo PalamingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power System Laboratory Experiment - 2023-24Dokument51 SeitenPower System Laboratory Experiment - 2023-24Manas Ranjan MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Te Etc Pe Lab Manual 2017-18Dokument36 SeitenTe Etc Pe Lab Manual 2017-18wondieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laboratory Manual For Ac Electrical CircuitsDokument75 SeitenLaboratory Manual For Ac Electrical CircuitsArnulfo LavaresNoch keine Bewertungen
- EM Observation - Expts-Back To Back 45Dokument102 SeitenEM Observation - Expts-Back To Back 45Y RohitNoch keine Bewertungen
- LaboratoryManualforACElectricalCircuits PDFDokument78 SeitenLaboratoryManualforACElectricalCircuits PDFAnonymous 8sqB76HcNoch keine Bewertungen
- CT Ratio TestingDokument20 SeitenCT Ratio TestingUzair Ul HaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 2: Power Converters and their ControlVon EverandPower Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 2: Power Converters and their ControlBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- STEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10Von EverandSTEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10Noch keine Bewertungen
- Differential Forms on Electromagnetic NetworksVon EverandDifferential Forms on Electromagnetic NetworksBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- Power Electronics: Switches and ConvertersVon EverandPower Electronics: Switches and ConvertersBewertung: 2 von 5 Sternen2/5 (1)
- Introduction To MayaDokument22 SeitenIntroduction To MayaChaitanya SingumahantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 19070S25Dokument43 Seiten19070S25Chaitanya SingumahantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Result 1st Stage CBT ALP & Tech CEN-01-2018 02.11.18Dokument110 SeitenResult 1st Stage CBT ALP & Tech CEN-01-2018 02.11.18Chaitanya SingumahantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- RRB ALP and Technician ExaminationDokument1 SeiteRRB ALP and Technician ExaminationChaitanya SingumahantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CPP, Godavari TrainsDokument1 SeiteCPP, Godavari TrainsChaitanya SingumahantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bhimadolu RjyDokument1 SeiteBhimadolu RjyChaitanya SingumahantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- LaxmanDokument4 SeitenLaxmanChaitanya SingumahantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Working of Wound Rotor Type IMDokument12 SeitenWorking of Wound Rotor Type IMChaitanya SingumahantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CPP To VSKPDokument1 SeiteCPP To VSKPChaitanya SingumahantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Health TipDokument1 SeiteHealth TipChaitanya SingumahantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Slip Ring and BrushDokument2 SeitenSlip Ring and BrushChaitanya SingumahantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Health TipDokument1 SeiteHealth TipChaitanya SingumahantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5529nr-Power Electronic Control of DC DrivesDokument1 Seite5529nr-Power Electronic Control of DC DrivesChaitanya SingumahantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hafner - 1969 - The New Reality in Art and ScienceDokument14 SeitenHafner - 1969 - The New Reality in Art and ScienceEyeVeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- VVBVBVBBDokument19 SeitenVVBVBVBBnasimakhtarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Performance Analysis of A Dual Cycle Engine With Considerations of Pressure Ratio and Cut-Off RatioDokument6 SeitenPerformance Analysis of A Dual Cycle Engine With Considerations of Pressure Ratio and Cut-Off RatioRajanish BiswasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kanban Card Creator v1.1Dokument30 SeitenKanban Card Creator v1.1bukdownload04Noch keine Bewertungen
- Wells Fargo Preferred CheckingDokument4 SeitenWells Fargo Preferred Checkingjames50% (2)
- Injectable Polyplex Hydrogel For Localized and Long-Term Delivery of SirnaDokument10 SeitenInjectable Polyplex Hydrogel For Localized and Long-Term Delivery of SirnaYasir KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ETE Micro ProjectDokument7 SeitenETE Micro ProjectPadale MoneshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Results and Discussion of Lipid Solubility, Identification, and AnalysisDokument5 SeitenResults and Discussion of Lipid Solubility, Identification, and AnalysisStarrrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem Set 3 Solution Angular Momentum Set 14Dokument7 SeitenProblem Set 3 Solution Angular Momentum Set 14Ayush DubeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Sample Demonstration Lesson PlanDokument9 SeitenA Sample Demonstration Lesson PlanMarie Patrize Punzalan100% (1)
- Jamel P. Mateo, Mos, LPTDokument7 SeitenJamel P. Mateo, Mos, LPTmarieieiemNoch keine Bewertungen
- HissDokument17 SeitenHissJuan Sánchez López67% (3)
- Charlie Mouse OutdoorsDokument48 SeitenCharlie Mouse OutdoorsMarwa AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- M3M Paragon57 Gurgaon Sales, Brochure, PPT, PDFDokument18 SeitenM3M Paragon57 Gurgaon Sales, Brochure, PPT, PDFm3mgurgaonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem For Ledger and Trial BalanceDokument39 SeitenProblem For Ledger and Trial BalanceSumita MathiasNoch keine Bewertungen
- PIP Checklist PDFDokument3 SeitenPIP Checklist PDFGaspar TorresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iso 128-34-2001 PDFDokument18 SeitenIso 128-34-2001 PDFAhmed MaaloulNoch keine Bewertungen
- RAM TP Report 2021Dokument15 SeitenRAM TP Report 2021Sowmya AnanthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blinding Guideline EssentialsDokument13 SeitenBlinding Guideline EssentialsAbdullah Dinsuhaimi100% (1)
- CCE Student Wise SA1 Marks Report for Class 3 Section ADokument1 SeiteCCE Student Wise SA1 Marks Report for Class 3 Section AKalpana AttadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PTC Creo Elements/Direct Modeling ExpressDokument5 SeitenPTC Creo Elements/Direct Modeling ExpressladydaladyNoch keine Bewertungen
- How to Write Formal IELTS LettersDokument5 SeitenHow to Write Formal IELTS Lettersarif salmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project Globe Integra 2G Cluster Case Study AnalysisDokument19 SeitenProject Globe Integra 2G Cluster Case Study AnalysisRAMPRASATHNoch keine Bewertungen
- CNNs: Convolutional Neural Networks for Image ClassificationDokument13 SeitenCNNs: Convolutional Neural Networks for Image ClassificationRahul VasanthNoch keine Bewertungen
- Liquid Dosage Forms: Classification, Manufacturing and Quality Control TestsDokument43 SeitenLiquid Dosage Forms: Classification, Manufacturing and Quality Control Testsbee859550% (4)
- TarminatinDokument102 SeitenTarminatingmnatigizawNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Teach Grammar Using PPP ModelDokument3 SeitenHow To Teach Grammar Using PPP ModelThao NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- DR Bob Jantzen's Differential GeometryDokument485 SeitenDR Bob Jantzen's Differential GeometryBGMoney5134Noch keine Bewertungen
- Prosedur Penggajian: Payroll ProcedureDokument5 SeitenProsedur Penggajian: Payroll ProcedureVira TrianaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wiring 87T E01Dokument4 SeitenWiring 87T E01Hau NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen