Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Measurement and Control QB
Hochgeladen von
umakrishnanOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Measurement and Control QB
Hochgeladen von
umakrishnanCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
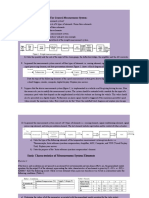
MEASUREMENTS AND CONTROL UNIT-I PART-A 1.
Distinguish between i) Accuracy and precisions ii) Threshold and resolution List the types of errors in measurement system (and explain) What is meant by dispersion? What is drift? Define relative limiting errors? What is the purpose of Measurement? Define 1) Fundamental units 2) Derived units What are the classification of standards? Write a derived units for the following a) Density b) Velocity c) Pressure d) Luminance e) Illumination Define Relative limiting error? Define standard Deviation for a finite and an infinite number of observations. Define mean standard Deviation and probable error. A 600v Voltmeter is specified to be accurate within 2% at full scale. Calculate the limiting error. When the instrument is used to measure a voltage of 250 Define Absolute units. Define uncertainty in terms of expression. What is mean by a) Static Characteristics b) Dynamic Characteristics Define Calibration: Specify odds What are the calibration methods: Explain any one Explain Lenearity
2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16.
17. 18. 19. 20.
PART-B 1.Explain what is meant by: (a) active instruments (b) passive instruments. Give examples of each and discuss the relative merits of these two classes of instruments. 2. Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of null and deflection types of measuring instrument. What are null types of instrument mainly used for and why? 3. Briefly define and explain all the static characteristics of measuring instruments. 4. Explain the difference between accuracy and precision in an instrument. 5. Write down the general differential equation describing the dynamic response of a second order measuring instrument and state the expressions relating the static sensitivity, undamped natural frequency and damping ratio to the parameters in this differential equation. Sketch the
instrument response for the cases of heavy damping, critical damping and light damping, and state which of these is the usual target when a second order instrument is being designed. 6. Define sensitivity drift and zero drift. What factors can cause sensitivity drift and zero drift in instrument characteristics? 7. Explain the difference between systematic and random errors. What are the typical sources of these two types of error? 8. In what ways can the act of measurement cause a disturbance in the system being measured? 9. What steps can be taken to reduce the effect of environmental inputs in measurement systems? 10. (a) What do you understand by the term probability density function? (b) The following ten measurements are made of the output voltage from a high gain amplifier that is contaminated due to noise fluctuations: 1.53, 1.57, 1.54, 1.54, 1.50, 1.51, 1.55, 1.54, 1.56, 1.53 Determine the mean value and standard deviation. Hence estimate the accuracy to which the mean value is determined from these ten measurements. If one thousand measurements were taken, instead of ten, but _ remained the same, by how much would the accuracy of the calculated mean value be improved? UNIT-II
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- M& I 2marks, 16marks, ProblemsDokument22 SeitenM& I 2marks, 16marks, ProblemsAnantha Krishnan VenkatesanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measurement QuestionsDokument2 SeitenMeasurement QuestionsRobert PotterNoch keine Bewertungen
- M&I 2marksDokument35 SeitenM&I 2marksragra214Noch keine Bewertungen
- MeasurementsDokument8 SeitenMeasurementsSethu Naidu0% (1)
- Experiment 1 - Uncertainty & Error AnalysisDokument3 SeitenExperiment 1 - Uncertainty & Error AnalysisrawjaatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 Measurement DevicesDokument38 SeitenChapter 1 Measurement DevicesF1090 ALIF IKHWANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial Sheet-1: Kec-057: Electronic Instrumentation & MeasurementsDokument4 SeitenTutorial Sheet-1: Kec-057: Electronic Instrumentation & MeasurementsBrahmanand SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blow Up - SensorsDokument9 SeitenBlow Up - SensorsbobblytasticNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit-1 Performance CharacteristicsDokument19 SeitenUnit-1 Performance CharacteristicswisorowNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measurements: InstructorDokument42 SeitenMeasurements: InstructorAhmad AbdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Esa QBDokument28 SeitenEsa QBSathish KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- EMI Unit 1 NotesDokument18 SeitenEMI Unit 1 Notesswetha bagadi it's good but how it will workNoch keine Bewertungen
- Instrumentation and Measurement (Meng3261)Dokument53 SeitenInstrumentation and Measurement (Meng3261)Addisu DersoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 1Dokument3 SeitenTutorial 1dfsdsdfsdfsdfsdfsdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ei Model Test Question BankDokument7 SeitenEi Model Test Question BankbcemailidNoch keine Bewertungen
- EI6401 TransducerEngineeringDokument16 SeitenEI6401 TransducerEngineeringPatel DipenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emi MCQDokument27 SeitenEmi MCQgautam100% (3)
- QP AE 1353 Experimental Stress AnalysisDokument16 SeitenQP AE 1353 Experimental Stress AnalysisVignesh ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- EMI Previous Question Papers Topic Wise PDFDokument24 SeitenEMI Previous Question Papers Topic Wise PDFjaganmohanrsNoch keine Bewertungen
- My Own Etm2 Class NotesDokument3 SeitenMy Own Etm2 Class NotessiennaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oic751-Transducer Engineering 2 Marks, 13 Marks and Problem With AnswersDokument32 SeitenOic751-Transducer Engineering 2 Marks, 13 Marks and Problem With AnswersPoovarasan S100% (1)
- EE8403 2marks IqDokument18 SeitenEE8403 2marks IqG Krishna swamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measurement and Instrumentation Theory and Application 2nd Edition Morris Solutions ManualDokument36 SeitenMeasurement and Instrumentation Theory and Application 2nd Edition Morris Solutions Manualraymondferguson5259h100% (26)
- Assignment I: 4Ec3A Electronic Measurement & Instrumentation B.Tech. (EC) 4 SemDokument1 SeiteAssignment I: 4Ec3A Electronic Measurement & Instrumentation B.Tech. (EC) 4 SemSantosh AgrahariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Instrumentation QBDokument5 SeitenInstrumentation QBHIMANSHU SHARMANoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 Preparation For Determining Instrument Channel SetpointsDokument12 Seiten5 Preparation For Determining Instrument Channel SetpointsMauricio Javier DuranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metrology QuestionsDokument5 SeitenMetrology QuestionsWaqaar JowataNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1Dokument51 SeitenChapter 1Kelkiyas TaurusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 - Electrical MeasurementDokument4 SeitenChapter 1 - Electrical MeasurementAin IzzatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- TOPIC 1 Measurement DevicesDokument32 SeitenTOPIC 1 Measurement DevicesBryan MatthiasNoch keine Bewertungen
- ESA-experimental Stress AnalysisDokument12 SeitenESA-experimental Stress AnalysisVINOTHKUMAR SAMPATHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Static C/cs of MeasurementsDokument3 SeitenStatic C/cs of MeasurementssamadonyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dwnload Full Measurement and Instrumentation Theory and Application 2nd Edition Morris Solutions Manual PDFDokument36 SeitenDwnload Full Measurement and Instrumentation Theory and Application 2nd Edition Morris Solutions Manual PDFjherallapizm100% (8)
- Question Bank and Syllabus For MTE - 1 (Sensors, Actuators and Measurement)Dokument2 SeitenQuestion Bank and Syllabus For MTE - 1 (Sensors, Actuators and Measurement)Vinayak DakreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Esa 2 Mark Q & Answer PDFDokument11 SeitenEsa 2 Mark Q & Answer PDFChadwickajiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ee121 Measurements and InstrumentationDokument62 SeitenEe121 Measurements and InstrumentationJoseph Samir FaikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rajalakshmi Engineering College: AE-2304 / Experimental Stress Analysis Two Mark QuestionsDokument16 SeitenRajalakshmi Engineering College: AE-2304 / Experimental Stress Analysis Two Mark QuestionsArjunan ArjuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design and Implementation of Portable Impedance AnalyzersVon EverandDesign and Implementation of Portable Impedance AnalyzersNoch keine Bewertungen
- M& I 2mark Q& ADokument21 SeitenM& I 2mark Q& Asathyasony100% (1)
- Topic 1Dokument32 SeitenTopic 1AzWia MkhtrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 1Dokument32 SeitenTopic 1amirNoch keine Bewertungen
- On The Uncertainty in The Immunity Standards of The IEC 61000-4-x SeriesDokument4 SeitenOn The Uncertainty in The Immunity Standards of The IEC 61000-4-x SeriesS.V.SubrahmanyamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sri Ramakrishna Institute of Technology, Coimbatore-10: Mechatronics QUIZ-3Dokument5 SeitenSri Ramakrishna Institute of Technology, Coimbatore-10: Mechatronics QUIZ-3Veerakumar SNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE8403 M&I AT I QN BankDokument7 SeitenEE8403 M&I AT I QN BankKeerthana SahadevanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solution Manual Measurement and Instrume PDFDokument14 SeitenSolution Manual Measurement and Instrume PDFHamza YousafNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1Dokument33 SeitenChapter 1Addisu DersoNoch keine Bewertungen
- EI6401-Transducer Engineering PDFDokument16 SeitenEI6401-Transducer Engineering PDFVinoth KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- EI6401-Transducer Engineering PDFDokument16 SeitenEI6401-Transducer Engineering PDFJeyamalar RajarajanNoch keine Bewertungen
- MT8591 S&I IA1 Q&A IIIyearDokument60 SeitenMT8591 S&I IA1 Q&A IIIyearILYASNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch2-Error in MeasurementDokument28 SeitenCh2-Error in Measurementzuliana_ismail8564Noch keine Bewertungen
- Multimeters and Ohm's LawDokument6 SeitenMultimeters and Ohm's LawFranchette Mirzi CortejosNoch keine Bewertungen
- KhlanbvDokument71 SeitenKhlanbvAdityaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ei1252 - Transducer EngineeringDokument18 SeitenEi1252 - Transducer Engineeringguru.rjpmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eee 207 - Chapter 3Dokument18 SeitenEee 207 - Chapter 3Naija RonaldoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question Bank EMI (KEE-302)Dokument10 SeitenQuestion Bank EMI (KEE-302)sukh gugranaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1Dokument2 Seiten1Ralph AironNoch keine Bewertungen
- EMM 2 & 16 MarksDokument23 SeitenEMM 2 & 16 MarksbijuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Photonics, Volume 2: Nanophotonic Structures and MaterialsVon EverandPhotonics, Volume 2: Nanophotonic Structures and MaterialsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diffuse Algorithms for Neural and Neuro-Fuzzy Networks: With Applications in Control Engineering and Signal ProcessingVon EverandDiffuse Algorithms for Neural and Neuro-Fuzzy Networks: With Applications in Control Engineering and Signal ProcessingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Combining Pattern Classifiers: Methods and AlgorithmsVon EverandCombining Pattern Classifiers: Methods and AlgorithmsNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDokument15 Seiten6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- 104 21 GenerationDokument6 Seiten104 21 GenerationumakrishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nanometer CMOS VLSI CircuitsDokument108 SeitenNanometer CMOS VLSI CircuitsumakrishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- PSEWDokument3 SeitenPSEWumakrishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- GSB Based Digital NebulizerDokument3 SeitenGSB Based Digital NebulizerumakrishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- DE-BME Lesson - PlanDokument2 SeitenDE-BME Lesson - PlanumakrishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cat II Machines-1Dokument2 SeitenCat II Machines-1umakrishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Te Lab Exp ListDokument1 SeiteTe Lab Exp ListumakrishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Csir FormDokument8 SeitenCsir FormumakrishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ME M.tech Project ManualDokument13 SeitenME M.tech Project ManualSP AravindNoch keine Bewertungen
- ME M.tech Project ManualDokument13 SeitenME M.tech Project ManualSP AravindNoch keine Bewertungen
- III Year Name ListDokument1 SeiteIII Year Name ListumakrishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.4.24. Identification and Control of Residual Solvents 20424eDokument6 Seiten2.4.24. Identification and Control of Residual Solvents 20424eNageshwar ThadakamallaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pla Sci Ze CatalogueDokument9 SeitenPla Sci Ze CatalogueAdi SuwandiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tfy-125 4341 List of Possible Exam Questions Part 1 2Dokument1 SeiteTfy-125 4341 List of Possible Exam Questions Part 1 2arifur.dhakaunivNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.3 Analysing Series and Parallel CircuitsDokument16 Seiten2.3 Analysing Series and Parallel CircuitssfwongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis of Arishta Yoga For Happy Married LifeDokument3 SeitenAnalysis of Arishta Yoga For Happy Married LifegeorgeinpuneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pressure HeadDokument3 SeitenPressure Headkraytos kriegerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid StaticDokument24 SeitenFluid StaticNurhidayah AzmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Identification System Kks Chapter I KksDokument280 SeitenIdentification System Kks Chapter I KksSupratim PalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drag ForceDokument7 SeitenDrag ForceehsankotNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strategic Voting in TV Game Show "The Weakest Link"Dokument47 SeitenStrategic Voting in TV Game Show "The Weakest Link"Abhishek BhasinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report 1galvanic and Concentrated CellDokument12 SeitenReport 1galvanic and Concentrated CellOmar SamirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plastic Limit State of Frame StructuresDokument62 SeitenPlastic Limit State of Frame Structuresprabhu81Noch keine Bewertungen
- HasselbladDokument78 SeitenHasselbladMajor_RavenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thrust Bearing CalculationsDokument162 SeitenThrust Bearing Calculationslahiru1983100% (1)
- Printing - Obtaining and Assigning Beam Cross-Section Properties Using HyperBeam - HM-3020Dokument14 SeitenPrinting - Obtaining and Assigning Beam Cross-Section Properties Using HyperBeam - HM-3020api-19817003Noch keine Bewertungen
- Problem Solving RAEDokument15 SeitenProblem Solving RAEGeraldNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11) Modulus of Subgrade ReactionDokument3 Seiten11) Modulus of Subgrade ReactionSubinDesarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trigonometric Leveling - Heights and Distances Problem (Two Exercises)Dokument1 SeiteTrigonometric Leveling - Heights and Distances Problem (Two Exercises)RadhaAnanthalekshmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stars and Solar System McqsDokument4 SeitenStars and Solar System McqsDev RajuNoch keine Bewertungen
- HVD-10 50MP ApDokument4 SeitenHVD-10 50MP Apdinhhai1613Noch keine Bewertungen
- Vinodhini B. - Mercury PorosimetryDokument35 SeitenVinodhini B. - Mercury PorosimetryHarry JakeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Auto Materials BrochureDokument7 SeitenAuto Materials BrochuresNoch keine Bewertungen
- In Physics and Fiction, A Wormhole IsDokument5 SeitenIn Physics and Fiction, A Wormhole IsSouktik_Roy_2983Noch keine Bewertungen
- Challenging Glass 2Dokument7 SeitenChallenging Glass 2Vassil VassilevNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lateral Torsional Buckling of Steel BeamsDokument8 SeitenLateral Torsional Buckling of Steel BeamsapirakqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energy: Eugenia D. Mehleri, Haralambos Sarimveis, Nikolaos C. Markatos, Lazaros G. PapageorgiouDokument9 SeitenEnergy: Eugenia D. Mehleri, Haralambos Sarimveis, Nikolaos C. Markatos, Lazaros G. Papageorgiounana yawNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problemario B.E. Segundo ParcialDokument4 SeitenProblemario B.E. Segundo ParcialjorgeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Book Very ExDokument1.772 SeitenPhysics Book Very Exapi-19875617Noch keine Bewertungen
- Observer-Based Super Twisting Sliding Mode Control For Fixed Wing Unmanned Aerial VehicleDokument6 SeitenObserver-Based Super Twisting Sliding Mode Control For Fixed Wing Unmanned Aerial VehiclemailtosshettyNoch keine Bewertungen
- MTL 200 OutlineDokument3 SeitenMTL 200 OutlineputhiawanNoch keine Bewertungen