Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Know About Gall Bladder Introduction
Hochgeladen von
fredrickstorrs01Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Know About Gall Bladder Introduction
Hochgeladen von
fredrickstorrs01Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
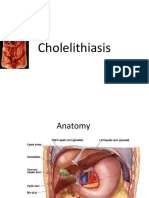
Know About Gall-bladder Introduction
Gall-bladder is a small organ lies just below liver on right upper abdomen. Gall-bladder stores bile (juice formed by liver) and help in digestion of fatty meals. Development of stones in gall-bladder indicates malfunction of gallbladder and surgical removal of gall-bladder is easily tolerated by the body. Type of Gall-stones: There are 3 types of gall-stones.
1. Cholesterol gallstones develop when bile contains too much cholesterol and not enough bile salts. is! factors for cholesterol stones are obesity" women ta!ing estrogen either as family planning pill or for peri-menopausal hormonal supplement" diabetic person and those losing weight rapidly. #ealthy lifestyle may minimi$e the development of cholesterol gall-stones. %. &igmented stone are made up of bilirubin and ris! factors for pigment stones includes hemolytic anemias (such as sic!le-cell disease and hereditary spherocytosis)" cirrhosis ('iver failure)" and biliary tract infections. (. )i*ed stones" is the most common type seen in +ndian-,sian population. -hey are composed of both cholesterol and salts.
Risk factor .actors that may increase your ris! of gallstones include/ 1. 0omen between %1 and 21 years of age are twice as li!ely to develop gallstones as men. %. ,ge/ more common in the (13s 4 513s. (. 6besity 5. 7*cess estrogen (women on oral contraceptive pills etc. 8. Diabetes 2. ®nancy 9. apid weight loss
:. &rolonged fasting ;. #ereditary blood disorders. y!pto!s 1. <iliary Colic/ Gallstones may remains asymptomatic or may lead to =gallstone attac!= (<iliary colic)/ an unforgettable intense pain in the upper-right side of the abdomen" often accompanied by nausea and vomiting" that steadily increases for appro*imately (1 minutes to several hours. 6ften" attac!s occur after a particularly fatty meal. %. 6ther symptoms include abdominal bloating" intolerance of fatty foods" belching" gas" and indigestion. "iagnosis >ltrasound is the most useful test to identify gallstones. ?ometime ) C& @ 7 C& may be reAuired to loo! for presence of stones in common-bile duct (C<D). outine blood test (C<C) ,BD 'iver function test ('.-) are done to loo! for any infection @ jaundice. #o!plications
#o!plications ,cute Cholecystitis (+nflammation of the gallbladder). , gallstone that becomes lodged in the nec! of the gallbladder can cause inflammation of the gallbladder (cholecystitis). +n some case this may lead to pus formation in gall-bladder" leading to severe pain and fever that reAuire hospitalisation and treatment. $aundice % #holangitis &'lockage of the co!!on bile duct % (e)er*. Gallstones can bloc! the tubes (ducts) through which bile flows from your gallbladder or liver to your small intestine. Caundice and bile duct infection (Cholangitis) can result. Acute +ancreatitis &'lockage of the pancreatic duct*. -he pancreatic duct is a tube that runs from the pancreas to the common bile duct. &ancreatic juices" which aid in digestion" flow through the pancreatic duct. , gallstone can cause a bloc!age in the pancreatic duct" which can lead to inflammation of the pancreas (&ancreatitis). &ancreatitis causes intense" constant abdominal pain and usually reAuires hospitali$ation. Gallbladder cancer. &eople with a history of gallstones have an increased ris! of gallbladder cancer. <ut gallbladder cancer is very rare" so even though the ris! of cancer is elevated" the li!elihood of gallbladder cancer is still very small. Treat!ent Asy!pto!atic Gall-stones:
1. ,symptomatic gall-stones are usually observed. 6nly high ris! asymptomatic patients (those having more probability to develop gallstone related complications) are advised for surgery. -he #igh ris! asymptomatic patients are diabetic" person on chemotherapy 4 immunocompromised person (#+D). y!pto!atic Gall-stones: 1. ?urgery/ ?ymptomatic patients should consult to medical e*pert for surgery. 'aparoscopic (Eey hole) gall-bladder surgery is a worldwide accepted treatment. %. ?tone dissolving therapy in ineffective for mi*ed and pigmented gallstones and has inconsistent result for cholesterol stones. +nability to identify stone composition and high prevalence of mi*ed stones" limits the use of Fstone dissolving therapyG in +ndian-,sian population. Disit for )ore about "r A)inash Tank
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- CholecystitisDokument27 SeitenCholecystitisKadek Ariarta MahartamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ntroduction: (1) (2) (3) Go ToDokument6 SeitenNtroduction: (1) (2) (3) Go ToretnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common Name:: Gallstones Description: Gallstones Are A Collection of One or More Stones in The GallbladderDokument4 SeitenCommon Name:: Gallstones Description: Gallstones Are A Collection of One or More Stones in The GallbladderKaren BumatayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gallstones Symptoms, Causes and TreatmentDokument7 SeitenGallstones Symptoms, Causes and TreatmentImtiazAhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- ReportDokument12 SeitenReportTomi Basallo BarriosNoch keine Bewertungen
- CholelithiasisDokument5 SeitenCholelithiasisrgflores1979100% (2)
- Cholelithiasis: Group MembersDokument12 SeitenCholelithiasis: Group MembersShiela GutierrezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Background: Cholecystitis Choledocholithiasis Cholangitis Gallbladder CancerDokument47 SeitenBackground: Cholecystitis Choledocholithiasis Cholangitis Gallbladder CancerPoe Peligrino-Felisilda Bagarinao JrNoch keine Bewertungen
- GALLSTONES (Cholelithiasis) : Medical Term: Common Name: DescriptionDokument3 SeitenGALLSTONES (Cholelithiasis) : Medical Term: Common Name: DescriptionAeyCh BaylenNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Diseases of GallbladderDokument27 SeitenThe Diseases of GallbladderAroosha IbrahimNoch keine Bewertungen
- GallstoneDokument6 SeitenGallstoneMushfique HussainNoch keine Bewertungen
- YunisDokument5 SeitenYunisEunice BautistaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gallbladder Inflammation: Causes, Symptoms and Treatment of CholecystitisDokument9 SeitenGallbladder Inflammation: Causes, Symptoms and Treatment of CholecystitisFerreze AnnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Progesterone Has Been Shown To Decrease Gall-Bladder Motility, WhichDokument9 SeitenProgesterone Has Been Shown To Decrease Gall-Bladder Motility, WhichFerreze AnnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cholelithiasis GallstoneDokument22 SeitenCholelithiasis GallstoneBheru LalNoch keine Bewertungen
- GallstonesDokument3 SeitenGallstonestesfahuntekletilahunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gallbladder DiseaseDokument67 SeitenGallbladder DiseaseKhadira MohammedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cholecystitis With CholecystolithiasisDokument33 SeitenCholecystitis With CholecystolithiasisDino V EscalonaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chole Lithia SisDokument22 SeitenChole Lithia SisriantyceceNoch keine Bewertungen
- B. Synthesis of The DiseaseDokument5 SeitenB. Synthesis of The DiseaseQaz ZaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pancreaticobiliary Lesions: DR Rofanda BakeerDokument29 SeitenPancreaticobiliary Lesions: DR Rofanda BakeerKareem DawoodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Common Bile Duct StonesDokument3 SeitenAnatomy, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Common Bile Duct StonesPao AcelajadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cholecystitis Gallbladder Liver Gallbladder: Cholecystitis - Overview What Is Cholecystitis?Dokument4 SeitenCholecystitis Gallbladder Liver Gallbladder: Cholecystitis - Overview What Is Cholecystitis?wizardebmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Goo 2021Dokument72 SeitenGoo 2021eviltohuntNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chole Lithia SisDokument16 SeitenChole Lithia SisAnonymous yJpblP7CgNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Diagnosis and Management of Gallstones in The Elderly: Liver DiseasesDokument5 SeitenThe Diagnosis and Management of Gallstones in The Elderly: Liver Diseasessusanto kusumaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Disorders of Biliary SystemDokument29 SeitenDisorders of Biliary SystemAjibola OlamideNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cholelithiasis: Introduction: General Illness InformationDokument9 SeitenCholelithiasis: Introduction: General Illness InformationJhangot Abad GabucoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cholelithiasis: - Other Names: - Gallbladder Attack - Biliary Colic - Gallstone Attack - Bile Calculus - Biliary CalculusDokument101 SeitenCholelithiasis: - Other Names: - Gallbladder Attack - Biliary Colic - Gallstone Attack - Bile Calculus - Biliary CalculusYvonne100% (1)
- Abdominal DistensionDokument10 SeitenAbdominal DistensionMorad ImadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute AbdomenDokument56 SeitenAcute AbdomenponekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problems in Digestion, Metabolism and Elimination/Nutrition: Nursing Facts in BriefDokument2 SeitenProblems in Digestion, Metabolism and Elimination/Nutrition: Nursing Facts in BriefAdrienne SumarinasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Colilithiasis 2Dokument53 SeitenColilithiasis 2Worku KifleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crohn'S Disease: Rivera, Roel PDokument22 SeitenCrohn'S Disease: Rivera, Roel PwellYONGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cholecystitis and Biliary Colic: Learning ObjectivesDokument37 SeitenCholecystitis and Biliary Colic: Learning Objectivesapi-19641337Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cirrhosisoftheliver 2016Dokument4 SeitenCirrhosisoftheliver 2016Nazimr RazaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease Dinesh K lamsal:MDDokument20 SeitenInflammatory Bowel Disease Dinesh K lamsal:MDMadhu Sudhan PandeyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Liver AbscessDokument18 SeitenLiver AbscessBheru Lal100% (2)
- Jarvis 6th Ed - Chapter 21Dokument6 SeitenJarvis 6th Ed - Chapter 21edoble100% (4)
- Gall Bladder Diseases 2023Dokument58 SeitenGall Bladder Diseases 2023Ebuka AniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Intestinal Obstruction...Dokument42 SeitenAcute Intestinal Obstruction...Ali100% (2)
- Batu EmpeduDokument51 SeitenBatu EmpedustellaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical Clerk Seminar Series: Approach To Gi BleedsDokument11 SeitenClinical Clerk Seminar Series: Approach To Gi BleedsAngel_Liboon_388Noch keine Bewertungen
- FUMC ReportDokument8 SeitenFUMC Reportlordkurt14Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gall Stones: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentDokument35 SeitenGall Stones: Causes, Symptoms and Treatmentjitendra magarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Right Hypochondrium Pain CausesDokument34 SeitenRight Hypochondrium Pain CauseskhansamrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hepato-Biliary System: Mirizzi'S Syndrome Cholecystitis & Gulran DiseaseDokument53 SeitenHepato-Biliary System: Mirizzi'S Syndrome Cholecystitis & Gulran DiseaseGemgem AcostaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Cholecystitis:: Etiological TypesDokument5 SeitenAcute Cholecystitis:: Etiological Typesvivek yadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gallstones Risk Factors & ComplicationsDokument7 SeitenGallstones Risk Factors & Complicationsmonica_valderramaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exocrine Pancreatic and Biliary Disorders and ManagementDokument77 SeitenExocrine Pancreatic and Biliary Disorders and ManagementAnthon Kyle TropezadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Causes, Symptoms and Treatment of Intestinal ObstructionDokument15 SeitenCauses, Symptoms and Treatment of Intestinal ObstructionEmmeline Dycangchon-GarmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Act 3Dokument29 SeitenAct 3Nicole SorianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- AscitesDokument71 SeitenAscitessohilaw210Noch keine Bewertungen
- Colon Surgery Procedures ExplainedDokument9 SeitenColon Surgery Procedures ExplainedAgung Choro de ObesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gastro POMDokument63 SeitenGastro POMLionell Castillo100% (1)
- Primary Billiary CirrhosisDokument6 SeitenPrimary Billiary CirrhosisElvantia MarilynNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity 8-Liver Cirrhosis-DonghitDokument8 SeitenActivity 8-Liver Cirrhosis-DonghitAllona Jane Beatrice DonghitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Liver Cirrhosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related DiseasesVon EverandLiver Cirrhosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related DiseasesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ascites, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsVon EverandAscites, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nselec4 Lab m1p2 MahinaysmDokument5 SeitenNselec4 Lab m1p2 MahinaysmShaina Mercado MahinayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Primary Herpetic Gingivostimatitis 2019Dokument4 SeitenPrimary Herpetic Gingivostimatitis 2019HeinzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tooth Enamel Erosion-18639Dokument9 SeitenTooth Enamel Erosion-18639Charlie McdonnellNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exfoliative Cytology: Exfoliative - Dead Tissue Falling Off inDokument15 SeitenExfoliative Cytology: Exfoliative - Dead Tissue Falling Off indentalmementalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Encopresis Health TalkDokument15 SeitenEncopresis Health TalkAmit RanjanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common Stressors and Challenges of Being AdolescentDokument2 SeitenCommon Stressors and Challenges of Being AdolescentJohn Van Dave Taturo100% (1)
- Children of The Night - The Created PDFDokument98 SeitenChildren of The Night - The Created PDFFlavio Dupim Pires100% (1)
- 1 Introduction To AnemiaDokument60 Seiten1 Introduction To AnemiaKhisha RangasNoch keine Bewertungen
- DR Sylvia VighDokument33 SeitenDR Sylvia Vighvaishu2488Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture PKDokument69 SeitenLecture PKrajyurafNoch keine Bewertungen
- Contoh Soal Bahasa InggrisDokument15 SeitenContoh Soal Bahasa InggrisSely SetiawatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multichannel Lung Sound Analysis For Asthma Detection PDFDokument13 SeitenMultichannel Lung Sound Analysis For Asthma Detection PDFskwijayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Attractiveness of Legs Length in Poland and Great Britain: Piotr SorokowskiDokument5 SeitenAttractiveness of Legs Length in Poland and Great Britain: Piotr SorokowskiAlcides camilo paez de la hozNoch keine Bewertungen
- EJO-20-0723 Proof HiDokument9 SeitenEJO-20-0723 Proof HiRasha Mounir Abdel-Kader El-TanamlyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Covid-19 Task Force Patrol PCP Building 13 September 2021Dokument26 SeitenCovid-19 Task Force Patrol PCP Building 13 September 2021Rifki WaliardiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physio Ex Exercise 6 Activity 1Dokument3 SeitenPhysio Ex Exercise 6 Activity 1Roland Calipayan Jr.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 12 Employee Counselling and Wellness Services : 12.0 ObjectivesDokument20 SeitenUnit 12 Employee Counselling and Wellness Services : 12.0 ObjectivesNIKITHAA ASHWINNoch keine Bewertungen
- SANIFECT - High Level DisinfectantDokument3 SeitenSANIFECT - High Level DisinfectantHa HoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Caffeine Addiction EffectsDokument16 SeitenCaffeine Addiction Effectsabin joy100% (1)
- Course Title: Large Animal Medicine-I: Systemic Diseases of Digestive SystemDokument35 SeitenCourse Title: Large Animal Medicine-I: Systemic Diseases of Digestive SystemFarhan NobelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aero PhoneDokument11 SeitenAero PhoneOlivia O.ONoch keine Bewertungen
- HFR Week 01 Step 01 Handout 9-16-21Dokument4 SeitenHFR Week 01 Step 01 Handout 9-16-21Damian SmithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample: Oncotype DX Breast Cancer AssayDokument2 SeitenSample: Oncotype DX Breast Cancer Assaybirhane gebreegziabiherNoch keine Bewertungen
- MSF 2020 Annual Report WebDokument62 SeitenMSF 2020 Annual Report WebDoctors Without Borders/Médecins Sans FrontièresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Robbins 7th Ed - Chapter 2 - Acute and Chronic Inflammation (1) Flashcards by Heli Sinnpson - BrainscapeDokument18 SeitenRobbins 7th Ed - Chapter 2 - Acute and Chronic Inflammation (1) Flashcards by Heli Sinnpson - BrainscapeCarlos MaingeNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNDERSTANDING VITAL SIGNS IN HORSESDokument5 SeitenUNDERSTANDING VITAL SIGNS IN HORSESamicrazyNoch keine Bewertungen
- MeningococcemiaDokument5 SeitenMeningococcemiaErhiecka BasaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Senior Paper Final 4Dokument23 SeitenSenior Paper Final 4api-612131991Noch keine Bewertungen
- NCM 109 Lab Finals TransesDokument10 SeitenNCM 109 Lab Finals TransesElaiza Anne SanchezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lingual VaricositiesDokument2 SeitenLingual VaricositiesDr. Nitish Bhat0% (1)