Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
A After A Nerve or Muscle Fires During The: Short Period Cell Cannot Respond To Additional Stimulation
Hochgeladen von
Arun PrakashOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
A After A Nerve or Muscle Fires During The: Short Period Cell Cannot Respond To Additional Stimulation
Hochgeladen von
Arun PrakashCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
1.
Define Action and rsting potential. Equilibrium is reached with a potential difference across the membrane such that negative on inside and positive on outside. This membrane potential caused by the different concentration of irons is called Resting Potential. Cell has a slightly positive potential on the inside due to imbalance of potassium ions. This positive potential of the cell membrane during excitation is called Action Potential and is about ! m". 2. What is meant by CNS? The central nervous system #C$%& is the part of the nervous system that functions to coordinate the activity of all parts of the bodies of multicellular organisms. 3. What is meant by refractory period?
A short period after a nerve or muscle cell fires during which the cell cannot respond to additional stimulation.
4. Write the e pression goldman!s e"#ation
E Na ) K )Cl =
RT P ( K ' + PNa ( Naout ' + PCl (Clin ' ln K out F PK ( K in ' + PNa ( Nain ' + PCl (Clout '
where P*) P$a) PCl + permeability constants for ma,or ionic species. E$a)*)Cl + equilibrium potential #volts& of the three ma,or ions R + gas constant T + absolute temp in -elvins . + .araday constant $. Compare Acti%e and passi%e transd#cers. Acti%e transd#cer / A transducer that gives its output without the use of an excitation voltage or modulation of a carrier signal is called an active transducer. &assi%e transd#cer ' A transducer that gives its output using an excitation voltage or modulation of a carrier signal is called a passive transducer. 0enerally the active transducer converts a non1 electrical energy into electrical energy and converts an electrical into non electrical energy.
&A() * +
2. Explain the bloc- diagram of biomedical instrument system. (3!'
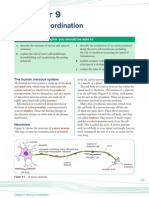
4. #a& i. Explain the structure of C$% with neat diagram.(5' Central ner%o#s system #CNS&
The central ner%o#s system #CNS& is the part of the nervous system that functions to coordinate the activity of all parts of the bodies of multicellular organisms. 6n vertebrates) the central nervous system is enclosed in the meninges. 6t contains the ma,ority of the nervous system and consists of the brain and the spinal cord. Together with the peripheral nervous system it has a fundamental role in the control of behavior. The C$% is contained within the dorsal cavity) with the brain in the cranial cavity and the spinal cord in the spinal cavity. The brain is protected by the s-ull) while the spinal cord is protected by the vertebrae. &eripheral ner%o#s system ,&NSThe peripheral nervous system #P$%& resides or extends outside the central nervous system #C$%&) which consists of the brain and spinal cord. The main function of the P$% is to connect the C$% to the limbs and organs. 7nli-e the central nervous system) the P$% is not protected by bone or by the bloodbrain barrier) leaving it exposed to toxins and mechanical in,uries. The peripheral nervous system is divided into the somatic nervous system) autonomic nervous system and the sensory system ii. Explain the function of heart with neat diagram.(4'
#b& i. Explain the bloc- diagram of a pie8oelectric ultrasonic transducer.(5'
The conversion of electrical pulses to mechanical vibrations and the conversion of returned mechanical vibrations bac- into electrical energy is the basis for ultrasonic testing. The active element is the heart of the transducer as it converts the electrical energy
to acoustic energy) and vice versa. The active element is basically a piece of polari8ed material #i.e. some parts of the molecule are positively charged) while other parts of the molecule are negatively charged& with electrodes attached to two of its opposite faces. 9hen an electric field is applied across the material) the polari8ed molecules will align themselves with the electric field) resulting in induced dipoles within the molecular or crystal structure of the material. This alignment of molecules will cause the material to change dimensions. This phenomenon is -nown as electrostriction. 6n addition) a permanently1polari8ed material such as quart8 #%i: & or barium titanate #;aTi:<& will produce an electric field when the material changes dimensions as a result of an imposed mechanical force. This phenomenon is -nown as the pie8oelectric effect. 7ltrasonic sensors #also -nown as transducers when they both send and receive& wor- on a principle similar to radar or sonar which evaluate attributes of a target by interpreting the echoes from radio or sound waves respectively. 7ltrasonic sensors generate high frequency sound waves and evaluate the echo which is received bac- by the sensor. %ensors calculate the time interval between sending the signal and receiving the echo to determine the distance to an ob,ect. This technology can be used for measuring/ wind speed and direction #anemometer&) fullness of a tan-) and speed through air or water. .or measuring speed or direction a device uses multiple detectors and calculates the speed from the relative distances to particulates in the air or water. To measure the amount of liquid in a tan-) the sensor measures the distance to the surface of the fluid. .urther applications include/ humidifiers) sonar) medical ultrasonography) burglar alarms) and non1destructive testing. ii. =escribe the function of respiratory system with neat diagram.(4'
Respiration refers to the mechanisms for obtaining oxygen from the air and delivering it to the tissues) while eliminating carbon dioxide from the body. 6t is related to cellular respiration) the biochemical processes that consume this oxygen and generate the carbon dioxide in the course of ma-ing adenosine triphosphate #ATP&. Respiration in the former sense involves four processes/ #3& breathing) or ventilation of the lungs # & gas exchange between air and blood in the lungs #<& gas transport in the blood and #>& gas exchange between the blood and target tissues. (espiratory rate ,((- ,a.a respiration rate/ p#lmonary %entilation rate or %entilation rate- is the number of breaths a living being) such as a human) ta-es within a certain amount of time #frequently given in breaths per minute&. The human respiration rate is usually measured when a person is at rest and simply involves counting the number of breaths for one minute by counting how many times the chest rises. Respiration rates may increase with fever) illness) :R other medical conditions. 9hen chec-ing respiration) it is important to also note whether a person has any difficulty breathing. Air enters the nostrils passes through the nasopharyn )
the oral pharyn through the glottis into the trachea into the right and left bronchi) which branches and rebranches into bronchioles) each of which terminates in a cluster of al%eoli ;reathing is controlled by the medulla of the brainstem. 6t repeatedly triggers contraction of the diaphragm initiating inspiration. The rate of breathing changes with activity level in response to carbon dioxide levels) and to a lesser extent) oxygen levels) in the blood. Carbon dioxide lowers the p? of the blood. 5. #a& i. Explain the structure of a $erve Cell with neat diagram.(5'
A nerve is an enclosed) cable1li-e bundle of peripheral axons #the long) slender pro,ections of neurons&. A nerve provides a common pathway for the electrochemical nerve impulses that are transmitted along each of the axons. $erves are found only in the peripheral nervous system. 6n the central nervous system) the analogous structures are -nown as tracts. $eurons are sometimes called nerve cells) though this term is technically inaccurate since many neurons do not form nerves) and nerves also include non1neuronal %chwann cells that coat the axons in myelin. The synapse is the connection between nerve cells #neurons& in animals including humans. The synapse ,oins the axons in one neuron to the dendrites in another. ?ere is a diagram showing how the synapse connects axons to dendrites/ The synapse consists of/ @The presynaptic terminal at the end of an axon. This contains tiny vesicles which contain neurotransmitters 1 the small molecules which carry the nerve impulse from the sending neuron to the receiving neuron. @The synaptic cleft 1 a gap between the two neurons across which the neurotransmitters migrate. @The postsynaptic terminal usually in the dendrites of receiving neurons. This contains receiving sites for the neurotransmitters. $erve impulses are transmitted down to the presynaptic terminal in the axon of one neuron and across the synaptic cleft to the postsynaptic terminal in the dendrite of another neuron. %ynapses do not only ,oin axons to dendrites #axodendritic synapses& 1 they can also ,oins axons to other axons #axoaxonic synapses& or to the soma A the neuronal cell body 1 #axosomatic synapses&. A typical neuron in the central nervous system #C$%& has around 3!!)!!! synapses. The effect of the release of neurotransmitters across the synapse may either be excitory 1 ma-ing the triggering of a nerve impulse #action potential& in the receiving neuron more li-ely 1 or inhibitory 1 ma-ing it less li-ely. An action potential is an on1off event and is always 1BB millivolts 1 there are no grades of nerve impulse. $eurotransmitters) on the other hand) are additive 1 if the net effect of all the excitory neurotransmitters minus all the inhibitory ones achieves this threshold then an action potential will be initiated. ii. Explain the characteristics of resting potential.(4'
The value of the resting potential is maintained as a constant until some -ind of the disturbance will upset the equillibrium. 6t strongly depends on temperature. The range of resting potential is 12! to 13!! m". The resting potential is derived by goldCsman equation.
E Na ) K )Cl =
RT P ( K ' + PNa ( Naout ' + PCl (Clin ' ln K out F PK ( K in ' + PNa ( Nain ' + PCl (Clout '
where P*) P$a) PCl + permeability constants for ma,or ionic species. E$a)*)Cl + equilibrium potential #volts& of the three ma,or ions R + gas constant T + absolute temp in -elvins . + .araday constant "R +152.5m" #b& i. Explain any one application of fibre optic transducer with neat diagram.(5'
a cell.
ii. ;riefly discuss the structure of (4'
C011/ The fundamental unit of every animal or plant is cells. Combination of cells is called T6%%7E%. Every :R0A$ in the body is made up of combination of many tissues. C011S/ All cells are same and they contain a gelatinous substance made up of or composed of water) protein) acids) fats) and various minerals. C011 202+(AN0' Cell membrane protects the cell and surrounds it that passes into and out of the cell. N3C103S/ The nucleus controls the structure of the cell. Cell reproduction process is directed by the nucleus only and which determines the function of the cell and the structure of the cell. C4(525S520S/ These are rod1li-e structures inside the cell. ?uman body cells #other than sex cells) the egg) and sperm cells& contain < pairs of chromosomes. %ex cells) such as sperm and egg cells have < single chromosomes only. 9hen one egg cell unites with a sperm cell to for an embryo) then the embryonic cell has >2 chromosomes i.e. < pairs...understand the difference... Chromosomes contains the regions called 0E$E%. Thousands of genes are in an orderly sequence on each chromosome. 0ene is made up of a chemical substance called =$A #deoxyribonucleic acid&. =$A is an important compound that regulates the activities of the cell in a sequential order on each chromosome. The =$A is a series of codes. 9hen =$A activity carries out of the nucleus to other parts of the cell) the activities of the cell i.e. cellular reproduction and the manufacture of proteins are controlled by =$A. C6)5&1AS2' 6t means cyto means cell) plasm means formation.Cytoplasm carries the wor- of a cell i.e. nerve cell conducts stimulation) muscle cell contracts. Cytoplasm contains D6T:C?:=R6A and E$=:PEA%D6C RET6C7E7D. 27)5C45ND(7A/ 6t is called power center of the cell. This is small and sausage1shaped bodies produce energy by burning food in the presence of oxygen. This process is called catabolism #cata1down) bolto cast) 1ism1process&. This process ma-es complex food particles into simpler substances and energy is released after this action to do the wor- of the cell 0ND5&1AS27C (0)7C3132/ These li-e canal1li-e structures1this is a networ- within the cell. These canals contain a very small structures called R6;:%:DE% li-e a tunnel system in this proteins are produced for the use of the cell. This process is called A$A;:E6%D #ana1up) bolto cast) 1ism1process&. After this process) complex proteins are made up from the simpler parts of food. %maller proteins lin-ed li-e a chain to become complex proteins in this process. ;oth these catabolism and anabolism in combination is called DETA;:E6%D #metachange) bol1to cast) 1ism1 process& i.e total chemical activities that occuring in a cell. 6n this process) the sugars and fat in the food are used up and burned quic-ly and so the E$ER0F is released
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Theory: History of EEGDokument7 SeitenTheory: History of EEGdipakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nervous System Review Answer KeyDokument18 SeitenNervous System Review Answer Keydanieljohnarboleda67% (3)
- Nervous SystemDokument20 SeitenNervous SystemIsheba Warren100% (3)
- Nervous System LectureDokument234 SeitenNervous System Lecturealyssa_marie_keNoch keine Bewertungen
- End Sem Report+ Final1 DocumentsDokument27 SeitenEnd Sem Report+ Final1 Documentsসাতটি তারার তিমিরNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nervous SystemDokument182 SeitenNervous SystemCarlos Enrique Pijo PerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Functions of The Synapses and Neurotransmitters (I) .: Selim Mahmoud Abdel-HakimDokument24 SeitenBasic Functions of The Synapses and Neurotransmitters (I) .: Selim Mahmoud Abdel-HakimAhmed TarekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group 9 Neuron Structure & FunctionDokument14 SeitenGroup 9 Neuron Structure & FunctionMosesNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 BMCDokument18 Seiten5 BMCRPh FarhatainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Units 1,2,3,5 Notes BMIDokument60 SeitenUnits 1,2,3,5 Notes BMITeja ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bmi-2 MarksDokument16 SeitenBmi-2 MarksmohanapriyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- End - Sem - For MergeDokument42 SeitenEnd - Sem - For Mergeমেঘে ঢাকা তারাNoch keine Bewertungen
- Husos de SueñoDokument37 SeitenHusos de SueñoYair FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sensory - Chap1Dokument74 SeitenSensory - Chap1Ahmed khanNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIO 201 Chapter 12, Part 1 LectureDokument35 SeitenBIO 201 Chapter 12, Part 1 LectureDrPearcyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 SynapsesDokument60 Seiten5 Synapsesrosario gonzalezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human Biology 3A/3B Revision.: Homeostasis The Maintenance of A Constant Internal EnvironmentDokument15 SeitenHuman Biology 3A/3B Revision.: Homeostasis The Maintenance of A Constant Internal EnvironmentLizz96Noch keine Bewertungen
- EI2311-Biomedical Instrumentation Question BankDokument20 SeitenEI2311-Biomedical Instrumentation Question BankrajapandiyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NervousDokument13 SeitenNervousJoan GalarceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intro Animal Physiology Ch-2.1Dokument97 SeitenIntro Animal Physiology Ch-2.1Jojo MendozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neurotransmitter, SynapseDokument8 SeitenNeurotransmitter, SynapseAnna Fe VillaverNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell PPT Grade 10 LukeDokument21 SeitenCell PPT Grade 10 LukeJuliusNoch keine Bewertungen
- NeuropsychologyDokument4 SeitenNeuropsychologyBrahmi SathyNoch keine Bewertungen
- TZ Engl363definition s20Dokument6 SeitenTZ Engl363definition s20api-511320115Noch keine Bewertungen
- Control & CoordinationDokument12 SeitenControl & CoordinationRajvir tradaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A12. Nervous SystemDokument184 SeitenA12. Nervous SystemAbdurahman TainyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nerve Muscle PhysioDokument30 SeitenNerve Muscle Physiopatel_hanisha06Noch keine Bewertungen
- Eeg Time Series Data Analysis in Focal Cerebral Ischemic Rat ModelDokument10 SeitenEeg Time Series Data Analysis in Focal Cerebral Ischemic Rat ModelAnonymous UXBSV13cNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ei 65 Unit 1Dokument40 SeitenEi 65 Unit 1Noor AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drugs and The BrainDokument7 SeitenDrugs and The Brainebola123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Notes - Nervous SystemDokument8 SeitenNotes - Nervous Systemdarkadain100% (1)
- Solution Manual For Experience Psychology 2nd Edition by King ISBN 0078035341 780078035340Dokument36 SeitenSolution Manual For Experience Psychology 2nd Edition by King ISBN 0078035341 780078035340jamieharriskmjzepawcq100% (28)
- Neurological SystemDokument21 SeitenNeurological Systemapi-292000448Noch keine Bewertungen
- Coordination and Control (IGCSE and O Level Biology 2023-2025)Dokument65 SeitenCoordination and Control (IGCSE and O Level Biology 2023-2025)Tashwaar TamimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes On THE NERVOUS SYSTEMDokument15 SeitenNotes On THE NERVOUS SYSTEMemanuel coatesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 (Coordination and Response)Dokument8 SeitenChapter 3 (Coordination and Response)Charles RavanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 Neuro PDFDokument16 Seiten10 Neuro PDFKamoKamoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 5 ElectricityDokument39 SeitenCH 5 ElectricityAbdullahi Mohamed IsakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scie6017 - PPT2 - W2 - S2 - R0Dokument45 SeitenScie6017 - PPT2 - W2 - S2 - R0Yudho KusumoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neurobiology IADokument81 SeitenNeurobiology IASıla DenizNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 NeuroDokument16 Seiten10 NeuroAriol ZereNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Marks Q & ADokument11 Seiten2 Marks Q & AJayaprakash JayaramanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch-9 Electricity Within The BodyDokument55 SeitenCh-9 Electricity Within The BodyLindsey AdalsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- PP P PPPPP P P PPPPP PPPPP PP PPDokument23 SeitenPP P PPPPP P P PPPPP PPPPP PP PPRohithGiridharanNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIO 361 Neural Integration LabDokument5 SeitenBIO 361 Neural Integration LabnwandspNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Connecting MechanismDokument11 SeitenThe Connecting MechanismmitxieeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Nervous System and Sense OrgansDokument75 SeitenThe Nervous System and Sense OrgansMik MiczNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laboratory Manual: 19EC3018 Lab Manual - July 2021 Odd SemDokument6 SeitenLaboratory Manual: 19EC3018 Lab Manual - July 2021 Odd SemKiran LsdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neuroglia Functions: Pathogens NeuronsDokument29 SeitenNeuroglia Functions: Pathogens NeuronsSumanta SabaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- In-Class Quiz Review - NeurophysiologyDokument7 SeitenIn-Class Quiz Review - NeurophysiologyWaqas GillNoch keine Bewertungen
- Synapse and Neuronal IntegrationDokument19 SeitenSynapse and Neuronal IntegrationAfif Fadhilah IrsyadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physiology-Introduction To Central Nervous SystemDokument62 SeitenPhysiology-Introduction To Central Nervous SystemAimie DagaleaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gen BioDokument86 SeitenGen BioPaul MagbagoNoch keine Bewertungen
- C-5 Signal TyransmissionDokument14 SeitenC-5 Signal TyransmissionSwad Abdul khalikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bme 1234Dokument40 SeitenBme 1234arunsaktheesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1 BiopsychologyDokument51 SeitenUnit 1 BiopsychologyWriternal CommunityNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and Physiology of NeuronsDokument4 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology of NeuronsVan Jasper Pimentel BautistaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bioactivity study of modified curcumin loaded polymeric nanoparticlesVon EverandBioactivity study of modified curcumin loaded polymeric nanoparticlesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design Development and Analysis of a Nerve Conduction Study System An Auto Controlled Biofeedback ApproachVon EverandDesign Development and Analysis of a Nerve Conduction Study System An Auto Controlled Biofeedback ApproachNoch keine Bewertungen
- Excitable Cells: Monographs in Modern Biology for Upper School and University CoursesVon EverandExcitable Cells: Monographs in Modern Biology for Upper School and University CoursesNoch keine Bewertungen
- B Iii: A G R F M R B B S: Common Shares Issued by The BankDokument6 SeitenB Iii: A G R F M R B B S: Common Shares Issued by The BankArun PrakashNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8 Ways To Boost Your ImmunityDokument13 Seiten8 Ways To Boost Your ImmunityvadlamudibiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Income Tax Circular-F.y 2018-19Dokument12 SeitenIncome Tax Circular-F.y 2018-19jamesapjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exam Frequently Asked QuestionsDokument3 SeitenExam Frequently Asked QuestionsArun PrakashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basel IIIDokument14 SeitenBasel IIIarunapecNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exam Frequently Asked QuestionsDokument3 SeitenExam Frequently Asked QuestionsArun PrakashNoch keine Bewertungen
- What NextDokument10 SeitenWhat NextbalajiNoch keine Bewertungen
- RECALLED QUESTIONS (2016-18) : (Ibps Different Banks Promotion Test)Dokument11 SeitenRECALLED QUESTIONS (2016-18) : (Ibps Different Banks Promotion Test)Arun PrakashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Achieve All Your Short Term Goals PDFDokument9 SeitenAchieve All Your Short Term Goals PDFkaran patelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shine at Your Workplace PDFDokument8 SeitenShine at Your Workplace PDFRavi KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- What NextDokument10 SeitenWhat NextbalajiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Mathematics Linear Algebra: Matrix Algebra, SystemsDokument2 SeitenEngineering Mathematics Linear Algebra: Matrix Algebra, Systemshemanthmahesh194729Noch keine Bewertungen
- What NextDokument10 SeitenWhat NextbalajiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Achieve All Your Long Term GoalsDokument17 SeitenAchieve All Your Long Term GoalsArun PrakashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simplification 2.text - MarkedDokument10 SeitenSimplification 2.text - MarkedArun PrakashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tangedco - Direct Recruitment 2015-2016Dokument1 SeiteTangedco - Direct Recruitment 2015-2016Arun PrakashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Achieve All Your Long Term Goals PDFDokument7 SeitenAchieve All Your Long Term Goals PDFArun PrakashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital CircuitDokument3 SeitenDigital CircuitArun PrakashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson-17:: Memory Organisation, and Types of MemoryDokument35 SeitenLesson-17:: Memory Organisation, and Types of Memoryrahulbiswas14789Noch keine Bewertungen
- Addressing ModeDokument5 SeitenAddressing ModeArun PrakashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Money MarketDokument1 SeiteMoney MarketArun PrakashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Baning Awareness Quiz Fo..Dokument14 SeitenBaning Awareness Quiz Fo..Arun PrakashNoch keine Bewertungen
- IBPS General AwarenessDokument1 SeiteIBPS General AwarenessArun PrakashNoch keine Bewertungen
- (216210835) Power - System - Analysis - System 2 Mark NamakkalDokument35 Seiten(216210835) Power - System - Analysis - System 2 Mark NamakkalArun PrakashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Mathematics Linear Algebra: Matrix Algebra, SystemsDokument2 SeitenEngineering Mathematics Linear Algebra: Matrix Algebra, Systemshemanthmahesh194729Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hindustan Aeronautics Limited - ScheduleDokument1 SeiteHindustan Aeronautics Limited - ScheduleArun PrakashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ec 2006Dokument29 SeitenEc 2006Arpit JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- WJR - Walajah Road Junction (2) Railway Station - Today's Train Arrival Timings - India Rail Info - A Busy Junction For Travellers & Rail EnthusiastsDokument2 SeitenWJR - Walajah Road Junction (2) Railway Station - Today's Train Arrival Timings - India Rail Info - A Busy Junction For Travellers & Rail EnthusiastsArun PrakashNoch keine Bewertungen
- University: (Karunya Institute of Technology & Sciences)Dokument5 SeitenUniversity: (Karunya Institute of Technology & Sciences)Arun PrakashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Idioms and Phrases For Banking ExamsDokument3 SeitenIdioms and Phrases For Banking ExamsShiv Ram Krishna100% (7)
- Seeley's Chapter 8 Nervous SystemDokument100 SeitenSeeley's Chapter 8 Nervous SystemChristine Tapawan88% (8)
- The Effect of Nacl 0.9% and Nacl 0.45% On Sodium, Chloride, and Acid - Base Balance in A Picu PopulationDokument7 SeitenThe Effect of Nacl 0.9% and Nacl 0.45% On Sodium, Chloride, and Acid - Base Balance in A Picu Populationzack dahlanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Renal Physiology PDFDokument12 SeitenRenal Physiology PDFLolitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Voicedisordersinthe Elderly: Karen M. Kost,, Robert T. SataloffDokument13 SeitenVoicedisordersinthe Elderly: Karen M. Kost,, Robert T. SataloffFernanda MerichesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Survival at Sea For Mariners, Aviators PDFDokument178 SeitenSurvival at Sea For Mariners, Aviators PDFTrịnh Minh Khoa100% (1)
- The Effects of High-Velocity, Low-Amplitude Manipulation and Muscle Energy Technique On Suboccipital TendernessDokument8 SeitenThe Effects of High-Velocity, Low-Amplitude Manipulation and Muscle Energy Technique On Suboccipital TendernessFlávio GuimarãesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Developmentofteeth StagesDokument45 SeitenDevelopmentofteeth Stagesimi4100% (1)
- Dr. Lakshmi Kiruba N Assistant Professor Department of Anatomy SmbtimsrcDokument25 SeitenDr. Lakshmi Kiruba N Assistant Professor Department of Anatomy Smbtimsrclakshmi kirubaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aki 2018Dokument45 SeitenAki 2018NURUL ROMADHONNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Membrane Structure and FunctionDokument10 SeitenCell Membrane Structure and FunctionkyleeebooggNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Effects of Tissue Flossing On Ankle Range of Motion and Tensiomyography Parameter - Matjaz Vogrin 2021Dokument8 SeitenAcute Effects of Tissue Flossing On Ankle Range of Motion and Tensiomyography Parameter - Matjaz Vogrin 2021YngaMarquezJairNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kreisberg-Zakarin Et Al IPNS Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 1999Dokument8 SeitenKreisberg-Zakarin Et Al IPNS Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 1999ElNoch keine Bewertungen
- Excretory ReviewDokument2 SeitenExcretory Reviewapi-240662720Noch keine Bewertungen
- Raddaily Ankle MRI ApproachDokument10 SeitenRaddaily Ankle MRI ApproachSandeep VodelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mumbai AyurvedaDokument2 SeitenMumbai AyurvedaAditya SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- 24 Cerebral Blood FlowDokument31 Seiten24 Cerebral Blood FlowZuhaib Ahmed100% (1)
- How Does Exercise Affect Heart Rate Alvin PDFDokument13 SeitenHow Does Exercise Affect Heart Rate Alvin PDFapi-134712575Noch keine Bewertungen
- Abbot, Diabetes ManagementDokument1 SeiteAbbot, Diabetes ManagementMelissa Grace DizonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nano DentistryDokument6 SeitenNano DentistryanugrasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neurovascular Holding PointsDokument8 SeitenNeurovascular Holding PointsAlexandru Baciu100% (1)
- Mitsunori M, Kagayaki K, Satoshi Y, Akihiro H, Naokazu H, Ken T, Hideki A, and Takatoshi SDokument14 SeitenMitsunori M, Kagayaki K, Satoshi Y, Akihiro H, Naokazu H, Ken T, Hideki A, and Takatoshi SJasper CubiasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bielenda Professional Catalogue enDokument88 SeitenBielenda Professional Catalogue enBielendaProfessionalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rula SheetDokument2 SeitenRula SheetCarl Christian CabelloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prinsip Penyusunan Gigi Artifisial Kelompok 7Dokument53 SeitenPrinsip Penyusunan Gigi Artifisial Kelompok 7gilangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Botulinum Toxins in Clinical Aesthetic Practice 3rd Edition Volume Two - Functional Anatomy and Injection Techniques 2018Dokument237 SeitenBotulinum Toxins in Clinical Aesthetic Practice 3rd Edition Volume Two - Functional Anatomy and Injection Techniques 2018Dogukan Demir75% (4)
- Haemoptysis Diagnosis and TreatmentDokument57 SeitenHaemoptysis Diagnosis and TreatmentMuhammad Cholid AlfahroziNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kingdom Animalia Pactical 1Dokument5 SeitenKingdom Animalia Pactical 1Alexson UndiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 5.: Facultad de Medicina Humana "Daniel Alcides Carrión Garcia"Dokument12 SeitenUnit 5.: Facultad de Medicina Humana "Daniel Alcides Carrión Garcia"MARCOABADNoch keine Bewertungen
- Voice Disorder 2011 PDFDokument6 SeitenVoice Disorder 2011 PDFfaidgustisyarifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dr. Vijetha Shenoy Belle Associate Professor & In-Charge Clinical Biochemistry Laboratory Department of Biochemistry KMC ManipalDokument53 SeitenDr. Vijetha Shenoy Belle Associate Professor & In-Charge Clinical Biochemistry Laboratory Department of Biochemistry KMC ManipalKavya GaneshNoch keine Bewertungen