Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
FICO Interview Questions Set 14
Hochgeladen von
vanam1409Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
FICO Interview Questions Set 14
Hochgeladen von
vanam1409Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
ACADEMY: FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING FI PAPER 14
1. Benefits of integration are a. processes can be done concurrently, rather than consecutively. This reduces process time b. data moves through internet platform and access becomes faster c. eliminates duplicate entries d. single entry accounting becomes easier 2. R/3 a. b. c. is called so because it requires three servers it integrates three basic modules, vi ., !", logistics and #R it has three tier architecture representing database, application and front end presentation d. it has three tier architecture representing $%", B&'" and R(!
3. application modules supported by R/3 include a. !", (), TR, *+,,,, '', ',,-,,#R,'*,.!,"* b. !",(),TR,*+,,,,'',',,-,,#R,'*,.!,"*,/( c. !",(),TR,*+,,,,'',',,-,,#R,'*,.!,"*,/(,(('(,(''& d. !",(),TR,*+,,,,'',',,-,,#R 0. "n standard business process of a manufacturing organi ation a sales order 1ould trigger in another application a. ,'* b. ,R' c. 'urchase requisition d. $oods delivery 2. ,ain components of !" are a. $3,&R,&&,3(,TR b. $3,&R,&',&&,TR c. $3,&R,&',&&,3(,TR,(, d. $3,&R,&',&&,3(,TR,T, 4. ,ain components of () are a. ()),,()'(,()'&,/('(&,()T, b. ()),,()'(,()'&,/('(&,()((& c. ()),,()'(,()'& d. ()),,()'(,()'&,/('(& 5. The sequence of business processes 6related to ra1 material for production7 in ,, can be described are a. 'R8,R'8$R,"9:)"(/ b. 'R8')8$R8"9:)"(/ :/R"!"(&T")9 c. 'R8')8$R8"9:)"(/ :/R"!"(&T")98:/9+)R '&;,/9T d. 'R8')8$R8"9:)"(/ :/R"!"(&T")98R/(/"'T )! +"*()%9T !R), :/9+)R <. "t is a must to create group company before any transaction processing a. completely true b. partially true c. completely false d. partially false =. it is a must to create company code before any transaction processing a. completely true
ACADEMY: FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING FI PAPER 14 b. partially true c. completely false d. partially false 1>. business area is a legal entity for 1hich you need a balance sheet a. completely true b. partially true c. completely false d. partially false 11. client is the highest level organi ation a. completely true b. partially true c. completely false d. partially false 12. many company codes can be attached to one plant a. completely true b. partially true c. completely false d. partially false 13. many company codes can be assigned to one controlling area a. completely true b. partially true c. completely false d. partially false 10. operating concern can encompass several controlling areas a. completely true b. partially true c. completely false d. partially false 12. credit control area is a concept in () a. completely true b. partially true c. completely false d. partially false 14. master data is created 1ith the help of ",$ a. completely true b. partially true c. completely false d. partially false 15. transaction data is core information that is shared across applications a. completely true b. partially true c. completely false d. partially false 1<. the user specific defaults are possible if setting is done in a. user profile b. company code parameters c. session managers
ACADEMY: FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING FI PAPER 14 d. terminal 1=. customi ed report trees are created through a. transaction menu of information system b. master creation of reports c. ",$ d. *tandard report functionality 2>. :ariant creation helps in a. calculating variance bet1een actual and standard b. processing repetitive transactions c. to coy repetitive field values in master creation d. to be a standardi ed selection criteria for repetitive use required to run program 21. credit control area may consist of one or more company codes a. completely true b. partially true c. completely false d. partially false 22. credit control area is used a. by the *+ and &R components to provide integrated credit management b. by !"/&' to prove credit 1orthiness to vendors c. independently by !" to monitor customer credit d. independently by *+ to monitor customer credit 23. a company code can be assigned 1ith a. three chart of accounts b. t1o charts of accounts c. only one chart of account d. a chart of account called as operating chart of account 20. association bet1een numbers from group chart of account and/or country/alternate chart of account can be established in a. company code global parameters b. master data of ledger account from operating chart of account c. group company details d. country details 22. account groups 1hich are assigned in account master creation helps a. to determine 1hich fields should be suppressed, required or optional 1hile processing transaction b. to determine 1hich fields should be suppressed, required or optional 1hile creating master in company code area c. to determine 1hich fields should be suppressed, required or optional 1hile processing transactions and master both d. in grouping the accounts 1ith specific logic and assign specific number interval 24. there are t1o areas8chart of account and company code8in 1hich $/3 account master has to b e created because a. data can be distributed and easy to process b. the same chart of account can be assigned to several company codes c. the company specific features can be maintained in company code areas
ACADEMY: FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING FI PAPER 14 d. creation of $/3 can be done in t1o stages 25. house ban?s are ban?s a. 1hich are used by the company code in 1hich they are created b. 1hich are used by customers/vendors c. located in the same building 1here company is located d. 1hich are nationali ed 2<. primary cost element is related to a. $/3 account code in one to one relationship b. $/3 account code in one to many relationship c. *everal secondary cost elements to group them d. "nternal order 2=. "t is a must to assign a standard hierarchy in cost center master a. completely true b. partially true c. completely false d. partially false 3>. statistical order permits a. settlement to cost center b. application of overhead to them c. evaluation of costs 1hich cannot be itemi ed in detail cost element or cost center accounting d. costing of product 31. for a. b. c. d. every transaction, system generates at least 0 documents 3 documents 2 documents 1 document
32. transactions 1hich have a financial impact generate along 1ith other documents a. material document b. *+ document c. *ystem document d. &ccounting document 33. 'urchase order creation is an e@ample of transaction a. 1hich also triggers accounting document b. 1hich does not create any accounting document c. 1hich creates document in *+ d. 1hich triggers document in '' 30. document has the follo1ing sections a. title and details b. open item and line items c. header and line items d. coding bloc? and line items 32. document type is assigned in the line item section of document a. true b. false 34. document type allo1s more than one account types 1hile processing the particular document type
ACADEMY: FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING FI PAPER 14 a. true b. false 35. number range id is assigned in a. account type b. document type c. document header d. document line item 3<. follo1ing are the account types a. &,+,A,,,* b. &,+,A,,,*,B,* c. &,+,A,,,*,T d. &,+,A,,,*,',3 3=. 9umber range can be defined as a. only internally system generated b. only e@ternally assigned by user c. either e@ternally or internally d. both e@ternally and internally at the same time 0>. posting ?eys determine a. account groups to 1hich account numbers belong b. debit/credit, account type and field status of the transaction c. debit/credit, account type, account group and field status of the transaction d. document type, account type and field status of the transaction 01. the relationship bet1een calendar months and posting period is defined in the properties of a. posting period variant b. field status variant c. fiscal year variant d. global parameters of company code 02. only one company code can be attached to a posting period variant a. true b. false 03 fiscal year can have a. ma@imum 12 regular posting periods and 0 special periods b. any number of posting periods c. 14 regular periods d. 14 special periods
00 account type essentially controls a. account group 1hich can be assigned to the account code b. 1hich account8$/3, customer, vendor, material, or asset can be used in a line item of transaction posting c. tolerance level of the accounts involved d. document type 1hich can be used
ACADEMY: FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING FI PAPER 14 02 account group in the conte@t of $/3 account determines status of fields in a. transaction b. chart of account segment of master data c. company code segment of master data d. none of the above 04 field status variant and posting ?ey both determine field status in a. chart of account segment of master data b. company code segment of master data c. document type d. none of the above 05 negative postings cause transaction figures of the account a. changed b. unchanged c. double d. none of the above 0< for a. b. c. negative posting, negative posting indicator needs to be chec?ed only in document type only in company code global parameters and reason code properties only in document type, company code global parameters and reason code parameters d. none of the above
0= follo1ing and the !" functionality offered for speedy posting a. posting 1ith reference, recurring entries, account assignment models, $/3 fast entry screens b. only $/3 fast entry screens c. only recurring entries d. none of the above 2>terms of payment can be assigned to a. $/3 master b. (ustomer or vendor master c. Transaction processing for customer/vendor d. 9one of the above 21 Base line date is a. a date on 1hich payment becomes due b. from 1hich due date is calculated depending on the settings in payment terms c. a base date after 1hich discount lapses d. none of the above
22 due date and cash discounts are dependent on a. settings in company code b. credit management settings c. payment term d. payment method 23 currency assigned in company code master is a. transaction currency b. group currency c. hard currency
ACADEMY: FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING FI PAPER 14 d. local currency 20 validations are used a. to substitute values in fields b. to support data entry c. to validate the data being entered is meeting certain criteria 1hen certain prerequisites are met d. none of the above 22 par?ing of document is a functionality a. 1hich can be used to complete and post subsequently the documents 1hich are incomplete b. to hold the document for the ne1 session c. to process documents faster d. none of the above 24 dunning process is used a. to generate payments b. to remind customer/vendor of account arrears c. to remit the payments d. none of the above 25 opening and closing of posting period is done a. customi ation of fiscal year b. customi ation related to opening and closing of posting period c. definition of posting period variant d. none of the above 2< updating of reconciliation account a. happens on a daily basis b. is real time update c. happens after the end of the posting period d. none of the above 2= customer and vendor master can b e maintained a. only in !" b. only in *+/,, c. centrally as 1ell as in respective functional areas d. none of the above 4>customer master is divided into a. t1o sections8company code and sales area b. three sections8general data, company code and sales organi ation c. four sections8general data, company code, salas organi ation and production d. none of the above 41 function of tolerance group is a. is to set tolerance level for foreign e@change b. is to define user groups 1ith different amount limits for documents and line items c. grouping tolerance levels of specific nature d. none of the above 42 posting ?eys are defined at a. business area level b. company code level
ACADEMY: FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING FI PAPER 14 c. client level d. none of the above 43 every company code must have its o1n document type a. true b. false 40 the a. b. c. d. standard posting ?eys used for $/3 posting are 0>, 2> 1=, 2>and 0> 2>, 3= none of the above
42 in case of cross company code transactions a. one has to post t1o documents individually b. posts a document in one company and system generates another document in concerned company 1ith common lin? of cross company code transaction number c. system lin?s documents based on user given number in cross company code transaction field d. none of the above
ACADEMY: FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING FI PAPER 14
KEY 1. &,( 2. ( 3. + 0. B 2. ( 4. & 5. B <. ( =. & 1>. ( 11. & 12. ( 13. & 10. & 12. .. 14. & 15. ( 1<. & 1=. .. 2>. B 21. & 22. & 23. &,B,(,+ 20. B 22. B,+ 24. &,B,+ 25. & 2<. & 2=. & 3>. .. 31. + 32. + 33. B,+ 30. ( 32. B 34. & 35. B 3<. & 3=. ( 0>. B 01. &,( 02. B 03. & 00. B 02. ( 04. ( 05. & 0<. ( 0=. & 2>. B,( 21. B 22. (
ACADEMY: FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING FI PAPER 14 23. + 20. ( 22. & 24. B 25. B 2<. B 2=. ( 4>. B 41. B, ( 42. ( 43. B 40. & 42. B
10
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Entrepreneur’S Dictionary of Business and Financial TermsVon EverandThe Entrepreneur’S Dictionary of Business and Financial TermsNoch keine Bewertungen
- FICO Interview Questions Set 1Dokument5 SeitenFICO Interview Questions Set 1Jai Kiran VasistaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SAP TFIN52 64 Practice Exercises Self Review #2 PDFDokument4 SeitenSAP TFIN52 64 Practice Exercises Self Review #2 PDFAllen WsyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Academy: Managerial and Financial Accounting Fi Paper: 1Dokument5 SeitenAcademy: Managerial and Financial Accounting Fi Paper: 1user_descargaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCCC CCC CC C !"# $#$ !%"Dokument11 SeitenCCCC CCC CC C !"# $#$ !%"Archit MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sap MCQDokument12 SeitenSap MCQSharanyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sap Fi Paper 02Dokument4 SeitenSap Fi Paper 02baburam100% (1)
- Sap Fico Certification Questions and Answers 1Dokument22 SeitenSap Fico Certification Questions and Answers 1Prakash WaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sap Resumen 1Dokument16 SeitenSap Resumen 1hfiehfhejfhneifNoch keine Bewertungen
- SAP FI/CO Interview and Certification Questions - Part 1Dokument13 SeitenSAP FI/CO Interview and Certification Questions - Part 1sudheerfriendNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dokumen - Tips - Latihan Soal Sap Finance Lengkap Ada JawabanDokument6 SeitenDokumen - Tips - Latihan Soal Sap Finance Lengkap Ada Jawabanurbae chaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sap Fi Paper 04Dokument6 SeitenSap Fi Paper 04baburam100% (1)
- Managerial and Financial Accounting Q & A # 1Dokument7 SeitenManagerial and Financial Accounting Q & A # 1Bijon Kumarr DuttaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PDF Contoh Soal Sap 010 Financial Accounting Batch 1amp2 CompressDokument19 SeitenPDF Contoh Soal Sap 010 Financial Accounting Batch 1amp2 CompressIrvanNoch keine Bewertungen
- FIDokument17 SeitenFIChirag SolankiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sap Fico - Sample Questions and AnswersDokument9 SeitenSap Fico - Sample Questions and AnswersAJNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sap Fi Paper 15Dokument31 SeitenSap Fi Paper 15baburam100% (5)
- Latihan Soal Sap Finance Lengkap BLM Ada Jawaban (45 Soal)Dokument6 SeitenLatihan Soal Sap Finance Lengkap BLM Ada Jawaban (45 Soal)Mersa NovantyNoch keine Bewertungen
- FICO Interview QuestionsDokument177 SeitenFICO Interview QuestionsNagaratna ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- FICO Interview Questions Set 3Dokument4 SeitenFICO Interview Questions Set 3sachinvernekarNoch keine Bewertungen
- SAP QuestionsDokument14 SeitenSAP QuestionsGulshan PTNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multiple ChoiceDokument4 SeitenMultiple ChoiceAriston B. Manansala Jr.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment (IS-Utilities) : Questions: 50 Time Limit: 60 MinsDokument9 SeitenAssessment (IS-Utilities) : Questions: 50 Time Limit: 60 MinsNeeraj GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- C TS4FI 1909 Final 2 QuestionDokument20 SeitenC TS4FI 1909 Final 2 QuestionOriol CasesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kuis - AKDokument8 SeitenKuis - AKElaineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Contoh Soal SAP 010 - Financial Accounting (Batch 1&2)Dokument19 SeitenContoh Soal SAP 010 - Financial Accounting (Batch 1&2)Jhoni100% (3)
- SAP FICO Certification Questions and AnswersDokument3 SeitenSAP FICO Certification Questions and Answersvanam140973Noch keine Bewertungen
- B) Depreciation Data Section C) Master Data SectionDokument10 SeitenB) Depreciation Data Section C) Master Data Sectionzulkhairahmi amiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Academy: Managerial and Financial Accounting Fi Paper: 8Dokument4 SeitenAcademy: Managerial and Financial Accounting Fi Paper: 8baburamNoch keine Bewertungen
- C Ts4fi 2020Dokument27 SeitenC Ts4fi 2020nageswara kuchipudi100% (2)
- C Ts4fi 1909Dokument26 SeitenC Ts4fi 1909Oriol CasesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ctfin 5066Dokument5 SeitenCtfin 5066hfiehfhejfhneifNoch keine Bewertungen
- AIS101 - Midterm ExaminationDokument11 SeitenAIS101 - Midterm ExaminationGhiann TolibatNoch keine Bewertungen
- SAP FICO Certification Test 6Dokument18 SeitenSAP FICO Certification Test 6arfaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soal Sapac010Dokument7 SeitenSoal Sapac010ulfanysmn100% (2)
- AIS ReviewerDokument7 SeitenAIS ReviewerLeah May M. FamorNoch keine Bewertungen
- AP CertifDokument28 SeitenAP CertifShakhir MohunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soal Sapac010 PDFDokument7 SeitenSoal Sapac010 PDFEnzlika MirandhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management Advisory Services - PreboardDokument13 SeitenManagement Advisory Services - PreboardAngelica Estrada100% (4)
- Kisi 4Dokument30 SeitenKisi 4Kelvin JunusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alliance - SAP B1 ExamDokument8 SeitenAlliance - SAP B1 ExamTrisha VillarealNoch keine Bewertungen
- SAP FI ECC 6 - Week1 Coll92Dokument13 SeitenSAP FI ECC 6 - Week1 Coll92senthilhappyNoch keine Bewertungen
- SAP - AR Answers V1Dokument6 SeitenSAP - AR Answers V1vbkishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soal Ujian KompreDokument26 SeitenSoal Ujian KompreVania Dewi UtamiNoch keine Bewertungen
- LaluGdeMuhammadFarizt - UTS Impl Sistem Ent 2Dokument3 SeitenLaluGdeMuhammadFarizt - UTS Impl Sistem Ent 2lalu gdeNoch keine Bewertungen
- (PDF) Latihan Soal Sap Finance Lengkap Ada JawabanDokument6 Seiten(PDF) Latihan Soal Sap Finance Lengkap Ada JawabanRoftadiaWgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practical C++20 Financial Programming: Problem Solving for Quantitative Finance, Financial Engineering, Business, and EconomicsVon EverandPractical C++20 Financial Programming: Problem Solving for Quantitative Finance, Financial Engineering, Business, and EconomicsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Official Guide to Financial Accounting using TallyPrime: Managing your Business Just Got SimplerVon EverandOfficial Guide to Financial Accounting using TallyPrime: Managing your Business Just Got SimplerNoch keine Bewertungen
- How to Estimate with RSMeans Data: Basic Skills for Building ConstructionVon EverandHow to Estimate with RSMeans Data: Basic Skills for Building ConstructionBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (2)
- Small Business Accounting Guide to QuickBooks Online: A QuickBooks Online Cheat Sheet for Small Businesses, Churches, and NonprofitsVon EverandSmall Business Accounting Guide to QuickBooks Online: A QuickBooks Online Cheat Sheet for Small Businesses, Churches, and NonprofitsNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Comparative Analysis of Tax Administration in Asia and the Pacific: Fifth EditionVon EverandA Comparative Analysis of Tax Administration in Asia and the Pacific: Fifth EditionNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Beginners Guide to QuickBooks Online: The Quick Reference Guide for Nonprofits and Small BusinessesVon EverandA Beginners Guide to QuickBooks Online: The Quick Reference Guide for Nonprofits and Small BusinessesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wiley CMAexcel Learning System Exam Review 2017: Part 2, Financial Decision Making (1-year access)Von EverandWiley CMAexcel Learning System Exam Review 2017: Part 2, Financial Decision Making (1-year access)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Adjusting EntriesDokument11 SeitenAdjusting EntriesShruti SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- LSMW ExercisesDokument6 SeitenLSMW ExercisesJibu JoseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Product Costing PowerPointDokument20 SeitenProduct Costing PowerPointPrincessFabulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parallel Accounting in New General LedgerDokument7 SeitenParallel Accounting in New General Ledgerfylee74100% (1)
- Adjusting EntriesDokument11 SeitenAdjusting EntriesShruti SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- LSMW Ned Internal OrderDokument6 SeitenLSMW Ned Internal Ordervanam1409Noch keine Bewertungen
- LSMW Ned CcuploadDokument7 SeitenLSMW Ned Ccuploadvanam1409Noch keine Bewertungen
- Parallel Accounting in New General LedgerDokument7 SeitenParallel Accounting in New General Ledgerfylee74100% (1)
- CK11NDokument11 SeitenCK11Nvanam1409Noch keine Bewertungen
- RAJA RAO-DEVOTEE OF HINDU PHILOSOPHY - A STUDY (With Special Reference To On The Ganga Ghat, The Cat PDFDokument9 SeitenRAJA RAO-DEVOTEE OF HINDU PHILOSOPHY - A STUDY (With Special Reference To On The Ganga Ghat, The Cat PDFvanam1409Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bank AccountingDokument25 SeitenBank Accountingvanam1409Noch keine Bewertungen
- I50011 CMRDokument6 SeitenI50011 CMRvanam1409Noch keine Bewertungen
- I50011 E.SDokument11 SeitenI50011 E.Svanam1409Noch keine Bewertungen
- FICO Interview Questions Set 13Dokument7 SeitenFICO Interview Questions Set 13vanam1409Noch keine Bewertungen
- I50011 BPDokument7 SeitenI50011 BPvanam1409Noch keine Bewertungen
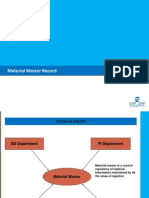
- I50011 MMRDokument8 SeitenI50011 MMRvanam1409Noch keine Bewertungen
- FICO Interview Questions Set 4Dokument6 SeitenFICO Interview Questions Set 4vanam1409Noch keine Bewertungen
- SAP Lan ScapeDokument2 SeitenSAP Lan Scapevanam1409Noch keine Bewertungen
- FICO Interview Questions Set 3Dokument4 SeitenFICO Interview Questions Set 3vanam1409Noch keine Bewertungen
- FICO Interview Questions Set 15Dokument31 SeitenFICO Interview Questions Set 15vanam1409Noch keine Bewertungen
- Product CostingDokument9 SeitenProduct Costingvanam1409Noch keine Bewertungen
- SAP FI Bank ConfigurationDokument68 SeitenSAP FI Bank Configurationhassan sabry92% (25)
- Elevator Controler Part 3 TKDokument15 SeitenElevator Controler Part 3 TKalfreliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Controller Option (M416) PC 120912Dokument8 SeitenController Option (M416) PC 120912Dawood AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 4's & Mind 5's Sheet3Dokument2 Seiten4 4's & Mind 5's Sheet3Lisa BejaranoNoch keine Bewertungen
- PRO8432 - Service Manual - R4Dokument143 SeitenPRO8432 - Service Manual - R4Larry Linch100% (1)
- 9010 9020 9020 4 LCD Data SheetDokument8 Seiten9010 9020 9020 4 LCD Data SheetBD MNNoch keine Bewertungen
- A6V10452678Dokument7 SeitenA6V10452678ABI RAJESH GANESHA RAJANoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is A WebsiteDokument9 SeitenWhat Is A WebsitemullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 Multiview DrawingsDokument85 SeitenChapter 2 Multiview DrawingsBereket KebedeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kotlin in Action - FunctionalDokument5 SeitenKotlin in Action - FunctionaljobaxyraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seminar On Airborne Internet: Submitted To Submitted byDokument22 SeitenSeminar On Airborne Internet: Submitted To Submitted byKranthi VenkatNoch keine Bewertungen
- OptimizerDokument593 SeitenOptimizerYeimmy Julieth Cardenas MillanNoch keine Bewertungen
- PS3 Slim PRAM Battery ReplacementDokument10 SeitenPS3 Slim PRAM Battery ReplacementJC PSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Google Authenticator As An Information SystemDokument6 SeitenGoogle Authenticator As An Information Systemapi-487349631Noch keine Bewertungen
- WMF3 0 RC Release NotesDokument18 SeitenWMF3 0 RC Release NotesTI09Noch keine Bewertungen
- Radar System Project ReportDokument38 SeitenRadar System Project ReportFaisal KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Social: 100 Best Free SEO ToolsDokument10 SeitenSocial: 100 Best Free SEO ToolsAhmed KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
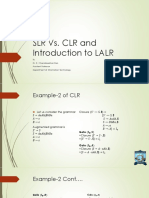
- SLR Vs CLR and LALRDokument14 SeitenSLR Vs CLR and LALRSmart BoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronic Transaction Act 2063: NITC/Ministry of Environment, Science and Technology)Dokument29 SeitenElectronic Transaction Act 2063: NITC/Ministry of Environment, Science and Technology)setup vpnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phantasm Digital Imaging and The Death of PhotographyDokument6 SeitenPhantasm Digital Imaging and The Death of Photographyteddy2689Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bhoite Shreyas Shekhar - Marketing Assignment - ITHDokument10 SeitenBhoite Shreyas Shekhar - Marketing Assignment - ITHshreyasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Plan, Test Cases.....Dokument10 SeitenTest Plan, Test Cases.....Asim JavedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Workflow - GEOPAK - 2 - Digital Terrain Model AnalysisDokument6 SeitenWorkflow - GEOPAK - 2 - Digital Terrain Model AnalysisdumitruusNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6689-Article Text-24334-1-10-20230730Dokument13 Seiten6689-Article Text-24334-1-10-20230730mei chee punNoch keine Bewertungen
- Attendance CAAT ProceduresDokument9 SeitenAttendance CAAT ProceduresMyles OlanNoch keine Bewertungen
- BGC Trust University Bangladesh: Presentation OnDokument12 SeitenBGC Trust University Bangladesh: Presentation OnRubel RudraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Google: Tab 01 XDokument10 SeitenGoogle: Tab 01 Xcyana andresNoch keine Bewertungen
- G.O. RCS Circular 2012Dokument146 SeitenG.O. RCS Circular 2012Arun MohanNoch keine Bewertungen
- DreamHome Case StudyDokument27 SeitenDreamHome Case StudyDoolah MargNoch keine Bewertungen
- Corona Lecture1Dokument26 SeitenCorona Lecture1Nana MagdyNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Influence of Online Applications and Social Media On The Learning Behavior of Grade 10 Students at Ocampo National High School S.Y. 2021 2022Dokument30 SeitenThe Influence of Online Applications and Social Media On The Learning Behavior of Grade 10 Students at Ocampo National High School S.Y. 2021 2022EARL ANDREW PAUSANOS100% (1)