Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Buckling: ST Al Y ST Y Al
Hochgeladen von
marknassefOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Buckling: ST Al Y ST Y Al
Hochgeladen von
marknassefCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Cairo University Faculty of Engineering Dept.
of Mechanical Design and Production Second Year Mechanical
uc!ling of Columns
First Semester Structural Mechanics Sheet "
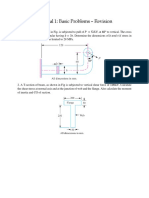
#. $ column of effective length % can &e made &y securely nailing together three identical 'ooden &lan!s in each of the arrangements sho'n. For the thic!ness of plan!s to &e identical( determine the ratio of the critical load using arrangement )a* to the critical load using arrangement )&*.
+. $ column of ".,-m effective length is made &y securely nailing together four 'ooden plan!s of "./#+.-mm cross section. Using E 0 #+., 1Pa( determine the critical load 'hen the plan!s are nailed together in each of the arrangements sho'n.
". 2he distri&uted loading is supported &y t'o pin-connected columns( each having a solid circular cross section. 3f $ is made of aluminum and CD of steel( determine the re4uired diameter of each column so that &oth 'ill &e on the verge of &uc!ling at the same time. Est 0 +.. 1Pa( Eal 0 5. 1Pa( )6Y*st 0 +,. MPa( and )6Y*al 0 #.. MPa.
7. 2he truss is made from steel &ars8 each has a circular cross section. 3f the applied load P 0 #. !9( determine the diameter of mem&er $ that 'ill prevent this mem&er from &uc!ling and yielding. 2he mem&ers are pin supported at their ends. )E 0 +.. 1Pa and 6Y 0 +,. MPa*.
,. :no'ing that a factor of safety of +.; is re4uired( determine the largest load P that can &e applied to the structure sho'n. Use E 0 +.. 1Pa and consider only &uc!ling in the plane of the structure.
;.
:no'ing that a factor of safety of " is re4uired( determine the largest load P 'hich may &e applied to the structure sho'n. Use E 0 +.. 1Pa and consider only &uc!ling in the plane of the structure.
5.
2he uniform aluminum &ar $ has a #;/".-mm rectangular cross section and is supported &y pins and &rac!ets as sho'n. Each end of the &ar may rotate freely a&out a hori<ontal a/is through the pin( &ut rotation a&out vertical a/is is prevented &y the &rac!ets. Using E 0 5. 1Pa )a* determine the length % for 'hich the critical load of the &ar is Pcr 0 #. !9. )&* if % 0 #.+ m determine the allo'a&le centric load P if a factor of safety of +.= is re4uired.
=. 2he >i& crane sho'n in the figure is of capacity ?0 +. !9. For @ 0 ".o and using a factor of safety of "( calculate the re4uired minimum cross-sectional area for the circular steel &ar $ . )E 0 +.. 1Pa*.
A. 2'o e4ual round &ars are supported in line 'ith one another and are separated &y a small gap B. 1iven the coefficient of thermal e/pansion @ 0 #+/#.-;Coc( % 0 # m( d 0 +, mm and B 0 #.+ mm( determine the temperature rise necessary to cause them to )a* >ust touch. )&* uc!le elastically.
#.. $ vehicle >ac! is to &e designed to support a ma/imum 'eight of ++ !9. 2he opposite handed threads on the t'o ends of the scre' $C are cut to allo' the >ac! angle to vary from #,o to 5,o. 2he lin!s are hot rolled steel &ars 'ith a minimum yield strength of "7, MPa. Each of the four lin!s is to consist of t'o &ars( one on each side of the scre'. 2he &ars are ".. mm long and have a 'idth of +, mm. $ssuming the &ars are pin-connected( determine the thic!ness of the &ars &ased on a factor of safety of " for &uc!ling.
##. Mem&er D$ can &e considered rigid and 'eightless. Columns C and DF are pin-ended 'ith solid circular cross-sections of diameter #. mm. Column C is made of structural steel )E 0 +.. 1Pa* and column DF is made of an aluminum alloy )E 0 5+ 1Pa*. Determine the magnitude of E that 'ill first cause one of the columns to &uc!le.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- 52 Leadership IdeasDokument40 Seiten52 Leadership IdeasmarknassefNoch keine Bewertungen
- Happy Startup EbookDokument72 SeitenHappy Startup EbookLucca CinquarolliNoch keine Bewertungen
- DME Assignment 1Dokument2 SeitenDME Assignment 1sumikannuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Robotics Course StructureDokument4 SeitenRobotics Course StructurerohitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Incarnational Theory of Atonement 10-2-09 VersionDokument25 SeitenIncarnational Theory of Atonement 10-2-09 VersionmarknassefNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment Ch2Dokument4 SeitenAssignment Ch2alireza_malekyNoch keine Bewertungen
- B.Tech Assgn-1Dokument6 SeitenB.Tech Assgn-1K Pushpendu PrashantNoch keine Bewertungen
- DME Question Bank - 3171917Dokument4 SeitenDME Question Bank - 3171917fgyjnsv786Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 10.3: Single Span Beams: Objective/ScopeDokument21 SeitenLecture 10.3: Single Span Beams: Objective/ScopeDenis DimićNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 4 AssignmentsDokument5 SeitenUnit 4 AssignmentsbattuarunNoch keine Bewertungen
- LabManual MDID2016 2016 02 24 16 29 36Dokument23 SeitenLabManual MDID2016 2016 02 24 16 29 36Rajat MehtaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CEM081 Steel Building DesignDokument8 SeitenCEM081 Steel Building DesignJehad ChowdhuryNoch keine Bewertungen
- DMM - I Question Bank For StudentsDokument11 SeitenDMM - I Question Bank For StudentsDushyanthkumar DasariNoch keine Bewertungen
- DMM - I Question Bank For StudentsDokument11 SeitenDMM - I Question Bank For StudentsDushyanthkumar DasariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Important Questions Unit 1,2Dokument7 SeitenImportant Questions Unit 1,2rajeswariNoch keine Bewertungen
- MODEL QUESTION PAPER Mechanical VibrationsDokument3 SeitenMODEL QUESTION PAPER Mechanical VibrationsDarani PriyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DMM 1Dokument9 SeitenDMM 1andhracollegesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial Sheet - 1 On Design of Spring': Department of Mechanical EngineeringDokument2 SeitenTutorial Sheet - 1 On Design of Spring': Department of Mechanical EngineeringSrimanthula SrikanthNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optimization of The Tendon Layout For Box-Girder Multiple-Span Prestressed Concrete BridgesDokument8 SeitenOptimization of The Tendon Layout For Box-Girder Multiple-Span Prestressed Concrete BridgesFiras SalmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tension Member Design & Structural Steel ConnectionsDokument17 SeitenTension Member Design & Structural Steel ConnectionsAnuj Chandiwala100% (1)
- (PDF) AASHTO M-55-03ddDokument5 Seiten(PDF) AASHTO M-55-03ddCristian RubioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ilm College of Engineering & Technology: Model Exam - Novenber-2015Dokument2 SeitenIlm College of Engineering & Technology: Model Exam - Novenber-2015Deepak V DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maximizing Shear Strength with Steel FibersDokument58 SeitenMaximizing Shear Strength with Steel FiberswtfisfNoch keine Bewertungen
- Designing of An Administrative Building, Located in Bucharest, With Steel StructuresDokument12 SeitenDesigning of An Administrative Building, Located in Bucharest, With Steel StructuresDasdasd SadasdNoch keine Bewertungen
- LEEA Correspondence Courses: Assignment 2.8Dokument4 SeitenLEEA Correspondence Courses: Assignment 2.8jithinjose86Noch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 1Dokument4 SeitenAssignment 1sonawanepmsNoch keine Bewertungen
- MD Tut PDFDokument6 SeitenMD Tut PDFNelsan PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Total No. of Pages 02 Roi/No ......... .. Machine Design ME-262 Fourth SEM., B.Tech. (PE)Dokument2 SeitenTotal No. of Pages 02 Roi/No ......... .. Machine Design ME-262 Fourth SEM., B.Tech. (PE)Clash GodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dss - Question BankDokument10 SeitenDss - Question Bankapi-306484475Noch keine Bewertungen
- Time Allowed: 1.5 Hours Full Marks: 70: 604 (S) August 2021Dokument3 SeitenTime Allowed: 1.5 Hours Full Marks: 70: 604 (S) August 2021Sourav BhowmikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question Bank MD IDokument15 SeitenQuestion Bank MD IvsambardekarNoch keine Bewertungen
- School of Mechanical Engineering: Lab Manual of Semester - V U5AEA20 - Aircraft Structures Repair LabDokument31 SeitenSchool of Mechanical Engineering: Lab Manual of Semester - V U5AEA20 - Aircraft Structures Repair LabAasto Ashrita AastikaeNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Monumental Bridge With A Problem Caused by Oversights in DesignDokument18 SeitenA Monumental Bridge With A Problem Caused by Oversights in Designevan_arendseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Individual Qeustions 1springsDokument17 SeitenIndividual Qeustions 1springsslv_prasaadNoch keine Bewertungen
- DMM I Assignment - 4Dokument2 SeitenDMM I Assignment - 4Konduru Vinay Kumar ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strength of Materials - Department of Mechanical Engineering PDFDokument7 SeitenStrength of Materials - Department of Mechanical Engineering PDFM.Thirunavukkarasu100% (2)
- Screws, Fasteners, and Nonpermanent Joint DesignDokument5 SeitenScrews, Fasteners, and Nonpermanent Joint DesignMohamed AshrafNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASTM A184 Welded Deformed Steel Bar Mats For Concrete ReinforcementDokument2 SeitenASTM A184 Welded Deformed Steel Bar Mats For Concrete ReinforcementAmanda Ariesta Aprilia100% (1)
- SM 1Dokument1 SeiteSM 1Technical4uNoch keine Bewertungen
- S. E. (Mechanical / Mechanical - SW / Automobile) 2012 CourseDokument3 SeitenS. E. (Mechanical / Mechanical - SW / Automobile) 2012 CourseTejas AdakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment No. 3 &4 B.Tech Mechanical Engineering Third YearDokument4 SeitenAssignment No. 3 &4 B.Tech Mechanical Engineering Third Yearharish_kumar201301Noch keine Bewertungen
- Structural Engineering - Questions SuggestionDokument13 SeitenStructural Engineering - Questions SuggestionPritam DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- OPTIMAL VOLTAGE DETERMINATION FOR POWER TRANSMISSION LINES CONSIDERING TECHNICAL AND ECONOMIC FACTORSDokument4 SeitenOPTIMAL VOLTAGE DETERMINATION FOR POWER TRANSMISSION LINES CONSIDERING TECHNICAL AND ECONOMIC FACTORSTalia WileyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kings: Department of Mechanical EngineeringDokument14 SeitenKings: Department of Mechanical EngineeringAdam AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- DME4THDokument17 SeitenDME4THManivannanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design Project (Scisor Jack) - 2021Dokument2 SeitenDesign Project (Scisor Jack) - 2021luqman.sheikh20Noch keine Bewertungen
- Snist Dom Previous PaperDokument9 SeitenSnist Dom Previous PaperKapil Siddhant DevulapalliNoch keine Bewertungen
- End Semester SY Question Paper MDD May 2021Dokument3 SeitenEnd Semester SY Question Paper MDD May 2021FelishiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- COMPRESSION MEMBER DESIGNDokument3 SeitenCOMPRESSION MEMBER DESIGNvivekNoch keine Bewertungen
- MSN612215/MSN616218 Elemen Mesin I: Welding JointsDokument36 SeitenMSN612215/MSN616218 Elemen Mesin I: Welding JointsDavid TaradeNoch keine Bewertungen
- ME102: Engineering Mechanics Homework #7Dokument3 SeitenME102: Engineering Mechanics Homework #7RahulAggarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanics of Solids Exam QuestionsDokument10 SeitenMechanics of Solids Exam QuestionsNandu Sreekumar SNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2004 Engineering Studies Notes OhmzDokument6 Seiten2004 Engineering Studies Notes OhmzSuman SahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solid Mechanics Question BankDokument10 SeitenSolid Mechanics Question BankMugilan VinsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strength of Materials Q ADokument7 SeitenStrength of Materials Q AMuthukumar SoundarrajanNoch keine Bewertungen
- D MDokument9 SeitenD MMuthu KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strength of Materials Question BankDokument8 SeitenStrength of Materials Question BankkalirajgurusamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Correlation Between Pipe Bend Geometry and Allowable Pressure in Pipe Bends Using Artificial Neural Network PDFDokument13 SeitenCorrelation Between Pipe Bend Geometry and Allowable Pressure in Pipe Bends Using Artificial Neural Network PDFshyfxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 1: Young's ModulusDokument18 SeitenExperiment 1: Young's ModulusSepi Itu IndahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cylindrical Compression Helix Springs For Suspension SystemsVon EverandCylindrical Compression Helix Springs For Suspension SystemsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scientific American Supplement, No. 392, July 7, 1883Von EverandScientific American Supplement, No. 392, July 7, 1883Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gypsum BoqDokument1 SeiteGypsum BoqmarknassefNoch keine Bewertungen
- Church and IntercessionDokument3 SeitenChurch and IntercessionmarknassefNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1Dokument9 Seiten1marknassefNoch keine Bewertungen
- HickDokument4 SeitenHickmarknassefNoch keine Bewertungen
- Penal Substitution vs. Christus Victor: Part Two: Legalism vs. RelationshipDokument10 SeitenPenal Substitution vs. Christus Victor: Part Two: Legalism vs. RelationshipmarknassefNoch keine Bewertungen
- 24th December Phase 2 MeetingDokument5 Seiten24th December Phase 2 MeetingmarknassefNoch keine Bewertungen
- Change Order No: Rev (0) 7/2010 F-AMG-PR-13-14Dokument2 SeitenChange Order No: Rev (0) 7/2010 F-AMG-PR-13-14marknassefNoch keine Bewertungen
- Client: Netherlands Embassy in Cairo Project: Renovation & Maintenace Works of Embassy of Netherlands PROECT NO.: 636 DATE: 3rd MAR, 2013 Rev: 0Dokument1 SeiteClient: Netherlands Embassy in Cairo Project: Renovation & Maintenace Works of Embassy of Netherlands PROECT NO.: 636 DATE: 3rd MAR, 2013 Rev: 0marknassefNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ardamana Ace Steel Bar Tests DetailsDokument1 SeiteArdamana Ace Steel Bar Tests DetailsmarknassefNoch keine Bewertungen
- Serial Description Unit Quantity Unit Cost Total Cost Unit Price Total PriceDokument1 SeiteSerial Description Unit Quantity Unit Cost Total Cost Unit Price Total PricemarknassefNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gregs Letter1Dokument3 SeitenGregs Letter1marknassefNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4T11 Variation Order v4-0Dokument1 Seite4T11 Variation Order v4-0RajanRanjanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Netherlands EmbassyDokument1 SeiteNetherlands EmbassymarknassefNoch keine Bewertungen
- Internal Problems and Question List 2 8 10 Part2Dokument6 SeitenInternal Problems and Question List 2 8 10 Part2marknassefNoch keine Bewertungen
- Are There Carnal ChristiansDokument6 SeitenAre There Carnal ChristiansmarknassefNoch keine Bewertungen
- -یO ی @ا ةاو ی +ی) @ا:f2ﺱإ (5 Dﺝ> " = Dﺕ .ﺱ و نuا ةF;ا: Arabic Bible Outreach MinistryDokument8 Seiten-یO ی @ا ةاو ی +ی) @ا:f2ﺱإ (5 Dﺝ> " = Dﺕ .ﺱ و نuا ةF;ا: Arabic Bible Outreach MinistrymarknassefNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bible Study Plans - A Legacy of CaringDokument2 SeitenBible Study Plans - A Legacy of CaringmarknassefNoch keine Bewertungen
- Client: Netherlands Embassy in Cairo Project: Renovation & Maintenace Works of Embassy of Netherlands PROECT NO.: 636 DATE: 3rd MAR, 2013 Rev: 0Dokument1 SeiteClient: Netherlands Embassy in Cairo Project: Renovation & Maintenace Works of Embassy of Netherlands PROECT NO.: 636 DATE: 3rd MAR, 2013 Rev: 0marknassefNoch keine Bewertungen
- International Commercial Terms-Mezinarodni Obchodni ZkratkyDokument2 SeitenInternational Commercial Terms-Mezinarodni Obchodni ZkratkymarknassefNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bible Study Plans - 7 Reasons I BelieveDokument2 SeitenBible Study Plans - 7 Reasons I Believemarknassef100% (1)
- 12 - 24 - 09 UpdateDokument2 Seiten12 - 24 - 09 UpdatemarknassefNoch keine Bewertungen
- Internal Problems and Question List 2 21 10Dokument4 SeitenInternal Problems and Question List 2 21 10marknassefNoch keine Bewertungen
- Internal Problems and Question List 2 8 10 Part2Dokument6 SeitenInternal Problems and Question List 2 8 10 Part2marknassefNoch keine Bewertungen
- Internal Problems and Question List 2 8 10Dokument4 SeitenInternal Problems and Question List 2 8 10marknassefNoch keine Bewertungen
- Where Are We On The Void Release?Dokument2 SeitenWhere Are We On The Void Release?marknassefNoch keine Bewertungen
- You Say It Is Heresy To Speak of The Holy Scriptures in EnglishDokument1 SeiteYou Say It Is Heresy To Speak of The Holy Scriptures in EnglishmarknassefNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bible Study Plans - A Commitment To ExcellenceDokument1 SeiteBible Study Plans - A Commitment To ExcellencemarknassefNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fast Arithmetic TipsDokument10 SeitenFast Arithmetic TipsTej CharanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leadership and Management Spotting The DifferencesDokument10 SeitenLeadership and Management Spotting The DifferencesRaisa RomerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ipcrf - Teacher I - IIIDokument16 SeitenIpcrf - Teacher I - IIIMc Clarens LaguertaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bezier and B-Spline TechniquesDokument58 SeitenBezier and B-Spline TechniquesPranav GujarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Open NebulaDokument7 SeitenOpen NebulaNaresh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Master's Thesis on Social Work Field WorkDokument18 SeitenMaster's Thesis on Social Work Field WorkJona D'john100% (1)
- Problems SIH2019Dokument16 SeitenProblems SIH2019hksNoch keine Bewertungen
- Additional C QuestionsDokument41 SeitenAdditional C Questionsvarikuti kalyaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Souvenirs Messengers of MeaningDokument7 SeitenSouvenirs Messengers of MeaningAna BrunetteNoch keine Bewertungen
- 16. SO2ndEdAAchTest5.doc - Google ДокументиDokument4 Seiten16. SO2ndEdAAchTest5.doc - Google ДокументиAlinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Working platforms for tracked plant designDokument16 SeitenWorking platforms for tracked plant designLeandroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Allegory of The CaveDokument2 SeitenAllegory of The CaveVanessa SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Higher Education Catalogue 2017Dokument59 SeitenHigher Education Catalogue 2017AtifNazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wormhole: Topological SpacetimeDokument14 SeitenWormhole: Topological SpacetimeHimanshu GiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- ZMMR34Dokument25 SeitenZMMR34Himanshu PrasadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Booklet - EpfpclDokument9 SeitenBooklet - EpfpclAnonymous G5Od0CTrmeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Morton, Donald - Return of The CyberqueerDokument14 SeitenMorton, Donald - Return of The Cyberqueerjen-leeNoch keine Bewertungen
- LESSON PLAN EnglishDokument7 SeitenLESSON PLAN EnglishMarie Antonette Aco BarbaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Truth Is A Thorny Issue'1 Lesbian Denial in Jackie Kay's TrumpetDokument12 SeitenThe Truth Is A Thorny Issue'1 Lesbian Denial in Jackie Kay's TrumpetTahir KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Learner Understands The Guidelines and Criteria in The Selection and Evaluation of Health InformationDokument3 SeitenThe Learner Understands The Guidelines and Criteria in The Selection and Evaluation of Health InformationANACORITA O. SILAGANNoch keine Bewertungen
- (ENGL2112) Week 012-Course ModuleDokument3 Seiten(ENGL2112) Week 012-Course ModuleKaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- National Territory of the Philippines Defined in <40 CharactersDokument13 SeitenNational Territory of the Philippines Defined in <40 CharactersMarianne AngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Performance Appraisal IntroductionDokument8 SeitenPerformance Appraisal IntroductionRohit KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Setting Advertising Objectives and Formulating StrategiesDokument12 SeitenSetting Advertising Objectives and Formulating StrategiesAnonymous bTh744z7E6Noch keine Bewertungen
- AltimeterDokument8 SeitenAltimeterwolffoxxxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Absences Add Up:: How School Attendance Influences Student SuccessDokument16 SeitenAbsences Add Up:: How School Attendance Influences Student SuccessMJSwayNoch keine Bewertungen
- CG Lab Manual ProgramsDokument61 SeitenCG Lab Manual ProgramsVivek KvNoch keine Bewertungen
- SRS For VCSDokument14 SeitenSRS For VCSKartikay SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen