Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Intro To Navi
Hochgeladen von
amplifiergeekOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Intro To Navi
Hochgeladen von
amplifiergeekCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
BEFORE NAVISmeans ship AGEREmeans to drive TODAY!
Y! Art & Science Recording , planning & controlling Craft Safe Route Time Position Experience & Decision How to determine the position? >Longitude, Latitude, and Altitude. Parameters: >Time, Distance, Speed, and Direction.
UT1 is also known as the GMT Time References Ephemeris Time Universal Time (UT) Greenwich Mean time (GMT) Atomic Time Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) Atomic Time based on the transitions in the atom. 9,192,631,770 cycles of cesium atom = 1 second. The first cesium atomic beam clock as portrayed by Ripley's "Believe It or Not" in September 1953 UTC is a high-precision Atomic Time Standard Early Navigational Tools Magnetic Compass Navigational Chart Marine Sextant Almanac Chronometer Lighthouse Buoys
Early Navigational Techniques 1. Celestial Navigation 2. Geo-Navigation a. Piloting b. Dead-Reckoning Celestial Navigation It is the art and science of finding one's geographic position by means of astronomical observations, particularly by measuring altitudes of celestial objects sun, moon, planets, or stars. It usually requires a chronometer, sextant , an almanac, a set of sight reduction tables, and a chart of the region. Piloting A position fixing technique that uses fixed visual references on the ground or sea by means of sight to guide oneself to a destination, with the help of a chart. Common types of visual references are: Natural: Mountains, hills, lakes, rivers, cliffs, rocks, and beaches. Man made: sea marks such as lighthouses, and buoys, and land marks like airports, piers, dams, highways, etc. Dead Reckoning It is the process of estimating one's position based upon a previously determined position, or fix, and advancing that position based upon the known speed, elapsed time, and course. This fix is then advanced, mathematically or directly on the chart, by means of recorded heading, speed, and time. The world wars encouraged the development of an all weather and accurate Electronic Radio Navigation Systems. A method of position fixing using radio and electronic means. Types: Passive Radio Navigation Range = C*t Active Radio Navigation Range = C*t/2 Ground Based Radio Navigation Space Based Radio Navigation Sample Problem A ship has its chronometer reading of 0430 hrs, while the ships local time is 1042 hrs. What is the position of the ship in longitude? Answer: 93 East is the ships longitude.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
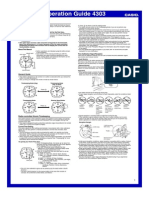
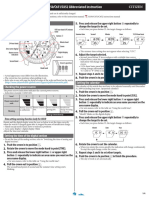
- Manual Casio RadioControladoDokument3 SeitenManual Casio RadioControladosoy1masNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Manual For Casio Prayer Watch Model 5266Dokument10 SeitenManual For Casio Prayer Watch Model 5266mohdsanieNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Citizen Blue Angels Skyhawk C650Dokument4 SeitenCitizen Blue Angels Skyhawk C650Matthew PlantNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Astro NavigationDokument308 SeitenAstro Navigationlivlaser100% (3)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- Manual Book Casio QW 3198Dokument5 SeitenManual Book Casio QW 3198Dondy Agung PramonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Armchair Celestial NavigatorDokument121 SeitenThe Armchair Celestial Navigatorbjmoose100% (1)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Operation Guide 3199: About This ManualDokument3 SeitenOperation Guide 3199: About This ManualReskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- OACI Doc8126 PDFDokument556 SeitenOACI Doc8126 PDFEmmanuel CasadiegosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Anglisht, Detyre KursiDokument10 SeitenAnglisht, Detyre Kursigretaa avdylajNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Operation Guide 3100: About This ManualDokument3 SeitenOperation Guide 3100: About This ManualJames GeustNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 44 48 en 104 PDFDokument533 Seiten1 44 48 en 104 PDFSang Phan ThanhNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Casio Baby G User ManualDokument5 SeitenCasio Baby G User ManualLiviu_55Noch keine Bewertungen
- Manual - Casio Protrek Prg270-7Dokument14 SeitenManual - Casio Protrek Prg270-7Jenny CarissimaeNoch keine Bewertungen
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- User Manual: ConsoleDokument60 SeitenUser Manual: ConsoleFirman Al AhyarNoch keine Bewertungen
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- Social Grade 7Dokument127 SeitenSocial Grade 7dewey jovan dormitorioNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- The Career CaféDokument26 SeitenThe Career CaféJane ridriguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- GEH-6408E Control System Toolbox For A Trend Record PDFDokument56 SeitenGEH-6408E Control System Toolbox For A Trend Record PDFmeirangongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Casio Qw5028Dokument4 SeitenCasio Qw5028Giovanni DrogoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculate Hexadecimal DHCPDokument4 SeitenCalculate Hexadecimal DHCPTiago SoaresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clients Class Workbook v5.1 CBTDokument192 SeitenClients Class Workbook v5.1 CBTmich0pNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Lesotho National Frequency Allocation PlanDokument185 SeitenLesotho National Frequency Allocation PlanNtsane MoleNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Satellite CommunicationsDokument202 SeitenSatellite CommunicationsSachin Korgaonkar50% (2)
- Casio Liw w610Dokument8 SeitenCasio Liw w610bedernazsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Satellite Communication NotesDokument50 SeitenSatellite Communication NotesPreetham SaigalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Time Conversion UTCDokument1 SeiteTime Conversion UTCi8o9zNoch keine Bewertungen
- Book Pdgps Gage Nav 08Dokument339 SeitenBook Pdgps Gage Nav 08premnerellaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rlibrary WmtsaDokument78 SeitenRlibrary WmtsaKim SamejimaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- IEC618503Dokument992 SeitenIEC618503Huấn PhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- QW 4335Dokument5 SeitenQW 4335doombuggyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)