Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Mefenamic
Hochgeladen von
Sam Angelo EstrellaOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Mefenamic
Hochgeladen von
Sam Angelo EstrellaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
35
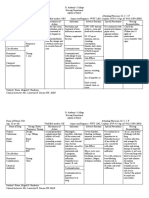
Generic & Brand Name Generic: Mefenamic acid Brand: Dolfenal
Dose, Strength & Formulation Ordered: mefenamic acid 500 mg 1 tab PRN for pain Timing: PRN
Classification: Central Nervous System agent; analgesic; nsaid; antipyretic Duration: Unknown Other forms: Capsule
Indication/ Mechanism of Action Indications: Mild to moderate pain, inflammation, stiffness, swelling or tenderness caused by surgical procedure. (Lippincott W; 2009) Mechanism of Actions: The analgesic effect of NSAIDs may result from interference with the prostaglandins involved in pain.Prostaglan dins appear to sensitize pain receptors to mechanical
Adverse Effects & Drug Interaction Adverse Effect: CNS:Drowsiness, insomnia, dizziness, nervousness, confusion, headache. GI: Abdominal pain, dyspepsia, epigastric distress, nausea, nephrotoxicity occurs occasionally. Skin:Urticaria, rash, facial edema. BodyWhole:Perspira tion. CV:Palpitation. Respiratory:Dyspne a; acute exacerbation of asthma; bronchoconstriction (in patients sensitive to aspirin). Interaction: Drug to Drug:
Aminoglycosides (eg, tobramycin)
Nursing Responsibilities 1.Assess patients level of pain and inflammation before therapy. (Lippincott W; 2009)
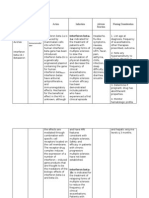
Rationale
Client Teaching 1.Encourage patient to take drug as directed to achieve desired effect. (Lippincott W; 2009) 2. Review methods to prevent or minimize GI upset. (Lippincott W; 2009) 3. Work with patient on long-term therapy to arrange for monitoring of laboratory values, especially BUN,
1.To indicate baseline data and to monitor patient. (Lippincott W; 2009) 2. To detect toxicity. (Lippincott W; 2009)
2. Monitor ophthalmic and auditory function before and periodically during therapy. (Lippincott W; 2009) 3. Monitor CBC, platelet count, and hepatic and renal function studies periodically. (Lippincott W; 2009) 4. Be alert for adverse reactions and drug interactions. (Lippincott W; 2009)
Pregnancy Category: C
3. To detect abnormalities. (Lippincott W; 2009)
The risk of acute
4.To indicate proper precautionary measures and management for possible adverse
36
stimulation or to other chemical mediators. NSAIDs inhibit synthesis of prostaglandins peripherally and possibly centrally. Like salicylates, NSAIDs exert an antiinflammatory effect that may result in part from inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis and release during inflammation. (Lippincott W; 2009)
renal failure may be increased. Avoid coadministration. 5. Asses patients and Antacids containing magnesium hydroxide familys knowledge of drug therapy. (Lippincott W; 2009) Antacids containing magnesium hydroxide increase the rate and extent of mefenamic acid 6. Give oral NSAIDs absorption. with 8 oz. (240 ml) of water. Anticoagulants (Lippincott W; 2009) Increased risk of gastric erosion and 7. Have patient sit up bleeding. Use with for 15 to 30 minutes caution and close after taking the drug. monitoring. (Lippincott W; 2009) Smoking and Alcohol 8. Crush tablets or mix with food or The risk of GI fluid. bleeding may be (Lippincott W;2009) increased.
reactions. (Lippincott W; 2009) 5. Proper patient and family education promotes good quality care. (Lippincott W; 2009) 6. To ensure adequate passage into the stomach. (Lippincott W; 2009) 7. To prevent it from lodging in esophagus. (Lippincott W; 2009) 8. To aid in swallowing. (Lippincott W; 2009)
creatinine levels, liver function test result and CBC. (Lippincott W; 2009) 4. Instruct patient to notify prescriber about severe or persistent adverse reaction. (Lippincott W; 2009) 5. Inform patient tof potential drug interaction and how to manage them.
37
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- HeartsInHarmony PDFDokument103 SeitenHeartsInHarmony PDFVanessa100% (9)
- Magneto Therapy NotesDokument5 SeitenMagneto Therapy NotesMadan Kumar100% (2)
- 13-5-2010 MCQ FrcaDokument79 Seiten13-5-2010 MCQ FrcaMohmd Abdulhameed Sayed100% (2)
- Drug Study - Caloy PartDokument3 SeitenDrug Study - Caloy PartCarlos LleverNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2nd Drug Study FinalDokument6 Seiten2nd Drug Study FinalMariella Saavedra Aranda CercadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study For Mefenamic Acid, Tramadol and CefuroximeDokument7 SeitenDrug Study For Mefenamic Acid, Tramadol and CefuroximeChristian Karl B. LlanesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Care Study CAESARIAN SECTIONDokument29 SeitenCare Study CAESARIAN SECTIONNoreen EndinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument11 SeitenDrug StudyNedemar OcampoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study 1 Ferrous SulfateDokument2 SeitenDrug Study 1 Ferrous SulfateKrizzia Mae ColladoNoch keine Bewertungen
- DengueDokument5 SeitenDengueSam Angelo EstrellaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DengueDokument5 SeitenDengueSam Angelo EstrellaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lymphatic System and San JiaoDokument6 SeitenLymphatic System and San JiaoΒιβιλάκη Γεωργία100% (1)
- Drug StudyDokument14 SeitenDrug Studycruz_johnraymond100% (1)
- HNBB Drug StudyDokument4 SeitenHNBB Drug StudyYu, Denise Kyla BernadetteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study DulcolaxDokument2 SeitenDrug Study DulcolaxReisha Fungo0% (1)
- RPSGT Exam BlueprintDokument2 SeitenRPSGT Exam BlueprintKarloveyNoch keine Bewertungen
- PATIENT M.G.'S MEDICATIONS AND NURSING CONSIDERATIONSDokument5 SeitenPATIENT M.G.'S MEDICATIONS AND NURSING CONSIDERATIONSGrace MellaineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument11 SeitenDrug StudyMichelle TamorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument23 SeitenDrug StudyfortunelobsterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Art TherapyDokument4 SeitenArt TherapyfaitheeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Five Shu PointsDokument1 SeiteFive Shu Pointsyilongwei.comNoch keine Bewertungen
- GENTAMICINDokument3 SeitenGENTAMICINjacquejackieNoch keine Bewertungen
- CPAPDokument11 SeitenCPAPpreeti19987100% (1)
- Metronidazole Drug StudyDokument3 SeitenMetronidazole Drug StudySiafei RabeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument6 SeitenDrug StudyArdrina SappariNoch keine Bewertungen
- KetorolacDokument5 SeitenKetorolacMichelle Ann P. NacuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mefenamic Acid Drug StudyDokument2 SeitenMefenamic Acid Drug StudyJude LabajoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tranexamic Acid (Drug Study)Dokument2 SeitenTranexamic Acid (Drug Study)nin_0967% (6)
- Drug Study: Davao Doctors College General Malvar ST., Davao City Nursing ProgramDokument3 SeitenDrug Study: Davao Doctors College General Malvar ST., Davao City Nursing ProgramJear RomeroNoch keine Bewertungen
- DRUGSTUDY: Dolfenal - Mefenamic AcidDokument2 SeitenDRUGSTUDY: Dolfenal - Mefenamic AcidYum CNoch keine Bewertungen
- CiprobayDokument2 SeitenCiprobayianecunar100% (1)
- TB DrugsDokument14 SeitenTB DrugsLexy CadigalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study: CalfactantDokument1 SeiteDrug Study: CalfactantAngelokeizer GavinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study PonstanDokument1 SeiteDrug Study PonstanRainier IbarretaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study - CefotaximeDokument5 SeitenDrug Study - CefotaximeAngel laurestaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CefuroximeDokument11 SeitenCefuroximeAlmira Ballesteros CestonaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tranexamic Acid Drug StudyDokument3 SeitenTranexamic Acid Drug Studyswitchlers anneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study Amlodipine & HydrocortisoneDokument4 SeitenDrug Study Amlodipine & HydrocortisoneJohn Kristoffer JisonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study - Metronidazole (Flagyl)Dokument1 SeiteDrug Study - Metronidazole (Flagyl)Jule SantoyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing care plan for post-operative patientDokument3 SeitenNursing care plan for post-operative patientAya BolinasNoch keine Bewertungen
- RD - Perineal FlushingDokument3 SeitenRD - Perineal FlushingJiwi YuNoch keine Bewertungen
- CiprofloxacinDokument2 SeitenCiprofloxacinx483xDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study AzithromycinDokument2 SeitenDrug Study Azithromycinkuro hanabusaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study SummaryDokument7 SeitenDrug Study SummaryKateLayaogNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study CefuroximeDokument2 SeitenDrug Study CefuroximeTipey Segismundo100% (1)
- AMIKACINDokument2 SeitenAMIKACINJesrel DelotaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iron supplements and antianginal drug studyDokument4 SeitenIron supplements and antianginal drug studyLene ThereseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sal But AmolDokument2 SeitenSal But AmolCalimlim KimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Generic Name Brand Name Drug Class Action Indication Contra-Indication S/E Nsg. Consideratio NSDokument1 SeiteGeneric Name Brand Name Drug Class Action Indication Contra-Indication S/E Nsg. Consideratio NSKenny CastroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Duavent Drug Study - CunadoDokument3 SeitenDuavent Drug Study - CunadoLexa Moreene Cu�adoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study IsoniazidDokument1 SeiteDrug Study IsoniazidEphraim MaravillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument2 SeitenDrug StudyNicole Blanch BuenavistaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DRUGSTUDY RANITIDINE, METRONIDAZOLE, CEFUROXIME, KEtorolac NUBainDokument7 SeitenDRUGSTUDY RANITIDINE, METRONIDAZOLE, CEFUROXIME, KEtorolac NUBainKyle Cholo CholoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument7 SeitenDrug StudyCandace DarleneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Interferon Drug StudyDokument3 SeitenInterferon Drug Studyjogzzz13100% (1)
- Chap. 6 - 8 MaternalDokument16 SeitenChap. 6 - 8 MaternalKaryll RomeroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cefuroxime, Celecoxib, ChloridineDokument2 SeitenCefuroxime, Celecoxib, ChloridinekrizzywhizzyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Co AmoxiclavDokument2 SeitenCo AmoxiclavkaijeiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study (CEFUROXIME)Dokument1 SeiteDrug Study (CEFUROXIME)NE TdrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dazomet DrugDokument2 SeitenDazomet Drugashley11Noch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study Pen G FuroDokument3 SeitenDrug Study Pen G Furokuro hanabusaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ivf StudyDokument2 SeitenIvf StudyJannine Bensi100% (1)
- College of Nursing: Pharmacological ManagementDokument3 SeitenCollege of Nursing: Pharmacological ManagementNathanielle Keith PENASONoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug NystatinDokument1 SeiteDrug NystatinSrkocherNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study FinalDokument5 SeitenDrug Study FinalJackie Ann Marie DapatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cetirizine 2Dokument2 SeitenCetirizine 2ianNoch keine Bewertungen
- MefenamicDokument1 SeiteMefenamicChristian Clyde N. ApigoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ketorolac DRUG STUDYDokument3 SeitenKetorolac DRUG STUDYA.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudiesDokument16 SeitenDrug Studiesvitcloud23100% (2)
- Mefenamic AcidDokument3 SeitenMefenamic AcidVaibhav MehtaNoch keine Bewertungen
- .docxDokument4 Seiten.docxSam Angelo EstrellaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Easy Brownies Made With Cocoa: IngredientsDokument2 SeitenEasy Brownies Made With Cocoa: IngredientsSam Angelo EstrellaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nvic 03-06 FinalDokument55 SeitenNvic 03-06 FinalSam Angelo EstrellaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DSDSDSDokument2 SeitenDSDSDSSam Angelo EstrellaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 Pieces of Fruit A DayDokument2 Seiten5 Pieces of Fruit A DaySam Angelo Estrella100% (1)
- Abcd Abcd Trapezoid Trapezium Trapezoid Trapèze Trapezio Trapez Trapezium Trapezium Trapézion Trápeza Tetrás Péza Trapezoid TrapézoeideDokument17 SeitenAbcd Abcd Trapezoid Trapezium Trapezoid Trapèze Trapezio Trapez Trapezium Trapezium Trapézion Trápeza Tetrás Péza Trapezoid TrapézoeideSam Angelo EstrellaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 001461Dokument13 Seiten001461Sam Angelo EstrellaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BMS1 - K10 - The Role of B Vitamins As An Adjuvant AnalgesicDokument45 SeitenBMS1 - K10 - The Role of B Vitamins As An Adjuvant AnalgesicAndreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thyroid Disease Anesthetic ConsiderationsDokument30 SeitenThyroid Disease Anesthetic ConsiderationsmirzaoctaNoch keine Bewertungen
- TU3000 Manual 00 102915Dokument19 SeitenTU3000 Manual 00 102915alanbrannNoch keine Bewertungen
- 360 Comprehensive Exam: Assessment Form Completion Guide 2018Dokument1 Seite360 Comprehensive Exam: Assessment Form Completion Guide 2018Altus GoldenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Breast Abscess After Autologous Fat TransferDokument3 SeitenBreast Abscess After Autologous Fat TransferInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology100% (1)
- Endodontic Working WidthDokument13 SeitenEndodontic Working WidthbkprosthoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hot Stone Massage BenefitsjhxnjDokument2 SeitenHot Stone Massage Benefitsjhxnjsecondstove31Noch keine Bewertungen
- Schizophrenia NotesDokument8 SeitenSchizophrenia NotesAdam WilsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case AnaDokument12 SeitenCase AnaBiel DelcanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parkinsons Disease Vs ParkinsonismsDokument2 SeitenParkinsons Disease Vs ParkinsonismsFlorian RoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jambi Cardiology Update WorkshopDokument3 SeitenJambi Cardiology Update WorkshopFahrurrozi SyarifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mitchell, Carol - ResumeDokument2 SeitenMitchell, Carol - Resumeapi-238460511Noch keine Bewertungen
- IDDT Clinical GuidelinesDokument2 SeitenIDDT Clinical Guidelinesramel5217780Noch keine Bewertungen
- TMP - Neonatal Sundries CHeRP 2007522642027Dokument2 SeitenTMP - Neonatal Sundries CHeRP 2007522642027sofyanbachriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nasrallah 2018Dokument7 SeitenNasrallah 2018atikahanifahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Investigation, Primary Health Care (PHC)Dokument77 SeitenInvestigation, Primary Health Care (PHC)api-3710926Noch keine Bewertungen
- N-Acetylcarnosine (NAC) Drops For Age-Related Cataract (Review)Dokument20 SeitenN-Acetylcarnosine (NAC) Drops For Age-Related Cataract (Review)rahayuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phenobarbital Elixir BP - Electronic Medicines Compendium (eMC) - Print FriendlyDokument5 SeitenPhenobarbital Elixir BP - Electronic Medicines Compendium (eMC) - Print FriendlyBrian HarrisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction to the Aspects and Origins of Personal DevelopmentDokument15 SeitenIntroduction to the Aspects and Origins of Personal DevelopmentLhiet Aguilar HipolitoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Dosage Calculation Formulas and Practice ExercisesDokument15 SeitenDrug Dosage Calculation Formulas and Practice ExercisesIhtesham Ul Haq100% (1)
- Mood Disorders StudentDokument32 SeitenMood Disorders StudentRafly FernandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Freud - Fetishism (1927e)Dokument6 SeitenFreud - Fetishism (1927e)I Smith100% (1)