Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Duration DQ
Hochgeladen von
permafrostXxOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Duration DQ
Hochgeladen von
permafrostXxCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
1
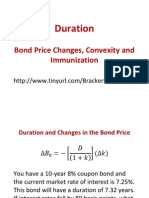
Session 5: Duration
A. Duration is the weighted average time for investors to recover the cost of their
investment from the cash flows of the investment. The weight attached to each
cash flow is defined as the present value of the cash flow divided by the cost. The
time attached to each cash flow is defined as the time period when the cash flow
is received.
B.
Answers:
Coupon rate Duration Years to maturity Duration YTM Duration
10% 1.8684 2 1.8684 5 1.8684
12% 1.8473 4 3.4483 7 1.8657
14% 1.8276 6 4.8175 9 1.8630
16% 1.8091 8 6.0257 11 1.8602
18% 1.7918 10 7.1066 13 1.8575
20% 1.7754 12 8.0833 15 1.8547
Relationship between Dur ation & Coupon Rate: 2-year bond with yield of 5%
1.7600
1.7800
1.8000
1.8200
1.8400
1.8600
1.8800
8% 10% 12% 14% 16% 18% 20% 22%
Coupon Rat e
D
u
r
a
t
i
o
n
Relat i ons hip bet w een Dur at ion & Mat ur i t y - 10% coupon bond w i t h yield of 5%
0.0000
2.0000
4.0000
6.0000
8.0000
10.0000
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14
Year s t o Mat ur i t y
D
u
r
a
t
i
o
n
Relat i ons hip bet w een Dur at ion & Yield - 2-year 10% coupon bond
1.8500
1.8550
1.8600
1.8650
1.8700
3 5 7 9 11 13 15 17
Yi el d t o Mat ur it y
D
u
r
a
t
i
o
n
2
The results and diagrams show that duration is
i) inversely related to coupon rate. The higher the coupon rate, the sooner the
investor will recover the cost of investment and hence the smaller duration.
ii) directly related to maturity. The longer the maturity, the longer it takes to
recover the cost of investment and hence the larger duration.
iii) inversely related to yield to maturity. If you plot a diagram to illustrate the
relationship between the yield and price of a bond, you should realise that the
bond price decreases at a decreasing rate with yield. This relationship implies
that the larger the yield, the lower the price sensitivity of a bond to interest
rate changes. But smaller duration also corresponds to lower bond price
sensitivity. Thus the larger the yield, the smaller the duration.
C. From the session on bond pricing:
As Coupon rate and maturity , price sensitivity .
From the previous question:
As Coupon rate and maturity , duration .
Thus a direct relationship between duration and price sensitivity is expected.
D. Since cash flows in the form of coupon interests are received prior to maturity, the
investor does not need to wait until maturity to recover the cost of investment.
Hence the duration of a coupon bond is generally smaller than its time to
maturity.
E. The duration is 0.5 years since the remaining cash flows (FV and final coupon
interest) are all received six months later when the bond matures and the present
value of the cash flows is equal to the cost of investment. Thus the duration of a
coupon bond is not always smaller than its time to maturity. It can be the same as or less
than the time to maturity.
F. Yes, this investment is risk-free since you are certain of the cost and terminal value of the
investment.
G. Assumption 1: The yield curve is flat at the time of bond investment. This
ensures that the expected return from the bond is the same return as its initial yield
to maturity.
Assumption 2: Any unexpected change in rates applies to the entire spectrum of
maturities, i.e., the yield curve experiences a parallel upward/downward shift.
This ensures that the unexpected rise (fall) in coupon reinvestment income offsets
the unexpected fall (rise) in the selling price of the bond completely.
Assumption 3: Prior to any unexpected change in rates, the bonds duration
matches the intended holding period. Otherwise, price risks will not offset
income risks completely.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Duration Convexity Bond Portfolio ManagementDokument49 SeitenDuration Convexity Bond Portfolio ManagementParijatVikramSingh100% (1)
- Valuation of Bonds and SharesDokument45 SeitenValuation of Bonds and SharessmsmbaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture Bond MGT StrategyDokument25 SeitenLecture Bond MGT StrategyKapil SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Analysis and Valuation of Bonds: Answers To QuestionsDokument4 SeitenThe Analysis and Valuation of Bonds: Answers To QuestionsIsmat Jerin ChetonaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Duration PDFDokument8 SeitenDuration PDFMohammad Khaled Saifullah CdcsNoch keine Bewertungen
- What is Bond DurationDokument4 SeitenWhat is Bond DurationBhowmik DipNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 16: Fixed Income Portfolio ManagementDokument20 SeitenChapter 16: Fixed Income Portfolio ManagementSilviu TrebuianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study BondsDokument5 SeitenCase Study BondsAbhijeit BhosaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Duration Basics ExplainedDokument12 SeitenDuration Basics ExplainedDeepak SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bonds ValuationsDokument57 SeitenBonds ValuationsarmailgmNoch keine Bewertungen
- FIXED INCOME DURATIONDokument111 SeitenFIXED INCOME DURATIONsawilson1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Duration of BondDokument9 SeitenDuration of BondUbaid DarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Market Valuation and Duration ReportsDokument30 SeitenMarket Valuation and Duration ReportsAleena BaigNoch keine Bewertungen
- R54-Understanding FI Risk and ReturnDokument37 SeitenR54-Understanding FI Risk and ReturnBad AnikiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fixed Income Securities Are Available Worldwide: Slide 1: Bond Yields and Interest RatesDokument19 SeitenFixed Income Securities Are Available Worldwide: Slide 1: Bond Yields and Interest RatesAlief AmbyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 10 - CH18-1Dokument4 SeitenTutorial 10 - CH18-1zachNoch keine Bewertungen
- Risk Management Options and DerivativesDokument13 SeitenRisk Management Options and DerivativesAbdu0% (1)
- CCRA Session 6Dokument17 SeitenCCRA Session 6Amit GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 12 Bond Portfolio MGMTDokument41 SeitenChapter 12 Bond Portfolio MGMTsharktale2828Noch keine Bewertungen
- Duration and ConvexityDokument10 SeitenDuration and ConvexityAssad AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 InclassDokument50 Seiten10 InclassTNoch keine Bewertungen
- VERY GOOD Ch7 Managing Bond Portfolios and Rate StrategiesDokument53 SeitenVERY GOOD Ch7 Managing Bond Portfolios and Rate StrategiesKapil AgrawalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measuring Interest-Rate Risk with DurationDokument7 SeitenMeasuring Interest-Rate Risk with DurationArif AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- MAS 2 Report (Autosaved) (Autosaved)Dokument18 SeitenMAS 2 Report (Autosaved) (Autosaved)Hazel Jane EsclamadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch2 Testbank Part 2 (2) .AnswerdDokument8 SeitenCh2 Testbank Part 2 (2) .Answerdtarek ahmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- DurationDokument5 SeitenDurationNiño Rey LopezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Duration Definition and Its Use in Fixed Income InvestingDokument4 SeitenDuration Definition and Its Use in Fixed Income InvestingACC200 MNoch keine Bewertungen
- IcrddcDokument7 SeitenIcrddcapi-213789026Noch keine Bewertungen
- BFC5935 - Tutorial 7 SolutionsDokument4 SeitenBFC5935 - Tutorial 7 SolutionsXue XuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Duration: Measuring Interest Rate SensitivityDokument19 SeitenDuration: Measuring Interest Rate SensitivityALNoch keine Bewertungen
- Use Duration and Convexity To Measure RiskDokument4 SeitenUse Duration and Convexity To Measure RiskSreenesh PaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yield Curve Concepts, Theories and MeasuresDokument10 SeitenYield Curve Concepts, Theories and Measurespriyanka mehtaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2268Dokument43 Seiten2268asmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Duration vs Convexity in Bond Portfolio ManagementDokument10 SeitenDuration vs Convexity in Bond Portfolio ManagementMilton ChinhoroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Term Structure of Interest Rates Explained in 40 CharactersDokument12 SeitenTerm Structure of Interest Rates Explained in 40 CharactersNikunj ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bond ValuationDokument20 SeitenBond ValuationSaravana KrishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Given Data: P TK 1075 Coupon Rate 9% Coupon Interest 9% / 2 1000 TK 45 Time To Maturity, N 10Dokument4 SeitenGiven Data: P TK 1075 Coupon Rate 9% Coupon Interest 9% / 2 1000 TK 45 Time To Maturity, N 10mahin rayhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- T10 pptDokument11 SeitenT10 pptstellaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 7. Bonds and Their Valuation: A B C D E F G H I 1 2 3 4Dokument13 SeitenChapter 7. Bonds and Their Valuation: A B C D E F G H I 1 2 3 4Naufal IhsanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 3Dokument5 SeitenTutorial 3KÃLÅÏ SMÎLĒYNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dr. Kashefi's bond portfolio immunization techniquesDokument3 SeitenDr. Kashefi's bond portfolio immunization techniqueslenovojiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Interest Rates Mean and What Is Their Role in ValuationDokument5 SeitenInterest Rates Mean and What Is Their Role in ValuationTito KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Term Structure of Interest RatesDokument13 SeitenTerm Structure of Interest RatesAnfal_Shaikh_3139Noch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding Duration and Volatility: Salomon Brothers IncDokument32 SeitenUnderstanding Duration and Volatility: Salomon Brothers IncoristhedogNoch keine Bewertungen
- 14 Fixed Income Portfolio ManagementDokument60 Seiten14 Fixed Income Portfolio ManagementPawan ChoudharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 5312312Dokument55 SeitenLecture 5312312Tam Chun LamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fabozzi Fofmi4 Ch11 ImDokument12 SeitenFabozzi Fofmi4 Ch11 ImYasir ArafatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Duracion TodasDokument42 SeitenDuracion Todasnumismatica.sanferNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fins 2624 Problem Set 3 SolutionDokument11 SeitenFins 2624 Problem Set 3 SolutionUnswlegend100% (2)
- Bond Duration QuestionDokument15 SeitenBond Duration QuestionranjusanjuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 04 Bond Portfolio ImmunizationDokument35 SeitenLecture 04 Bond Portfolio Immunizationandrewchen336Noch keine Bewertungen
- Features of Fixed Income SecuritiesDokument9 SeitenFeatures of Fixed Income Securitiesalmirb70% (1)
- Prepared By: Deveshree Raut Debjani Singha Jagruti ChauhanDokument22 SeitenPrepared By: Deveshree Raut Debjani Singha Jagruti Chauhanarunj49Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ch11 Concepts ReviewDokument4 SeitenCh11 Concepts ReviewCarl Ivan GambalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Two-3Dokument10 SeitenLesson Two-3Ruth NyawiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 10 - Forward and Futures Contracts ExamplesDokument65 SeitenChapter 10 - Forward and Futures Contracts ExamplesLeon MushiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Risk Management: A Simple IntroductionVon EverandFinancial Risk Management: A Simple IntroductionBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (7)
- High-Q Financial Basics. Skills & Knowlwdge for Today's manVon EverandHigh-Q Financial Basics. Skills & Knowlwdge for Today's manNoch keine Bewertungen