Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Construction Site Earthwork Calculation
Hochgeladen von
masteriragaOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Construction Site Earthwork Calculation
Hochgeladen von
masteriragaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
11/29/13
Construction Site Earthwork Calculation
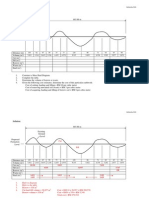
With advancement of Technology there is a lot of progress in the way we take Ground reading. Earlier only Auto Levels were used, whereas now Total Station, GPS, LIDAR are being used to take ground reading. Previously Earthwork Calculations were simply done on paper followed by some simple computer applications. Now, however, either Spread Sheets likes Excel are used or advanced software products which are specifically designed for earthwork calculation are used. But volumetric calculations done by software still have to presented in understandable manner even while getting different results from different software products. There are three different methods popularly used for doing Earthwork Calculation for Cutting/Filling Projects. Before discussing these in detail let us try to understand Some Basic definition of Terms related to Earthwork Calculation. Earthworks Earthworks are engineering works created through the moving and/or processing of massive quantities of soil or unformed rock. Earthwork is done to reconfigure the topography of a site to achieve the design levels. Earthwork involves cutting and filling to achieve the required topography. Cutting Cutting is the process of excavating earth material from a work location to achieve the desired topography. Filling Filling is the process of moving the excavated material or additional earth material to a work location to achieve the desired topography. Let us take 2 Simple Examples for our Study In the Example below the plot is 30 X 30 Meters and all the Grid levels measured at Grid level of 10M
Example 1 (Only Cutting) Example 2 (Both Cutting and Filling) Ground Level Ground Level Section 0 10 20 30 30 192.51 193.71 193.21 193.47 192.51 193.71 193.21 193.47 20 193.04 193.14 192.92 193.01 193.04 193.14 192.92 193.01 10 192.61 192.56 192.63 192.67 192.61 192.56 192.63 192.67 0 192.56 192.68 192.67 192.57 192.56 192.68 192.67 192.57 Formation Level Formation Level 191.9 193.1 192.6 192.87 193.4 193.5 193.3 193.2 192.43 192.53 192.31 192.4 193.5 193.3 193.2 193.4 192.01 191.96 192.03 192.06 193.4 193.6 193.4 193.4 191.95 192.07 192.07 191.97 193.1 193.4 193.5 193.3
Average method: In this method Levels at each grid point is found Levels multiplied by Area gives the Result. This is can be used only when there is cutting or filling. filling, Average method gives wrong result as averaging. out. Difference between the Average of Two Sets of a very simple and straight forward method. But this When Leveling of surface includes both cutting and cutting and filling values nullify each other while
Example 1(Only Cutting) Filling
Example 2 (Both Cutting and Filling)
1/4
www.nbmcw.com/equipments/surveying-testing/29427-construction-site-earthwork-calculation.html
11/29/13
Construction Site Earthwork Calculation
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Average 0 0 Cutting 0.61 0.61 0.61 0.6 0.61 0.61 0.61 0.61 0.6 0.6 0.6 0.61 0.61 0.61 0.6 0.6 Average 0.606 545.62
Volume = Average * 900 = 0.606 * 900 = 545.62 Block Method (Division of Square Method):
0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0
Filling 0 0.21 0 0.27 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Average 0.03 27 Cutting 0.89 0 0.09 0 0.46 0.16 0.28 0.39 0.79 1.04 0.77 0.73 0.54 0.72 0.83 0.73 Average 0.526 473.625
In this method, volume of cutting or filling is found out for each block and added together to get the final volume. This is mathematically simpler then Section Method, but more accurate than Average method. The problem of nullification is also encountered here when in the same block there is both cutting and filling. But here the margin of error is very small when compared to Average method for whole area. Example 1(Only Cutting): Difference in Average for Each 10 X 10 Block 0.61 0.605 0.605 0.61 0.605 0.6025 0.6075 0.6075 0.6025
Volume = Sum * 100 (Area of Each block) = 5.455 * 100 = 545.5 (Cutting) Note: Value 0.61 = Average (192.51, 193.71, 193.04, 193.14) Average (191.9, 193.1, 192.43, 192.53) [Values taken from first 2 rows and 2 columns of ground and formation level) Example 2 (Both Cutting and Filling) : Difference in Average for Each 10 X 10 Block 0.325 0.6125 0.7725 0.08 0.5625 0.84 0.1225 0.5425 0.765
Volume = Sum * 100 (Area of Each block) = 4.6225 * 100 = 462.25 (Filling). Note: Although in this example there is some cutting, because of nullification of value in same block we are not getting any value in Cutting. Section Method: In this method Sections are drawn for Each Line of Value. Area of Cutting and Filling is found out for each Section with Trapezoidal Method or Nett Area Calculation Method. Then volume is determined by multiplying Average Area with Distance between Sections. This method is more accurate, but for larger area, finding the area becomes difficult as we need to find intersection of points where lines representing Surfaces meet.
www.nbmcw.com/equipments/surveying-testing/29427-construction-site-earthwork-calculation.html
2/4
11/29/13
Construction Site Earthwork Calculation
Example 1(Only Cutting): Sl. Section No. 1 Cutting Volume Filling Volume Area Previous Average Volume Area Previous Average Volume Sq. Mtrs Area Sq. Mtrs Cu Meters Sq. Mtrs Area Sq. Mtrs Cu Meters 0.000 18.150 0.000 9.075 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 18.150 18.050 18.300 18.100 18.175 18.275 181.000 181.750 182.750 545.500 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000
2 10.000 18.050 3 20.000 18.300 4 30.000 18.250 Total
Sections Related to Example 2 (Both Cutting and Filling) :
Example 2 (Both Cutting and Filling) : Sl. Section No. 1 0.000 Cutting Volume Filling Volume Area Previous Average Volume Area Previous Average Volume Sq. Mtrs Area Sq. Mtrs Cu Meters Sq. Mtrs Area Sq. Mtrs Cu Meters 0.000 0.000 0.000 1.948 Total Summary of Results Sl. Method 1 2 3 Average Method Block method Section Method 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.974 0.000 21.850 0.000 25.700 0.000 8.650 9.740 9.740 3.848 0.000 21.850 25.700 8.650 10.925 23.775 17.175 6.249 0.000 237.750 171.750 62.490 471.990
2 10.000 3 20.000 4 30.000
Example 1 Cutting 545.62 545.5 545.500 Filling 0 0 0
Example 2 Cutting 27.000 0.000 9.740 Filling 473.625 462.25 471.990
Summary of Various Methods Methods /
www.nbmcw.com/equipments/surveying-testing/29427-construction-site-earthwork-calculation.html 3/4
11/29/13
Construction Site Earthwork Calculation
Methods Formula
Advantages
Disadvantages
Applicability
Volume=Depth of Average Easiest Method for cutting/filling* Method calculation area
Approximate, cannot be applied when Used for very small both cutting projects and filling are there
Volume=Sum of (Depth of Block cutting/filling* Method area of each block) Area to be found out using
Commonly used to Box method will find volume for nullify volume when It Is very easy to leveling projects both cutting and calculate the area before the filling are there in construction of a the same block building
Mathematically, Trapezoidal very good and Section Method hence adopted in Involves a lot of Method Nett area majority of calculations Method infrastructure projects Volume = Lx1/2(A1+ A2)
Used in most of the infrastructure Projects including Roads, Irrigation Projects, Rail Road Projects, etc.
Conclusion From the above examples, we can conclude that Section Method is complex compared to any other method but gives accurate results. Also if the Average method or Block Method is used for calculation then it is likely that Volume will be little lesser and the contractor will get lesser quantity and hence less payment for his work.
www.nbmcw.com/equipments/surveying-testing/29427-construction-site-earthwork-calculation.html
4/4
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Grid Method Contour LineDokument6 SeitenGrid Method Contour LineMherlieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Earthwork Calculation For Earthen BundsDokument4 SeitenEarthwork Calculation For Earthen BundsanbukgiNoch keine Bewertungen
- EarthworkDokument26 SeitenEarthworkWan MahiramNoch keine Bewertungen
- Earthwork, Cross Sections, Mass Haul DiagramDokument3 SeitenEarthwork, Cross Sections, Mass Haul Diagramarianboy74100% (2)
- Sub Grade Evaluation MethodsDokument83 SeitenSub Grade Evaluation MethodsSujitkumar BeheraNoch keine Bewertungen
- ReservoirDokument1 SeiteReservoirBernie QuepNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grid Method Earthwork CalculationDokument4 SeitenGrid Method Earthwork CalculationArbiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Earthwork Calculation For Earthen BundsDokument4 SeitenEarthwork Calculation For Earthen Bundsbemd_ali6990100% (1)
- Highway Geometric Design ElementsDokument93 SeitenHighway Geometric Design ElementsGERA AMITH KUMARNoch keine Bewertungen
- Highway SurveyDokument30 SeitenHighway SurveyVittal Kumar100% (1)
- Road AlignmentDokument17 SeitenRoad Alignmentrowaters100% (1)
- Road Design BasicsDokument13 SeitenRoad Design BasicsLJD211100% (1)
- A Guide To Good Quality Control Practices OnAsphalt Production and ConstructionDokument59 SeitenA Guide To Good Quality Control Practices OnAsphalt Production and ConstructionAmirrudin Johari100% (1)
- Earthwork and Mass-Haul DiagramDokument25 SeitenEarthwork and Mass-Haul Diagramሽታ ዓለሜNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Surveying Field Scheme ReportDokument6 SeitenEngineering Surveying Field Scheme ReportMohafisto SofistoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Earthwork Quantities & CalculationsDokument31 SeitenEarthwork Quantities & CalculationsabubekirNoch keine Bewertungen
- SP-23 Vertical Curves For HighwaysDokument28 SeitenSP-23 Vertical Curves For Highwaysimranmax13100% (5)
- Mass Haul Diagram TUTORIAL & SolutionDokument3 SeitenMass Haul Diagram TUTORIAL & SolutionNoor NadiahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intersection Control and Design IDokument30 SeitenIntersection Control and Design IKwaku SoloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chp0200 Geometric Design andDokument54 SeitenChp0200 Geometric Design andangelbarba100% (2)
- Infrastructure Design Report - G1!1!41Dokument41 SeitenInfrastructure Design Report - G1!1!41Hafizul ZaidanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flexible Pavement DesignDokument21 SeitenFlexible Pavement Designnunajihah0% (1)
- Basic Concepts of Traffic EngineeringDokument5 SeitenBasic Concepts of Traffic EngineeringAbdirizak HussienNoch keine Bewertungen
- D4254 - Maximum Index Density and Unit Weight of Soils and Calculation of Relative DensityDokument8 SeitenD4254 - Maximum Index Density and Unit Weight of Soils and Calculation of Relative DensityJhon Hilario AquinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cut and FillDokument16 SeitenCut and FillPongets SorianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- EarthworkDokument12 SeitenEarthworkJohny Lou LuzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Highway MaintenanceDokument13 SeitenHighway MaintenancePia CajayonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculating area and volume from field measurementsDokument16 SeitenCalculating area and volume from field measurementsPrashani Ulapane100% (1)
- Topic 3 - Flexible Pavement Stress AnalysisDokument22 SeitenTopic 3 - Flexible Pavement Stress AnalysisWelly Pradipta bin Maryulis100% (1)
- CEB 705 - Week 11 - Lecture 1 - Road Construction MethodsDokument37 SeitenCEB 705 - Week 11 - Lecture 1 - Road Construction MethodsCharles Taloboe100% (1)
- EARTHWORKS and VOLUMESDokument29 SeitenEARTHWORKS and VOLUMESDennis Narte100% (2)
- Areas Volumes MHD PDFDokument46 SeitenAreas Volumes MHD PDFIssa MagangaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unconfined Compression Test: Experiment No. 7Dokument8 SeitenUnconfined Compression Test: Experiment No. 7Carmela Ayessa PiguerraNoch keine Bewertungen
- School of Civil Engineering: A Project Report On Traffic Volume CountDokument20 SeitenSchool of Civil Engineering: A Project Report On Traffic Volume Countsai vandan100% (1)
- Sow Road Construction 022610Dokument25 SeitenSow Road Construction 022610Nercio BulaundeNoch keine Bewertungen
- KNS 3493 Highway Engineering Curve DesignDokument18 SeitenKNS 3493 Highway Engineering Curve DesignNur Hazirah SadonNoch keine Bewertungen
- MONGOLIA'S HIGHWAY DESIGN STANDARDDokument62 SeitenMONGOLIA'S HIGHWAY DESIGN STANDARDAtasi DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Highway Earthworks PlanningDokument11 SeitenHighway Earthworks PlanningamyamirulaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 Pavement Patching and RepairDokument28 SeitenChapter 3 Pavement Patching and RepairCollin Legaspina100% (1)
- EARTH WORK VOLUME FROM 16+520-20+980: Station Cut Area (SQ.M.) Cut Volume (Cu.M.) Fill Area (SQ.M.) Fill Volume (Cu.M.)Dokument5 SeitenEARTH WORK VOLUME FROM 16+520-20+980: Station Cut Area (SQ.M.) Cut Volume (Cu.M.) Fill Area (SQ.M.) Fill Volume (Cu.M.)Tewodros Tadesse100% (1)
- Classification of Highway CurvesDokument8 SeitenClassification of Highway CurvesMarc AlamoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculation of Foundation Settlement and Coefficient of Soil Subgrade ReactionDokument10 SeitenCalculation of Foundation Settlement and Coefficient of Soil Subgrade ReactionleodegarioporralNoch keine Bewertungen
- 04 Machine Design & DesignDokument22 Seiten04 Machine Design & DesignCholan PillaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter-10 - Gravel Road DesignDokument13 SeitenChapter-10 - Gravel Road DesignAbuye HDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iare E&c Lecture Notes PDFDokument110 SeitenIare E&c Lecture Notes PDFRichik MondalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exp 4 Unconfined TestDokument6 SeitenExp 4 Unconfined TestumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diploma in Civil Engineering: Dcc30112 - Geotechnical & Highway Engineering LaboratoryDokument12 SeitenDiploma in Civil Engineering: Dcc30112 - Geotechnical & Highway Engineering LaboratoryJames Michael ChuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flexible Pavement Design - AashtoDokument17 SeitenFlexible Pavement Design - AashtoFarhanah Binti FaisalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Proba MackintoshDokument18 SeitenProba Mackintoshnazlie170750% (2)
- Road Skid ResistanceDokument5 SeitenRoad Skid ResistanceMuhd Farhan Bin IbrahimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Specifications For Highway Drainage - OxfordshireDokument11 SeitenSpecifications For Highway Drainage - OxfordshirexkishanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geometric Design of HighwaysDokument75 SeitenGeometric Design of Highwayssuman subediNoch keine Bewertungen
- Earthwork Calculation MethodsDokument4 SeitenEarthwork Calculation MethodssanjoybapiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study of Crushing and GrindingDokument17 SeitenStudy of Crushing and Grindingmahbub1332Noch keine Bewertungen
- Optimal Design of Hollow Core PanelsDokument26 SeitenOptimal Design of Hollow Core Panelspaulo_arrieiroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Miracle G. Cabrera Ceqs 1 Activity 3Dokument3 SeitenMiracle G. Cabrera Ceqs 1 Activity 3Samantha CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measuring EarthworkDokument25 SeitenMeasuring EarthworkSHAHAN NAFEESNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cyclone Sizing Selection GuideDokument18 SeitenCyclone Sizing Selection GuideLuis VelasquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculation of End Area Method in Earthwork PDFDokument2 SeitenCalculation of End Area Method in Earthwork PDFSujithNoch keine Bewertungen
- A W, J W: Lbert Eckenmann Ohannes EickmannDokument10 SeitenA W, J W: Lbert Eckenmann Ohannes Eickmannkalvino314Noch keine Bewertungen
- Solution 283: Problem CornerDokument1 SeiteSolution 283: Problem CornermasteriragaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem 261Dokument1 SeiteProblem 261masteriragaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solution 282: Problem CornerDokument1 SeiteSolution 282: Problem CornermasteriragaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solution 284: Problem CornerDokument1 SeiteSolution 284: Problem CornermasteriragaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solution 270Dokument1 SeiteSolution 270masteriragaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Responsibilities of QSDokument1 SeiteResponsibilities of QSmasteriragaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem 262Dokument1 SeiteProblem 262masteriragaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solution 279: Problem CornerDokument1 SeiteSolution 279: Problem CornermasteriragaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solution 280 RevisedDokument1 SeiteSolution 280 RevisedmasteriragaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scheduled Training Machine Foundation 3-Day Training ProgramDokument1 SeiteScheduled Training Machine Foundation 3-Day Training ProgrammasteriragaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem Corner: by Benjamin Bloch, PHDDokument1 SeiteProblem Corner: by Benjamin Bloch, PHDmasteriragaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scheduled Training Machine Foundation 3-Day Training ProgramDokument1 SeiteScheduled Training Machine Foundation 3-Day Training ProgrammasteriragaNoch keine Bewertungen
- School of Civil Engineering: 410 201 Engineering Mechanics I Term 1/2000Dokument2 SeitenSchool of Civil Engineering: 410 201 Engineering Mechanics I Term 1/2000masteriragaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Curriculum VitaeDokument5 SeitenCurriculum VitaemasteriragaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transfer Beam Dead Plus Live LoadDokument1 SeiteTransfer Beam Dead Plus Live LoadAnitha Hassan KabeerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paper - VRK - Why Performance Specs - Delhi Seminar Write Up PDFDokument9 SeitenPaper - VRK - Why Performance Specs - Delhi Seminar Write Up PDFMarshall BravestarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Construction Manager ResponsibilitiesDokument1 SeiteConstruction Manager ResponsibilitiesmasteriragaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Message 2001-02-06 08-00 AMDokument0 SeitenMessage 2001-02-06 08-00 AMmasteriragaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Workshop Registration FormDokument4 SeitenWorkshop Registration FormmasteriragaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Message 2001-02-10 10-00 AMDokument0 SeitenMessage 2001-02-10 10-00 AMmasteriragaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transfer Beam Dead Plus Live LoadDokument1 SeiteTransfer Beam Dead Plus Live LoadAnitha Hassan KabeerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Curriculum VitaeDokument5 SeitenCurriculum VitaemasteriragaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solution 284: Problem CornerDokument1 SeiteSolution 284: Problem CornermasteriragaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solution 276: Problem CornerDokument1 SeiteSolution 276: Problem CornermasteriragaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Curriculum VitaeDokument5 SeitenCurriculum VitaemasteriragaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solution 270Dokument1 SeiteSolution 270masteriragaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem 275Dokument1 SeiteProblem 275masteriragaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem 264Dokument1 SeiteProblem 264masteriragaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem 266Dokument1 SeiteProblem 266masteriragaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solution 276: Problem CornerDokument1 SeiteSolution 276: Problem CornermasteriragaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atlas of TitanDokument380 SeitenAtlas of TitanJulius Adams86% (21)
- My CommunityDokument4 SeitenMy Communitymichietorres7Noch keine Bewertungen
- Concept of Region in GeographyDokument9 SeitenConcept of Region in GeographyPankaj MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter No. 05 Stream Flow and Streamflow MeasurementDokument71 SeitenChapter No. 05 Stream Flow and Streamflow MeasurementRahat ullah100% (3)
- Geology and Civil Engineering - 1939Dokument669 SeitenGeology and Civil Engineering - 1939Bluebelgian100% (3)
- Cleopatra Selene and Juba II: Exploring the Context of an Epigram on their MarriageDokument5 SeitenCleopatra Selene and Juba II: Exploring the Context of an Epigram on their MarriageRohan PhadkeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 'Nightfall' Chapter 1Dokument8 Seiten'Nightfall' Chapter 1mashablescribdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marta Sierra (Auth.) - Gendered Spaces in Argentine Women's Literature-Palgrave Macmillan US (2012) PDFDokument251 SeitenMarta Sierra (Auth.) - Gendered Spaces in Argentine Women's Literature-Palgrave Macmillan US (2012) PDFMayaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sedimentology and Stratigraphy Exam Review - Fall 2011 GEOS 315Dokument8 SeitenSedimentology and Stratigraphy Exam Review - Fall 2011 GEOS 315Anicentus NamangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Monografia en Ingles CajabambaDokument11 SeitenMonografia en Ingles CajabambaJhuno Marki AviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Great Nature GazetteDokument2 SeitenGreat Nature Gazetteapi-442331915Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mysterious Doomgrinder in Cairn HillsDokument2 SeitenMysterious Doomgrinder in Cairn Hillsmonel_24671Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ground Water Disertation Diss Ewusi NeuDokument186 SeitenGround Water Disertation Diss Ewusi NeuHasan AbdatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soal Ps NisfiaDokument4 SeitenSoal Ps NisfiaYosia'sNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class10 Geo ClimateofIndiaDokument5 SeitenClass10 Geo ClimateofIndiaJayapal HariNoch keine Bewertungen
- AnycareFMS Power PointDokument31 SeitenAnycareFMS Power Points_chendryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Job # 6. Study of Total StationDokument4 SeitenJob # 6. Study of Total StationWaqas ArshadNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Kankakee: River of HistoryDokument153 SeitenThe Kankakee: River of HistoryBrian Capouch100% (1)
- Geological Time-ScaleDokument9 SeitenGeological Time-ScaleNothing100% (1)
- Automated Lidar Analysis Tools - Global Mapper PDFDokument2 SeitenAutomated Lidar Analysis Tools - Global Mapper PDFAndrés MayorgaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Presentation in Grade 8Dokument36 SeitenFinal Presentation in Grade 8Michelle Casayuran - RegalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bernardus Ari - E2 - Reading Comprehension - Part 2 With Answer 2Dokument4 SeitenBernardus Ari - E2 - Reading Comprehension - Part 2 With Answer 2AmbadaYondaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Monsoon Report Tripura 2020Dokument12 SeitenMonsoon Report Tripura 2020satyakamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Population, Socio-Economic and Development Profile of PakistanDokument113 SeitenPopulation, Socio-Economic and Development Profile of Pakistanfardasa123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Language Diversity and the State: A Case Study of PakistanDokument3 SeitenLanguage Diversity and the State: A Case Study of PakistanFizza RaufNoch keine Bewertungen
- Population Dynamics Course SupportDokument22 SeitenPopulation Dynamics Course Supportalina_turbatu2796Noch keine Bewertungen
- IEHG - Encoding Guide 2.2.0 (2010) PDFDokument281 SeitenIEHG - Encoding Guide 2.2.0 (2010) PDFMarcelo L. OliveraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wind FarmDokument122 SeitenWind Farmriz2010Noch keine Bewertungen
- TP Puteri Shahirah NazihahDokument8 SeitenTP Puteri Shahirah Nazihahapi-439348424Noch keine Bewertungen
- Rf2D ReferenceManualDokument242 SeitenRf2D ReferenceManualWolfskull100% (1)