Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
DC Motor
Hochgeladen von
coolmaleankur0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
371 Ansichten6 SeitenDC motors can rotate in both directions depending on the polarity of current through the motor. They have free running torque and ideally zero current. DC motors have high speed that can be reduced with gears in exchange for increased torque. Speed is controlled through pulse width modulation which varies the current and thus the torque.
The L293D is a bipolar motor driver IC with high voltage and current capability. It can provide bidirectional current of up to 600mA at voltages from 4.5V to 36V to drive loads such as DC motors and stepping motors. It uses totem-pole drive circuits to control pairs of motors independently and reversibly based on the input signals.
Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
dc motor
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenDC motors can rotate in both directions depending on the polarity of current through the motor. They have free running torque and ideally zero current. DC motors have high speed that can be reduced with gears in exchange for increased torque. Speed is controlled through pulse width modulation which varies the current and thus the torque.
The L293D is a bipolar motor driver IC with high voltage and current capability. It can provide bidirectional current of up to 600mA at voltages from 4.5V to 36V to drive loads such as DC motors and stepping motors. It uses totem-pole drive circuits to control pairs of motors independently and reversibly based on the input signals.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
371 Ansichten6 SeitenDC Motor
Hochgeladen von
coolmaleankurDC motors can rotate in both directions depending on the polarity of current through the motor. They have free running torque and ideally zero current. DC motors have high speed that can be reduced with gears in exchange for increased torque. Speed is controlled through pulse width modulation which varies the current and thus the torque.
The L293D is a bipolar motor driver IC with high voltage and current capability. It can provide bidirectional current of up to 600mA at voltages from 4.5V to 36V to drive loads such as DC motors and stepping motors. It uses totem-pole drive circuits to control pairs of motors independently and reversibly based on the input signals.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 6
DC MOTORS:-
These are very commonly used in robotics. DC motors can rotate in
both
directions depending upon the polarity of current through the motor.
These
motors have free running torque and current ideally zero. These
motors have
high speed which can be reduced with the help of gears and traded
off for torque.
Speed Control of DC motors is done through Pulse Width Modulation
techniques,
i.e. sending the current in intermittent bursts. PWM can be
generated by 555
timer IC with adjusted duty cycle. Varying current through the
motor varies the
torque.
PICTURE OF DC MOTOR USED
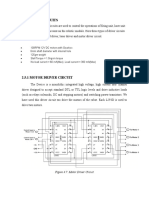
BIPOLAR MOTOR DRIVER:-
L293D is a bipolar motor driver IC. This is a high voltage, high
current pushpull
four channel driver compatible to TTL logic levels and drive
inductive loads. It
has 600 mA output current capability per channel and internal clamp
diodes.
The L293 is designed to provide bidirectional drive currents of upto 1
A at
voltages from 4.5 V to 36 V. The L293D is designed to provide
bidirectional drive
currents of up to 600-mA at voltages from 4.5 V to 36 V. Both devices
are
designed to drive inductive loads such as relays, solenoids, dc and
bipolar stepping
motors, as well as other high-current/high-voltage loads in positive
supply
applications. All inputs are TTL compatible. Each output is a
complete totem-pole
drive circuit, with a Darlington transistor sink and a pseudo-
Darlington source.
Drivers are enabled in pairs, with drivers 1 and 2 enabled by 1,2EN
and drivers 3
and 4 enabled by 3,4EN. When an enable input is high, the associated
drivers are
enabled, and their outputs are active and in phase with their inputs.
When the
enable input is low, those drivers are disabled, and their outputs are
off and in the
high-impedance state. With the proper data inputs, each pair of
drivers forms a
full-H (or bridge) reversible drive suitable for solenoid or motor
applications
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Von EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Bewertung: 2.5 von 5 Sternen2.5/5 (3)
- Description/ordering Information (Continued)Dokument4 SeitenDescription/ordering Information (Continued)Dimple AmudaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DirverDokument13 SeitenDirvermpkkbtechNoch keine Bewertungen
- DC MotorDokument5 SeitenDC MotorratheeshbrNoch keine Bewertungen
- L293D (Quadruple Half H-Drivers) : FeaturesDokument4 SeitenL293D (Quadruple Half H-Drivers) : FeaturesmunugotisumanthraoNoch keine Bewertungen
- PIC+l293d DocumentDokument5 SeitenPIC+l293d Documentmadduanil100% (1)
- Lab 910Dokument20 SeitenLab 910Malak Al-AshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- L293D Motor Driver ICDokument4 SeitenL293D Motor Driver ICUnknown424Noch keine Bewertungen
- Motor InterfacingDokument3 SeitenMotor InterfacingMemoh BranleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microcontroller Based DC Motor Control: Jayshree Sahu, S.K.Sahu, Jayendra KumarDokument4 SeitenMicrocontroller Based DC Motor Control: Jayshree Sahu, S.K.Sahu, Jayendra KumarJagdish PatankarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drv8825 DriveDokument9 SeitenDrv8825 DriveSimone MolinaroNoch keine Bewertungen
- L293D Is A DualDokument3 SeitenL293D Is A DualRamya IyerNoch keine Bewertungen
- WPCDokument14 SeitenWPCRahulNoch keine Bewertungen
- DC Motor ControlDokument5 SeitenDC Motor ControlSiddhasen PatilNoch keine Bewertungen
- 53 - 36765 - ME593 - 2014 - 1 - 1 - 1 - DC Motors PDFDokument56 Seiten53 - 36765 - ME593 - 2014 - 1 - 1 - 1 - DC Motors PDFDora TengNoch keine Bewertungen
- Autonomous Bot MakingDokument45 SeitenAutonomous Bot MakingSudhir ImperfectNoch keine Bewertungen
- DC Motor Fyp EdittdDokument20 SeitenDC Motor Fyp EdittdRabia BilalNoch keine Bewertungen
- WorkingDokument3 SeitenWorkingAnuj TripathiNoch keine Bewertungen
- l298 Dual H-Bridge Motor DriverDokument3 Seitenl298 Dual H-Bridge Motor DriverFelix Alfredo Vilchez TupayachiNoch keine Bewertungen
- l293d Based Arduino Motor ShieldDokument5 Seitenl293d Based Arduino Motor ShieldGabi CiobanuNoch keine Bewertungen
- PWMDokument16 SeitenPWMRICHIHOTS2100% (2)
- Interface L298N DC Motor Driver Module With ArduinoDokument16 SeitenInterface L298N DC Motor Driver Module With ArduinoIhot HarianjaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DC-Motor Driver Circuits: Using TransistorDokument14 SeitenDC-Motor Driver Circuits: Using TransistorSyar ArifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wireless DC Motor Speed and Direction Control Using RFDokument3 SeitenWireless DC Motor Speed and Direction Control Using RFNidhin MnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Módulo Driver MotorDokument8 SeitenMódulo Driver MotorgaioskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Datasheet 1182 PDFDokument6 SeitenDatasheet 1182 PDFabs0001Noch keine Bewertungen
- Self Collision DetectorDokument3 SeitenSelf Collision DetectorRavi BhardwajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circuit Stepper Motor DriverDokument17 SeitenCircuit Stepper Motor DriverkalpicoNoch keine Bewertungen
- AJJDokument10 SeitenAJJmandalapu91Noch keine Bewertungen
- Four Quadrant OperationDokument15 SeitenFour Quadrant OperationPrasanna KSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction Unit1Dokument34 SeitenIntroduction Unit1senthilku marNoch keine Bewertungen
- Line 6 Flextone 2 HD Service ManualDokument86 SeitenLine 6 Flextone 2 HD Service Manualrnrmf2082Noch keine Bewertungen
- Simulation of Power Electronic Converters Using Matlab SimulinkDokument19 SeitenSimulation of Power Electronic Converters Using Matlab SimulinkajithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 24 DC Motor ControlDokument9 SeitenLesson 24 DC Motor ControlYahya AIDARANoch keine Bewertungen
- Half-Bridge Bidirectional DC-DC Converter For Small Electric VehicleDokument5 SeitenHalf-Bridge Bidirectional DC-DC Converter For Small Electric VehiclePradeepChandraVarmaMandapati100% (1)
- Wi-Fi Home AutomationDokument23 SeitenWi-Fi Home Automationchandru_8Noch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Circuit Components: 1. BreadboardDokument9 SeitenBasic Circuit Components: 1. BreadboardkumarnishatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Earth Fault Relay in A Single Phase Power System.Dokument31 SeitenEarth Fault Relay in A Single Phase Power System.Soumya Bhattacharya100% (2)
- Advanced Communication Design For Mobile Disabling at Restricted Areas Microcontroller:-FeaturesDokument8 SeitenAdvanced Communication Design For Mobile Disabling at Restricted Areas Microcontroller:-FeaturesIndhumathi MohanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment # 3Dokument9 SeitenAssignment # 3styphenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hardware InterfacingDokument65 SeitenHardware Interfacingrajan palaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chopper ReportDokument37 SeitenChopper ReportcoolsinghrkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bipolar Stepper Motor Driver 74194Dokument12 SeitenBipolar Stepper Motor Driver 74194mekuannintmesfin100% (2)
- 1 Vacancy AnnouncementDokument5 Seiten1 Vacancy AnnouncementMehmood Khan MarwatNoch keine Bewertungen
- ProjectDokument5 SeitenProjectMohammed Al hennawiNoch keine Bewertungen
- DC - AC ConvertorsDokument3 SeitenDC - AC Convertorskarthick LNoch keine Bewertungen
- DC MotorDokument2 SeitenDC MotorSimmhadri SimmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2Dokument34 SeitenChapter 2meeedooo.abo.elenenNoch keine Bewertungen
- DC Motor Control Using 8085Dokument48 SeitenDC Motor Control Using 8085Bhavya Wadhwa100% (3)
- Design Consideration and Hardware Components of The SystemDokument8 SeitenDesign Consideration and Hardware Components of The SystemKyaw SoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- DC Motor Speed Controller Using IC 555 TimerDokument8 SeitenDC Motor Speed Controller Using IC 555 Timerfarazpayoneer21Noch keine Bewertungen
- Minor Project Report: Submitted byDokument20 SeitenMinor Project Report: Submitted byDurgesh ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- American ControllersDokument16 SeitenAmerican ControllersRenny PaoloneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applications of 8051 MicrocontrollersDokument23 SeitenApplications of 8051 MicrocontrollersUsama Spiffy100% (1)
- 12V To 24V DC DC ConverterDokument4 Seiten12V To 24V DC DC ConverterDavid Arrata ParralesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wireless DC Motor Speed Control System Using IgbtDokument5 SeitenWireless DC Motor Speed Control System Using Igbtparasuraman535Noch keine Bewertungen
- Power InverterDokument10 SeitenPower Inverterdakshina656087100% (1)
- Project Report Wireless Power Theft Monitoring Using 89C51Dokument1 SeiteProject Report Wireless Power Theft Monitoring Using 89C51Penchal RaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Motor InterfacingDokument3 SeitenMotor InterfacingVijay KrisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Misra CDokument59 SeitenMisra CcoolmaleankurNoch keine Bewertungen
- System Resets, Interrupts, and Operating Modes, System Control Module (SYS)Dokument269 SeitenSystem Resets, Interrupts, and Operating Modes, System Control Module (SYS)coolmaleankurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Angle CockesDokument4 SeitenAngle CockescoolmaleankurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Air Brake House CouplingDokument4 SeitenAir Brake House CouplingcoolmaleankurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Line Follower Using 89s52Dokument43 SeitenLine Follower Using 89s52coolmaleankur100% (2)
- Onboard Pin ConnectionsDokument2 SeitenOnboard Pin ConnectionscoolmaleankurNoch keine Bewertungen
- PCB DesignDokument1 SeitePCB DesigncoolmaleankurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Source CodeDokument5 SeitenSource CodecoolmaleankurNoch keine Bewertungen
- LogicDokument2 SeitenLogiccoolmaleankurNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Isp?Dokument2 SeitenWhat Is Isp?coolmaleankurNoch keine Bewertungen
- ControllerDokument4 SeitenControllercoolmaleankurNoch keine Bewertungen